Refining device and method for removing liquid steel inclusions in continuous casting tundish
A continuous casting tundish and refining device technology, applied in the iron and steel metallurgical continuous casting tundish field, can solve the problems of argon gas waste, cost increase, limited ability of argon bubbles to capture and remove inclusions, etc., to prolong service life and improve Cleanliness, effect of improving the ability to capture and remove inclusions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
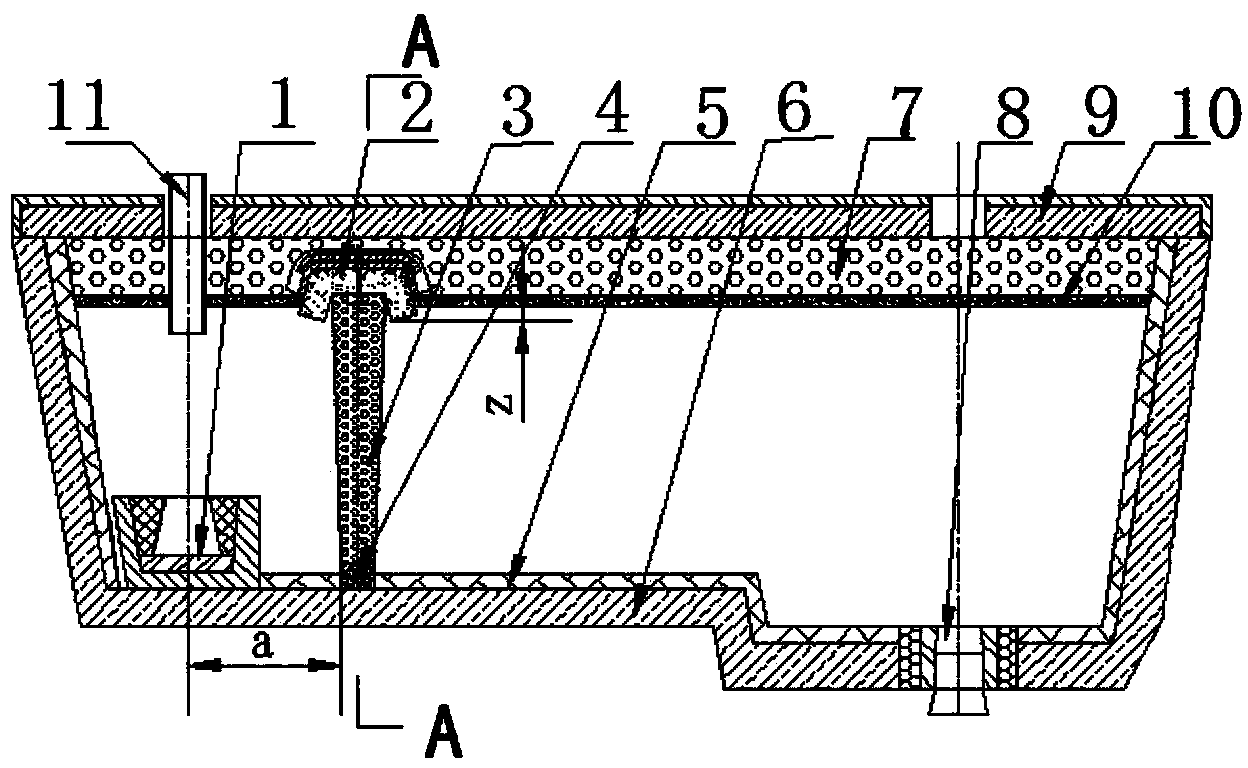
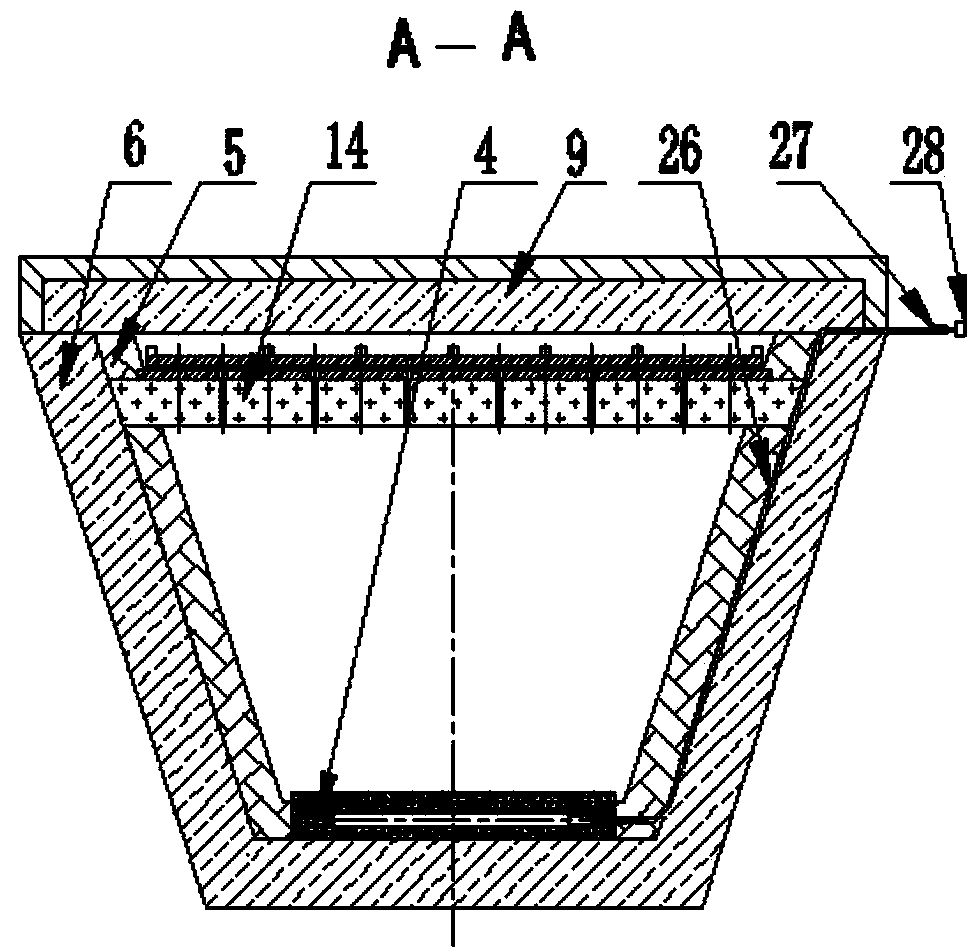
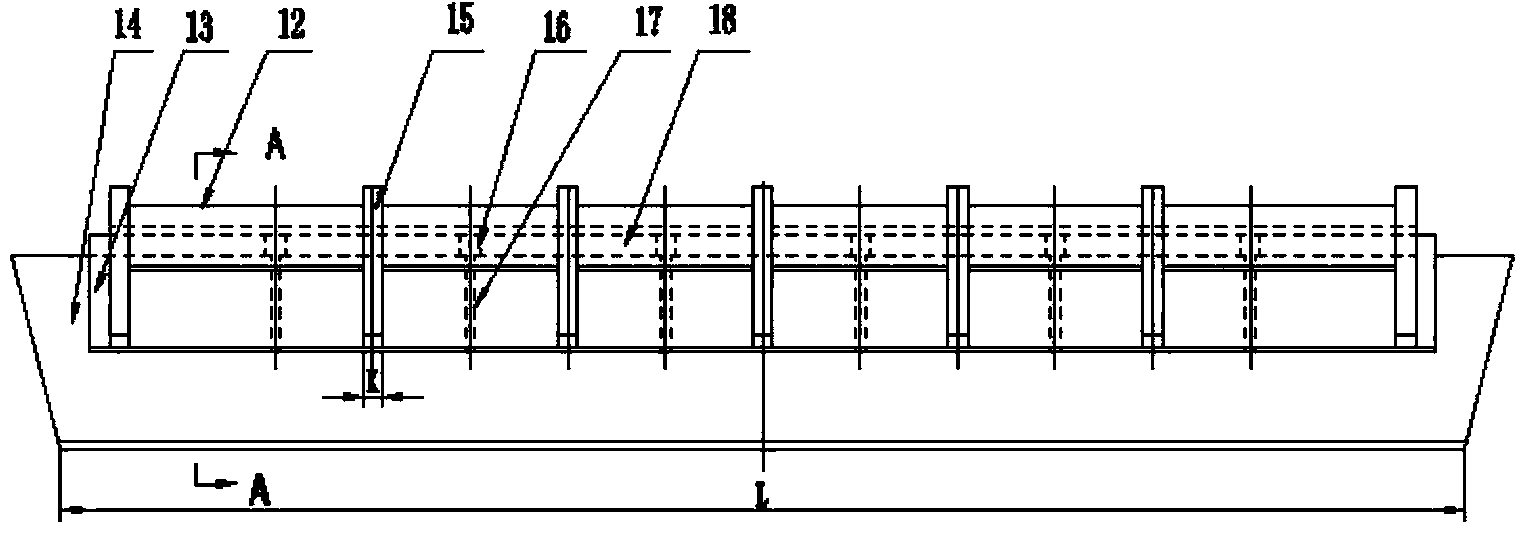
[0048] A refining device for removing inclusions in molten steel in a continuous casting tundish, with a structure such as Figure 1-Figure 7 As shown, it includes a turbulence controller 1, a refining cover 2, and an air curtain brick 4. The turbulence controller 1 is installed on the inner side of the working lining of the tundish wall in the injection impact area of the tundish. Line coincides, the air curtain permeable brick 4 is fixed on the permanent lining 6 at the bottom of the tundish, and partially embedded in the working lining 5 at the bottom of the tundish, the refining cover 2 is located directly above the air curtain permeable brick 4 and is in contact with the air The curtain air brick 4 is opposite, the longitudinal center line of the refining cover 2 coincides with the longitudinal center line of the air curtain air brick 4, the two sides of the refining cover 2 are fixed on the permanent lining 6 of the tundish wall, the refining cover 2, Including the out...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The refining device for removing molten steel inclusions in the continuous casting tundish as described in Example 1, the difference is:
[0054] The depth z of the lower end of the dipping cover 14 immersed in the molten steel is 50 mm, and the distance a between the center line of the turbulence controller 1 and the center of the air curtain permeable brick 4 is 400 mm.
[0055] The hollow in the middle of the turbulence controller core 30 is in the shape of a truncated cone with the diameter of the upper end smaller than that of the lower end. The diameter d of the upper port circle in the middle hollow of the turbulence controller core 30 is 300 mm, and the diameter D of the lower port circle is 360 mm.
[0056] The angle between the plane where the side plate is located and the plane where the transverse plate is located is 120°.
Embodiment 3
[0058] The refining device for removing molten steel inclusions in the continuous casting tundish as described in Example 1, the difference is:
[0059] The depth z of the lower end of the dipping cover 14 immersed in the molten steel is 40 mm, and the distance a between the center line of the turbulence controller 1 and the center of the air curtain permeable brick 4 is 300 mm.
[0060] The hollow in the middle of the turbulence controller core 30 is in the shape of a truncated cone with the diameter of the upper end smaller than that of the lower end. The diameter d of the upper port circle in the middle hollow of the turbulence controller core 30 is 320 mm, and the diameter D of the lower port circle is 380 mm.
[0061] The angle between the plane where the side plate is located and the plane where the transverse plate is located is 130°.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com