Gene carrier using cell-derived nanovesicles and method for preparing the same
a cell-derived nanovesicle and gene carrier technology, applied in the direction of microcapsules, active genetic ingredients, gene material ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of high efficacy, safety of a gene therapeutic agent, and extremely rare that they are actually commercialized, and achieve the effect of efficient introduction into the target cell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation examples
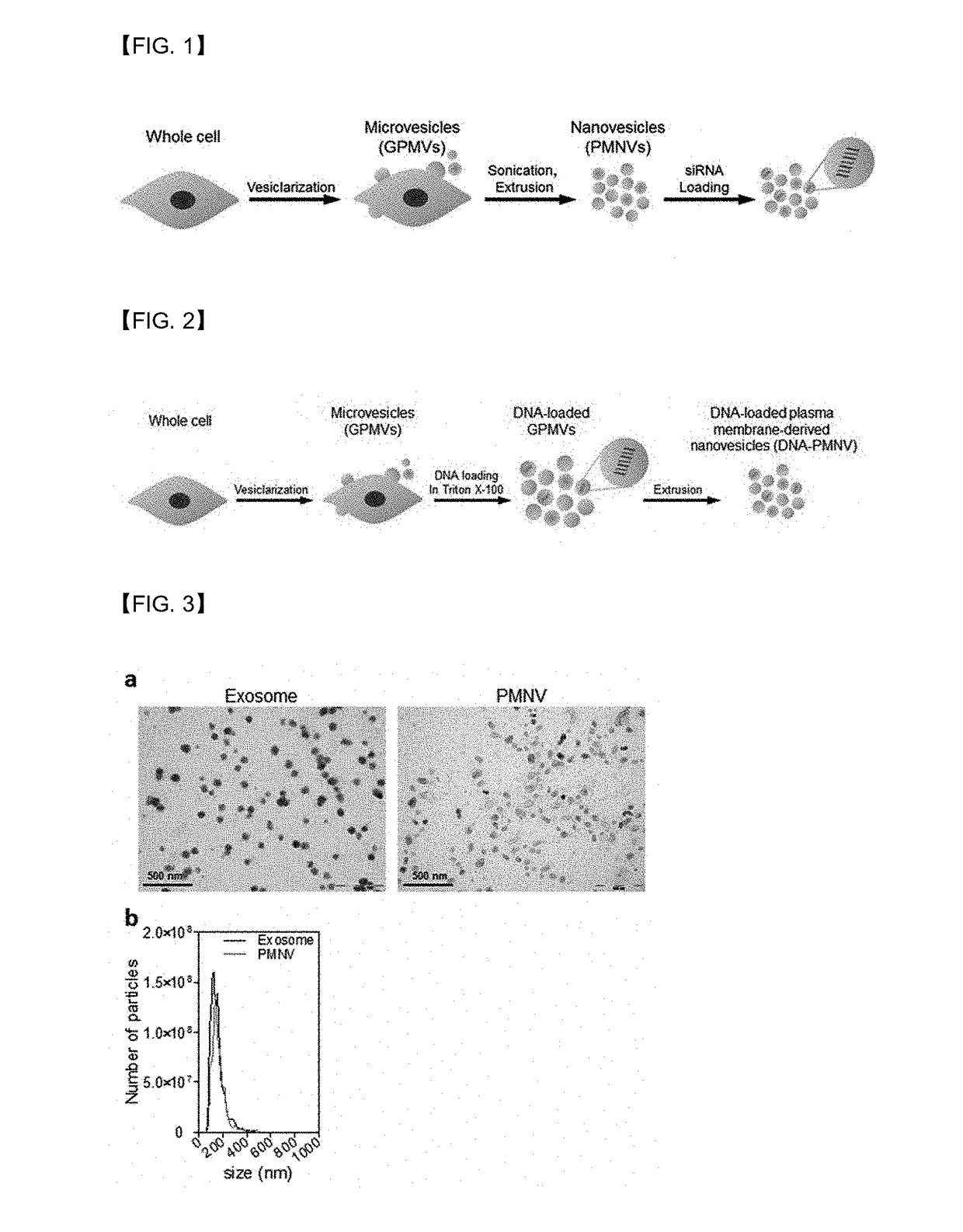
Preparation Example 1. Preparation of Gene Carrier Based on Cell-Derived Nanovesicles
[0056]1-1. Preparation of Gene Carrier for RNA Delivery
[0057]In a HEPES buffer (10 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2, pH 7.4) containing 25 mM parformaldehyde (PFA) and 2 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), a HEK-293 cell line was incubated at 37° C. for 3 to 4 hours to artificially outbud vesicles from the cells, and the culture dish was shaken every 30 minutes to obtain a higher yield of vesicles. Subsequently, the resulting suspension containing the vesicles was sequentially subjected to centrifugation, sonication and extrusion, thereby preparing cell-derived nanovesicles with a uniform size. Afterward, a nucleic acid molecule composed of RNA was introduced into the nanovesicles using electroporation, resulting in the preparation of a gene carrier for RNA delivery.
[0058]1-2. Production of Gene Carrier for DNA Delivery
[0059]According to the same method as described in Preparation Example 1-1, a HEK-293 cell ...
experimental examples
Experimental Example 1. Analysis of Physical Properties of Nanovesicles
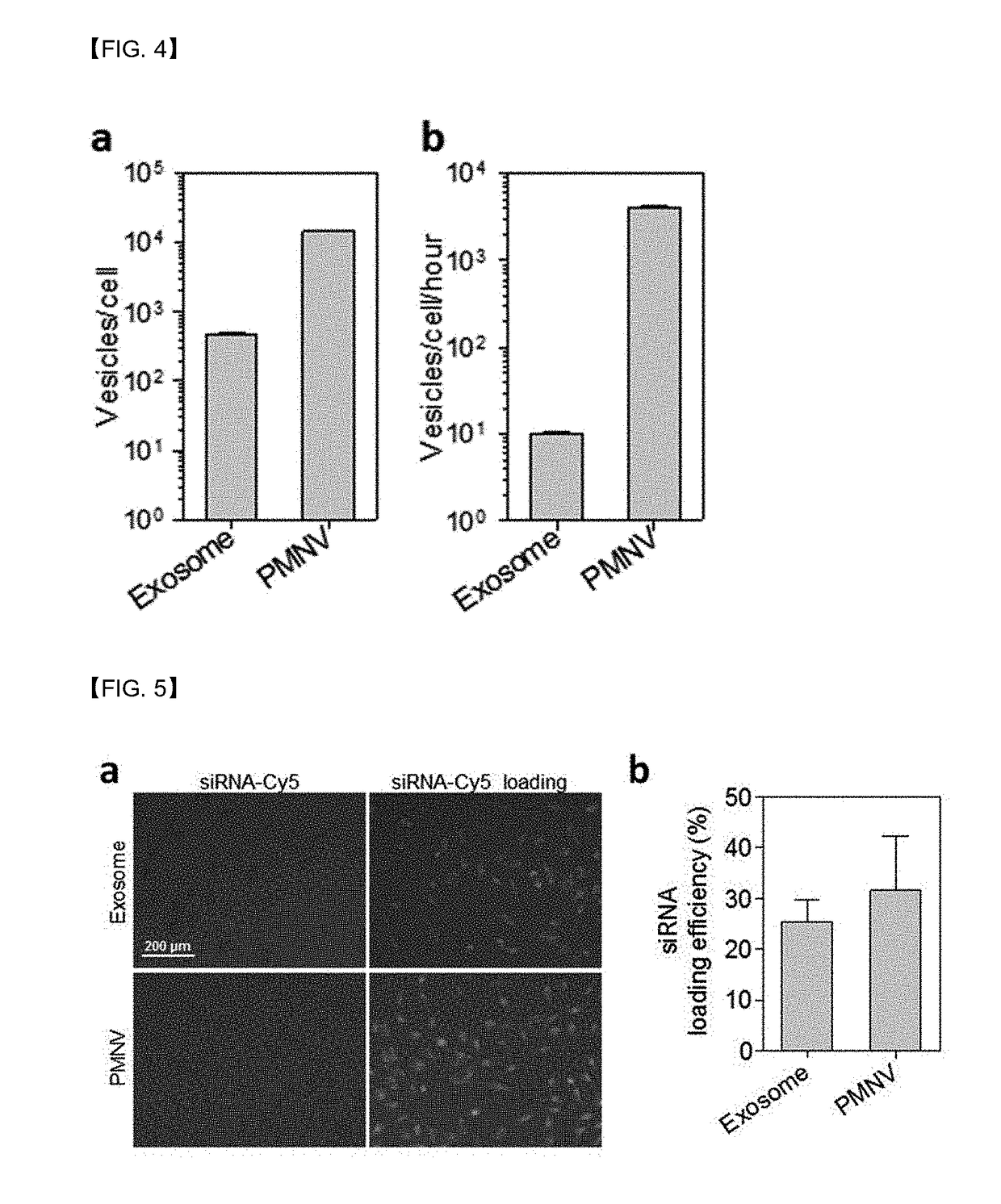
[0061]Exosomes are cell-derived natural substances, which have been known, according to a recent report, to be used as a gene carrier. Therefore, in this experimental example, physical properties of the nanovesicles prepared in Preparation Example 1-1 (plasma membrane-derived nanovesicles; PMNVs) were compared with those of the exosomes.
[0062]Specifically, a nanovesicle structure was observed using a transmission electron microscope (TEM), a zeta potential was measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and production per single cell and production per single cell per unit time were measured to compare productivities. In addition, fluorescence intensities were measured when Cy5-labeled siRNAs were delivered by simple mixing and by insertion, so as to verify that a gene carrier using nanovesicles or exosomes can be internalized in cells, and a quantity of siRNA inserted int...
experimental example 2
cle Yields and Gene Delivery Efficiency According to Treatment Condition
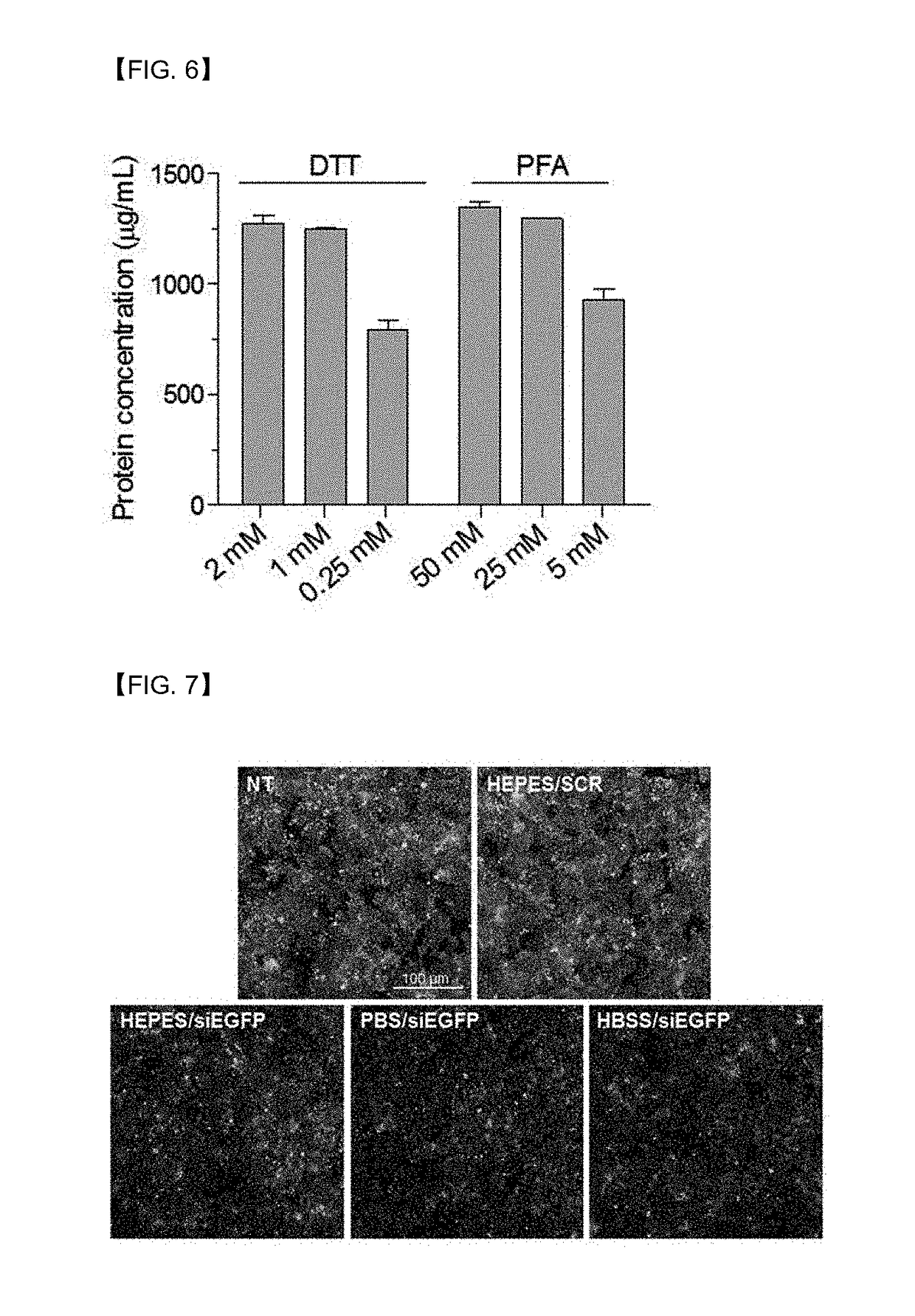
[0065]2-1. Comparison of Nanovesicle Yields According to PFA and DTT Treatment Conditions
[0066]In the preparation of the gene carrier of Preparation Example 1, a large quantity of vesicles could be artificially outbudded from cells by culturing the cells in a PFA and DTT-added HEPES buffer. In this experimental example, to deduce the optimal conditions for further enhancing the production yield of nanovesicles, various concentrations of PFA (5 mM, 25 mM, and 50 mM) or DTT (0.25 mM, 1 mM, and 2 mM) were added to a buffer solution, and the nanovesicles were prepared by the same method as described in Preparation Example 1-1 under conditions in which the DTT concentration was constantly maintained at 1 mM while the PFA concentration varied, and the PFA concentration was constantly maintained at 25 mM while the DTT concentration varied. Afterward, the nanovesicle yields per treatment concentration were quantitativel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| storage stability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com