Pulse thermal processing of functional materials using directed plasma arc
a technology of plasma arc and functional materials, which is applied in the direction of arc welding apparatus, plasma welding apparatus, electrical heating fuel, etc., can solve the problems of low melting point, temperature-sensitive substrates, low melting point,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
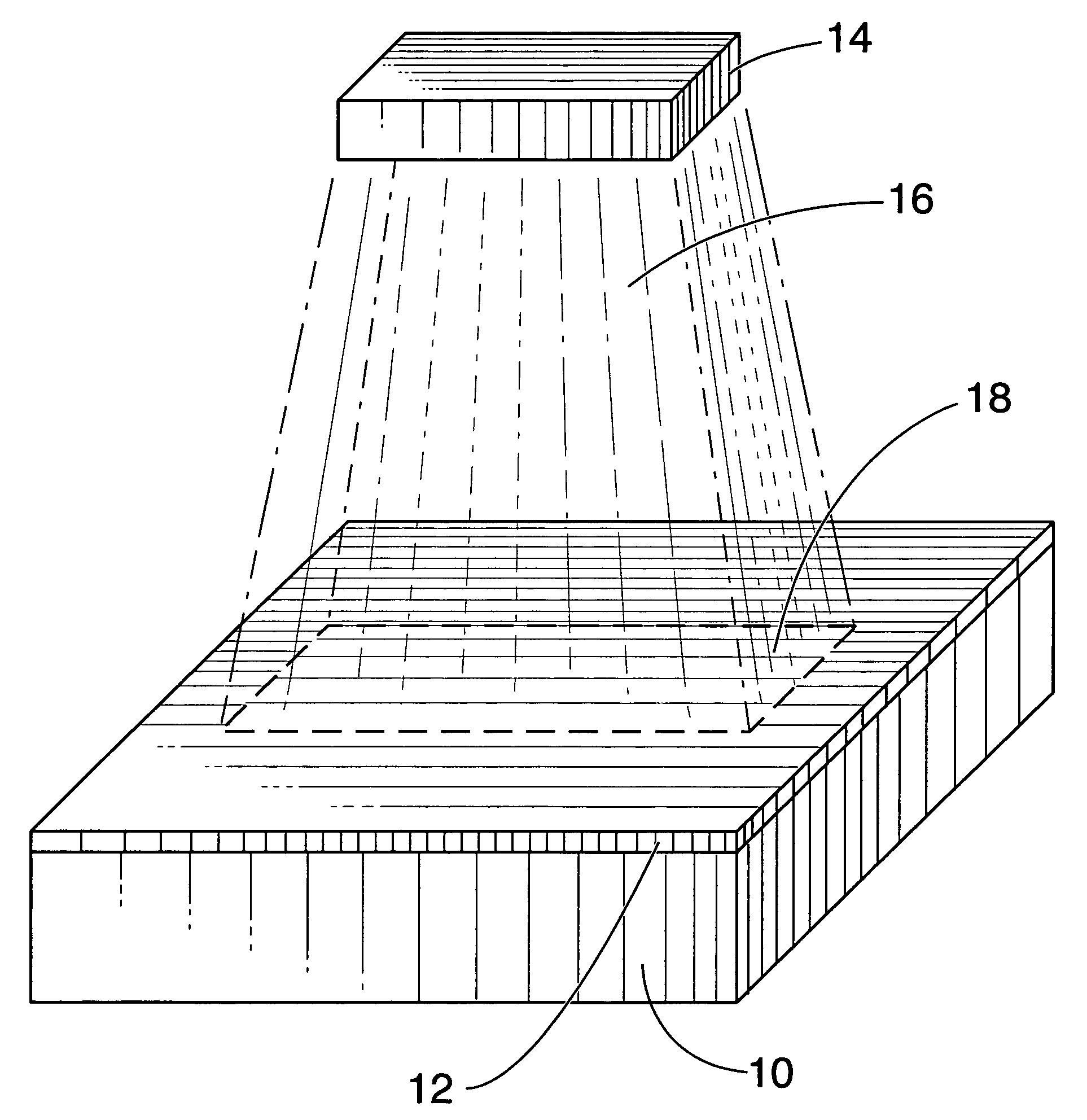
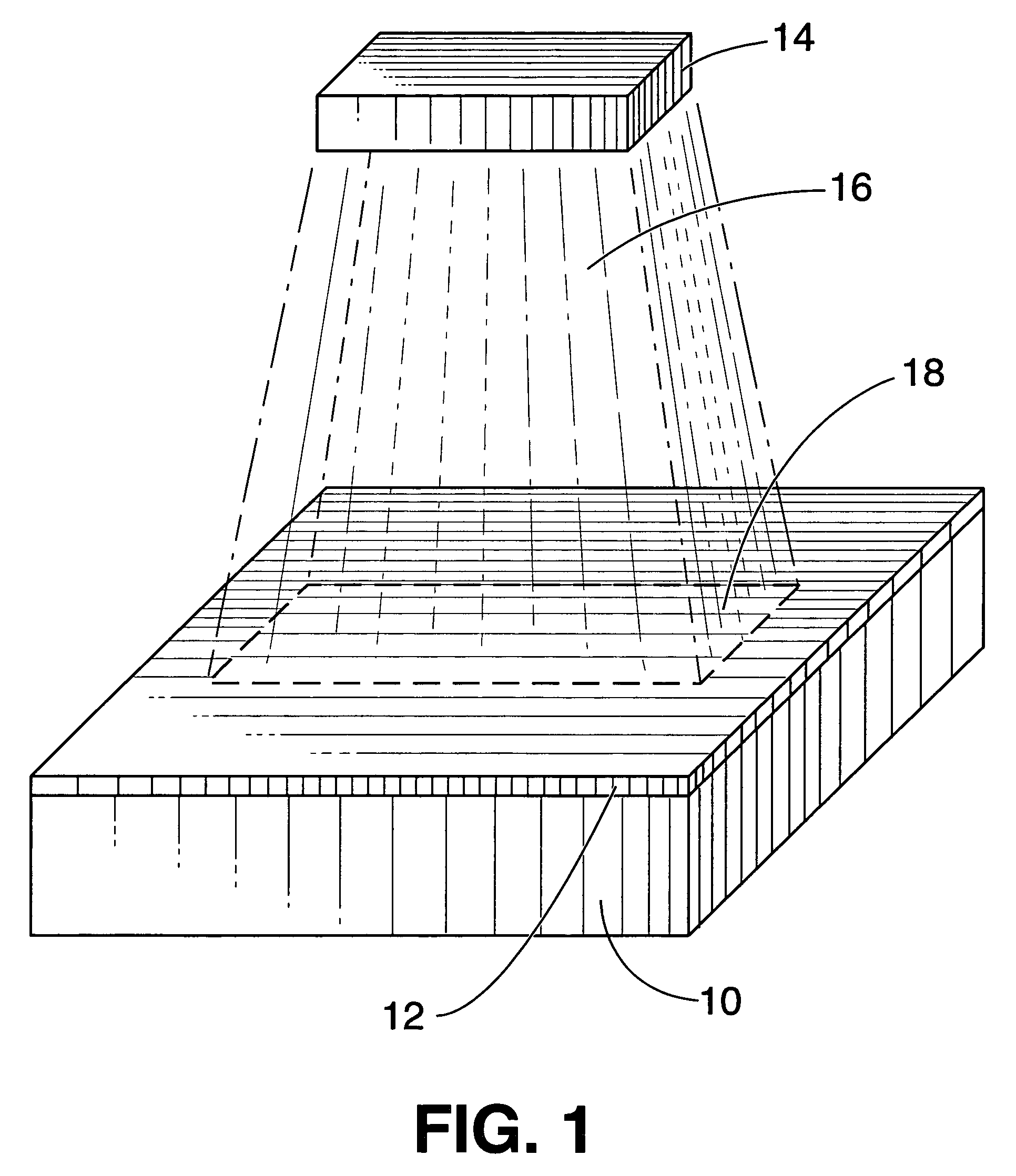
[0018]Pulsed energy from a directed, high density infrared plasma arc lamp, referred to hereinafter by the term “directed plasma arc” (DPA) is the basic tool used in the present invention. A suitable device that produces the necessary DPA is described in U.S. Pat. No. 4,937,490 (referenced above). The DPA can supply large power densities, up to 20,000 W / cm2, for example, depending on the setup, simultaneously over large areas, for example, 300 cm2, in short time frames in a completely controlled manner. The device is highly adaptable to meet the needs of many different applications.
[0019]The heating process utilizing the pulsed DPA is capable of quickly delivering large amounts of heat over large surface areas with little or no deleterious influence upon subsurface compositions. Pulses of IR energy from the DPA can be of as short in duration and / or periodicity as the physical limitations of the device that produces the DPA, preferably in a manner that allows precise control various ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com