Binding molecules derived from immunoglobulins which do not trigger complement mediated lysis
a technology of immunoglobulin and binding molecules, which is applied in the field of binding polypeptides, can solve the problems of inappropriate cell killing, opsonisation or in cytokine release and inflammation, and further complicated situation, and achieve the effect of increasing the therapeutic potential of the binding molecule and maximizing the number of matches
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation and Basic Characterisation of Antibodies
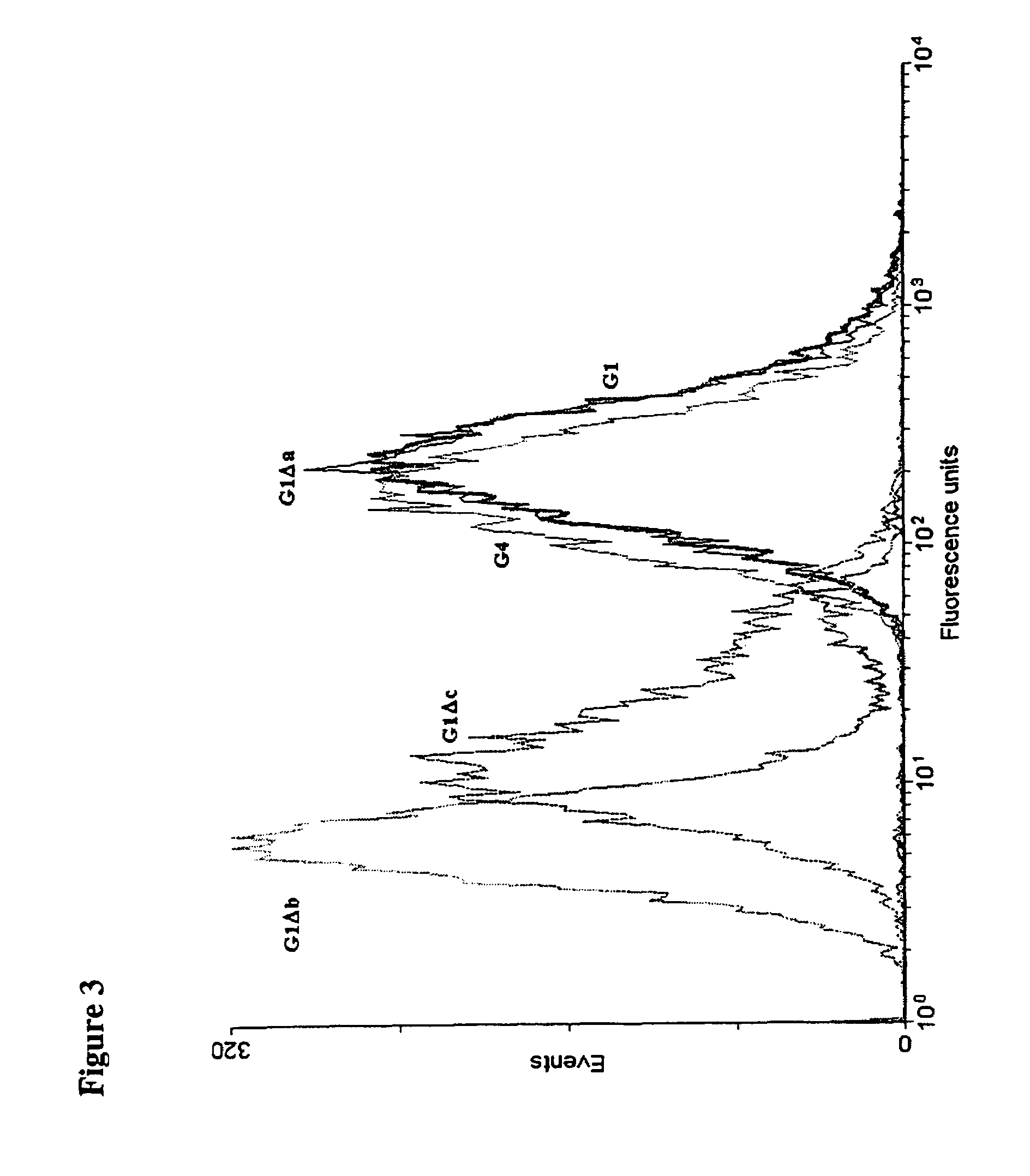
[0165]The mutations chosen to eliminate the effector functions are shown in Table 1 (FIG. 15). The Δa mutation made in IgG1 and IgG2 genes introduces the IgG4 residues at positions 327, 330 and 331. Similarly, the IgG2 residues at positions 233-236 were introduced into IgG1 and IgG4 but, since IgG2 has a deletion at 236 where the other subclasses have a glycine residue, the mutation was made omitting (Δb) or including (Δc) G236.
[0166]Vectors allowing expression of CAMPATH-1 or Fog-1 VH DNA in conjunction with the wildtype or mutant constant region genes were cotransfected with the appropriate light chain expression vectors into rat myeloma cells. Stable transfectants were isolated, expanded and Ab purified from the supernatant on protein A-agarose.
[0167]CAMPATH-1H was selected as it provides a good targeting system for studying complement and cell mediated lysis in vitro.
[0168]For the Fog-1 Ab, a precipitate formed after purificati...
example 2
FcγRI Binding
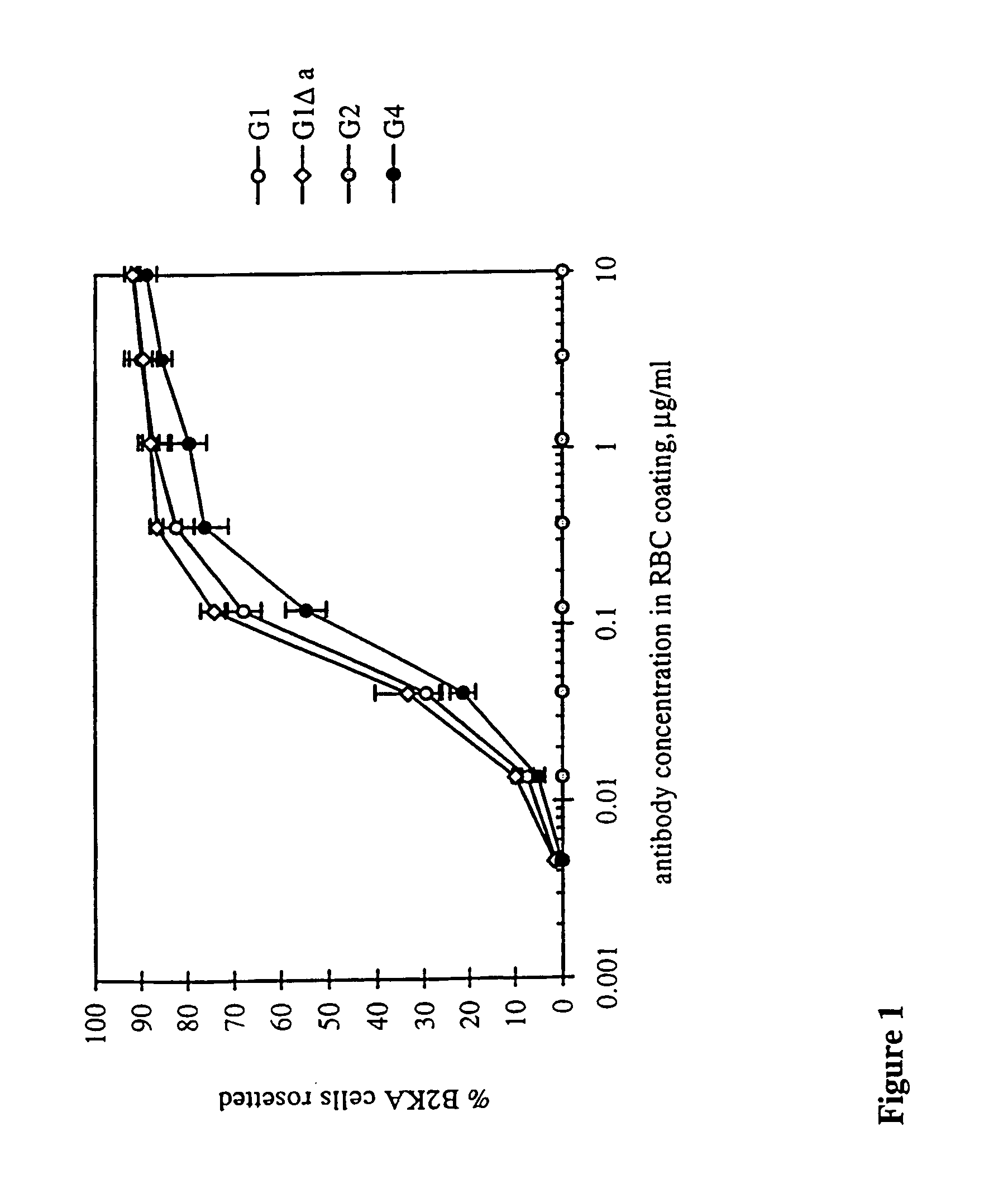
[0170]RBC with approximately 30 000 RhD sites per cell (R2R2) were coated with each of the 11 Fog-1 Ab over a range of concentrations and added to human FcγRI-expressing transfectants, B2KA, growing in wells. After incubation, excess RBC were washed away and the percentage of B2KA cells rosetted by RBC was recorded (FIG. 1). For G1 and G1Δa, where IgG4 residues are included at positions 327, 330 and 331, similar levels of resetting were achieved, with half-maximal resetting occurring when the RBC were coated with Ab at about 0.1 μg / ml, a concentration at which Fog-1 Ab would be expected to occupy approximately one-third of the RhD sites. Slightly higher concentrations of G4 were needed to obtain the same levels of rosetting. No rosettes were formed when using RBC coated with the G1 and G4 Ab containing the Δb and Δc mutations or the G2 Ab. In the experiment shown in FIG. 1, the highest coating concentration tested was 10 mg / ml, predicted to correspond to approximately 9...
example 3
FcγRI Triggering Measured By Chemiluminescence
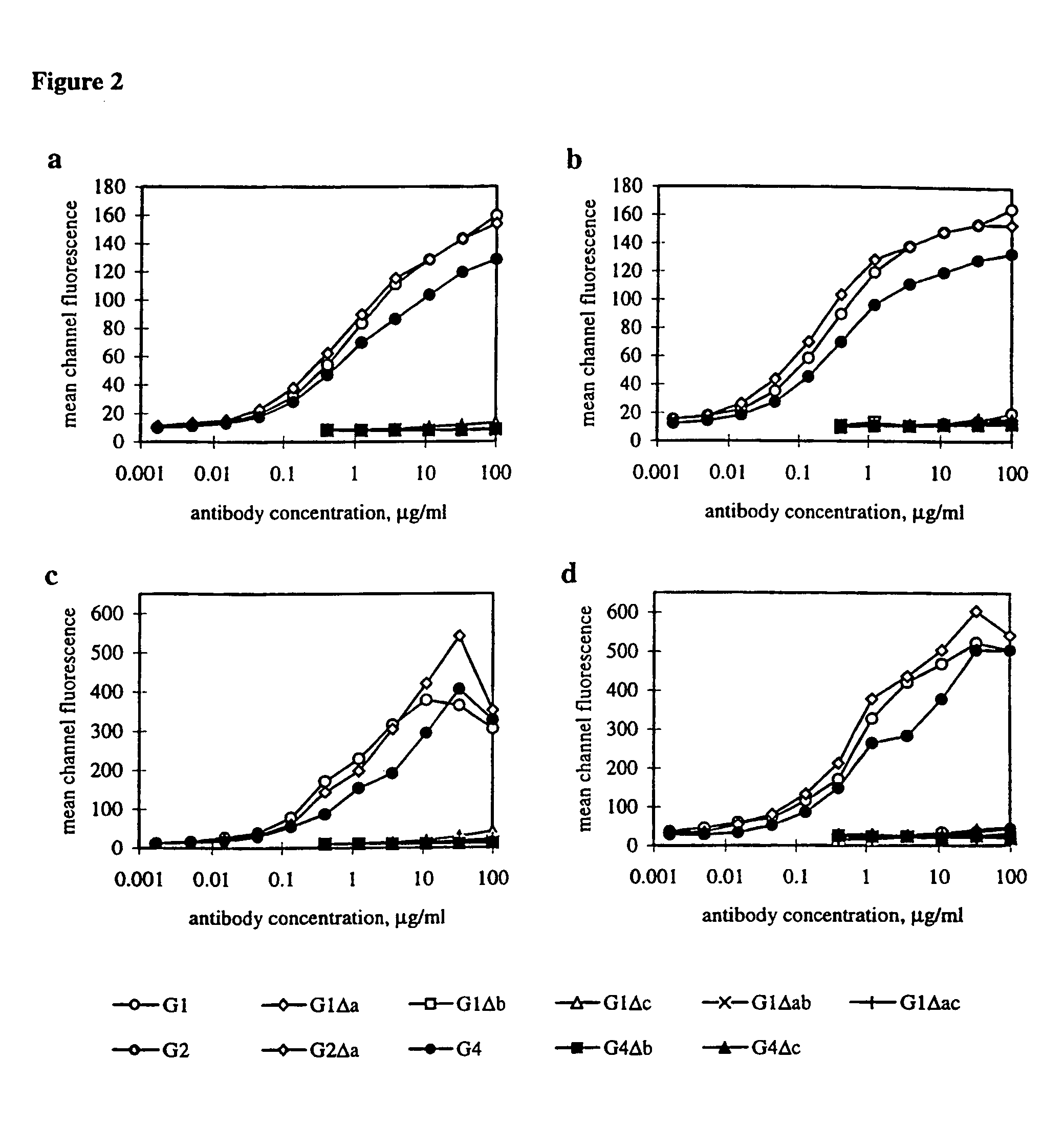
[0173]In order to measure functional activity through FcγRI / II, the chemiluminescent (CL) response of monocytes to RBC sensitized with Ab from the Fog-1 series was measured and plotted in relation to the number of Ab molecules bound per RBC (FIG. 4). A difference between the G1 and G1Δa Ab is seen with higher amounts of Ab but both are give higher responses than the G4 Ab across the range of Ab concentrations. Significant triggering is achieved by the G1Δc Ab and, to a lesser extent, by G1Δac and G4Δc but the other Ab do not give any response.
[0174]Ab, which were known to be deficient in the triggering of FcγRI from the previous section, were mixed in increasing concentrations with a constant amount of Fog-1 G1 and used to sensitize RBC. The CL response to the RBC is shown in FIG. 5. By comparing the CL response to that obtained when titering G1 alone, it appears that six of the eight Ab inhibit the reaction to an extent which predicted ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com