Pneumatic tool
a technology of pneumatic tools and tools, applied in the field of pneumatic tools, can solve the problems of reducing the utility or preclude the use of tools, hammers, and tool components being subjected to large destructive forces, so as to reduce the and reduce the kinetic energy of the impactor devi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
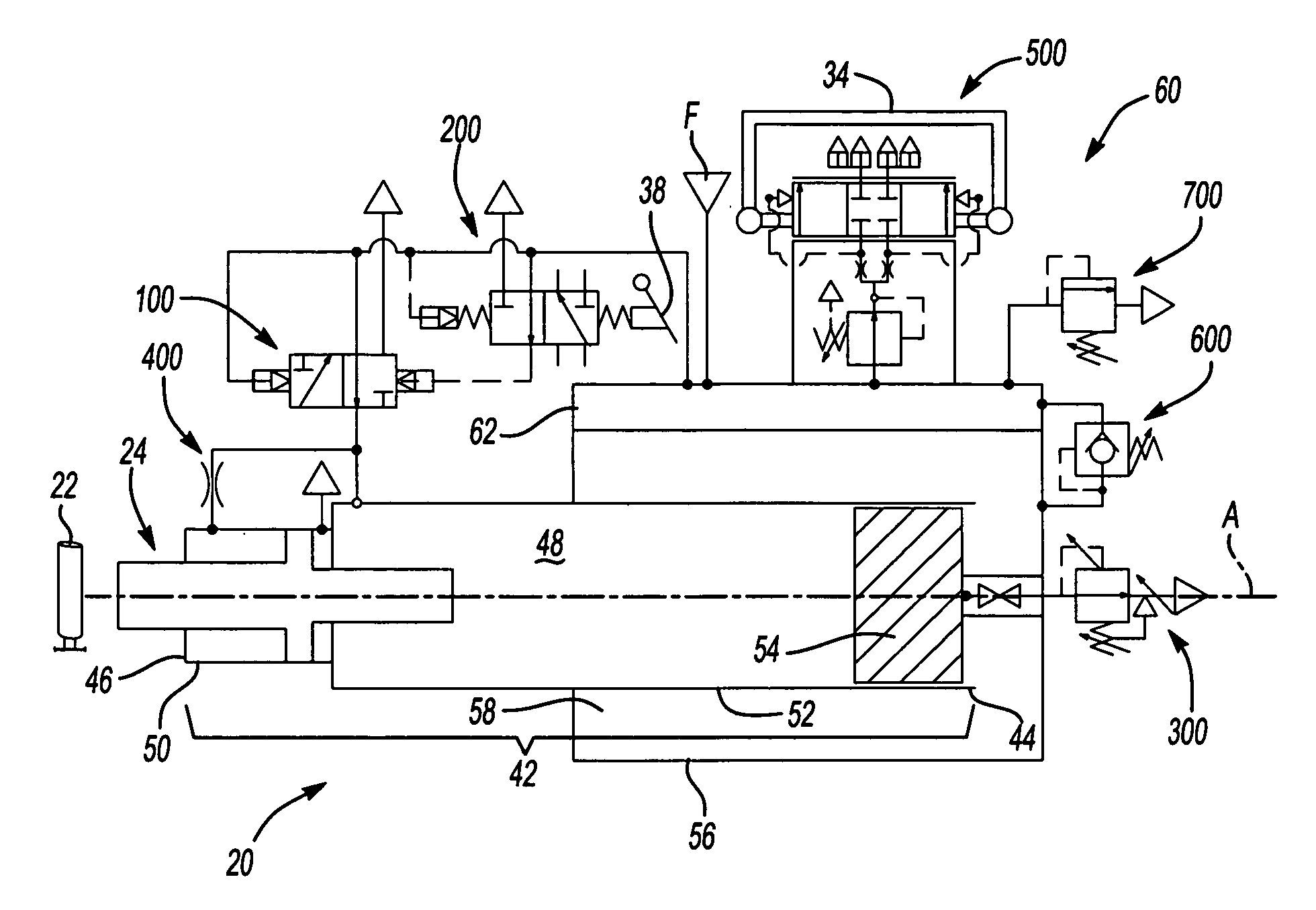
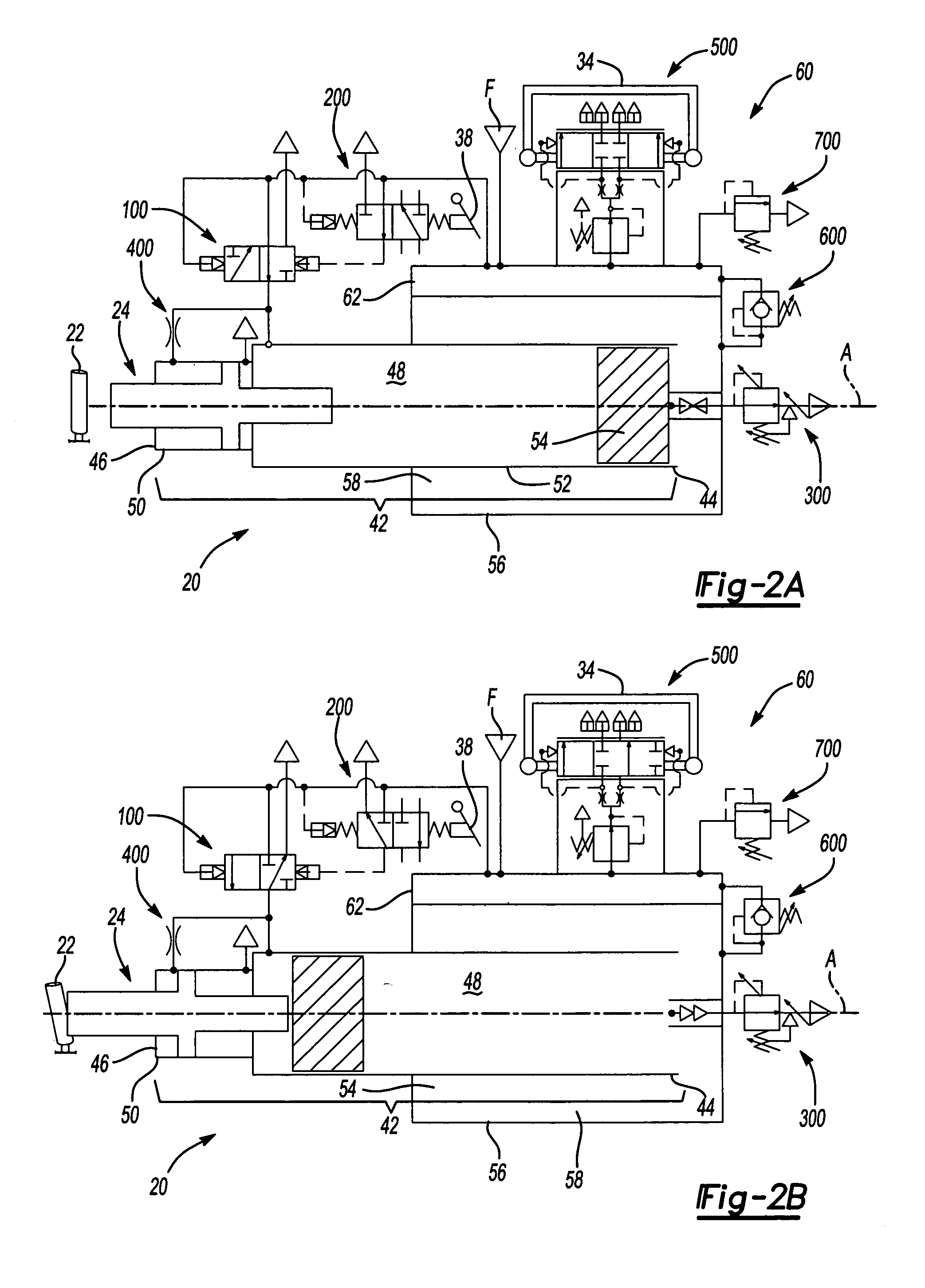
[0028]Referring to the Figures, wherein like numerals indicate like or corresponding parts throughout the several views, a tool for impacting a workpiece 22 is generally shown at 20. The tool 20 is preferably a pneumatic impacting tool for fracturing a gate or riser from a casting after a foundry pouring process. Of course, the tool 20 may be used for other applications including, but not limited to, breaking concrete or other similar demolition, driving fasteners in construction applications, seating large press-fit assemblies, and the like. The tool 20 is powered by a conventional pressurized fluid source F, e.g., an air compressor.
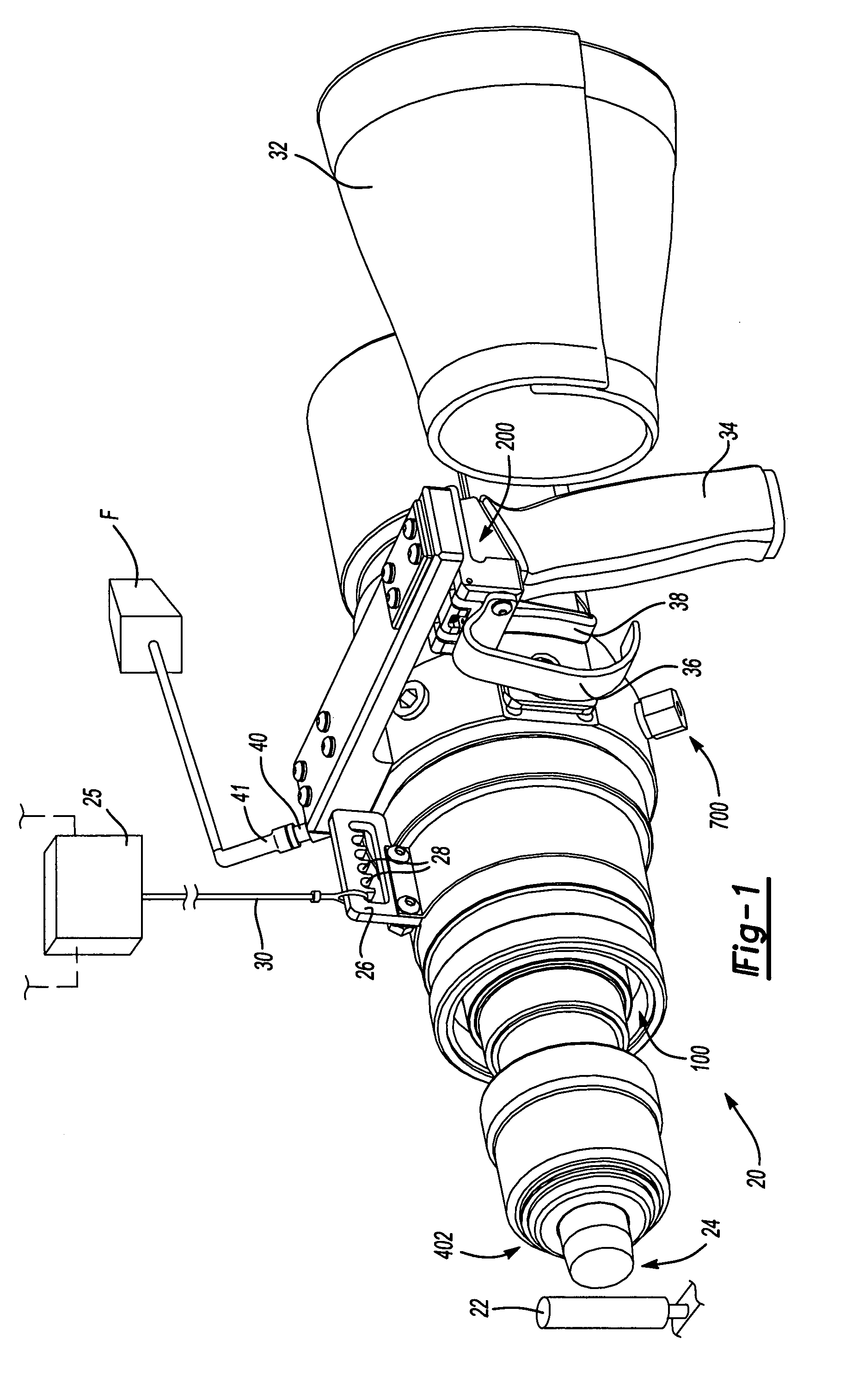
[0029]Referring to FIG. 1, the tool 20 is shown fully assembled and ready for use. A tool bit 24 is shown in a starting position. Upon actuation, the tool bit 24 slides distally to impact the workpiece 22. An adjuster plate 26 may be used to suspend the tool 20 from a tool balancer 25 to provide added versatility and maneuverability in positioning the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com