Power supply device and operations control method thereof
a power supply device and operation control technology, applied in the direction of automatic control, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of lowering overall conversion efficiency and difficulty in providing steady voltage, and achieve steady output voltage and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
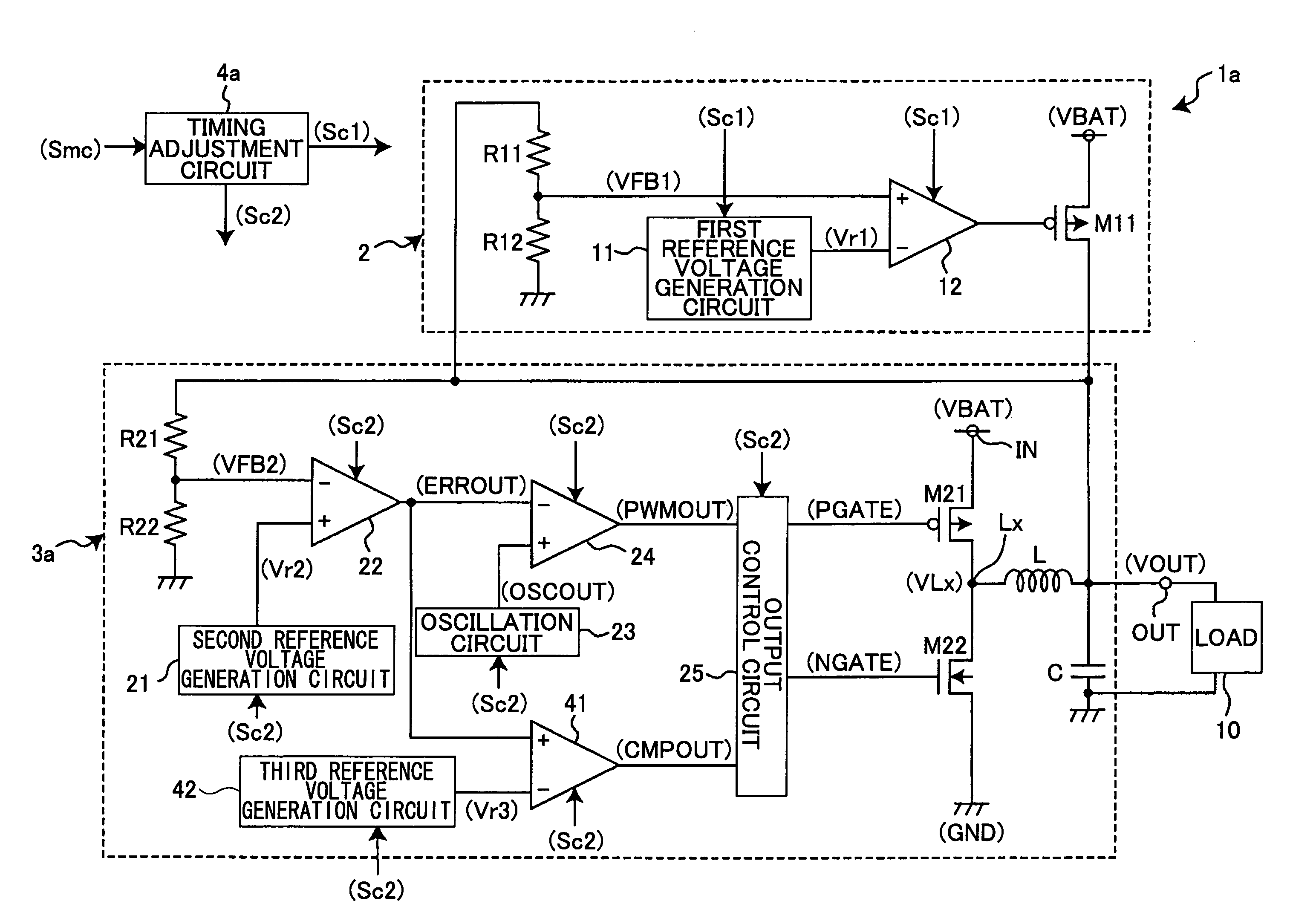
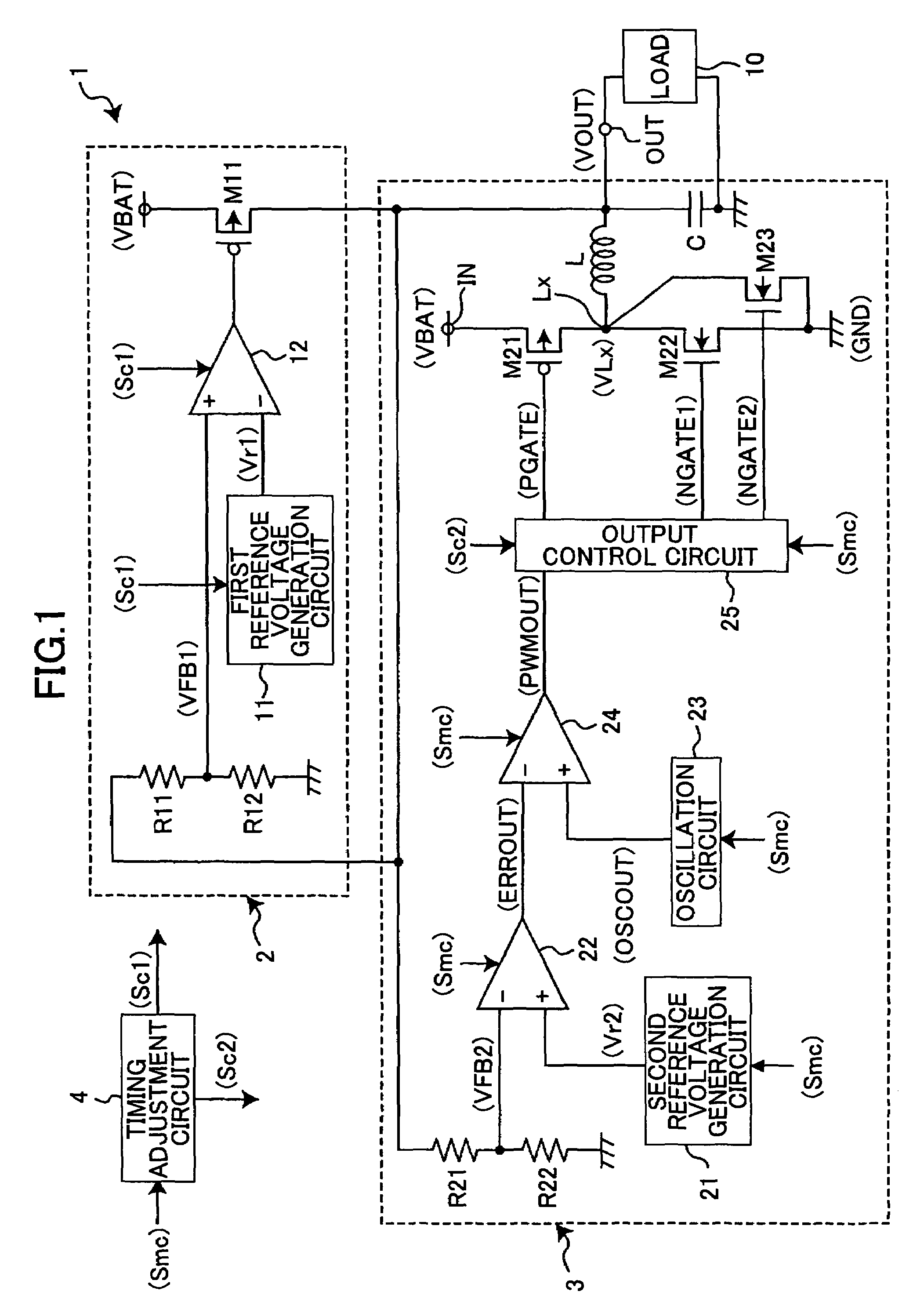
[0027]FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a circuit example of a power supply device of a first embodiment of the present invention.
[0028]In FIG. 1, the power supply device 1 converts an input voltage VBAT input to an input terminal IN into a predetermined constant voltage V1 and outputs the converted voltage to a load 10 from an output terminal OUT as an output voltage VOUT.
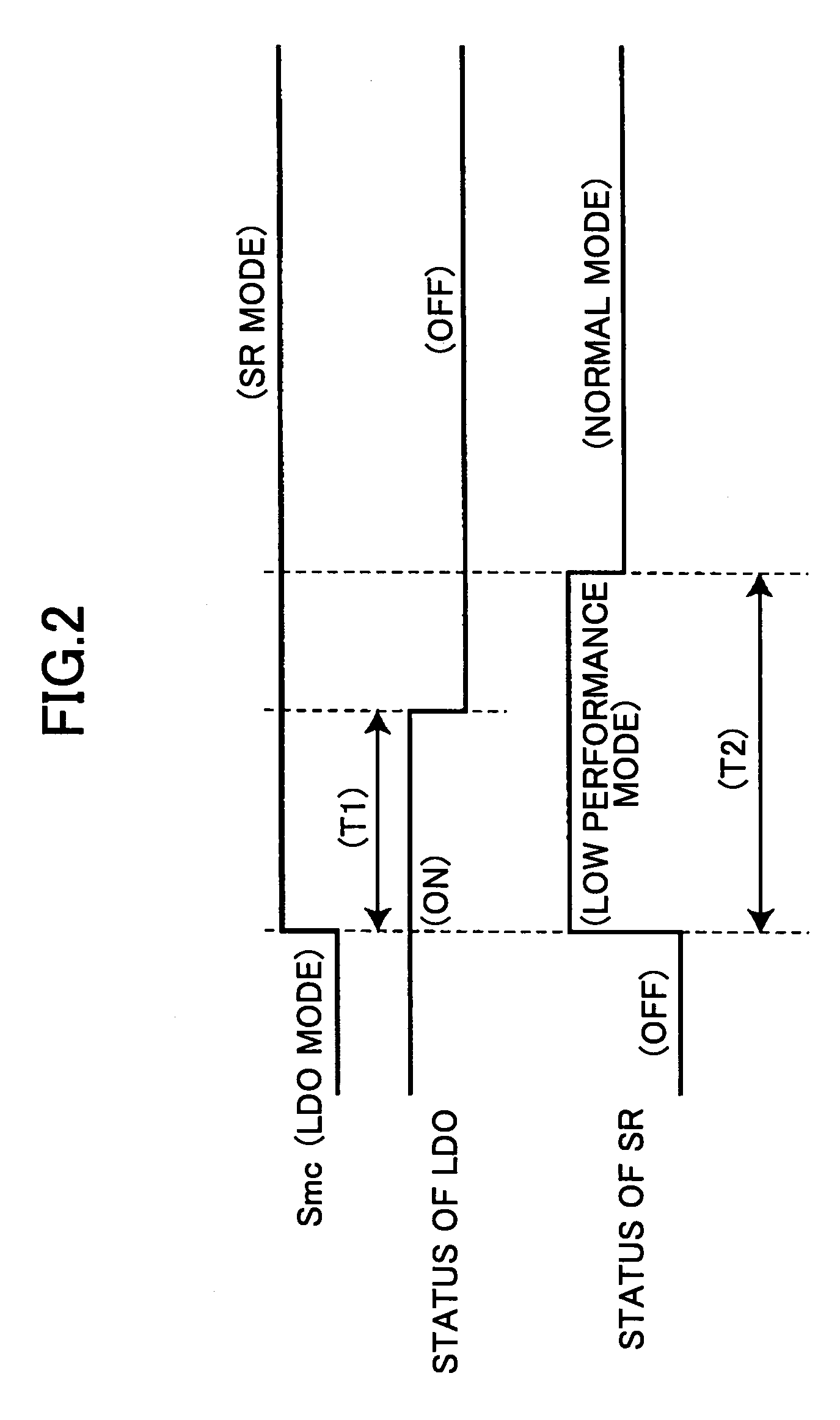
[0029]The power supply device 1 is composed of a LDO 2 serving as a linear regulator, a switching regulator 3 serving as a DC-DC converter, and a timing adjustment circuit 4 that controls driving of the LDO 2 and switching regulator 3 in accordance with a switching signal Smc input from the outside. The switching signal Smc is input so as to actuate the LDO 2 in a low current consumption operation mode such as a sleep mode and actuate the switching regulator 3 in a normal operation mode. The output terminals of the LDO 2 and the switching regulator 3 and their input terminals are connected to the output terminal OUT of ...
second embodiment
[0048]In the above first embodiment, the synchronous rectification transistor having the low current drive performance is used until the second predetermined time T2 has elapsed after the switching regulator 3 is started. Alternatively, both of the switching transistor and the synchronous rectification transistor may be turned off to cut off an electrical connection until the output voltage of the error amplification circuit 22 becomes equal to or greater than a predetermined value at the starting of the switching regulator 3. A description is now made of this modification as a second embodiment.
[0049]FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a circuit example of the power supply device according to the second embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 3, components the same as or similar to those of FIG. 1 are indicated by the same numerals and are not be described below. Here, only parts different from FIG. 1 are described.
[0050]FIG. 3 is different from FIG. 1 in that the synchronous rectific...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com