Semiconductor device
a technology of semiconductors and devices, applied in solid-state devices, basic electric elements, foundation engineering, etc., to prevent the strength of wire bonding from dropping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[Embodiment 1]
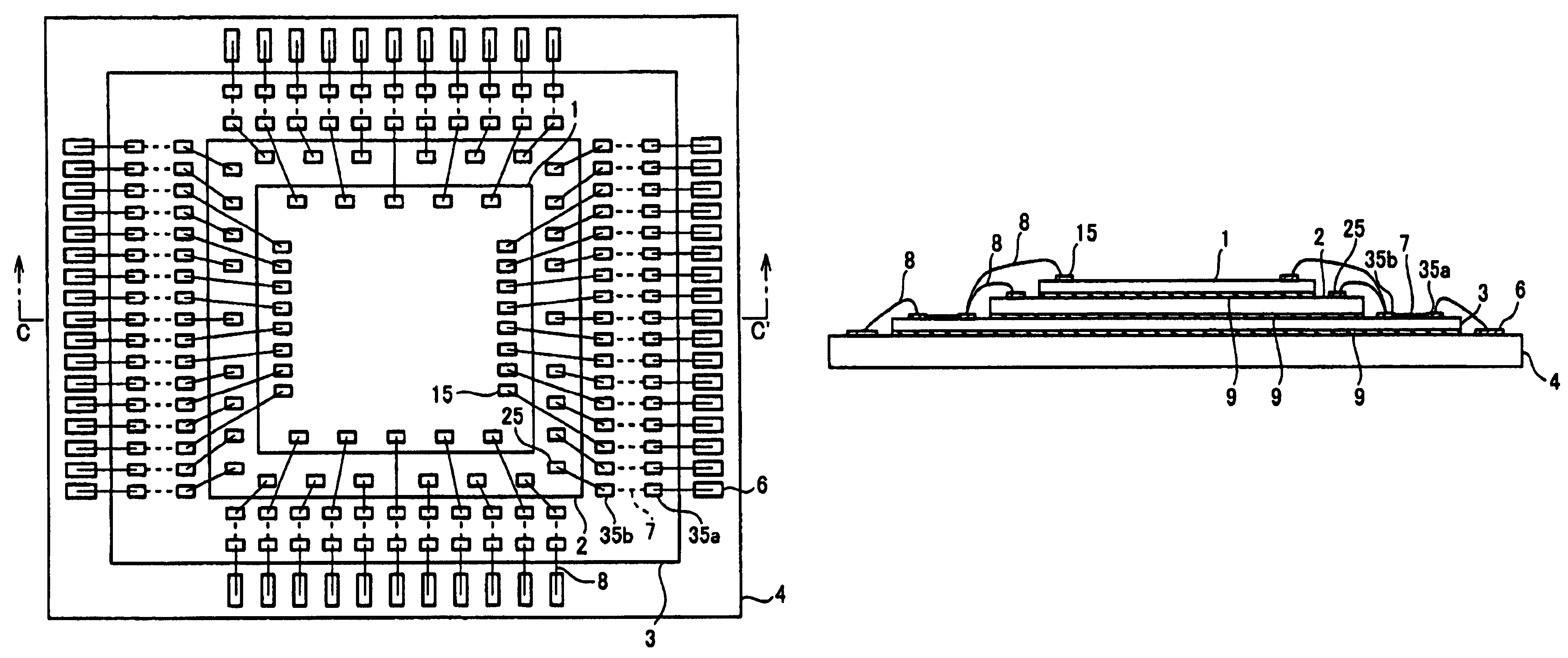
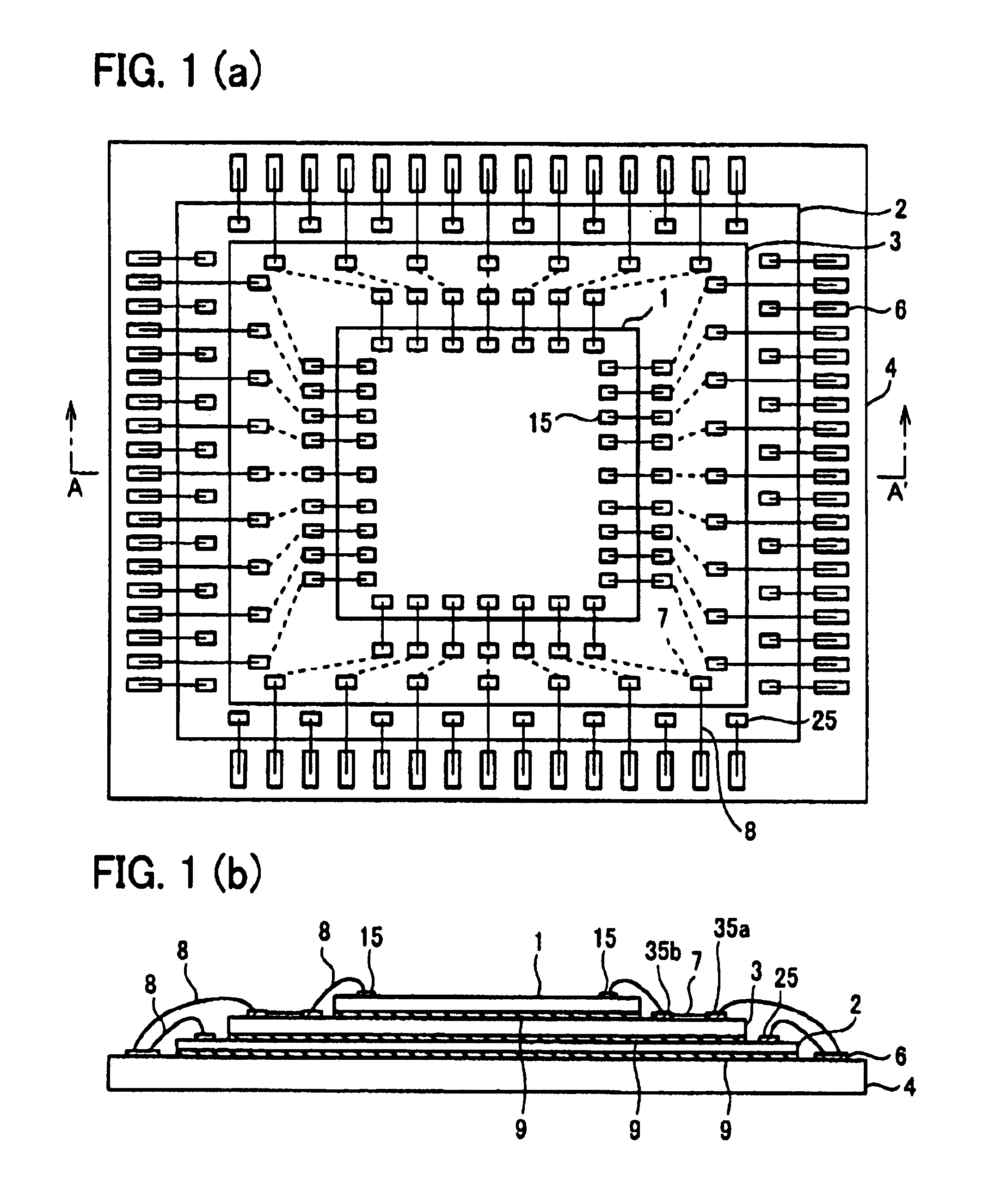
[0043]The following description will explain one embodiment of the semiconductor device of the present invention with reference to FIG. 1(a) and FIG. 1(b). Note that, the present invention is not limited to this.
[0044]FIG. 1(a) is a plan view obtained by viewing the semiconductor device of the present embodiment from above in a stacking direction, and FIG. 1(b) is a cross sectional view taken along A-A′ of FIG. 1(a).
[0045](Structure of the Semiconductor Device)
[0046]As shown in FIG. 1 (a) and FIG. 1 (b), the semiconductor device of the present embodiment is arranged so that: a substrate 4 is used as a stacking base, and a semiconductor chip 2, an interposer chip 3, and a semiconductor chip 1 are stacked on and above the stacking base in this order. Note that, by using die-bonding layers 9, the substrate 4 and the semiconductor chip 2 are bonded to each other, and the semiconductor chip 2 and the interposer chip 3 are bonded to each other, and the interposer chip 3 and ...
embodiment 2
[Embodiment 2]
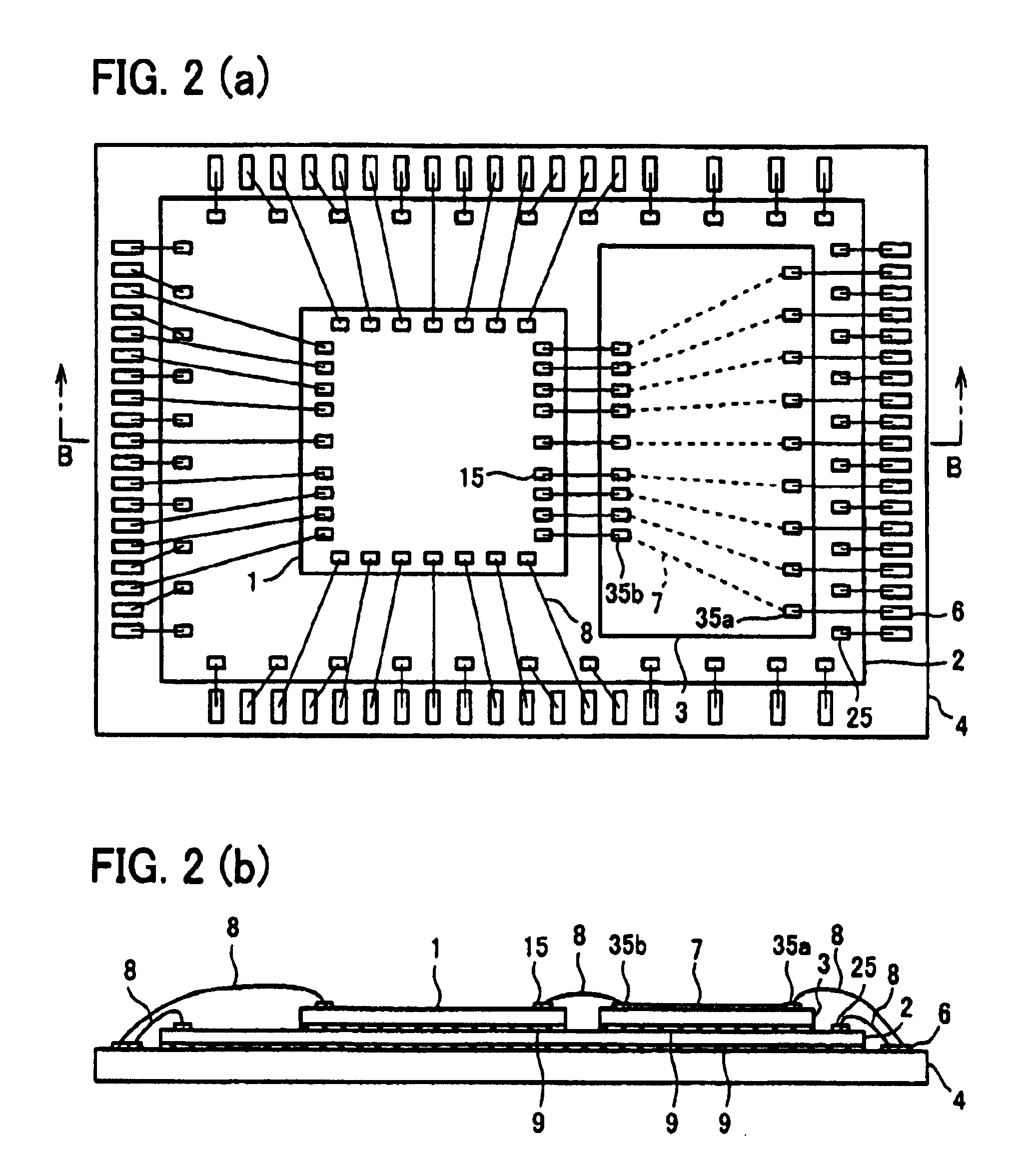
[0064]The following description will explain another embodiment of the semiconductor device of the present invention with reference to FIG. 2(c) and FIG. 2(b). Note that, for convenience in description, same reference signs are given to members having the same function as members described in Embodiment 1, and description thereof is omitted.
[0065]FIG. 2(a) is a plan view obtained by viewing the semiconductor device of the present embodiment from above in a stacking direction, and FIG. 2(b) is a cross sectional view taken along B-B′ of FIG. 2(b). As shown in FIG. 2(a) and FIG. 2(b), the semiconductor device of the present embodiment is arranged so that: the semiconductor chip 2 is stacked on an upper surface of the substrate 4, and the semiconductor chip 1 and the interposer chip 3 are stacked thereon so as to be positioned side by side. Note that, by using die-bonding layers 9, the substrate 4 and the semiconductor chip 2 are bonded to each other, and the semiconductor...
embodiment 3
[Embodiment 3]
[0072]The following description will explain still another embodiment of the semiconductor device of the present invention with reference to FIG. 3(a) and FIG. 3(b). Note that, for convenience in description, the same reference signs are given to members having the same functions as members described in Embodiment 1, and description thereof is omitted.
[0073]FIG. 3(a) is a plan view obtained by viewing the semiconductor device of the present embodiment from above in a stacking direction, and FIG. 3(b) is a cross sectional view taken along C-C′ of FIG. 3(a). As shown in FIG. 3(a) and FIG. 3(b), the semiconductor device of the present embodiment is arranged so that: the interposer chip 3 is stacked on an upper surface of the substrate 4, and the semiconductor chips 1 and 2 are stacked thereon and thereabove in this order. That is, in the present embodiment, the interposer chip 3 is formed between the substrate 4 and the semiconductor chip 2.
[0074]The bonding pads 15 . . ....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com