Frequency-scan traveling wave antenna
a traveling wave and antenna technology, applied in the direction of antennas, non-resonant long antennas, electric long antennas, etc., can solve the problems of interference with the use of such antennas, burdening the antenna, adversely affecting the quality of the performance, etc., and achieve high performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the various figures of the drawings.
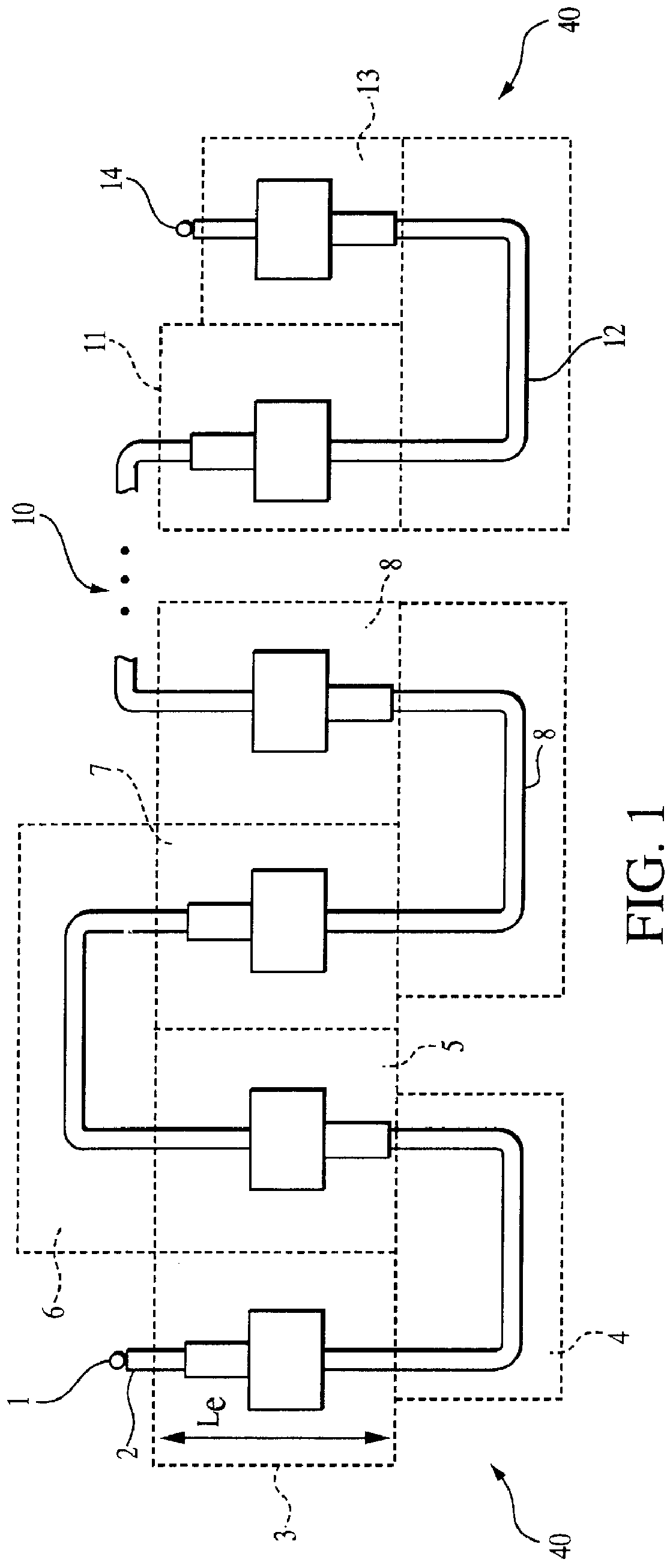
FIG. 1 is a diagrammatic representation of a preferred traveling wave antenna array employed in the present invention. As seen therein, the frequency-scan traveling wave antenna 40 of the present invention comprises the following elements: input port 1; quarter wave transformer 2; first radiator element 3; first delay line 4; second radiator element 5; second delay line 6; third radiator element 7; third delay line 8; fourth radiator element 9; intervening delay lines and radiator elements generally indicated by reference numeral 10; penultimate radiator element 11; final delay line 12; final radiator element 13; and output port 14.
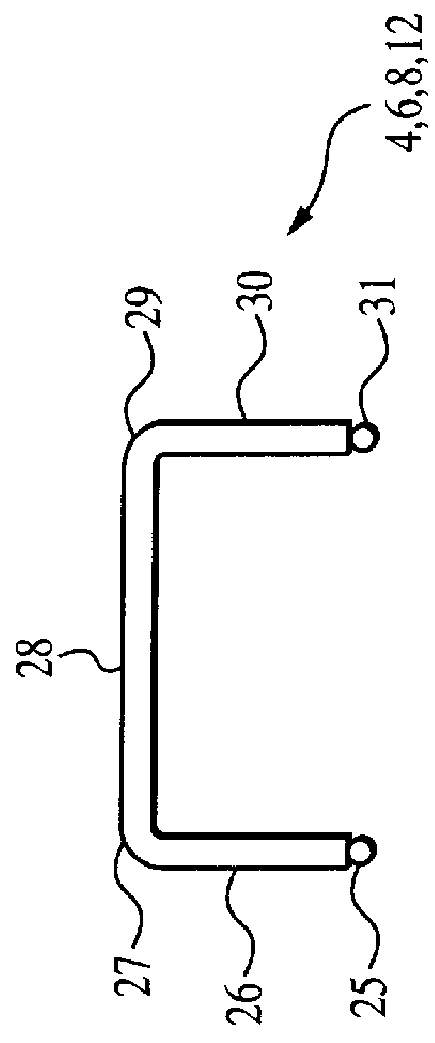
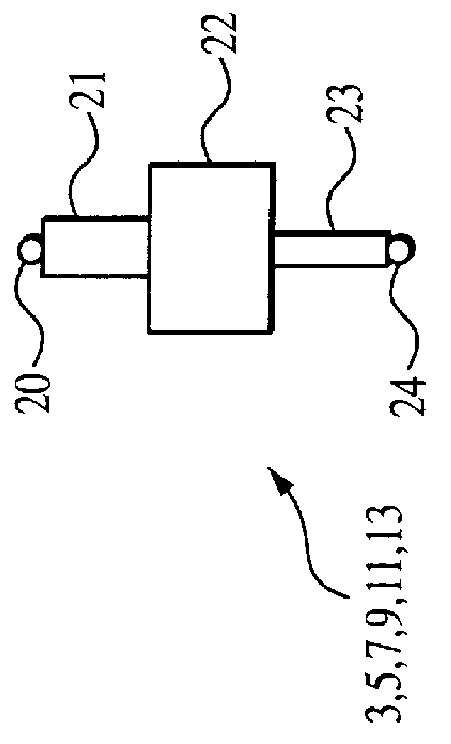
The composition of each radiator element 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 and 13 (and any intervening radiator elements) will be described in detail below with reference to FIG. 2A, while the composition of each delay line 4, 6, 8, and 12 (and any intervening delay line...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com