Cellular communications system with sectorization
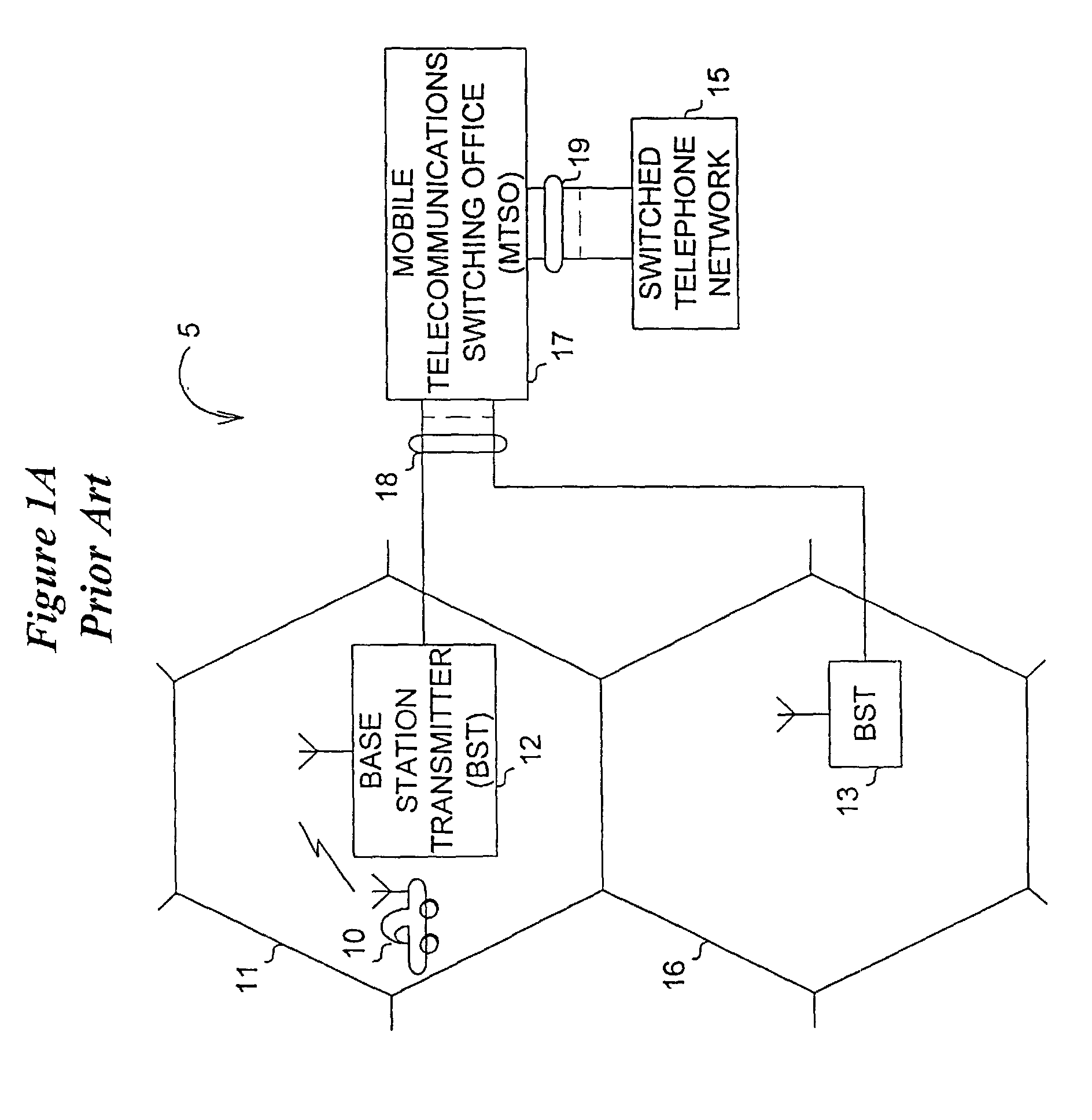
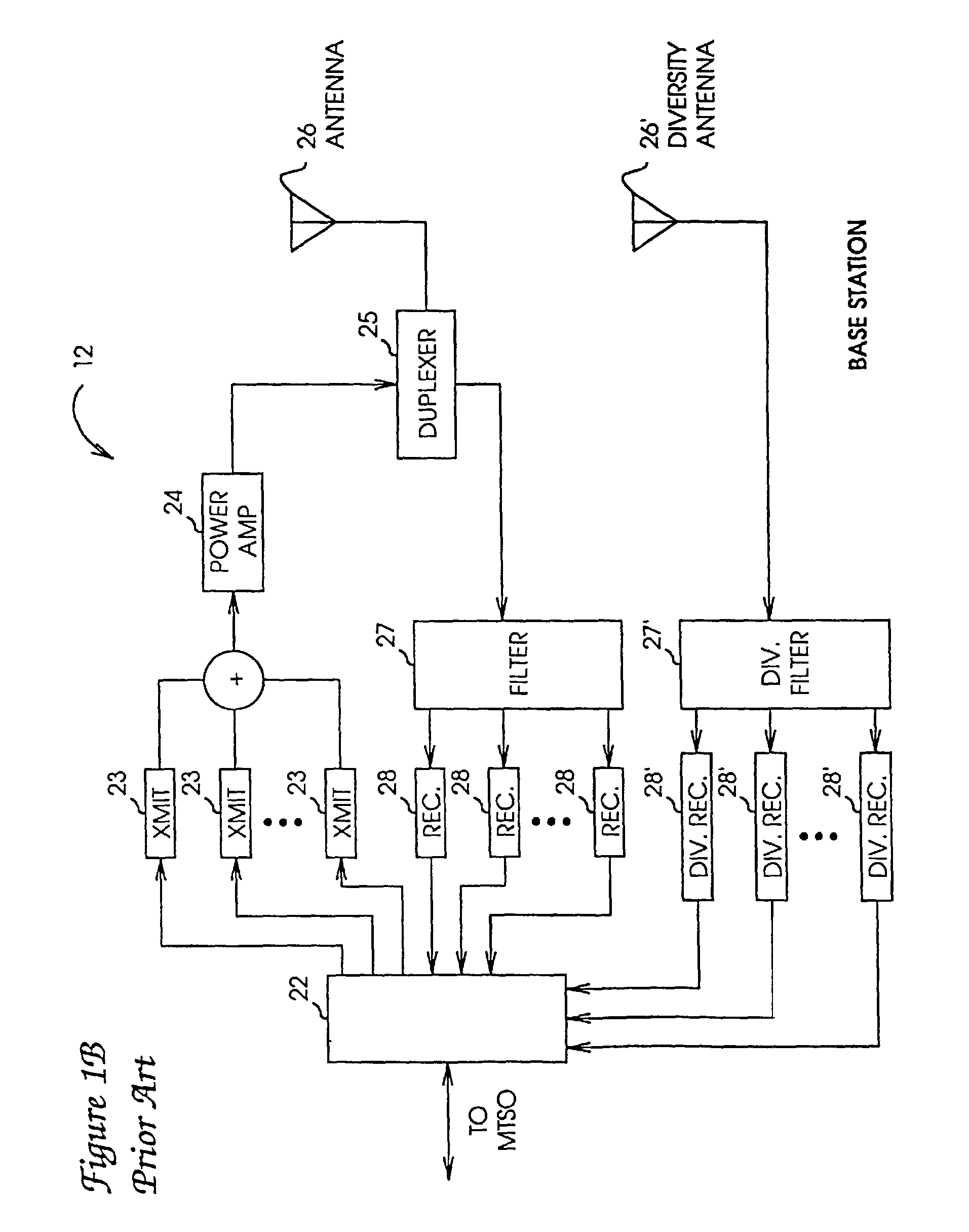
a cellular communication system and sectorization technology, applied in the field of high-capacity mobile communication systems, can solve the problems of limited coverage of urban cellular phone systems, severe limitations in the capacity of conventional systems, and poor dynamic range of suburban office buildings and complexes, so as to improve coverage, improve capacity, and improve the effect of dynamic rang
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
digital embodiment
All-Digital Embodiment
[0120]Referring now to FIG. 10, there is shown an alternate exemplary embodiment 200 of the present invention. Alternate embodiment 200 includes a remote antenna unit 102 as described with respect to FIG. 8. Remote antenna unit 102 is connected to an all-digital microcell base station 210 through fibers 104A and 104B. Microcell base station 210 is connected to an MTSO.
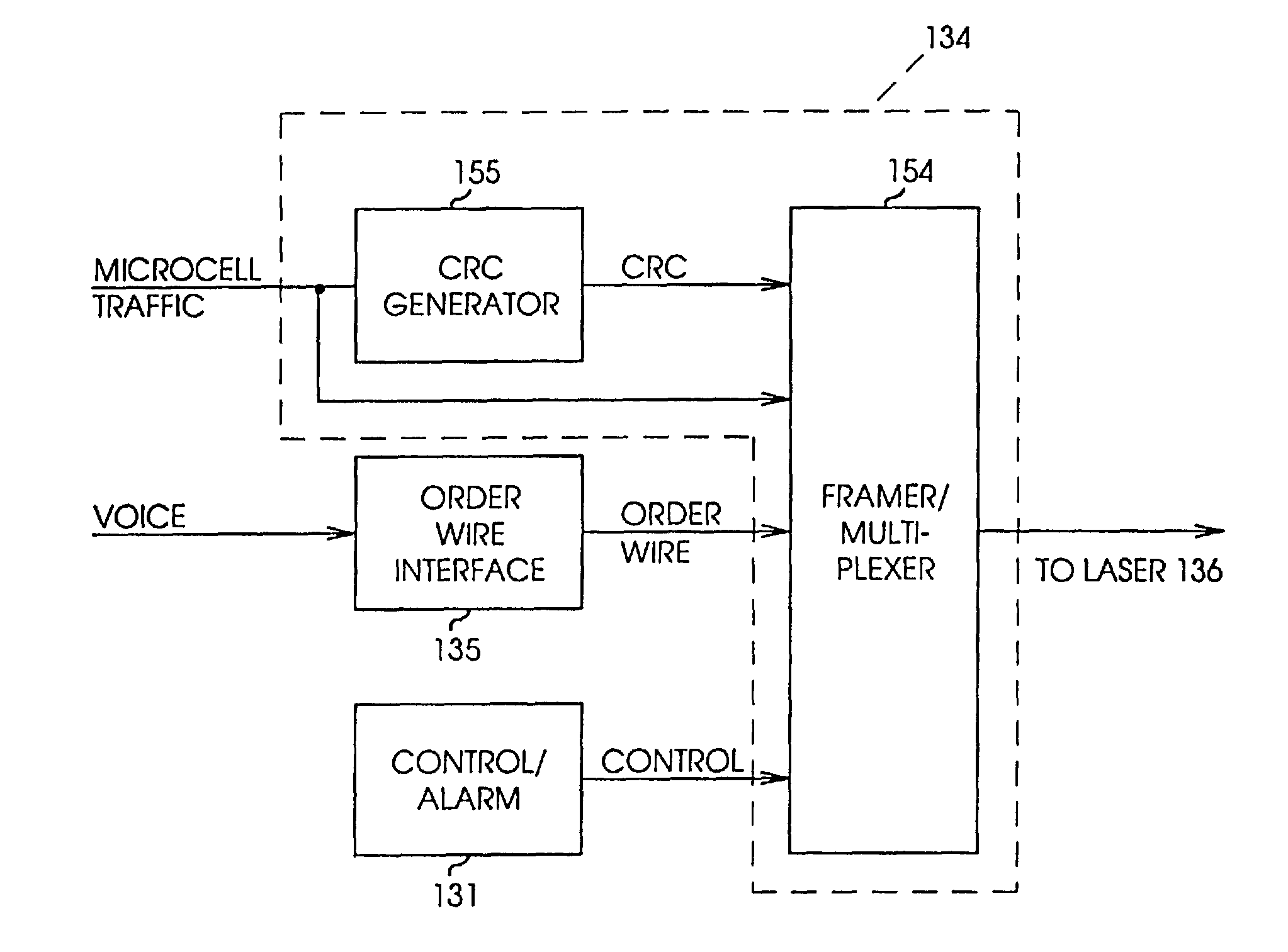
[0121]All-digital microcell base station 210 is shown in more detail in FIG. 11A. Circuit 210 includes a T1 interface 202, which extracts digitized voice channels carried by a T1 line or other carrier from an MTSO and applies those channels in digital form to digital synthesizer 212. Digital synthesizer 212 replaces transmitters 23 and the analog-to-digital converter 132 of the embodiment shown in FIG. 4. Digital synthesizer 212 constructs, with digital logic or software, an equivalent to the digitized output of broadband digitizer 132 for application to frame generator / multiplexer 214. Synthesis ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com