Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Facilitate reversible binding reactions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cheap micro-fluidic device for diagnosis of cholera and with specific liquid flow transmission manner
InactiveCN106990239AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionDisease diagnosisAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicrofluidic chipMicro fluidic
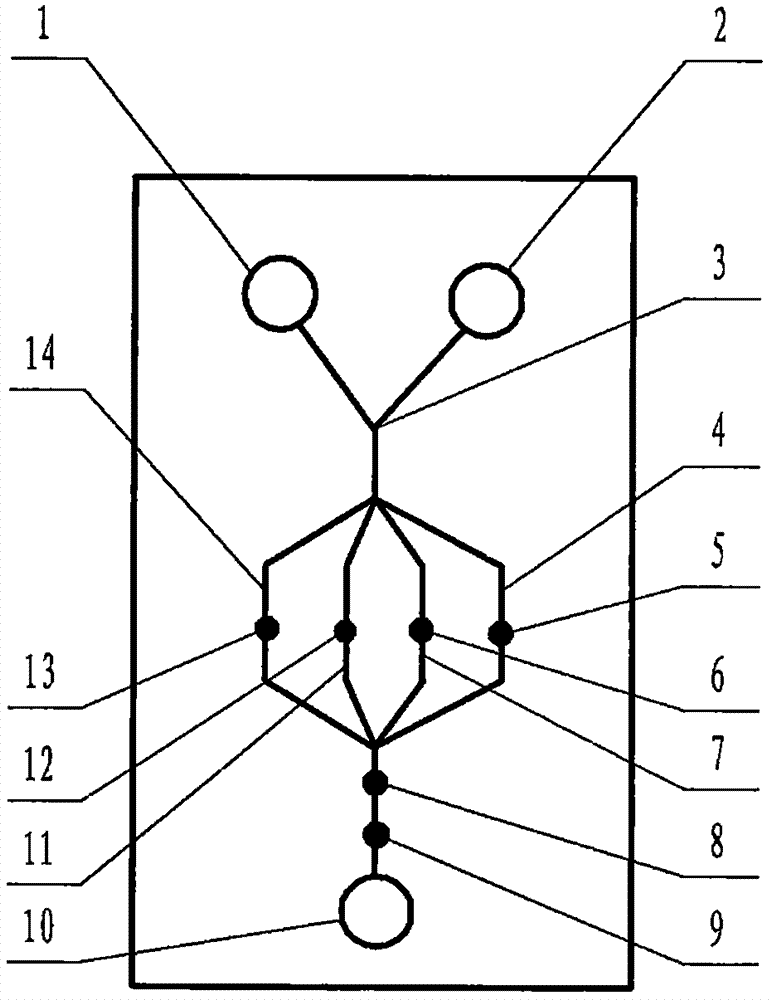
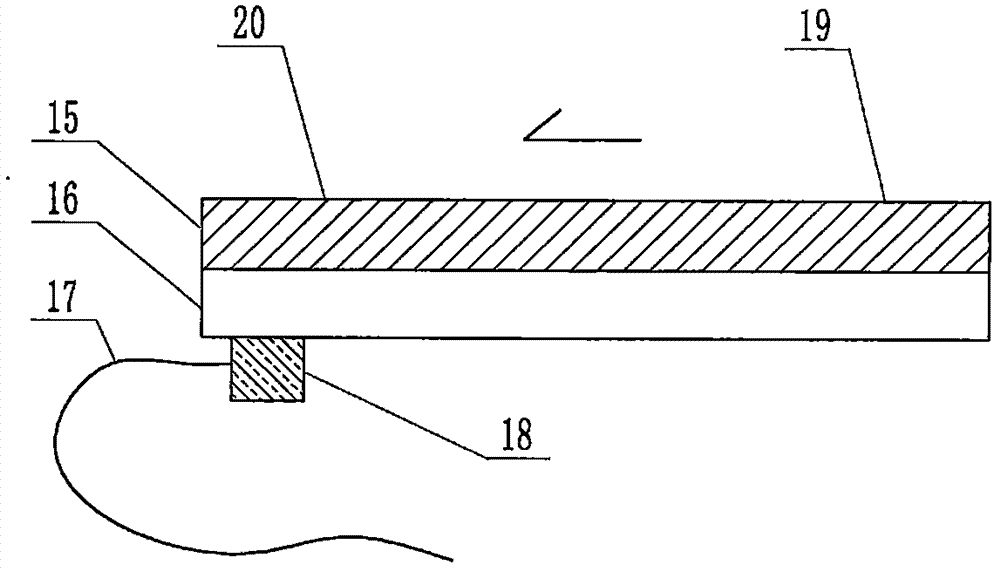
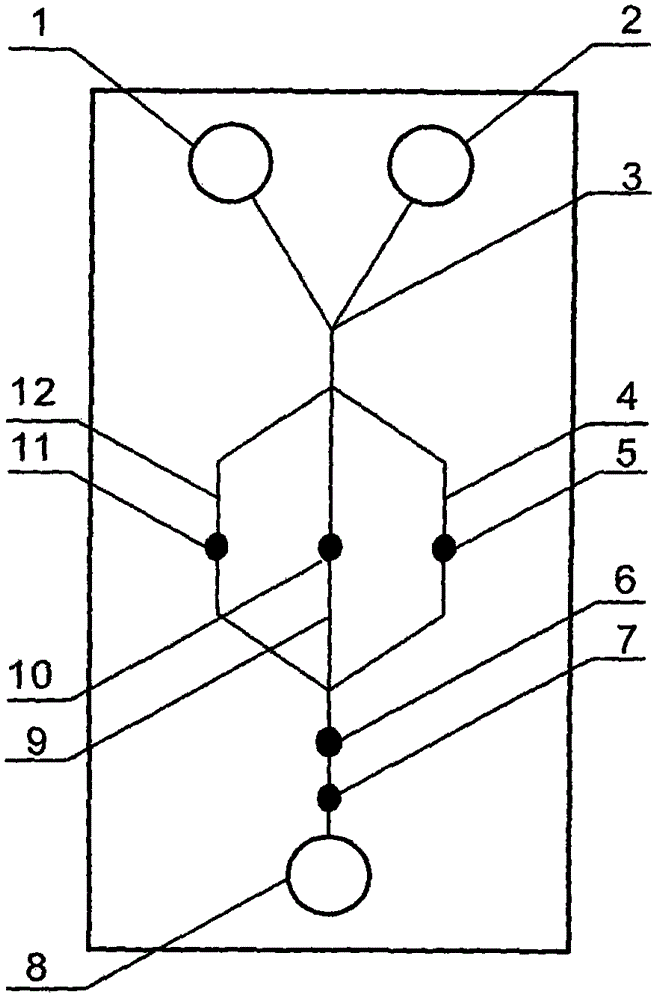
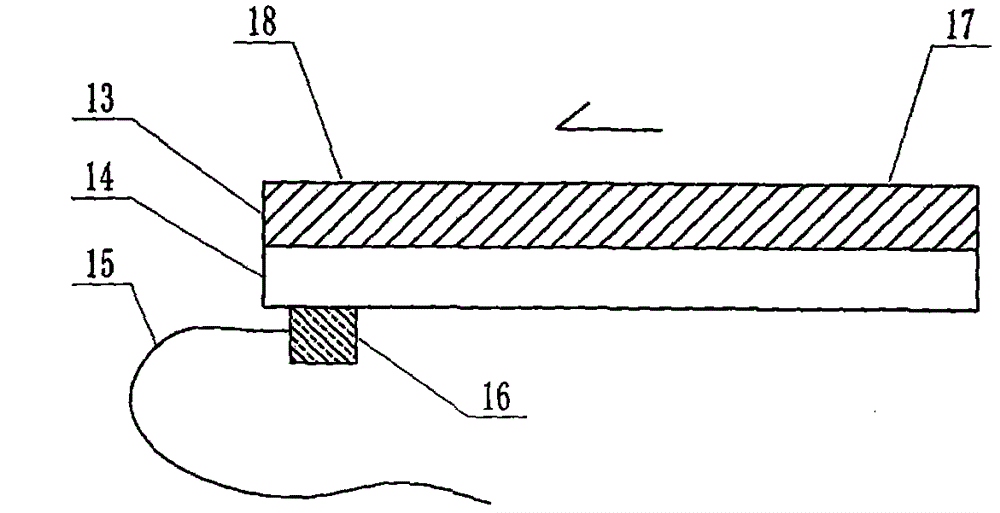
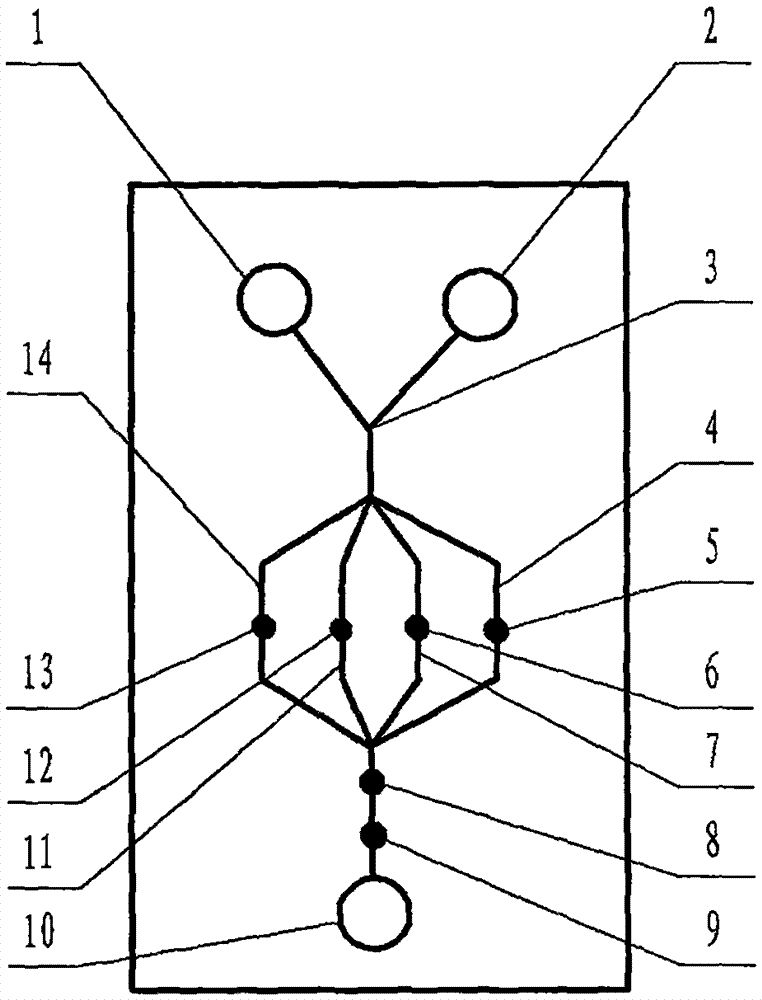
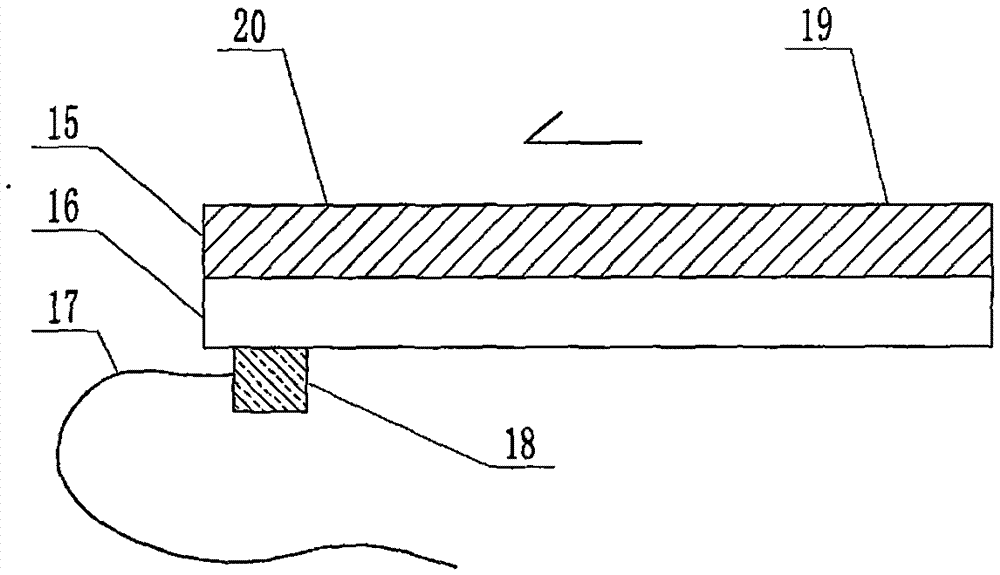
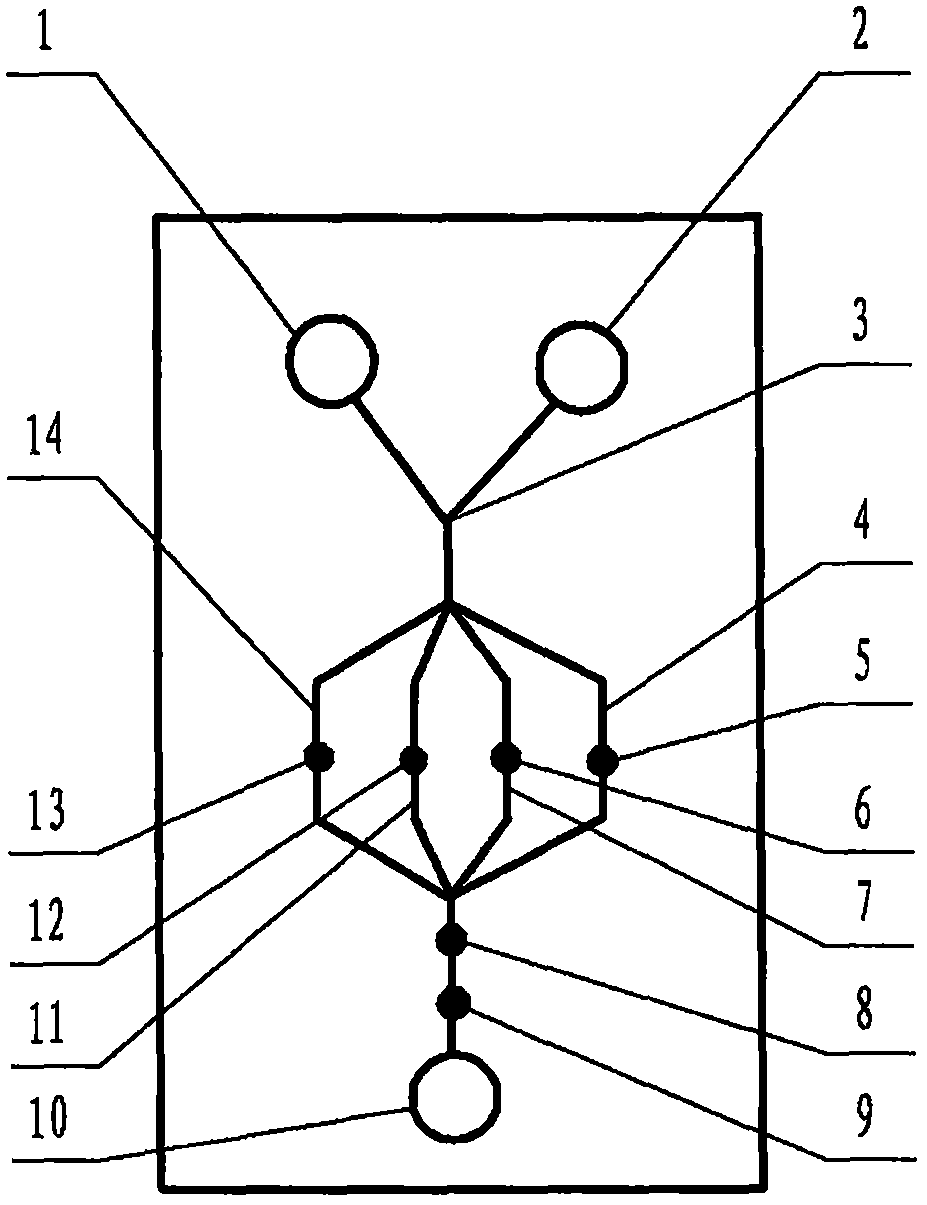
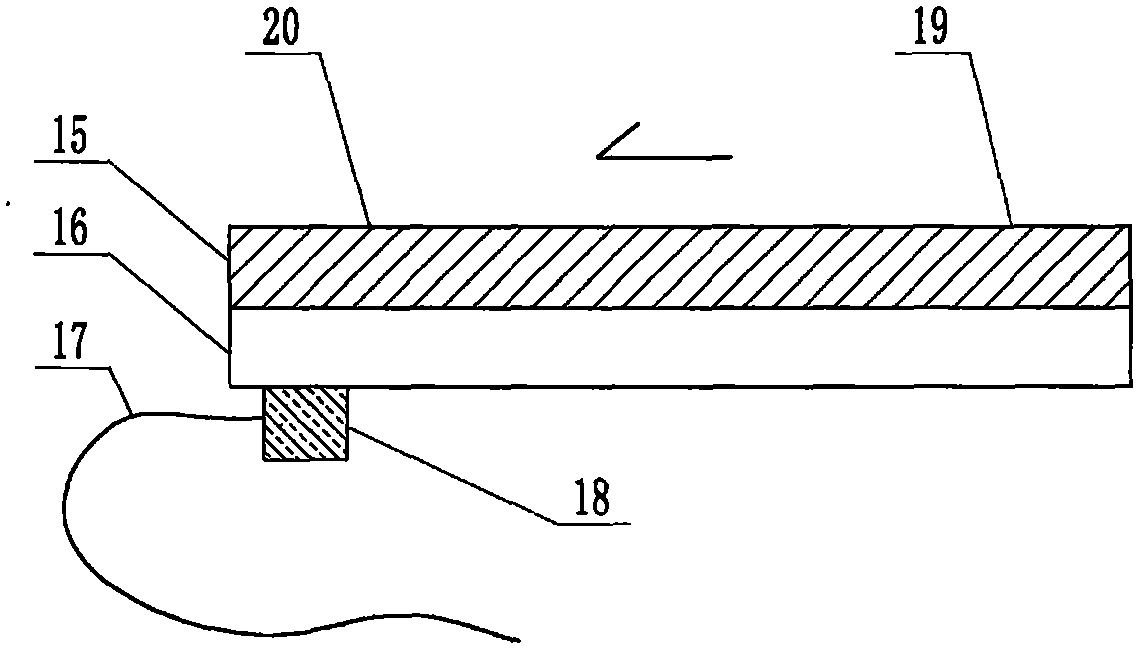
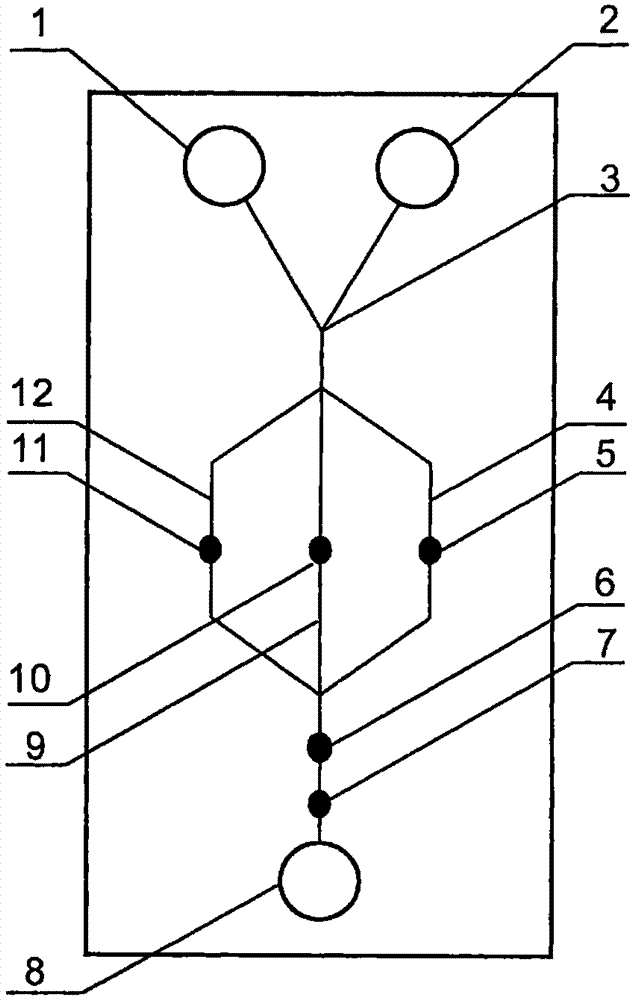
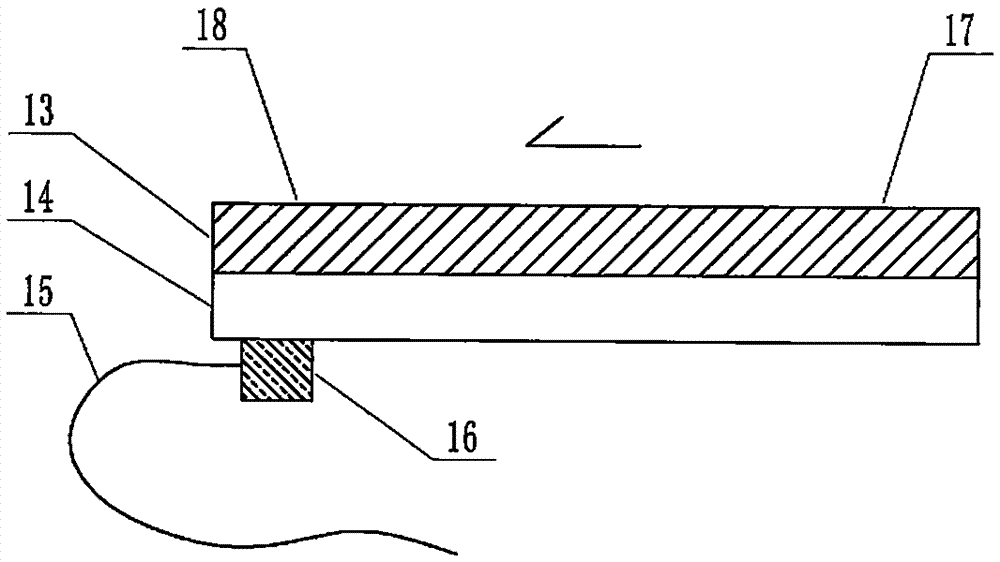
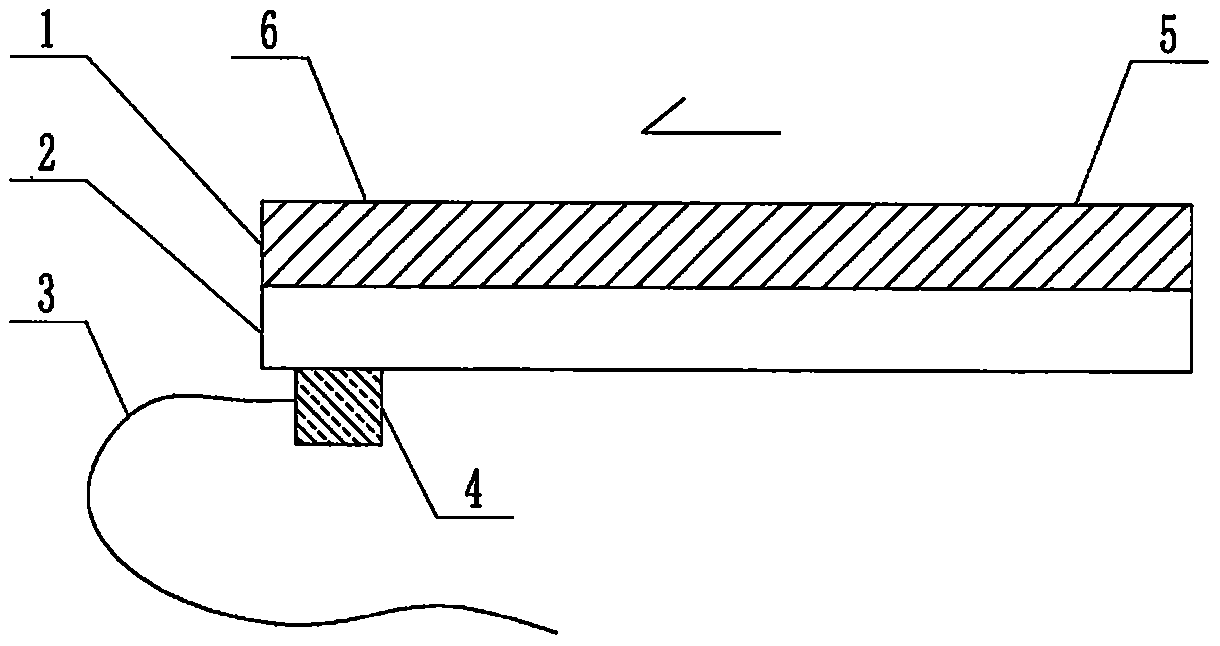
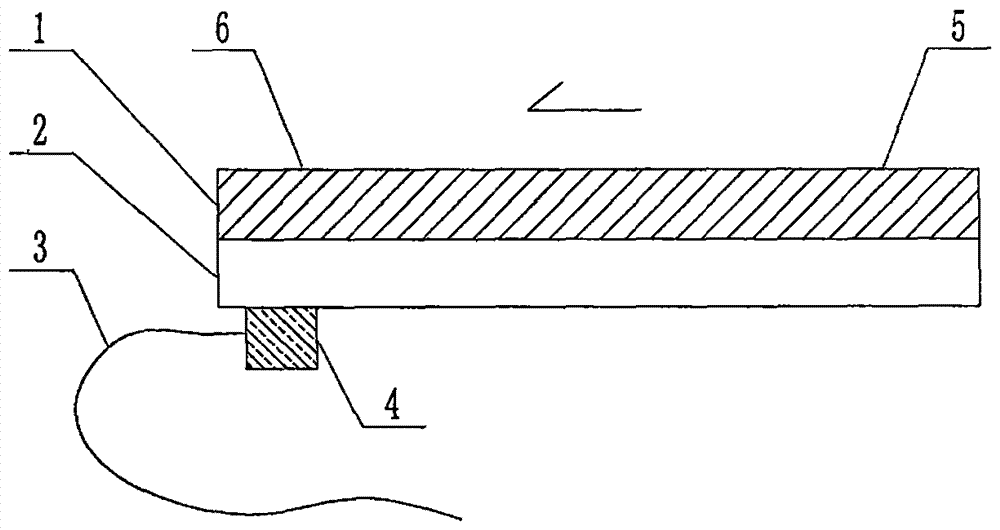
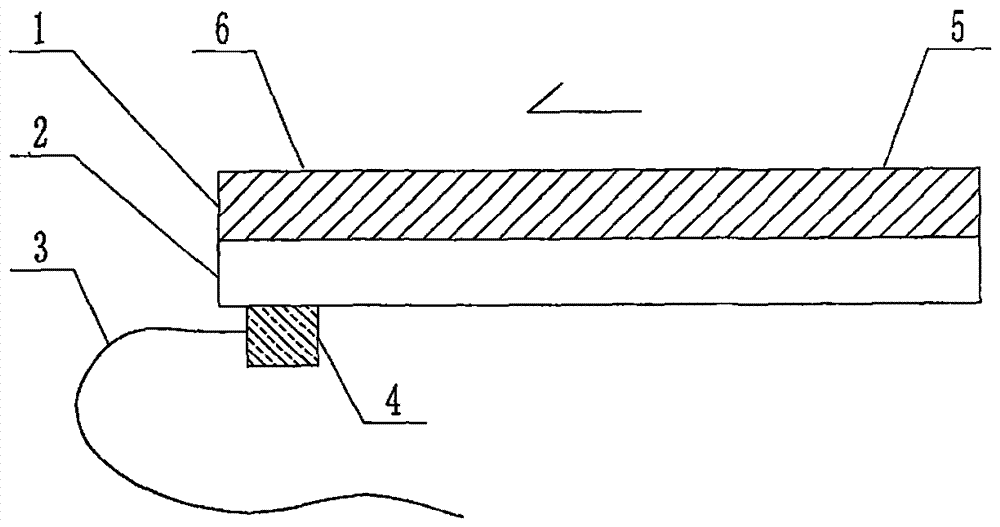
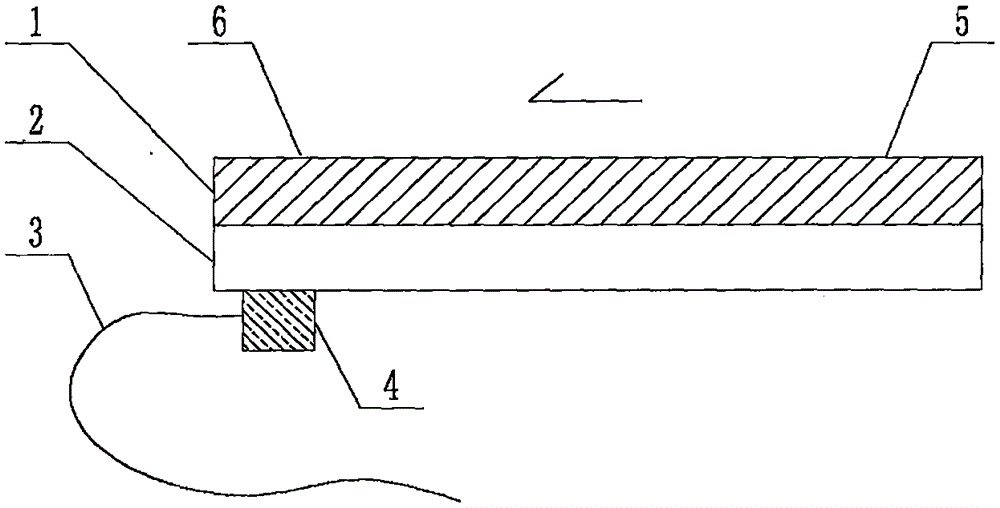
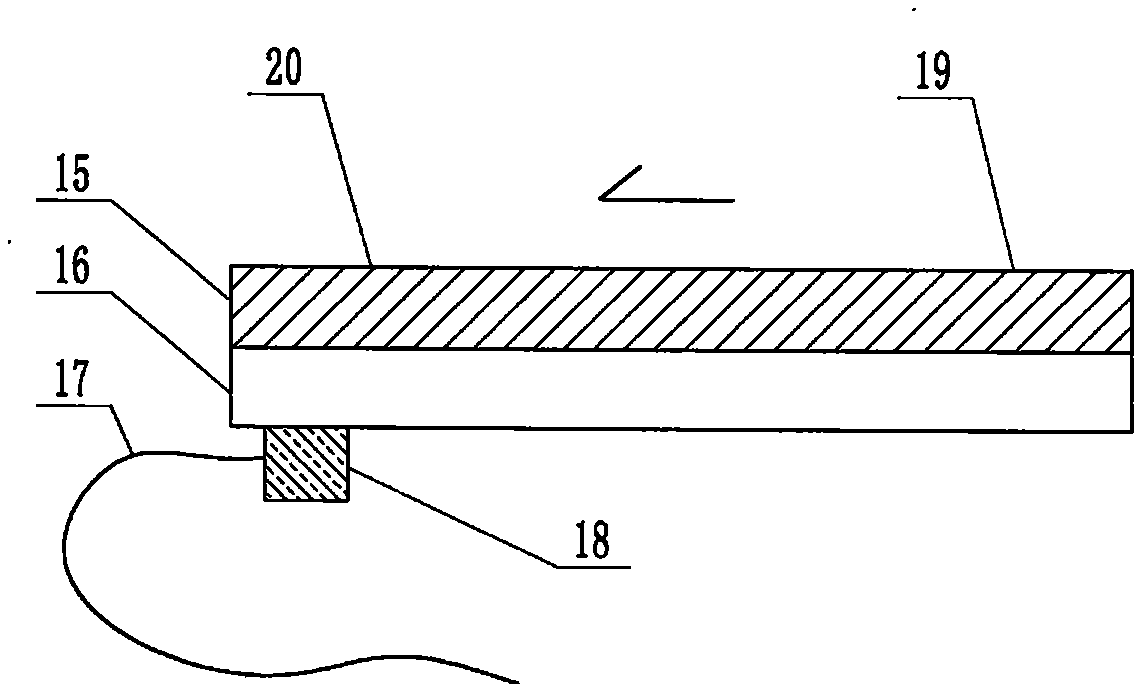
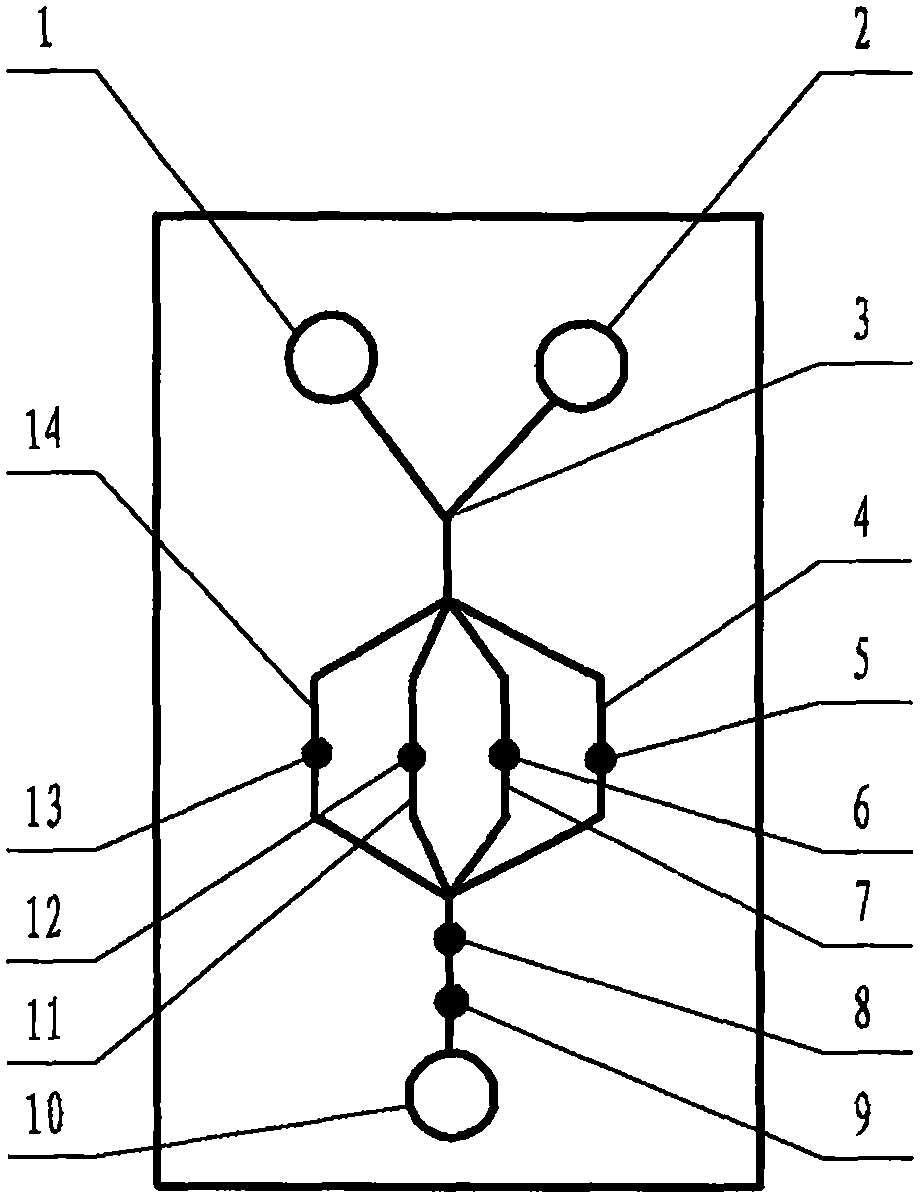
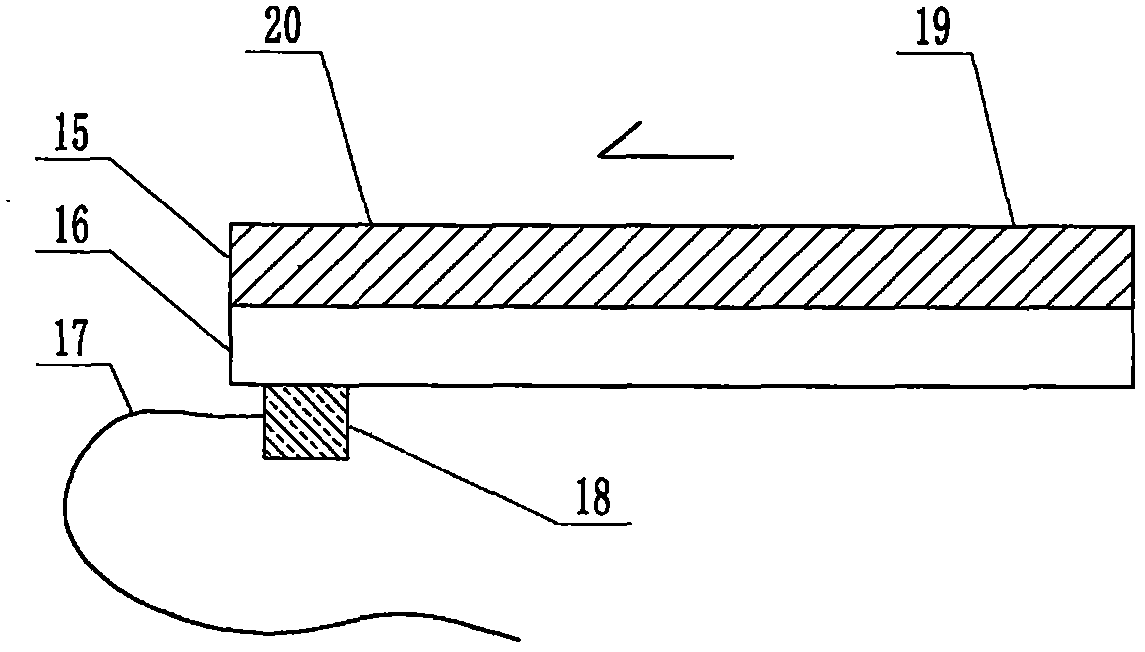
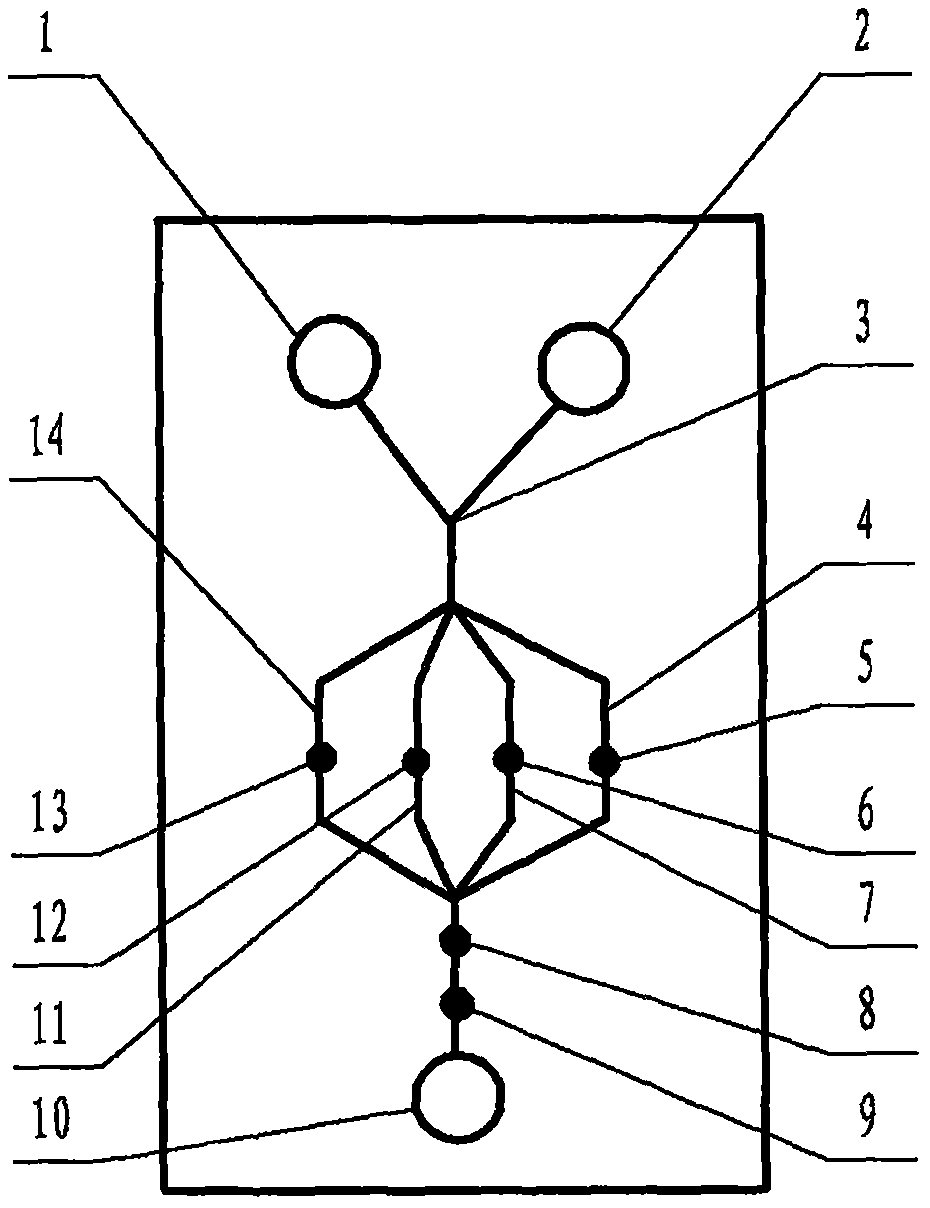
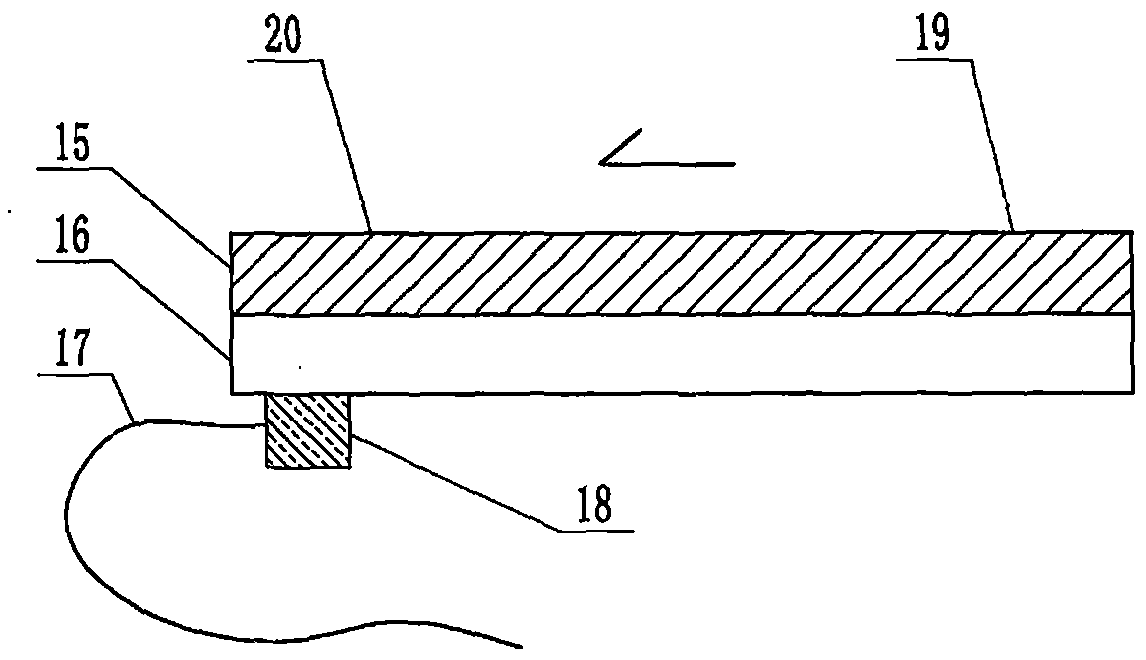
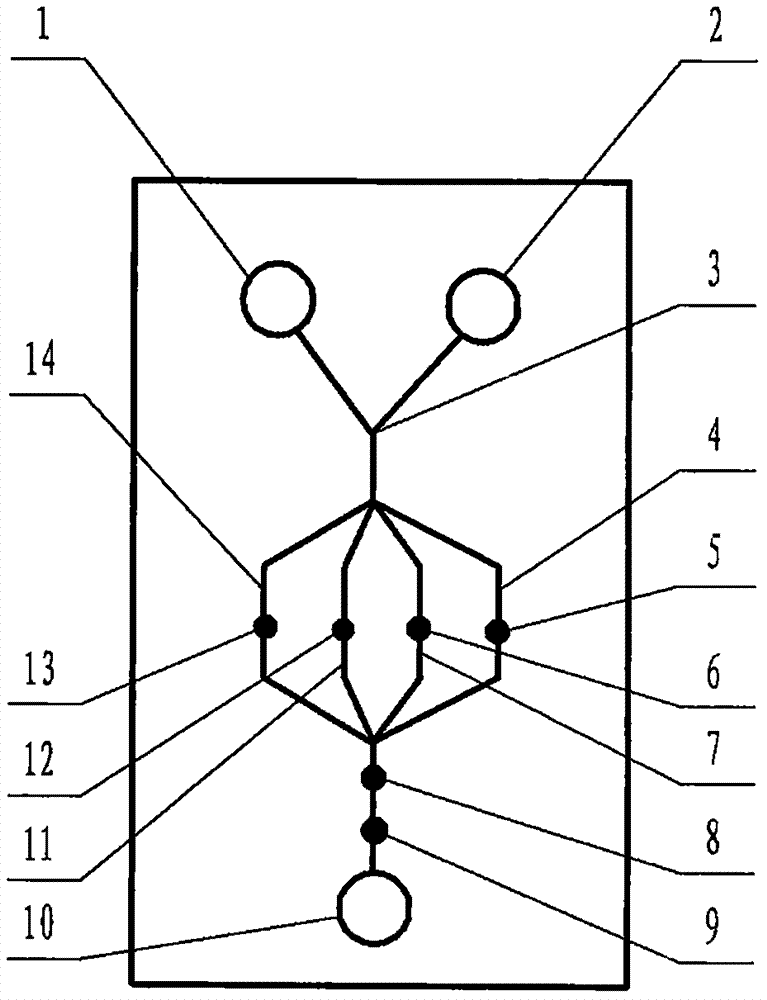
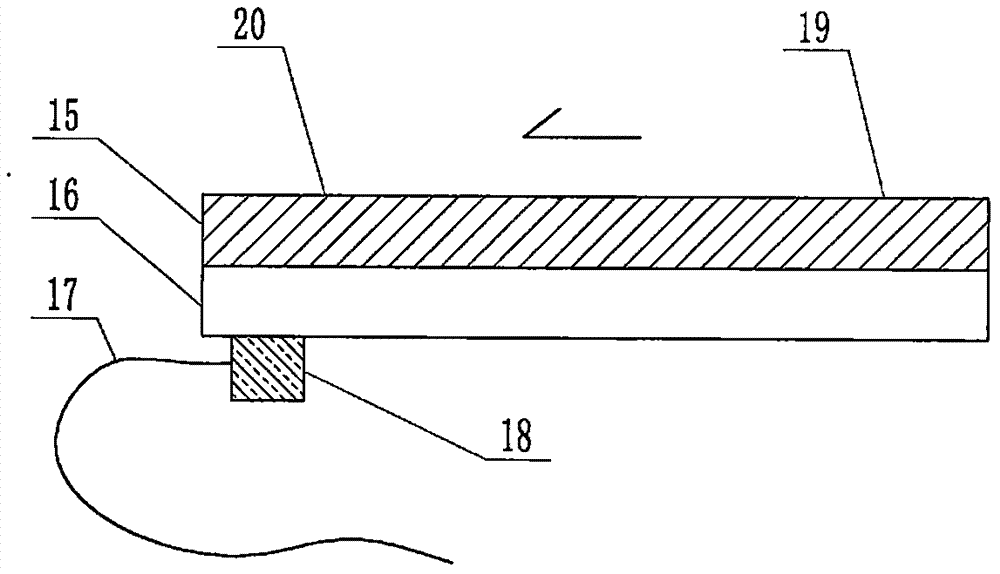
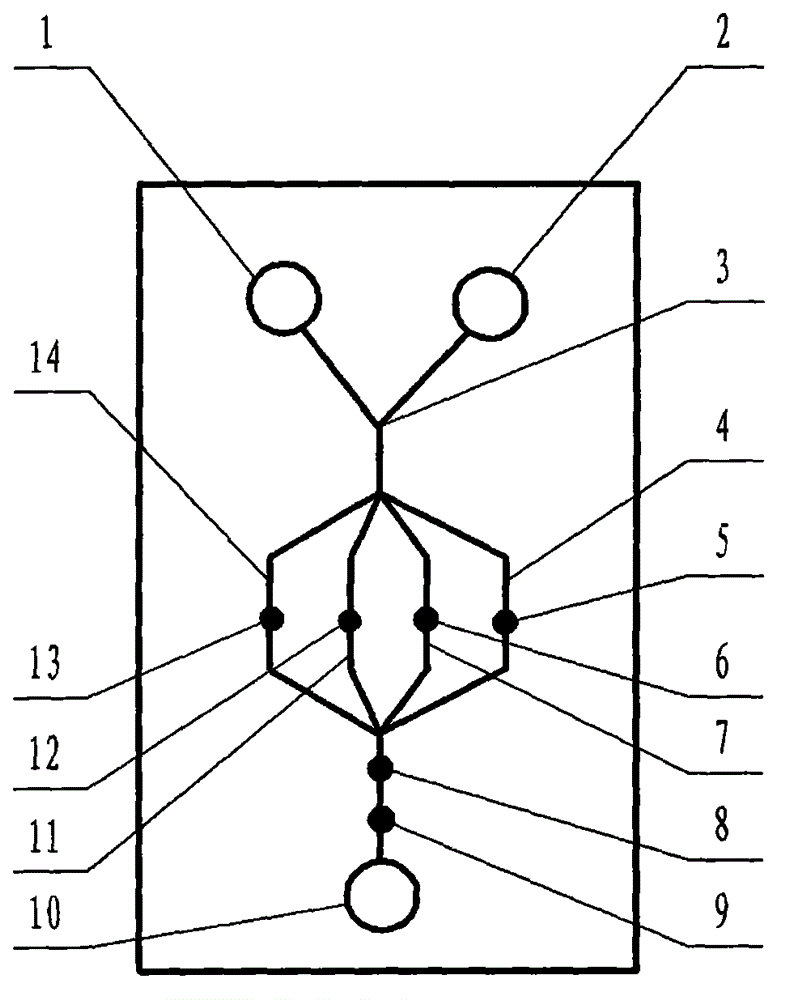
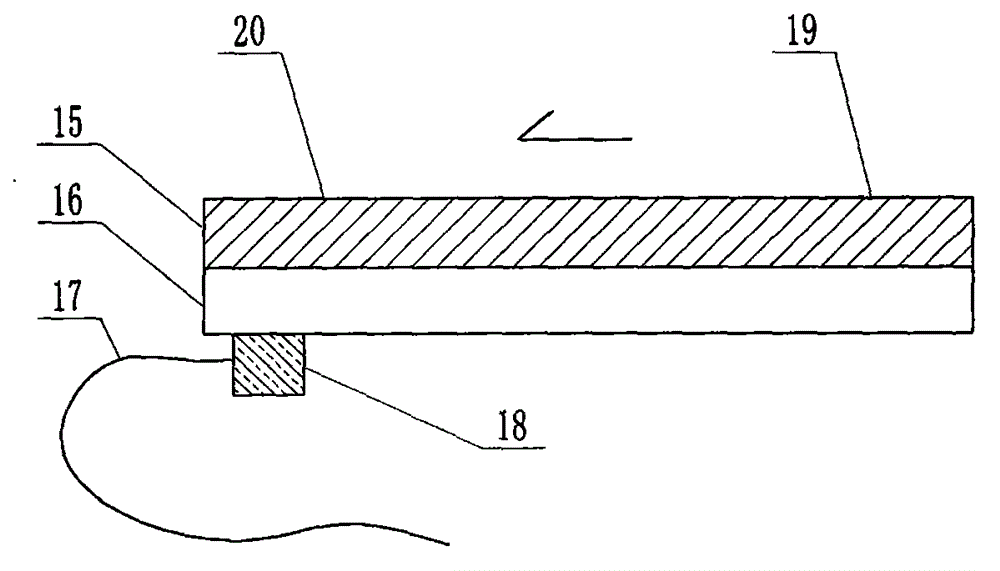
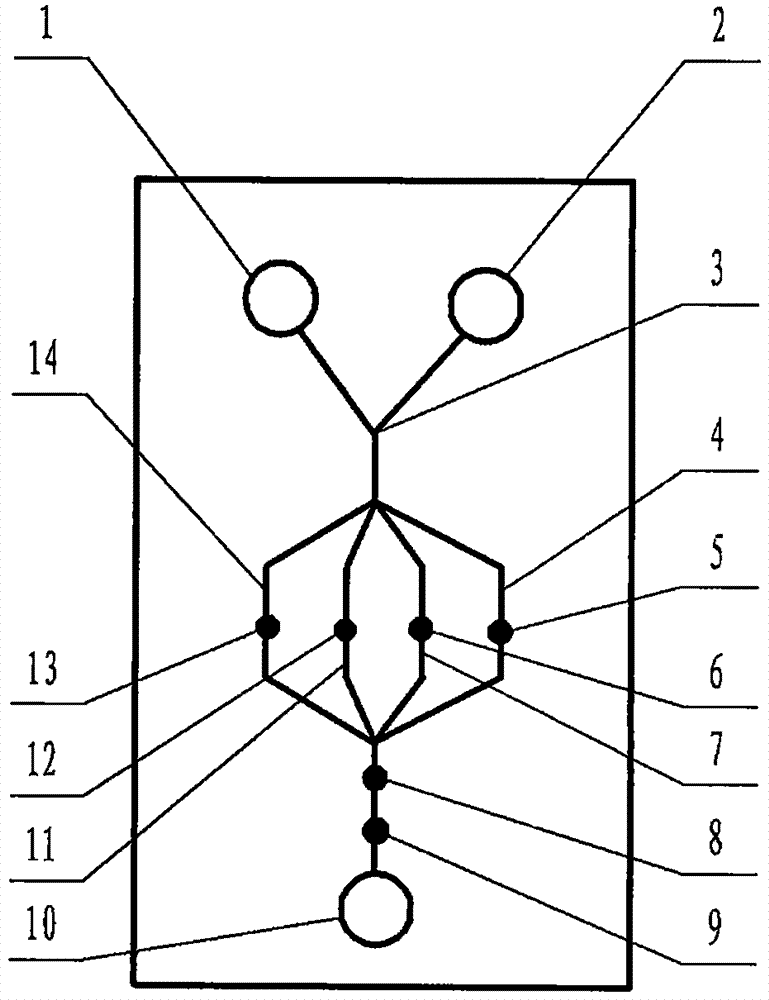
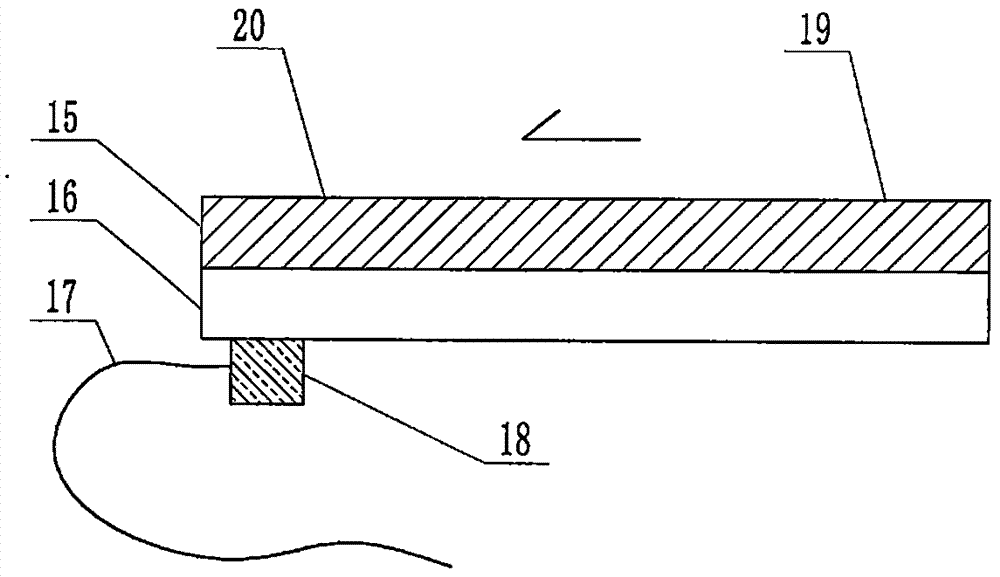
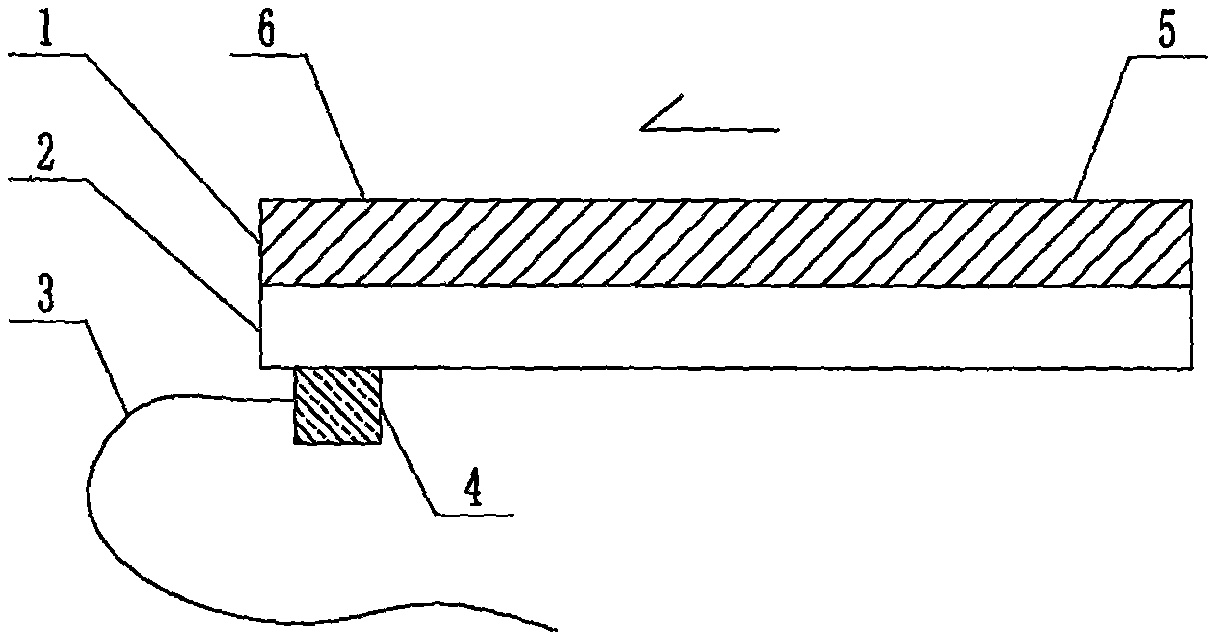
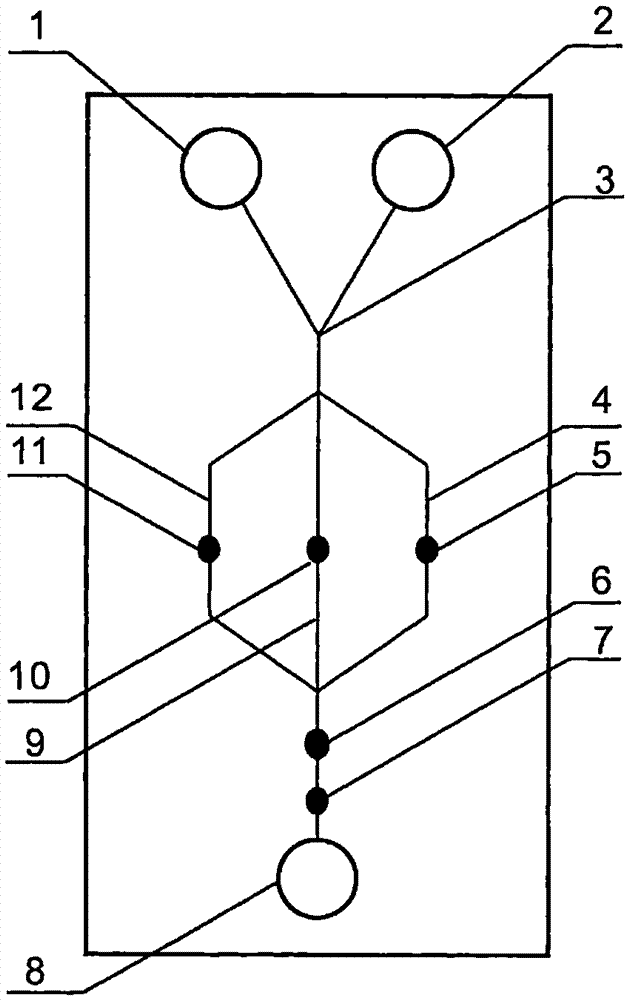
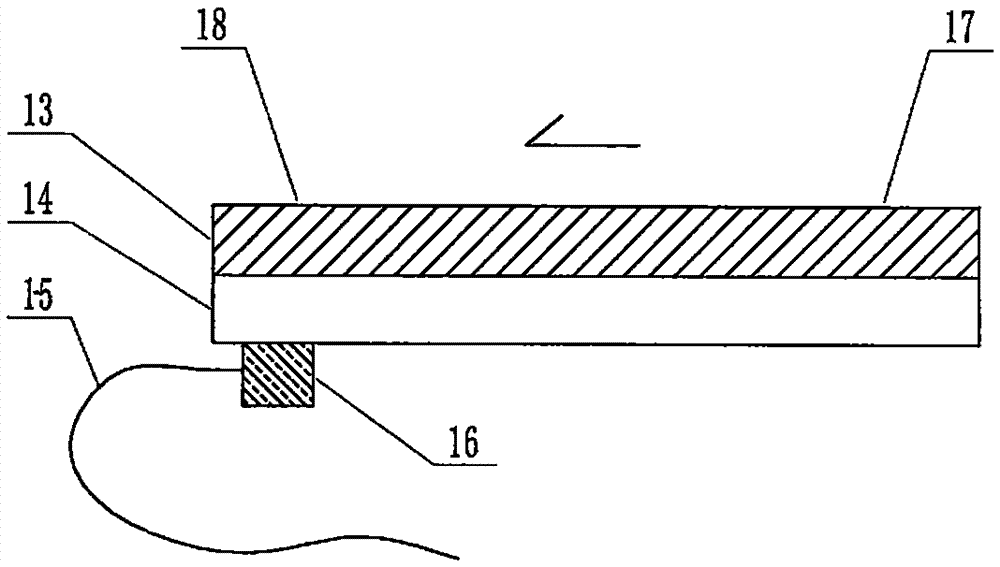
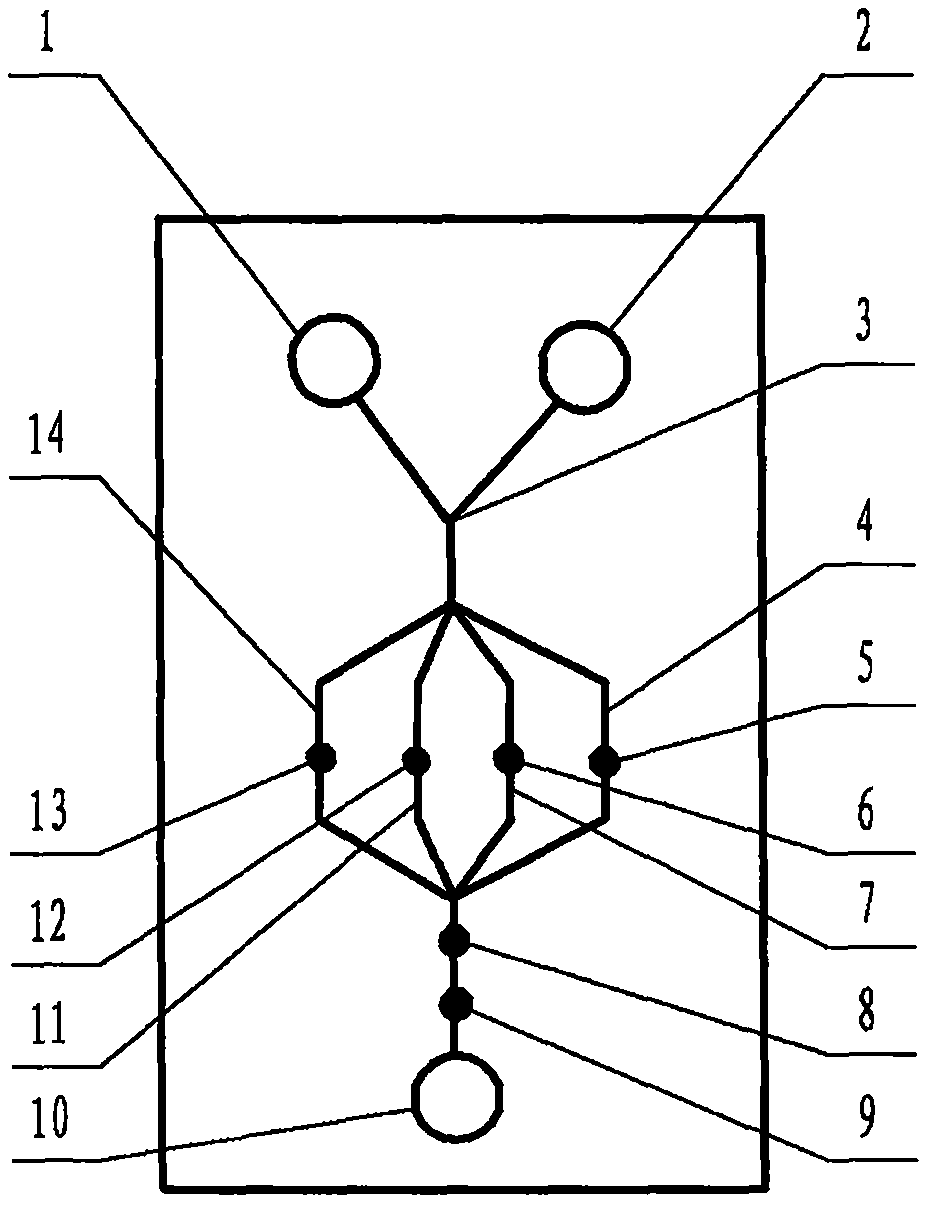
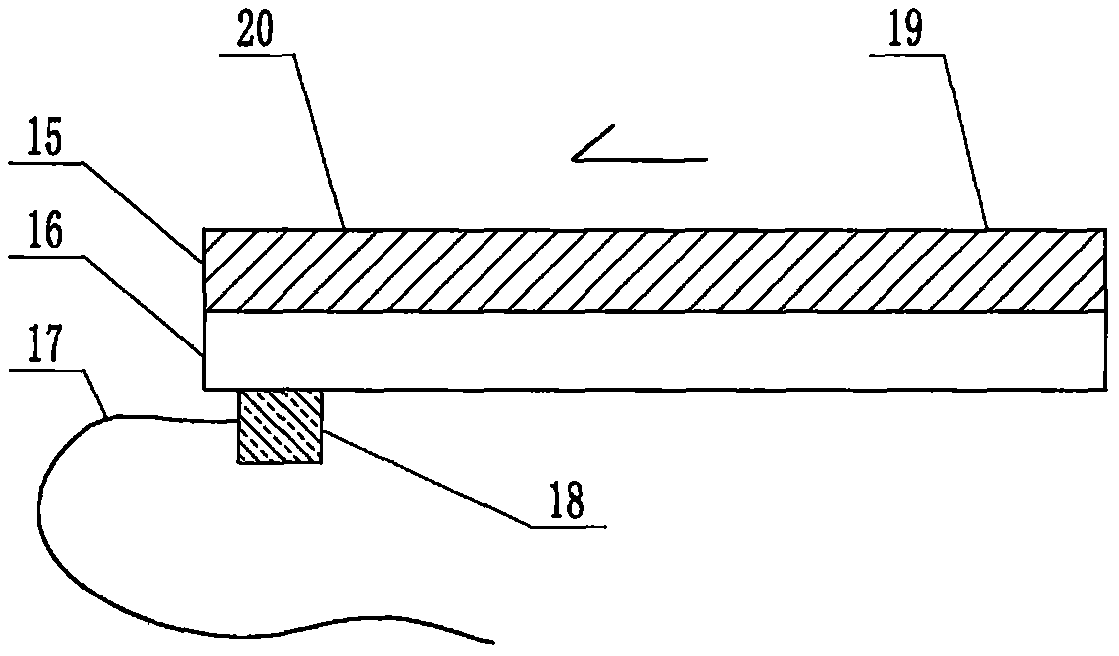
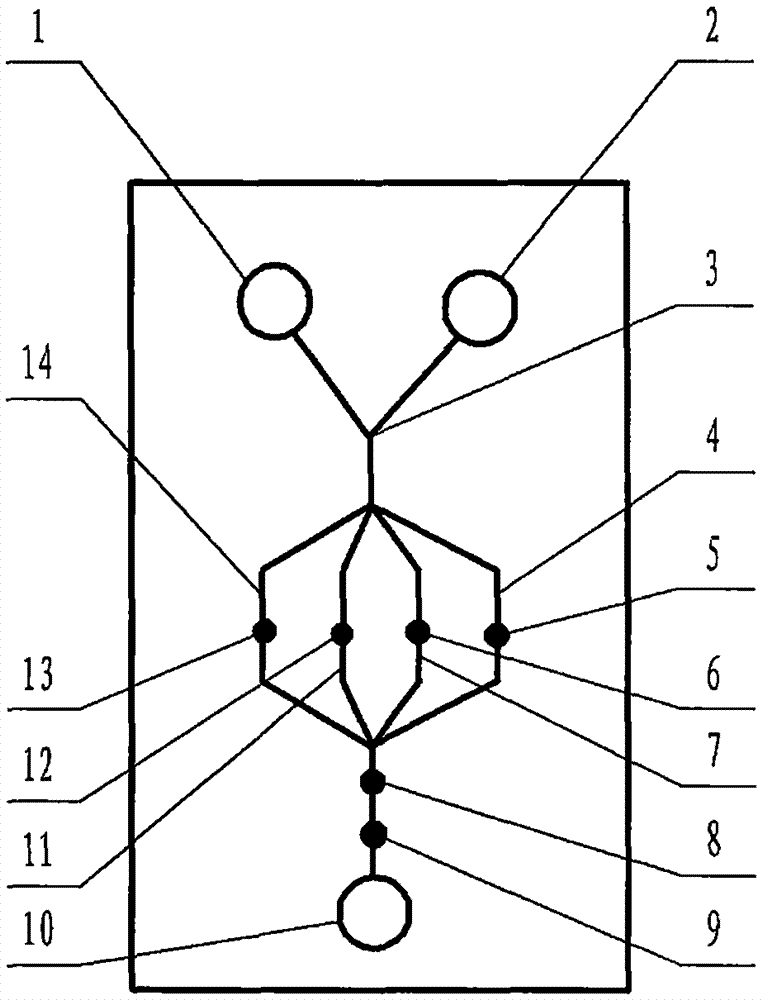
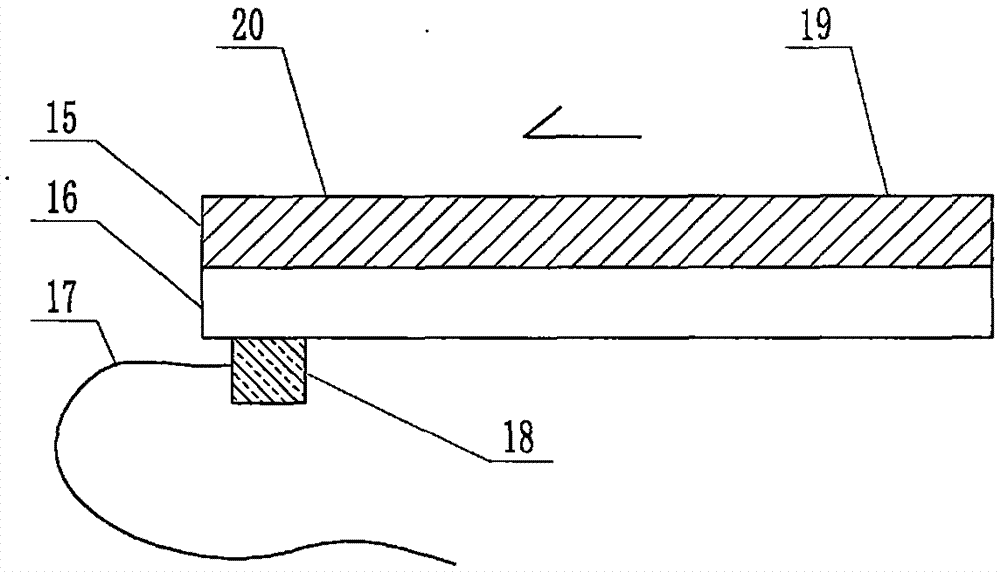
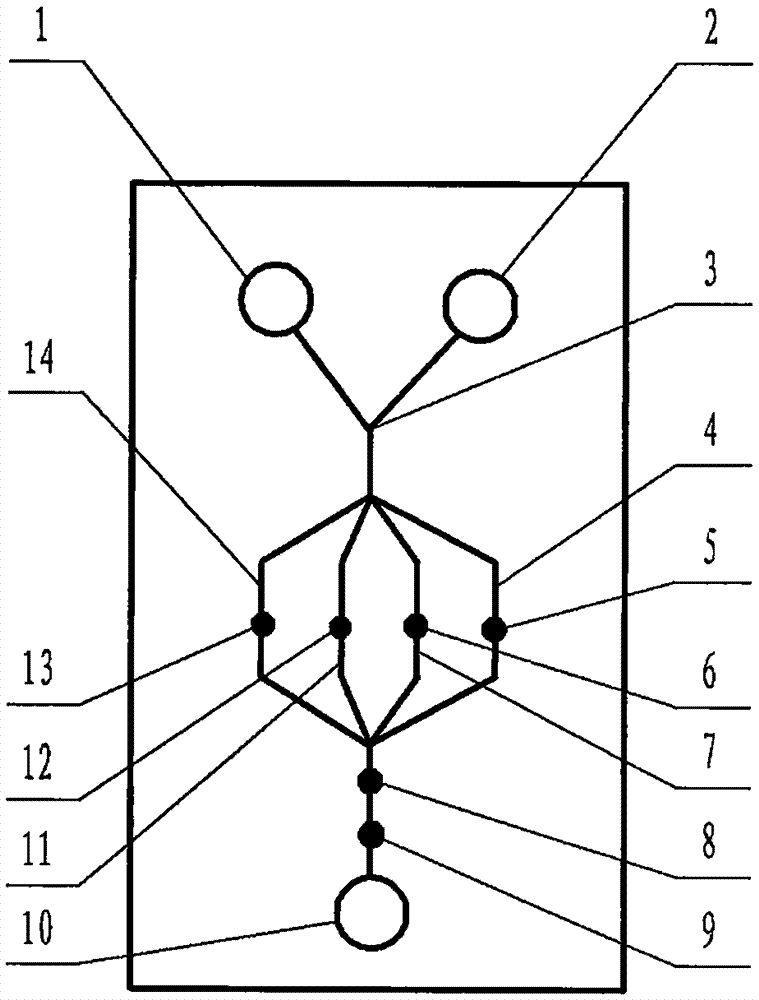
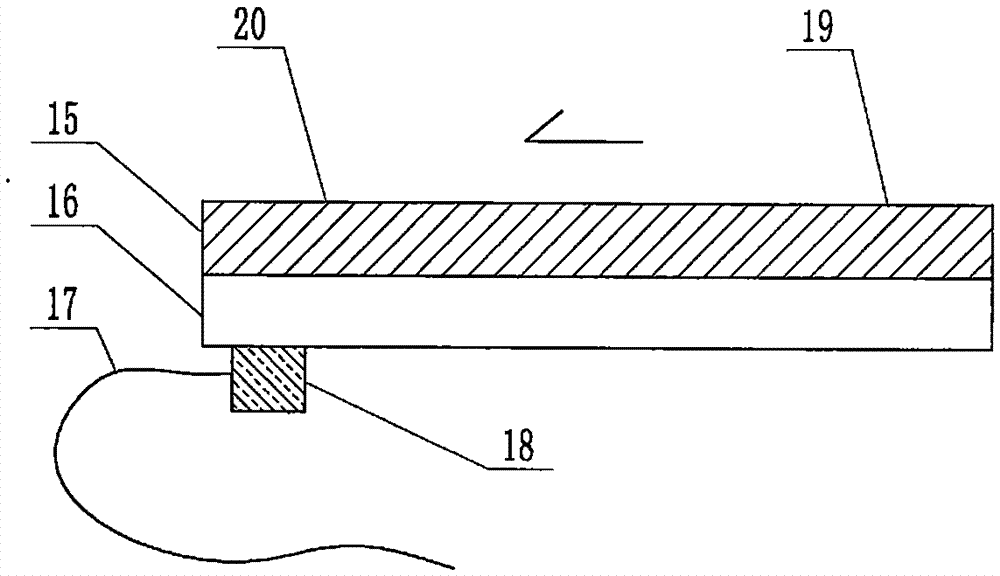
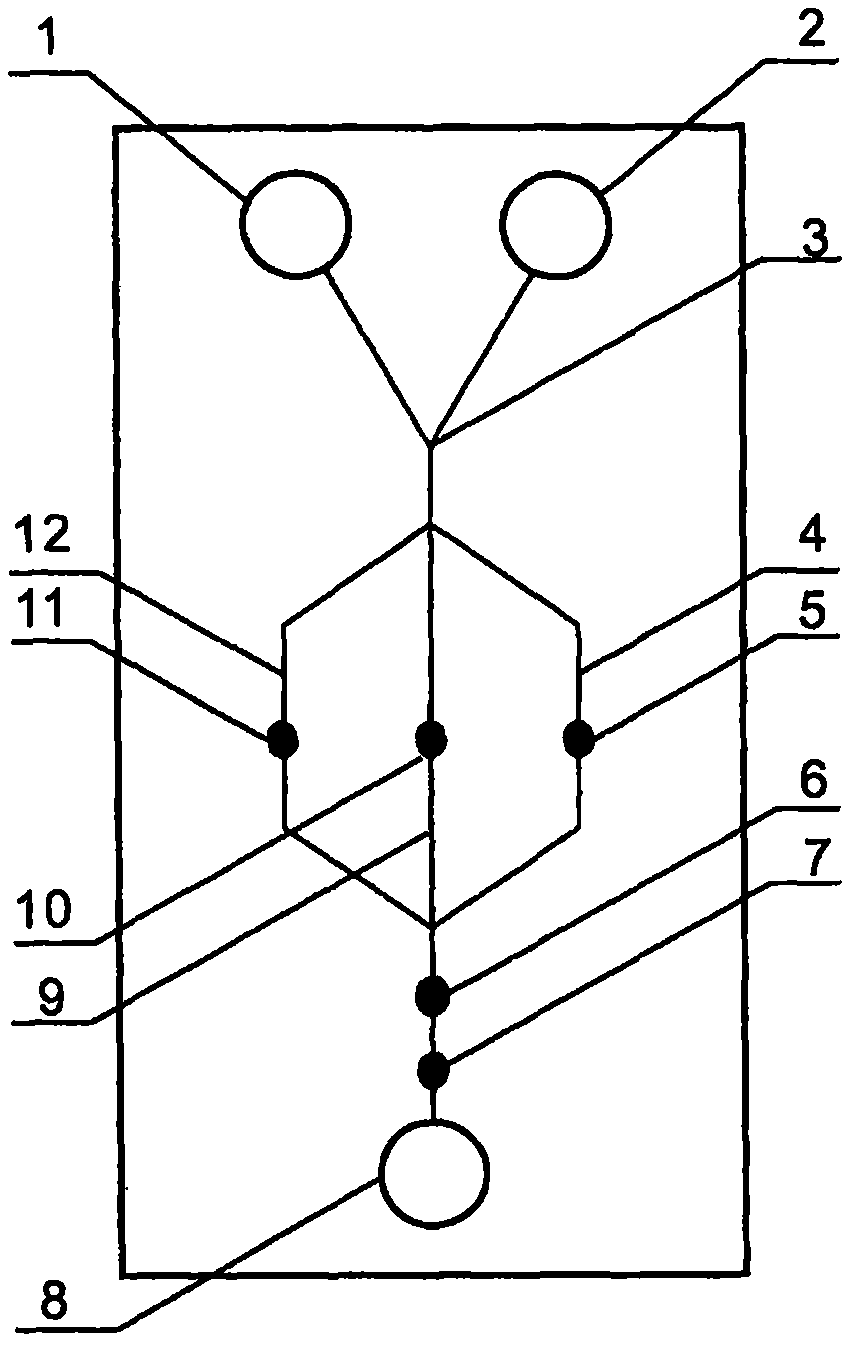
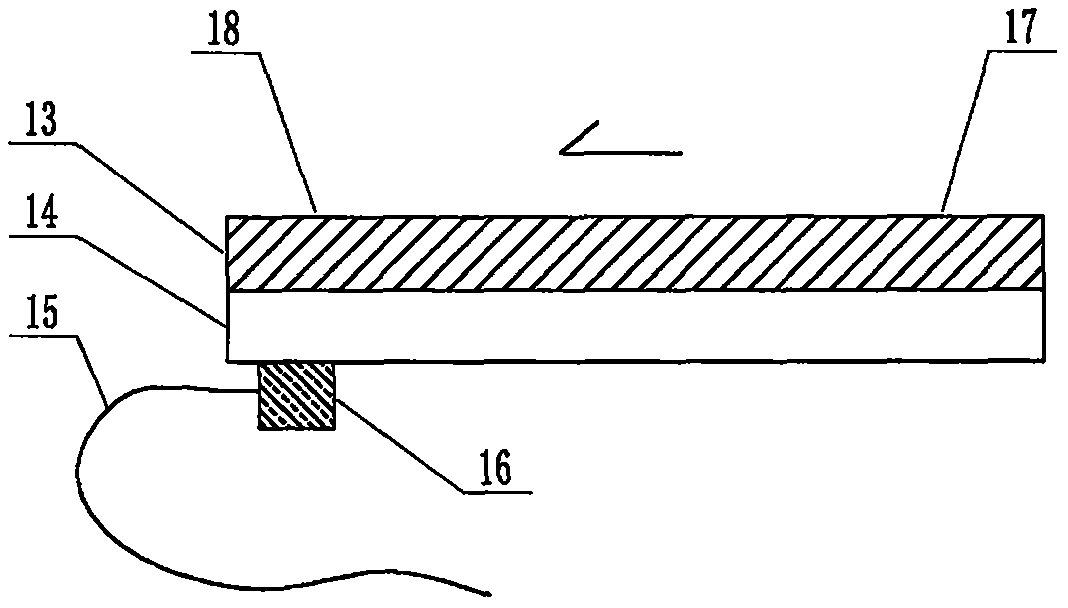
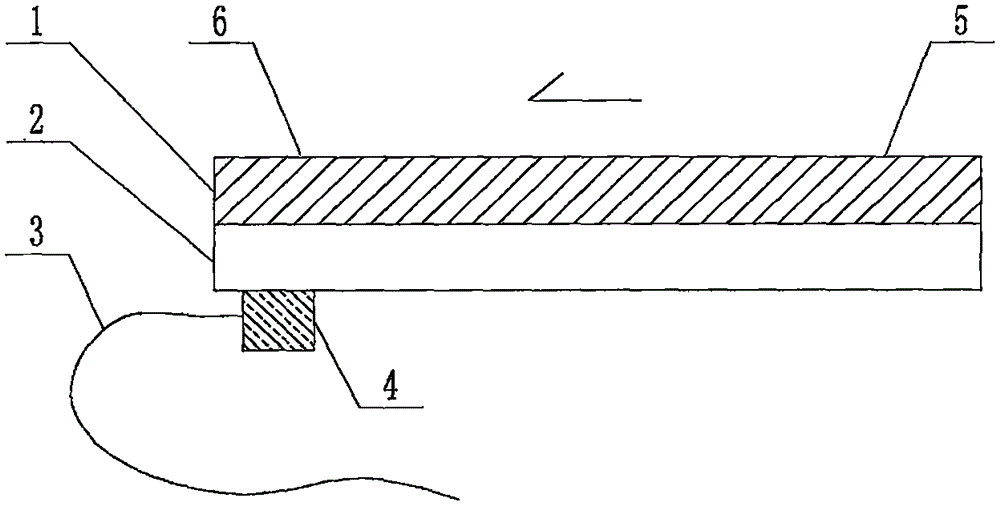
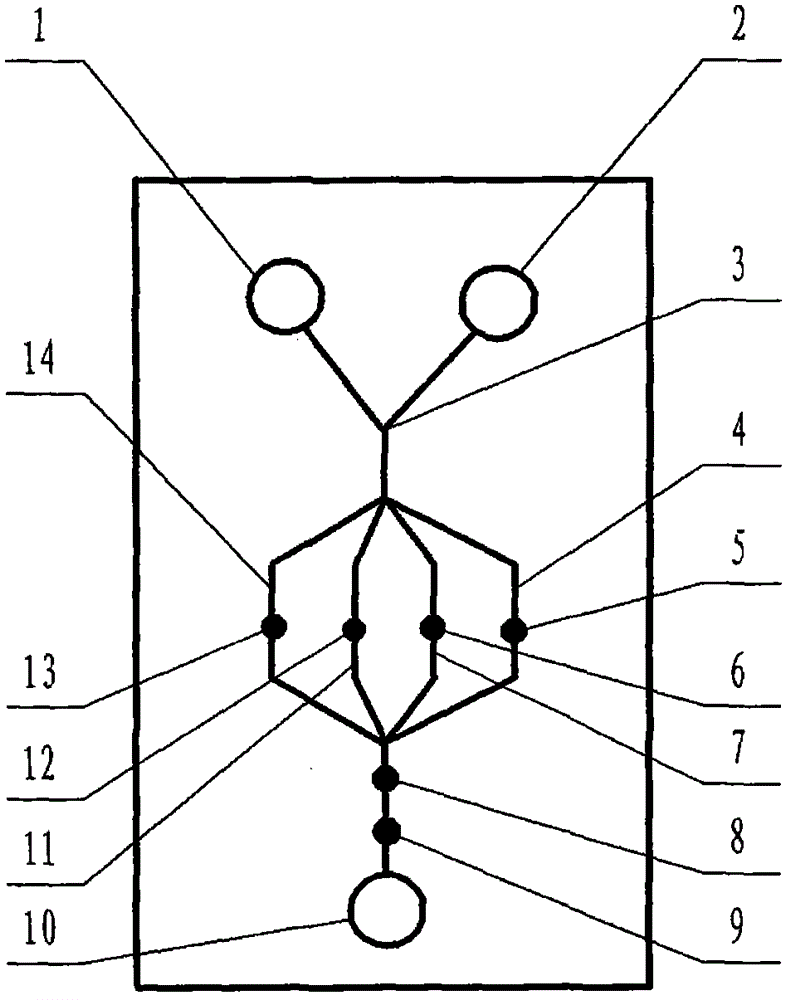
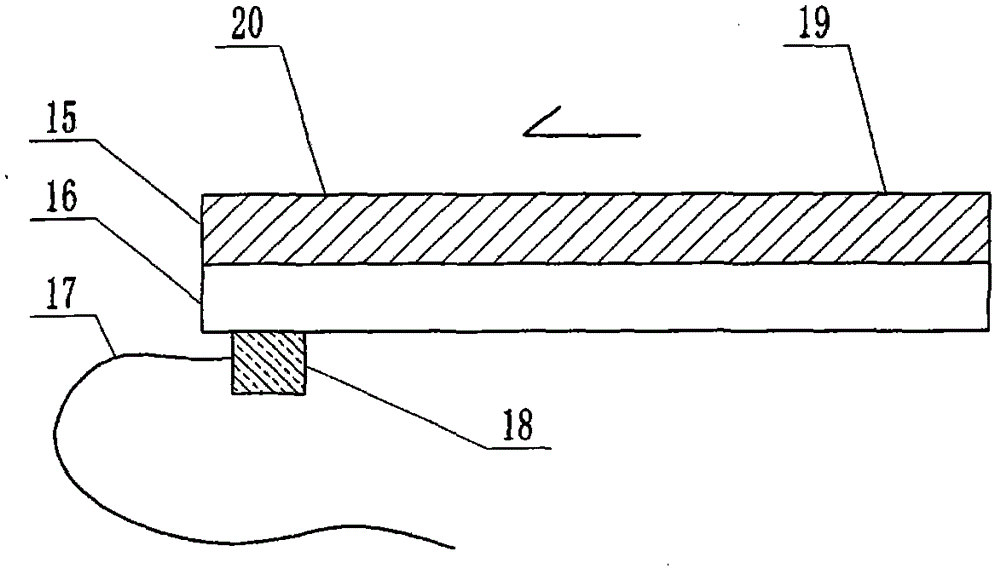
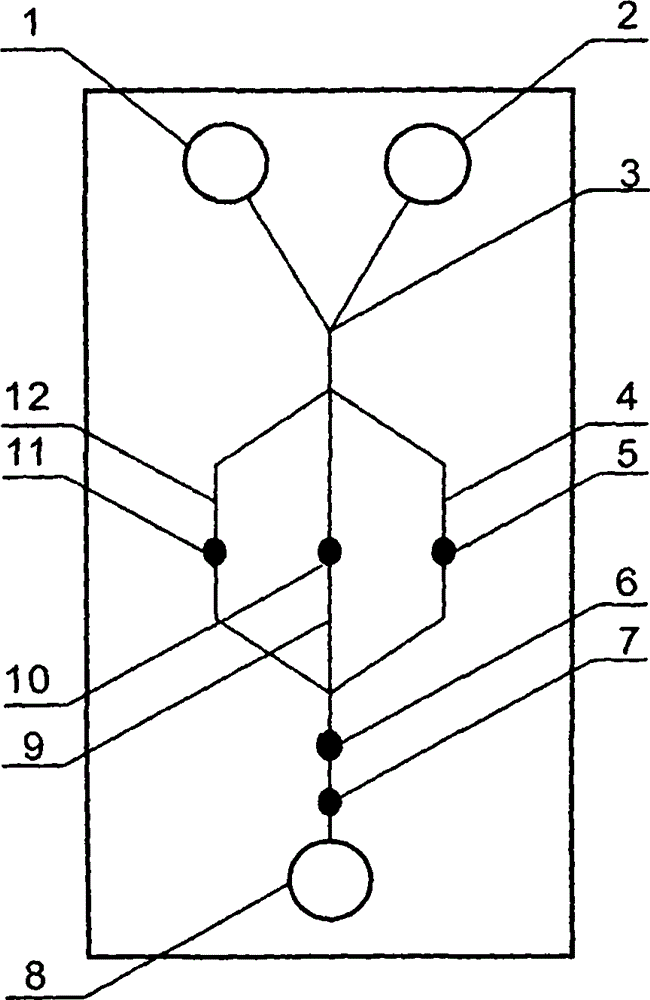
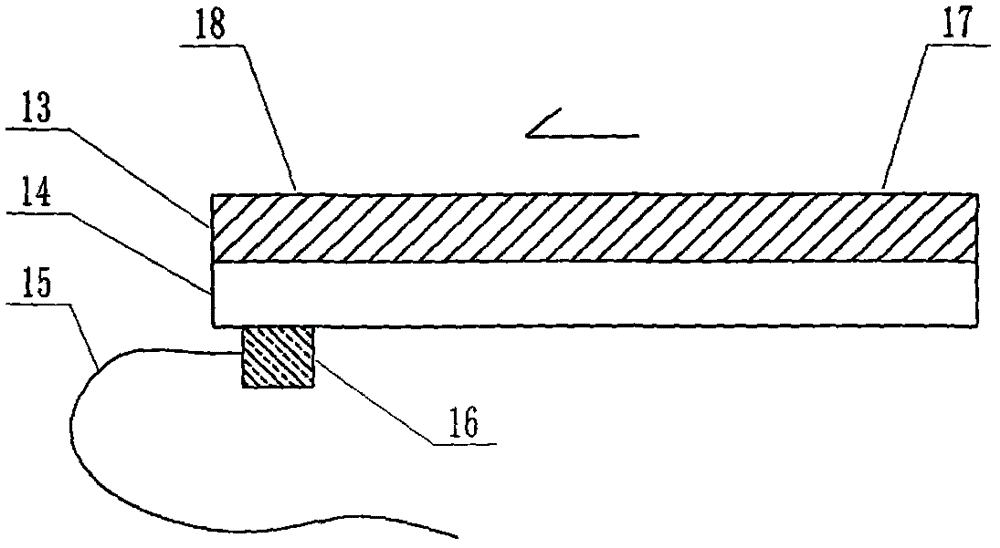
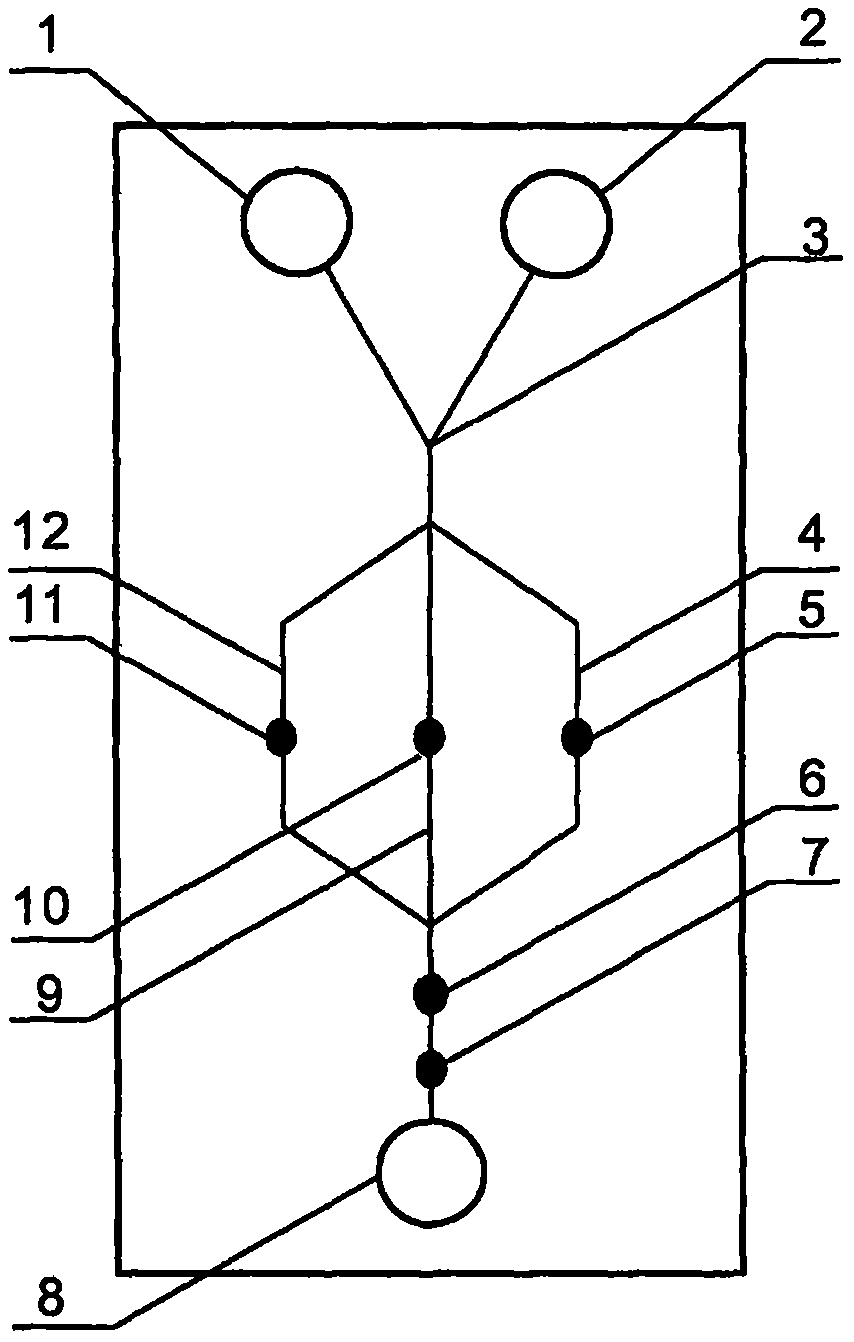
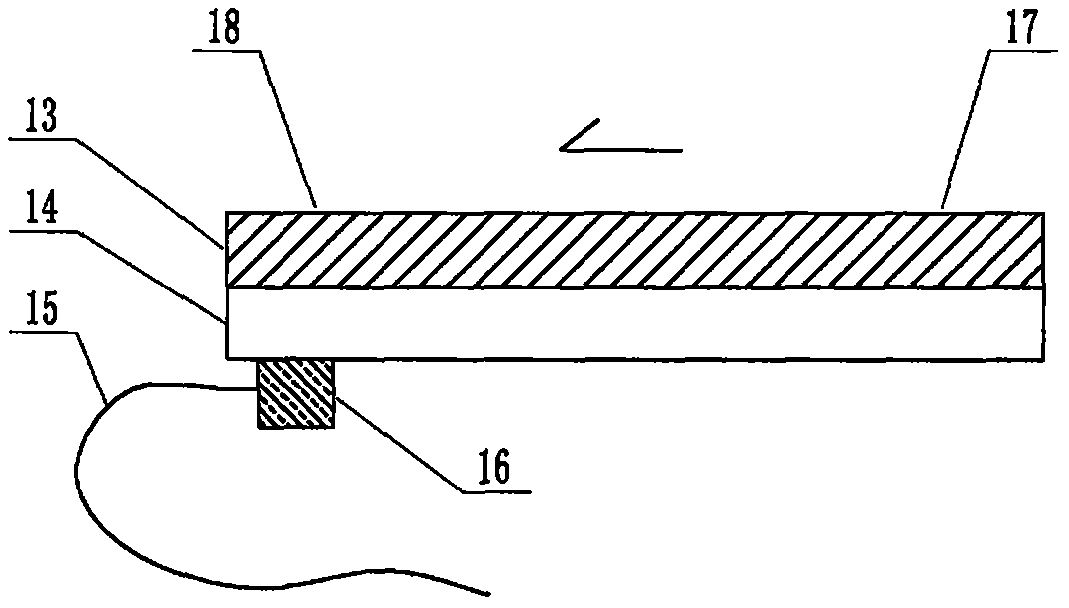
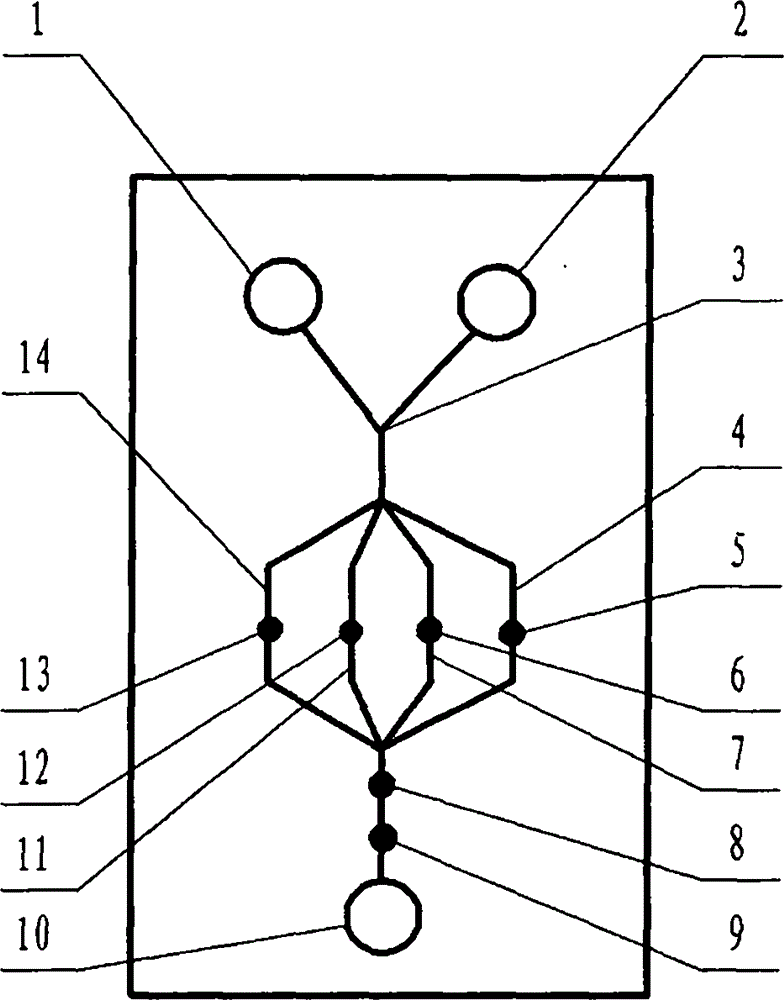
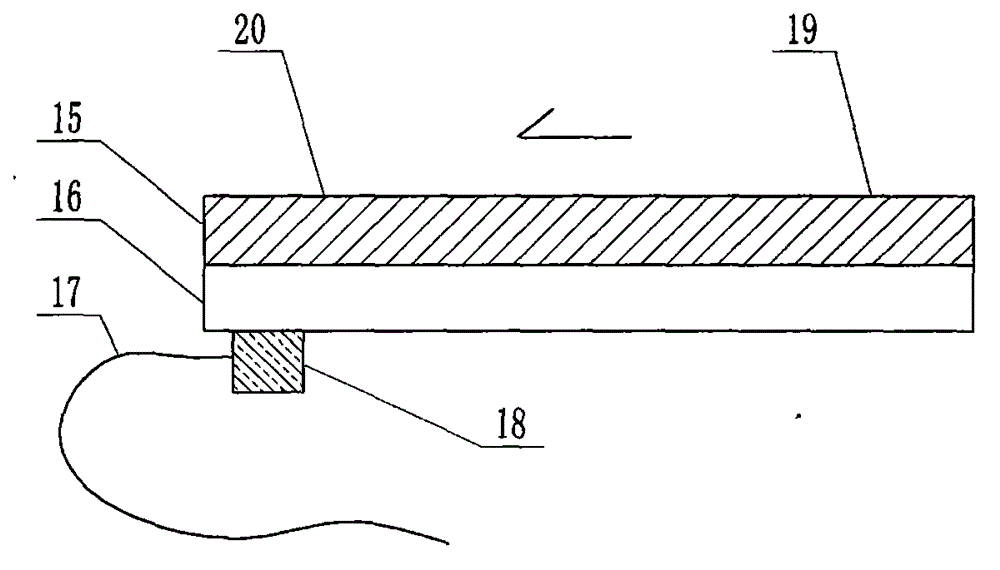
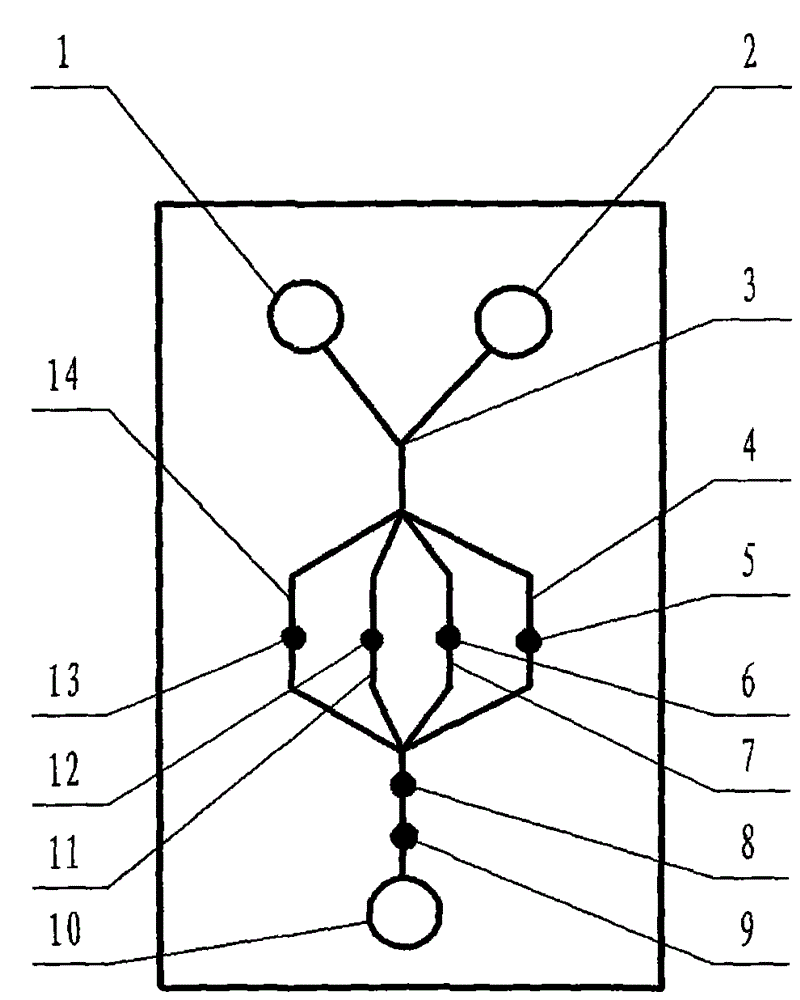
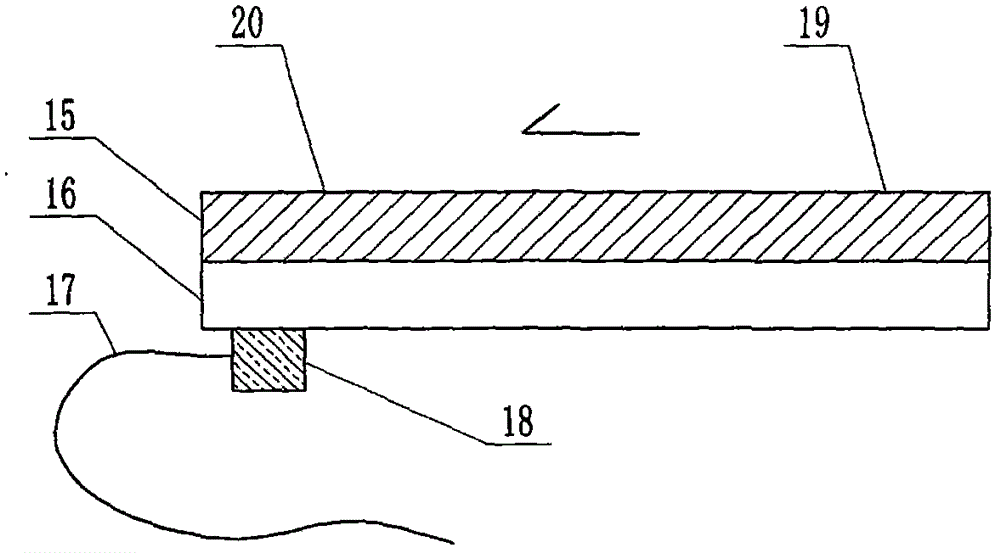
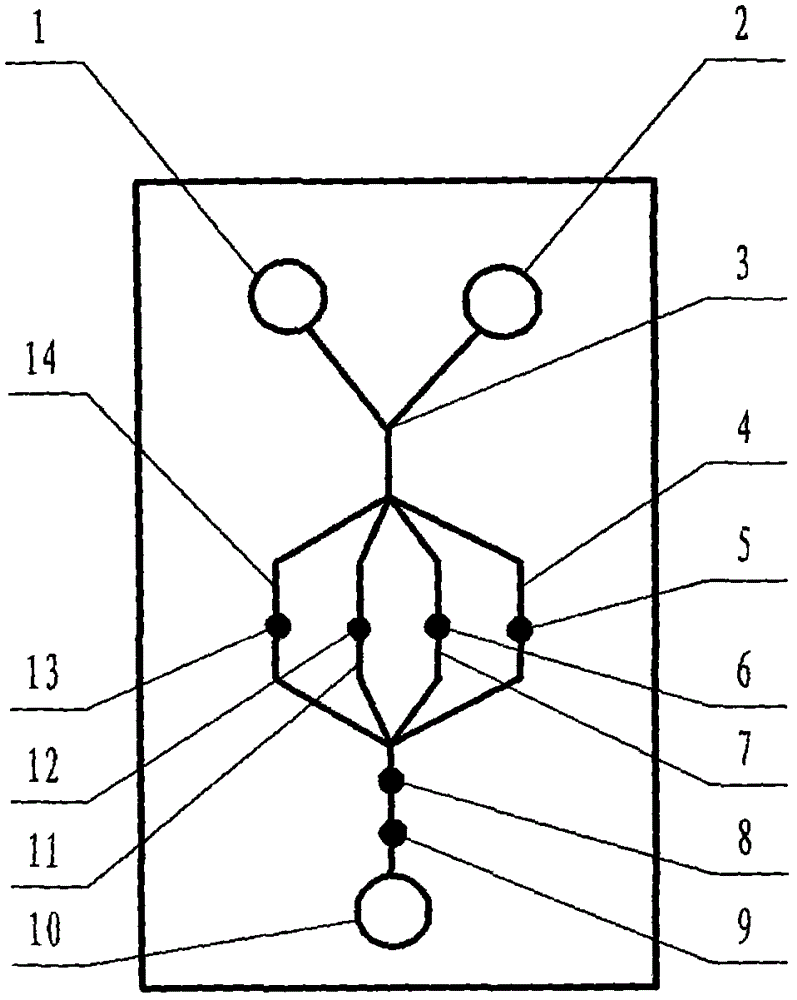
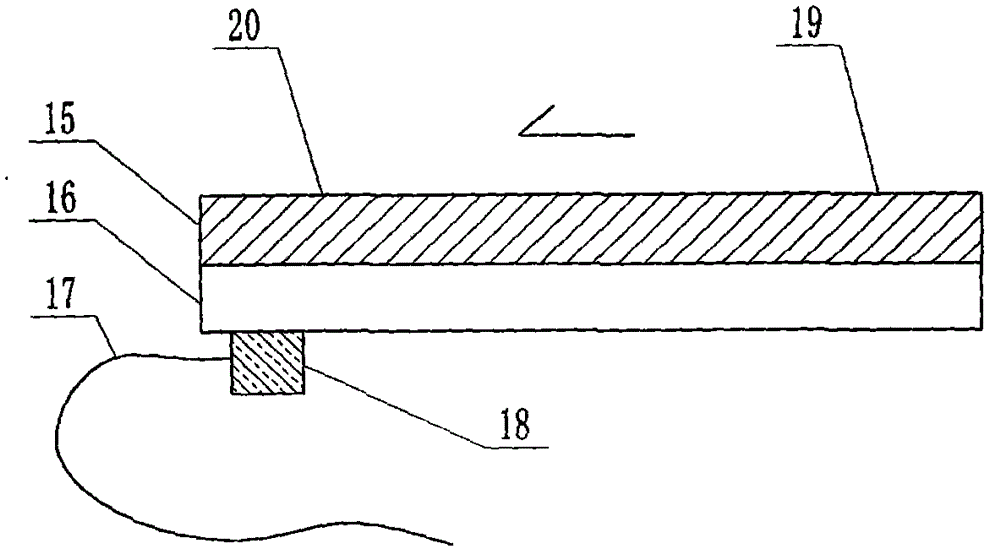
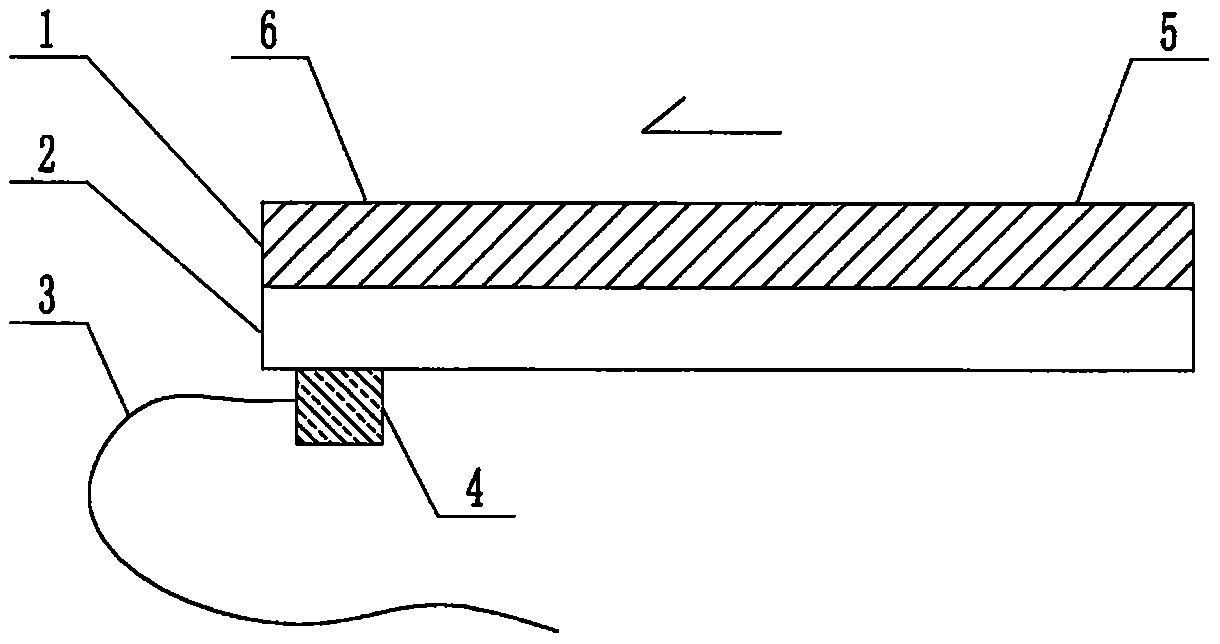
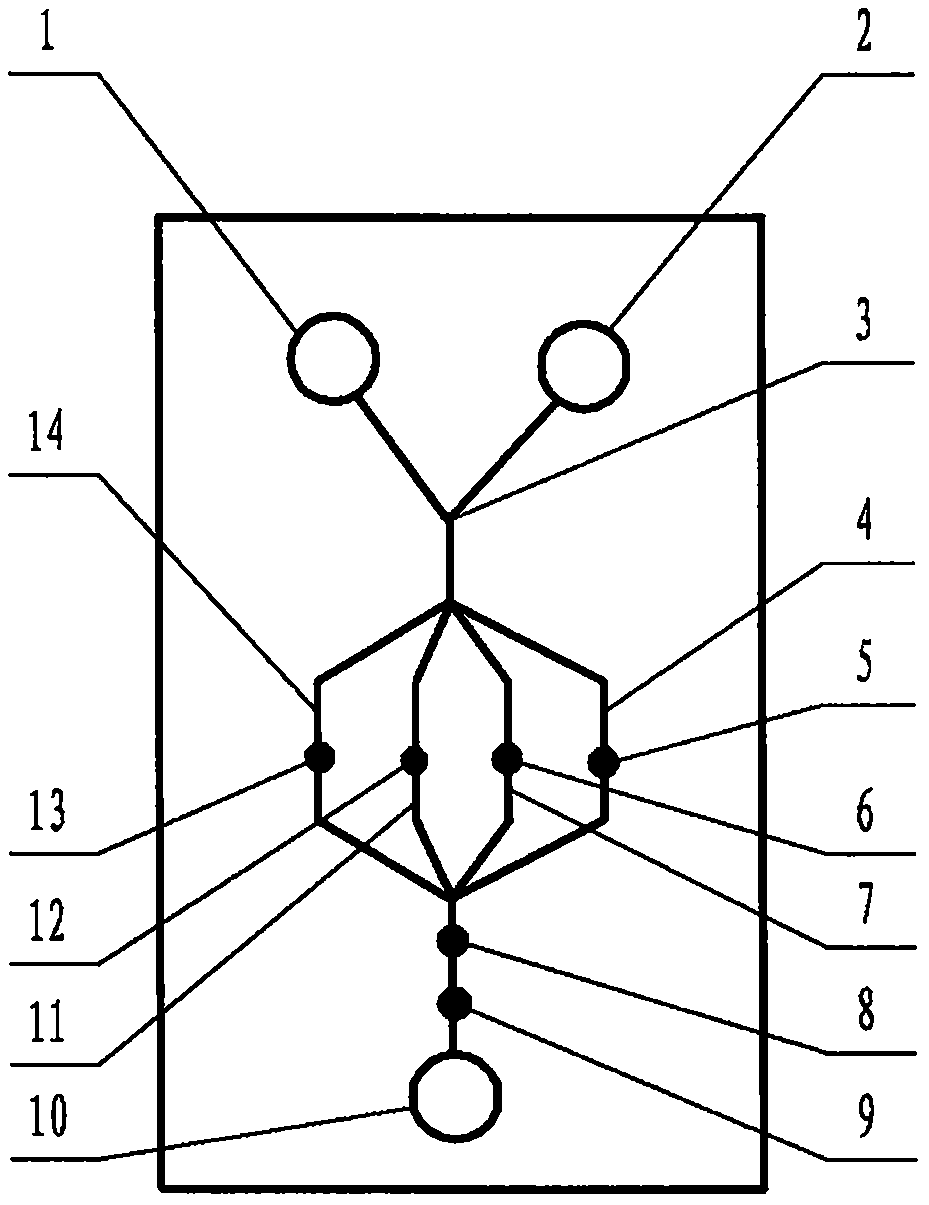
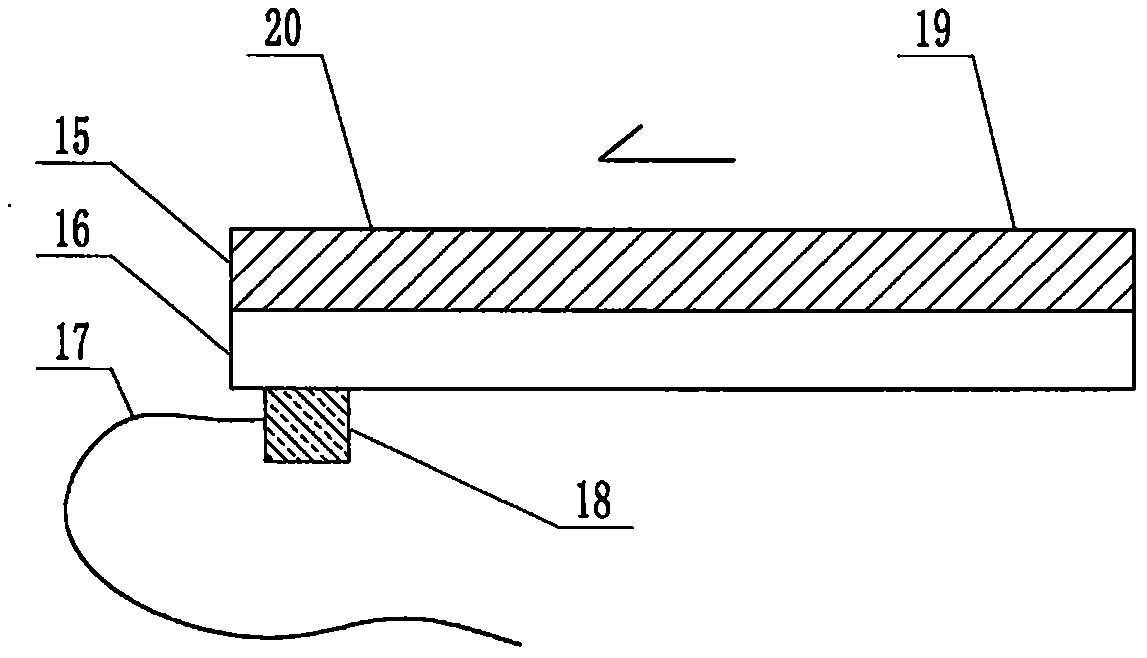
The invention relates to a cheap micro-fluidic device for diagnosis of cholera and with a specific liquid flow transmission manner, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. A series of obstacles exist in preparation of a substrate for a cholera diagnosis micro-fluidic chip from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS); a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time; and the invention aims to overcome a series of such problem. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Multi-channel micro-fluidic chip device for simultaneously detecting various kinds of subtype swine flu
InactiveCN105879932AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a multi-channel micro-fluidic chip device for simultaneously detecting various kinds of subtype swine flu and belongs to the field of analytical testing. When polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS, which is cheap and extremely easy to process is used for making a substrate of a micro-fluidic chip for diagnosing subtype swine flu, many obstacles exist; the surface of a PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic, while the effect of specific surface modification cannot last. According to the scheme, the multi-channel micro-fluidic chip device aims at solving the series of related problems, and is characterized in that PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate, a miniature ultrasonic transducer is attached to and arranged at the position close to the sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip, and interfacial tension is reduced with ultrasonic waves; meanwhile, the strong absorption capability of PDMS to ultrasonic waves is utilized for quickly reducing the intensity of the ultrasonic waves gradually in a short distance, an interfacial tension difference is formed at the two ends of the chip accordingly, a pressure difference is formed between the two ends, and the sample liquid flow is driven to flow towards the terminal along capillary channels by the pressure difference.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Cheap micro-fluidic device used for diagnosis of syphilis and realizing liquid flow transmission via interfacial characteristics
InactiveCN106990244AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesUltrasonic sensorSyphilis
The invention relates to a cheap micro-fluidic device used for diagnosis of syphilis and realizing liquid flow transmission via interfacial characteristics, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. A few problems exists in preparation of a substrate used for syphilis diagnosis micro-fluidic chips from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane, i.e., PDMS; a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time; and the invention aims to overcome a series of such problems. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Cheap microfluidic device with specific liquid flow transmission mode and for cholera diagnosis
InactiveCN107649191AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a cheap microfluidic device with specific liquid flow transmission mode and for cholera diagnosis and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. By using cheap and easily-processable polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS for manufacturing a substrate of a microfluidic chip for cholera diagnosis, a series of problems exist. The surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic. Through targeted surface modification, the effect is hard to last. The scheme aims to solve the series of related problems. According to main points of the scheme, PDMS with primitive surface is selected as the substrate, a miniature ultrasonic transducer is arranged near the terminal of a sample liquid fluid of the microfluidic chip, interfacial tension is reduced by ultrasonic wave, and by PDMS's strong absorption of ultrasonic wave, ultrasonic intensity is rapidly decreased progressively in a short distance to form interfacial tension difference between two ends of the chip. The interfacial tension difference leads to formation of pressure difference between the two ends, and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid fluid to flow along the capillary channel towards the terminal.
Owner:洪小女
Multichannel micro-fluidic chip device capable of simultaneously detecting multiple swine influenza virus subtypes
InactiveCN106984365AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a multichannel micro-fluidic chip device capable of simultaneously detecting multiple swine influenza virus subtypes, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. A series of obstacles practically exist in preparation of a substrate for a swine influenza virus subtype diagnosis micro-fluidic chip from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS); and a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface; and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time. The objective of the invention is to overcome the above problems. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Micro fluidic chip device for multichannel simultaneous detection of six typical tumor markers
InactiveCN107694635AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesAbnormal tissue growthShortest distance
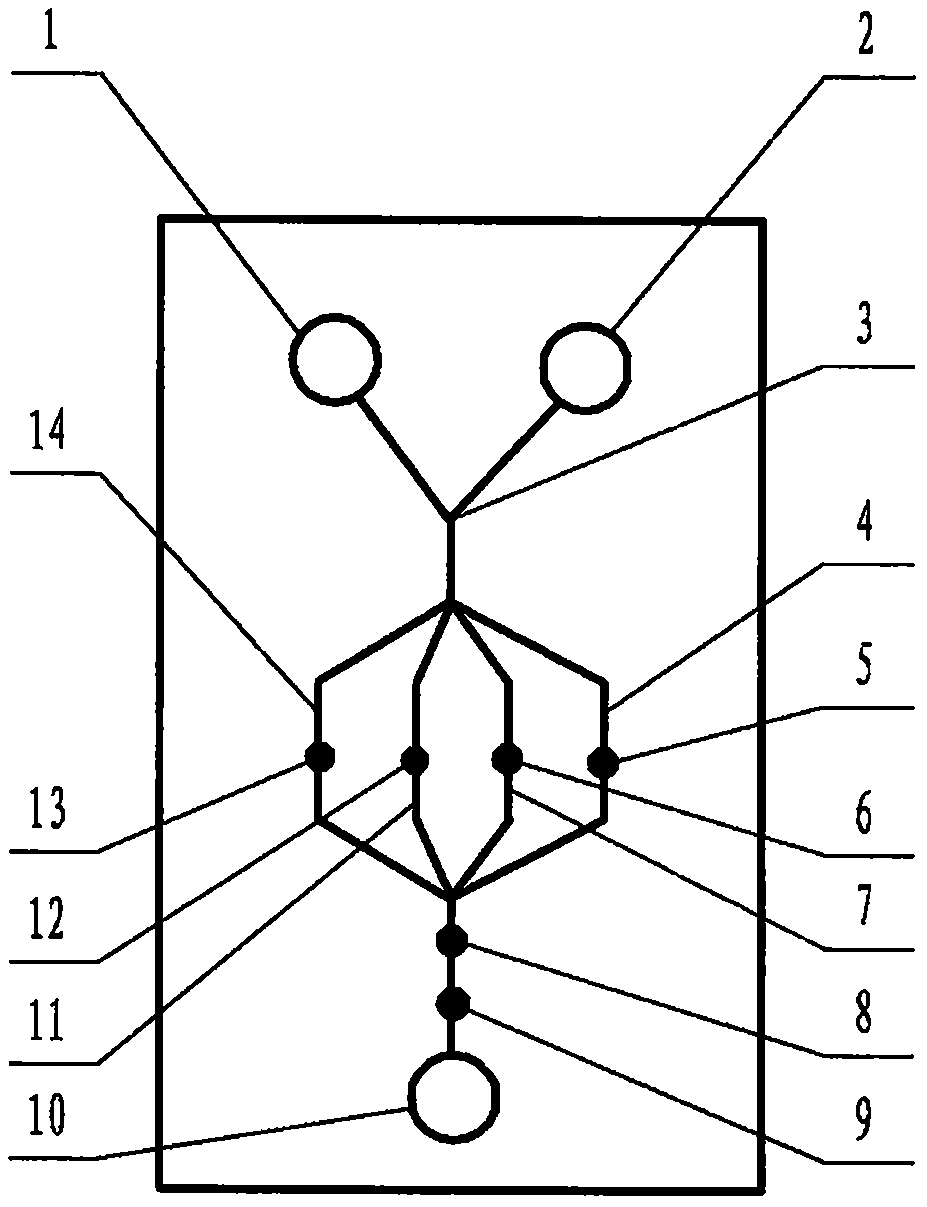
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip device for multi-channel simultaneous detection of six typical tumor markers, which belongs to the field of analysis and testing. Using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to make the substrate of the microfluidic chip for multi-channel joint detection of six typical tumor markers has obvious advantages, but there are also a series of problems; this case is aimed at this series of problems. The gist of this case is that the PDMS with an original ecological surface is selected as the substrate, and a micro-ultrasonic transducer is attached and installed in the vicinity of the liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip to reduce the interfacial tension with ultrasonic waves, thereby greatly increasing the correlation. The compatibility between the phases and the strong absorption ability of PDMS to ultrasonic waves are used to achieve a rapid decrease in the ultrasonic intensity within a short distance, and thus form a difference in interfacial tension at both ends of the chip, which leads to the difference in interfacial tension between the two A pressure differential is formed at the end of the pipe, which drives the flow toward the terminal along the otherwise strongly hydrophobic pipe.
Owner:宋岳
Microfluidic chip device for multi-channel simultaneous detection of six typical tumor markers
InactiveCN107225005AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip device for multi-channel simultaneous detection of six typical tumor markers, and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. Polydimethylsiloxane, i.e. PDMS, is used for preparing a substrate of the microfluidic chip for multi-channel combined detection of six typical tumor markers, which has obvious advantages but also has a series of challenges. Aiming at the series of challenges, the invention is provided. The key points of the invention are as follows: the PDMS with an original form surface is selected as the substrate; a micro ultrasonic transducer is attached to a position adjacent to a sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip; and meanwhile, the sample injection end of the microfluidic chip is provided with an ultrasonic attenuator, so that the ultrasonic strength quickly descends within a short distance, an interfacial tension difference is thus formed between the two ends of the chip, the interfacial tension difference causes a pressure difference between the two ends, and the pressure difference drives a liquid flow to flow towards the terminal along an original high-hydrophobicity pipeline.
Owner:葛宇杰
Microfluidic chip device for combined detection of typical tumor markers for female
InactiveCN107225002AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesAbnormal tissue growthUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip device for combined detection of typical tumor markers for a female, and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. PDMS, i.e. polydimethylsiloxane, is used for preparing a substrate of the microfluidic chip for combined detection of typical tumor markers for a female, which has price and process advantages but also has challenges. Aiming at the challenges, the invention is provided. The key points of the invention are as follows: the PDMS with an original form surface is selected as the substrate; a micro ultrasonic transducer is attached to a position adjacent to a sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip; and meanwhile, the sample injection end of the microfluidic chip is provided with an ultrasonic attenuator, so that the ultrasonic strength quickly descends within a short distance, an interfacial tension difference is thus formed between the two ends of the chip, the interfacial tension difference causes a pressure difference between the two ends, and the pressure difference drives a sample liquid flow to flow towards the terminal along an original high-hydrophobicity capillary level channel.
Owner:葛宇杰
Microfluidic chip device for multi-channel simultaneous detection of six typical tumor markers
InactiveCN106694064AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthAbsorption capacity
Belonging to the field of analytical testing, the invention relates to a microfluidic chip device for multi-channel simultaneous detection of six typical tumor markers. Use of polydimethylsiloxane PDMS to make a substrate for multi-channel combined detection of six typical tumor markers has obvious advantages, and also has a series of problems. The device provided by the invention is directed at the series of problems. According to key points of the invention, PDMS with an original ecological surface is selected as the substrate, a micro-ultrasonic transducer is attached and mounted at a neighboring position of a liquid flow terminal on the microfluidic chip, ultrasonic wave is utilized to reduce interfacial tension, thereby greatly increasing the compatibility of correlates, at the same time the strong absorption capacity of PDMS to ultrasonic wave is utilized to achieve rapid diminishing of ultrasonic intensity within a short distance, thus forming interfacial tension difference between two ends of the chip, the interfacial tension difference results in formation of pressure difference between the two ends, and the pressure difference drives a liquid flow to flow along an originally strongly hydrophobic pipeline in a terminal direction.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Cheap microfluidic device based on novel liquid fluid drive principle and for syphilis diagnosis
InactiveCN107649206AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesAbsorption capacitySyphilis
The invention relates to a cheap microfluidic device based on novel liquid flow drive principle and for syphilis diagnosis and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. It is a technical objectiveto use cheap and easily-processable polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS for manufacturing a substrate of a microfluidic chip for syphilis diagnosis. However, the surface of the material is strongly hydrophobic. Through targeted surface modification, the effect is hard to last. The scheme aims to solve the series of related problems. According to main points, PDMS with primitive surface is selectedas the substrate, a miniature ultrasonic transducer is arranged near the terminal of a sample liquid fluid of the microfluidic chip, interfacial tension is reduced by ultrasonic wave, and by PDMS's strong absorption of ultrasonic wave, ultrasonic intensity is rapidly decreased progressively in a short distance to form interfacial tension difference between two ends of the chip. The interfacial tension difference leads to formation of pressure difference between the two ends, and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid fluid to flow along the capillary channel towards the terminal.
Owner:洪小女
Cheap microfluidic device capable of transmitting liquid flow with new way and used for AIDS diagnosis
InactiveCN107649189AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorAbsorption capacity
The invention relates to a cheap microfluidic device capable of transmitting a liquid flow with a new way and used for AIDS diagnosis, belonging to the fields of analysis and testing. The invention aims to solve a series of related problems that manufacturing of a substrate of a microfluidic chip used for AIDS diagnosis from cheap and easily-processed polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) has a technical obstacle; and the cheap and easily-processed polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) has highly-hydrophobic surface and is difficult to obtain lasting effects through targeted surface modification or surface decoration. The invention has the following main points: PDMS with original ecological surface is selected as the substrate; the position close to the terminal of a sample liquid flow of the microfluidic chip is attached with a miniature ultrasonic transducer; ultrasonic wave is used to reduce the interfacial tension; meanwhile, by utilizing strong absorption capacity of the PDMS to the ultrasonic wave,rapid decrease of ultrasonic intensity in a short distance is realized, and an interfacial tension difference between two terminals of the chip is formed; the interfacial tension difference causes two terminals to form a pressure difference; and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid flow to flow to the terminal direction along capillary channels.
Owner:洪小女
Cheap microfluidic device for liquid flow drive by interface characteristics and for cholera diagnosis
InactiveCN107649204AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionBiological material analysisLaboratory glasswaresUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a cheap microfluidic device for liquid flow drive by interface characteristics and for cholera diagnosis and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. By using cheap and easily-processable polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS for manufacturing a substrate of a microfluidic chip for cholera diagnosis, a series of problems exist. The surface of the PDMS material is stronglyhydrophobic. Through targeted surface modification, the effect is hard to last. The scheme aims to solve the series of related problems. According to main points of the scheme, PDMS with primitive surface is selected as the substrate, a miniature ultrasonic transducer is arranged near the terminal of a sample liquid fluid of the microfluidic chip, interfacial tension is reduced by ultrasonic wave, and by PDMS's strong absorption of ultrasonic wave, ultrasonic intensity is rapidly decreased progressively in a short distance to form interfacial tension difference between two ends of the chip. The interfacial tension difference leads to formation of pressure difference between the two ends, and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid fluid to flow along the capillary channel towardsthe terminal.
Owner:洪小女
Cheap micro-fluidic device used for diagnosis of cholera and realizing liquid flow driving based on interfatial characteristics
PendingCN106990240AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysisAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicrofluidic chipMicro fluidic
The invention relates to a cheap micro-fluidic device used for diagnosis of cholera and realizing liquid flow driving based on interfatial characteristics, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. A series of obstacles exist in preparation of a substrate for a cholera diagnosis micro-fluidic chip from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS); a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time; and the invention aims to overcome a series of such problem. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Cheap cholera diagnosis micro-fluidic device with specific fluid flow transmission mode
InactiveCN105891472AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAgainst vector-borne diseasesUltrasonic sensorAbsorption capacity
The invention relates to a cheap cholera diagnosis micro-fluidic device with a specific fluid flow transmission mode, and belongs to the field of analytical tests. A series of problems exist if polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) which is cheap and extremely easy to process is used for manufacturing a substrate of a micro-fluidic chip for cholera diagnosis; the surface of PDMS is highly hydrophobic, and the effect of targeted surface modification is not lasting. The cheap cholera diagnosis micro-fluidic device with the specific fluid flow transmission mode aims at solving the series of related problems. The cheap cholera diagnosis micro-fluidic device with the specific fluid flow transmission mode is characterized in that PDMS with an original surface is selected as the substrate, a micro ultrasonic transducer is attached to the position close to the sample fluid flow terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, and interfacial tension is reduced with ultrasonic waves; meanwhile, the strong absorption capacity of PDMS to ultrasonic waves is utilized for rapidly and gradually reducing the intensity of ultrasonic waves in a short distance, an interfacial tension difference is formed at the two ends of the chip accordingly, a pressure difference is formed between the two ends due to the interfacial tension difference, and sample fluid is driven under the pressure difference to flow towards to the terminal along a capillary pipe.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Cheap micro-fluidic device used for diagnosis of AIDS and transmitting liquid flow in novel manner
PendingCN106984366AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a cheap micro-fluidic device used for diagnosis of AIDS and transmitting liquid flow in a novel manner, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. Few technical obstacles exist in preparation of a substrate for an AIDS diagnosis micro-fluidic chip from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS); a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface, and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time; and the invention aims to overcome a series of such problem. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Micro fluidic chip device for combined detection of typical tumor marker suitable for male
InactiveCN107694648AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthShortest distance
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip device for combined detection of typical tumor markers suitable for men, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. Using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to make the substrate of the microfluidic chip for the combined detection of typical male tumor markers has many advantages, but there are also a series of problems; this case is aimed at this series of problems. The gist of this case is that the PDMS with an original ecological surface is selected as the substrate, and a micro-ultrasonic transducer is attached to the position adjacent to the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip, so that the interfacial tension is reduced by ultrasonic waves, and the correlation is greatly increased. The compatibility between the phases and the strong absorption ability of PDMS to ultrasonic waves are used to achieve a rapid decrease in the intensity of ultrasonic waves in a short distance, and thus form a difference in interfacial tension at both ends of the chip, which leads to the difference in interfacial tension between the two A pressure difference is formed at the end, and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid flow to flow along the originally hydrophobic pipe toward the terminal. The device also eliminates the need for a micropump.
Owner:宋岳
Multichannel micro-fluidic chip device capable of simultaneously detecting multiple swine influenza virus subtypes
InactiveCN106990242AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a multichannel micro-fluidic chip device capable of simultaneously detecting multiple swine influenza virus subtypes, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. A series of obstacles practically exist in preparation of a substrate for a swine influenza virus subtype diagnosis micro-fluidic chip from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS); a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time; and the invention aims to overcome a series of such problem. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Cheap microfluidic device with specific fluid drive mode and for AIDS diagnosis
InactiveCN107649213AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesMicrofluidic chipBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a low-cost microfluidic device for AIDS diagnosis with a specific fluid driving mode, which belongs to the field of analysis and testing. It is a technical goal to use cheap and easy-to-process polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to make the substrate of microfluidic chips for AIDS diagnosis; however, the surface of this material is strongly hydrophobic, and targeted surface modification or Surface modification, its effect is difficult to last, this case aims to solve this series of related problems. The main point of this case is that the substrate is selected with PDMS with an original ecological surface, and a micro-ultrasonic transducer is attached to the position adjacent to the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip to reduce the interfacial tension with ultrasonic waves, and at the same time use PDMS The strong absorption ability of ultrasonic waves achieves the rapid decrease of ultrasonic intensity in a short distance, and thus forms a difference in interfacial tension at both ends of the chip. The difference in interfacial tension causes a pressure difference at the two ends, and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid. Flow flows along the capillary channel towards the terminal.
Owner:洪小女
Cheap micro-fluidic device for diagnosis of syphilis and based on novel liquid flow driving principles
InactiveCN106990243AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysisSyphilisUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a cheap micro-fluidic device for diagnosis of syphilis and based on novel liquid flow driving principles, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. A technical object of the invention is to prepare a substrate used for syphilis diagnosis micro-fluidic chips from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane, i.e., PDMS. However, a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface, and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time; and the invention aims to overcome the problem. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Cheap micro-fluidic device for diagnosis of AIDS and with specific fluid driving manner
InactiveCN106990241AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a cheap micro-fluidic device for diagnosis of AIDS and with a specific fluid driving manner, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. A technical object of the invention is to prepare a substrate for an AIDS diagnosis micro-fluidic chip from cheap and easily workable polydimethylsiloxane, i.e., PDMS. However, a PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface, and the effect of targeted surface modification cannot last for a long time; and the invention aims to overcome a series of such problem. According to main points of a technical scheme in the invention, PDMS with an original surface is selected as a substrate; a minisized ultrasonic transducer is arranged at a position close to a sample liquid flow terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in an adhesion manner, and an ultrasonic wave reducing device is arranged on the sample introduction terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so the intensity of ultrasonic waves rapidly and progressively decreases in a short distance; thus, difference of interfacial tension at the two terminals of the chip is formed, which leads to formation of pressure difference between the two terminals, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the sample liquid flow terminal along a capillary channel.
Owner:李榕生
Multichannel microfluidic chip device for simultaneous detection of various subtype swine influenzas
InactiveCN107649215AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisAbsorption capacityUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a multi-channel microfluidic chip device for simultaneously detecting multiple subtypes of swine influenza, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. There are many obstacles in using cheap and easy-to-process polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to make the substrate of the microfluidic chip for subtype swine influenza diagnosis; the surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic, and targeted surface modification Or surface modification, its effect is difficult to last, this case aims to solve this series of related problems. The main point of this case is that the substrate is selected with PDMS with an original ecological surface, and a micro-ultrasonic transducer is attached to the position adjacent to the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip to reduce the interfacial tension with ultrasonic waves, and at the same time use PDMS The strong ability to absorb ultrasonic waves achieves a rapid decrease in the intensity of ultrasonic waves within a short distance, and thus forms a difference in interfacial tension at both ends of the chip, thereby forming a pressure difference between the two ends, which drives the sample liquid flow along the The capillary channel flows in the direction of this terminal end.
Owner:洪小女
Micro-fluidic chip device used for typical tumor marker joint detection and suitable for males
InactiveCN106694063AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresDisease diagnosisHigh absorptionUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a micro-fluidic chip device used for typical tumor marker joint detection and suitable for males and belongs to the field of analytical test. Polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS is used for manufacturing a substrate of a micro-fluidic chip for male typical tumor marker joint detection, many advantages are generated, but a series of problems exist. The scheme aims at the problems. According to the scheme, the substrate is selected from PDMS with the original ecology surface, a minitype ultrasonic transducer is attached to a position adjacent to a sample liquid flow terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, interfacial tension is ultrasonically reduced, and the compatibility between relevant phases is greatly improved; through the high absorption capacity of PDMS to ultrasonic waves, the ultrasonic intensity is rapidly and gradually reduced within a short distance, the interfacial tension difference is formed between the two ends of the chip, the pressure difference is formed between the two ends through the interfacial tension difference, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow to the terminal along an original hydrophobic pipeline. No micro-pump needs to be used for the device.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
AIDS-diagnosis-used cheap microflow control device for transferring liquid flow in new mode
InactiveCN105891523AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysisMicrofluidic chipBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to an AIDS-diagnosis-used cheap microflow control device for transferring liquid flow in a new mode and belongs to the field of analytical tests. When polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) which is low in price and extremely easy to process is adopted to make a substrate of an AIDS-diagnosis-used cheap microflow control chip, a series of problems are caused; the surface of the PDMS material is highly hydrophobic, and the effect of targeted surface modification or surface decoration is difficult to endure; the device aims to solve the mentioned relevant problems. The device is mainly characterized in that PDMS having the originally-ecological surface is selected for making a substrate, a miniature ultrasonic transducer is arranged at the position, near a sample liquid flow terminal, of a microflow control chip in an attached mode, interfacial tension is lowered through ultrasonic waves, and meanwhile high absorption capacity of PDMS to the ultrasonic waves is utilized, so that the effect that the intensity of the ultrasonic waves is gradually decreased within a short distance rapidly is achieved, thereby interfacial tension difference is formed at the two ends of the chip, the pressure difference is formed at the two ends due to the interfacial tension difference, and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid flow to flow toward the terminal along a capillary tube channel.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Multi-channel micro-fluidic chip device for simultaneous detection of swine flu of multiple subtypes
InactiveCN105879934AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a multi-channel micro-fluidic chip device for simultaneous detection of swine flu of multiple subtypes, and belongs to the field of analytical testing. The device solves a series of problems existing actually when polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) low in cost and easy to process is used for manufacturing a substrate of a micro-fluidic chip for subtype swine flu diagnosis and the problems that the suface of the PDMS material is hydrophobic intensively, and the effect of specific surface modification or surface finishing cannot be lasting easily. The device is characterized in that the PDMS with the raw surface is selected as the substrate, a micro ultrasonic transducer is arranged at the adjacent position of a sample fluid flow terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, interfacial tension can be lowered in an ultrasonic mode, meanwhile, the strength of ultrasonic waves is rapidly and gradually lowered within the short distance by means of the strong ultrasonic absorbing capacity of the PDMS, the interface tension difference is formed between the two ends of the chip, then, the pressure difference between the two ends is formed, and the pressure difference drives sample fluid flow to flow towards the terminal along a capillary tube channel.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Multichannel microfluidic chip device for simultaneous detection of various subtype swine influenzas
InactiveCN107649212AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresAbsorption capacityUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a multi-channel microfluidic chip device for simultaneous detection of multiple subtypes of swine flu, and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. There are actually a series of difficulties in using the cheap and easy-to-process polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to fabricate the substrate of the microfluidic chip for the diagnosis of subtype swine flu; the surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic, and targeted surface modification. Sex or surface modification, the effect is difficult to last, this case aims to solve the series of related problems. The main point of this case is that the substrate selects PDMS with an original surface, and attaches a micro ultrasonic transducer to the adjacent position of the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip to reduce the interfacial tension with ultrasonic waves, and uses PDMS at the same time. The strong absorbing ability of ultrasonic waves achieves the rapid decrease of ultrasonic intensity in a short distance, and thus forms an interfacial tension difference between the two ends of the chip, thereby forming a pressure difference between the two ends, which drives the sample liquid flow along the The capillary channel flows in the direction of this terminal.
Owner:洪小女
Cholera-diagnosis-used cheap microflow control device for conducting liquid flow driving through interface characteristics
InactiveCN105891471AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorHigh absorption
The invention relates to a cholera-diagnosis-used cheap microflow control device for conducting liquid flow driving through interface characteristics and belongs to the field of analytical tests. When polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) which is cheap and extremely easy to process is adopted to make a substrate of a cholera-diagnosis-used cheap microflow control chip, a series of problems are caused; the surface of the PDMS material is highly hydrophobic, and the effect of targeted surface modification or surface decoration is difficult to endure; the device aims to solve the relevant problems. The device is mainly characterized in that PDMS having the originally-ecological surface is selected for making a substrate, a miniature ultrasonic transducer is arranged at the position, near a sample liquid flow terminal, of a microflow control chip in an attached mode, interfacial tension is lowered through ultrasonic waves, and meanwhile by means of high absorption capacity of PDMS to the ultrasonic waves, so that the effect that the intensity of the ultrasonic waves is gradually decreased within a short distance rapidly is achieved, thereby interfacial tension difference is formed at the two ends of the chip, the pressure difference is formed at the two ends due to the interfacial tension difference, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow toward the terminal along a capillary tube channel.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Low-cost acquired immune deficiency syndrome diagnosis micro-fluidic device with special fluid driving mode
InactiveCN105879933AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingUltrasonic sensorHigh absorption
The invention relates to a low-cost acquired immune deficiency syndrome diagnosis micro-fluidic device with a special fluid driving mode, belongs to the field of analytical testing, and aims at solving series of the related problems that when a substrate of a micro-fluidic chip for acquired immune deficiency syndrome diagnosis is manufactured from polydimethylsiloxane (that is, PDMS) which is low in cost and extremely easy to process, due to the fact that the surface of the material is highly hydrophobic, the effect of targeted surface modification is difficult to be lasting. The device is characterized in that PDMS with the original ecological surface is selected as the substrate, a mini-type ultrasonic transducer is arranged at the position adjacent to a sample liquid flow terminal of the micro-fluidic chip in an attached mode, and the interfacial tension is decreased through ultrasonic waves; meanwhile, the purpose that the ultrasonic wave intensity is gradually decreased quickly within a short distance is achieved through the high absorption capacity of PDMS to the ultrasonic waves, then interfacial tension differences are formed at the two ends of the chip, a pressure difference is formed between the two ends due to the interfacial tension differences, and sample liquid flow is driven by the pressure difference to flow towards the terminal direction along capillary tube channels.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Cheap syphilis diagnosis micro-fluidic device based on novel liquid flow driving principle
InactiveCN105891475AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysisMicrofluidic chipMicro fluidic
The invention relates to a cheap syphilis diagnosis micro-fluidic device based on the novel liquid flow driving principle and belongs to the field of analytical testing. It is a technical objective to use polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) which is low in cost and very easy to process for manufacturing a substrate of a syphilis diagnosis micro-fluidic chip; however, the surface of the material is highly hydrophobic, and the effect of targeted surface modification or surface finish is hard to last for long. The device aims at solving the problems and is characterized in that PDMS with an original ecological surface is selected as the substrate, a micro ultrasonic transducer is installed at the position adjacent to a sample liquid flow terminal of the micro-fluidic chip in an attached mode, interface tension is reduced through ultrasonic waves, the ultrasonic intensity is quickly and gradually reduced within a short distance through the strong ultrasonic wave absorption capacity of PDMS, an interface tension difference is formed between the two ends of the chip accordingly, a pressure difference is formed between the two ends due to the interface tension difference, and the pressure difference drives sample liquid flow to flow towards the terminal along a capillary pipe channel.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Micro fluidic chip device for combined detection of typical tumor markers suitable for women
InactiveCN107694633AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip device for combined detection of typical tumor markers suitable for women, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. Using PDMS or polydimethylsiloxane to make the substrate of a microfluidic chip for combined detection of typical tumor markers suitable for women has advantages in price and technology, but there are also difficulties; this case aims to overcome this difficulty. The gist of this case is that the PDMS with an original ecological surface is selected as the substrate, and a micro-ultrasonic transducer is attached to the position adjacent to the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip, so that the interfacial tension can be reduced by ultrasonic waves, and the solid state can be greatly increased. The compatibility between the two phases of the liquid, and the use of PDMS’s strong absorption capacity for ultrasonic waves, achieves a rapid decrease in the ultrasonic intensity within a short distance, and thus forms a difference in interfacial tension at both ends of the chip. The difference in interfacial tension leads to the A pressure differential is created at both ends, which drives the sample flow toward the terminal along the otherwise strongly hydrophobic capillary-level channel.
Owner:宋岳
Cheap microfluidic device for transmitting liquid flow by utilization of interface characteristics and for syphilis diagnosis
InactiveCN107656058AGood compatibilityEliminate adsorptionMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorSyphilis
The invention relates to a low-cost microfluidic device for syphilis diagnosis, which uses interface characteristics to transmit liquid flow, and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. There are some difficulties in making the substrate of the microfluidic chip for syphilis diagnosis with cheap and easy-to-process polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS); the surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic, and targeted surface modification or surface modification , its effect is difficult to last, this case aims to solve this series of related problems. The main point of this case is that the substrate is selected with PDMS with an original ecological surface, and a micro-ultrasonic transducer is attached to the position adjacent to the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip to reduce the interfacial tension with ultrasonic waves, and at the same time use PDMS The strong absorption ability of ultrasonic waves achieves the rapid decrease of ultrasonic intensity in a short distance, and thus forms a difference in interfacial tension at both ends of the chip. The difference in interfacial tension causes a pressure difference at the two ends, and the pressure difference drives the sample liquid. Flow flows along the capillary channel towards the terminal.
Owner:洪小女
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com