Aqueous two-phase emulsion gel systems for zone isolation
a technology of emulsion gel and zone isolation, which is applied in the direction of fluid removal, borehole/well accessories, chemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of less reliable sealing devices, bulky devices, and high cost, and achieves the effect of convenient and accurate delivery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Thermal Activation of a Two-Phase Polymer Solution to become an Elastic Gel
[0041]Experimentally, it has been found that solutions of guar and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) form aqueous phase-separated solutions over a range of polymer concentrations. A phase-separated mixture was formed by simultaneously dissolving 2 wt % dry guar and 2 wt % dry HPC in 100 ml of DI water in a stirred Waring blender. After stirring for approximately an hour, the sample was allowed to rest for an hour to confirm phase separation. The phase-separated solution was then gently stirred by hand to remix the guar-rich and HPC-rich phases.
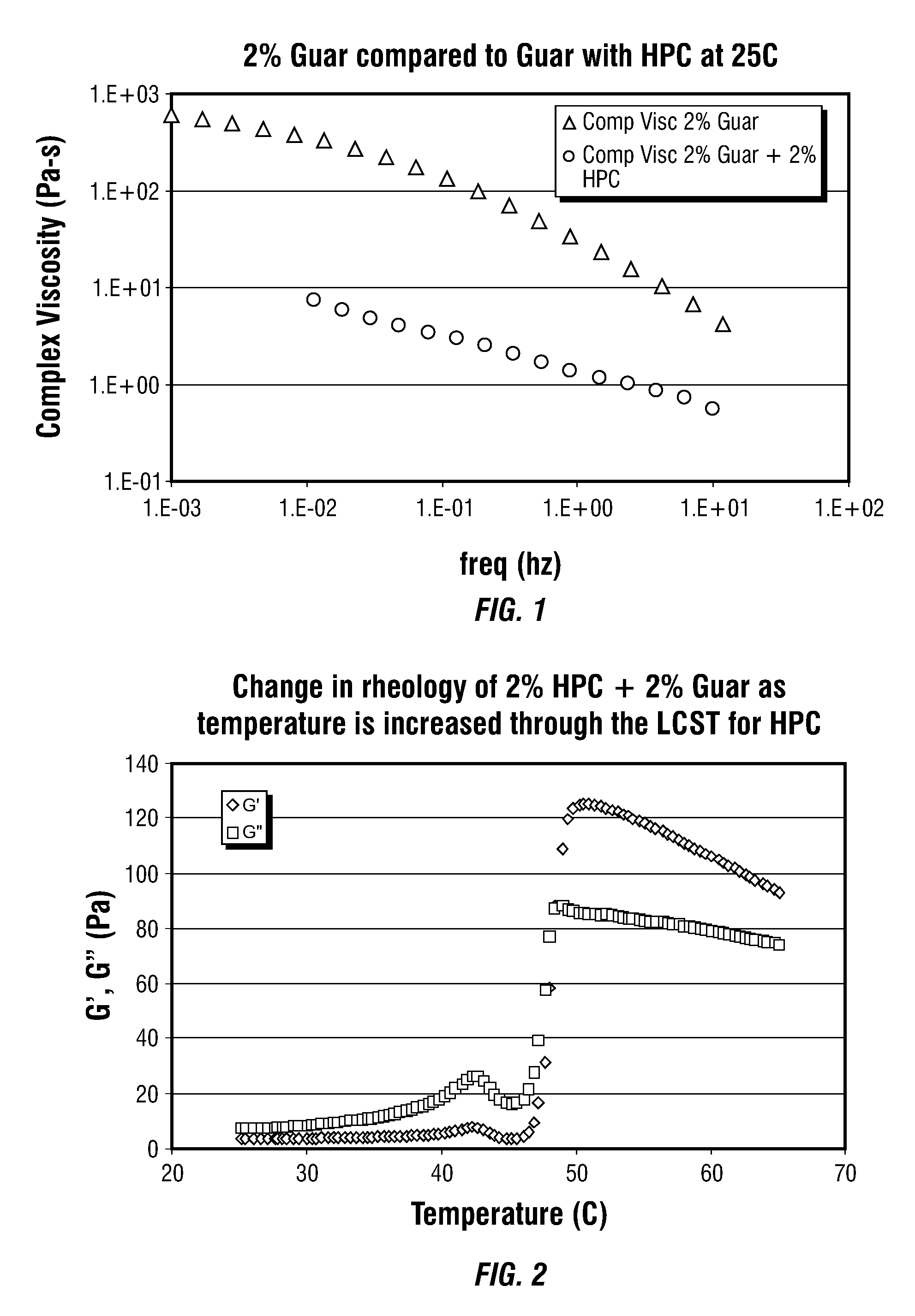
[0042]The rheology of this mixed two-phase polymer mixture was then measured at 25 C as shown in FIG. 1. The fluid is of sufficiently low viscosity to be easily pourable and pumpable. It is substantially less viscous than the 2% guar solution viscosity shown for comparison in FIG. 1. FIG. 1 illustrates how the presence of the HPC polymer phase dramatically reduces the rheol...
example 2
Thermal Activation of a Gel
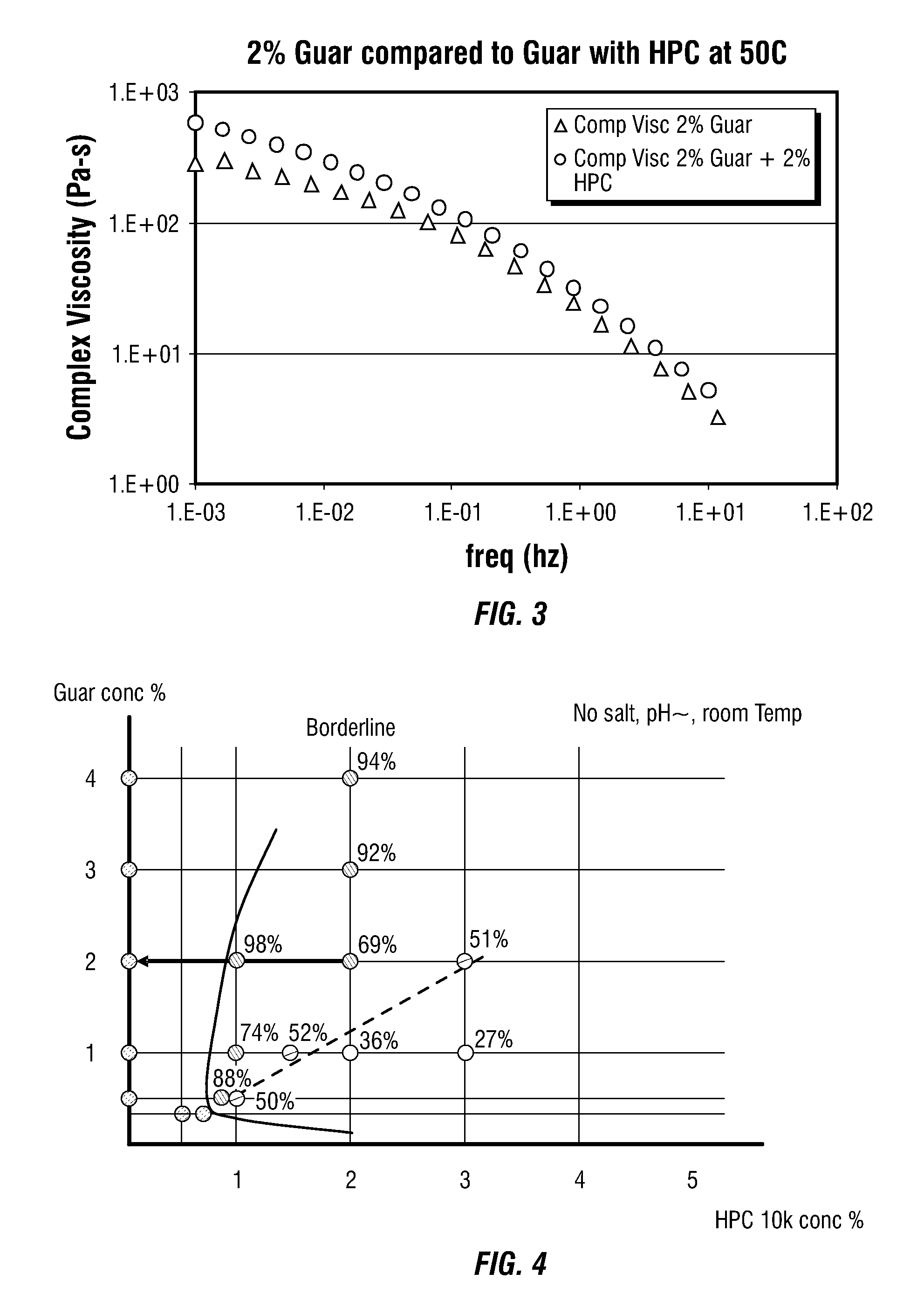
[0046]As a second example of thermal activation of a gel, guar was combined with HPC having a molecular weight of approximately 10,000 to make a low viscosity, pumpable mixture. This example was similar to the first example except that the HPC used had a molecular weight which was less by an order of magnitude. The phase diagram for this polymer combination is shown in FIG. 4.
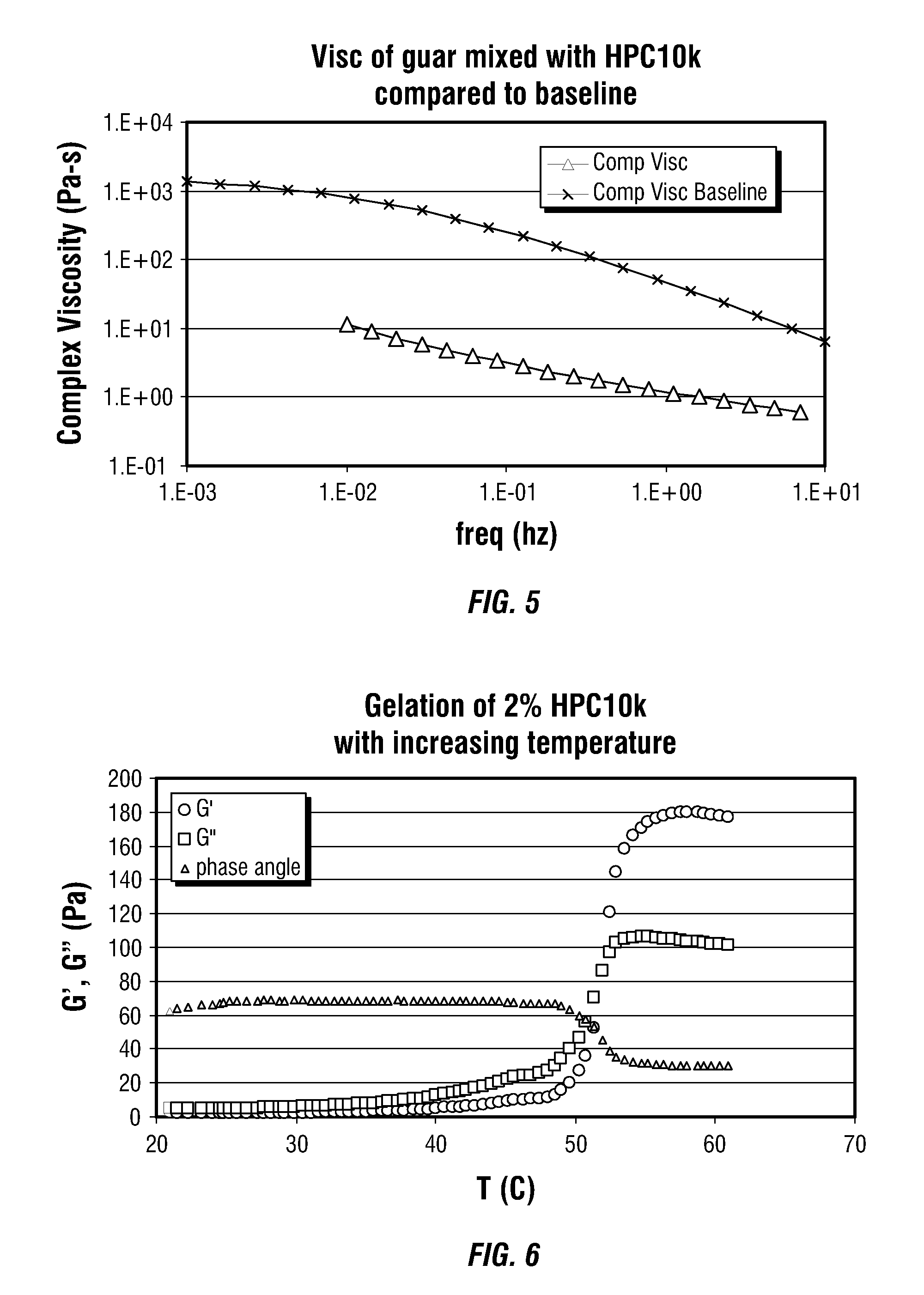
[0047]In FIG. 4, the red line in the phase diagram approximates the binodal for the system. Compositions to the right of the binodal are two phase fluids that will phase separate with time. Because of the phase separation, these fluids are low viscosity formulations that can easily be poured or pumped. Approximately 31% of the fluid volume is filled with a HPC-rich phase that prevent the full guar viscosity from developing. FIG. 5 provides measurements of the guar / HPC mixture at this condition and a comparison with 2% guar alone in water at this temperature. The addition of HPC 10,000...
example 3
Salt Activation of a Two-Phase Polymer Solution to become an Elastic Gel
[0048]A settable fluid was formed, that can set into a gel either by addition of salt or by exposure to increased temperature. Formulation was 2% guar and 2% Methocel®. The salt used in the example was NaCl. FIG. 6 shows the rheology of 2% guar in aqueous solution with 2% HPC10,000. For comparison, the rheology of 2% guar in solution is also shown.
[0049]FIG. 6 shows the effect on the mixture rheology as the temperature is increased from 21 C to 60 C over a 30 minute time period. The rheology has been quantified in FIG. 6 by monitoring the elastic and viscous moduli continuously with a 10% strain oscillation at a frequency of 0.5 Hz. At lower temperatures, the solution behaves as a low viscosity fluid with the viscous modulus being greater than the elastic modulus. As the temperature exceeds the LCST for the HPC10000, the solution changes to behave like an elastic solid with the elastic modulus increasing by near...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com