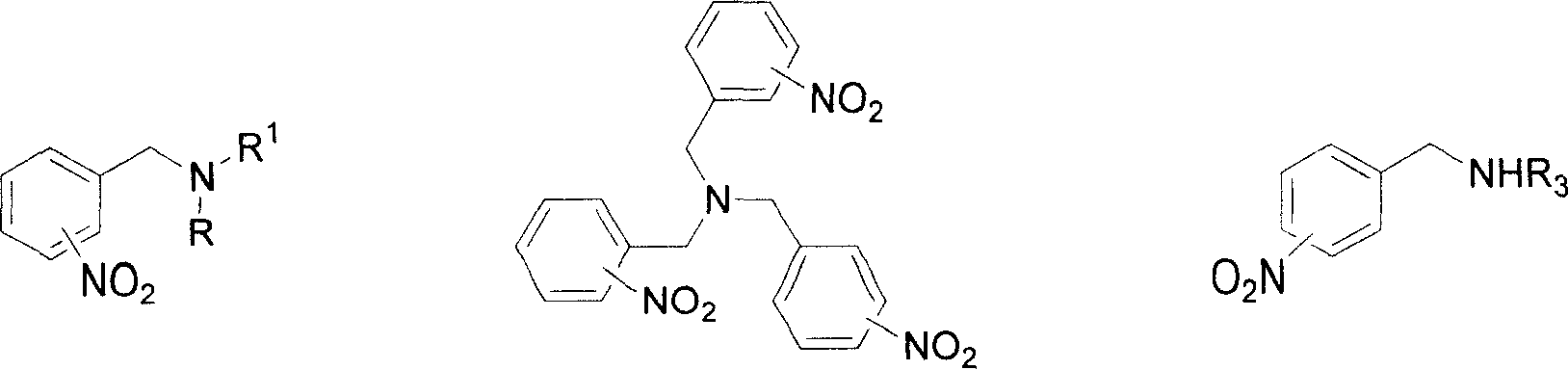
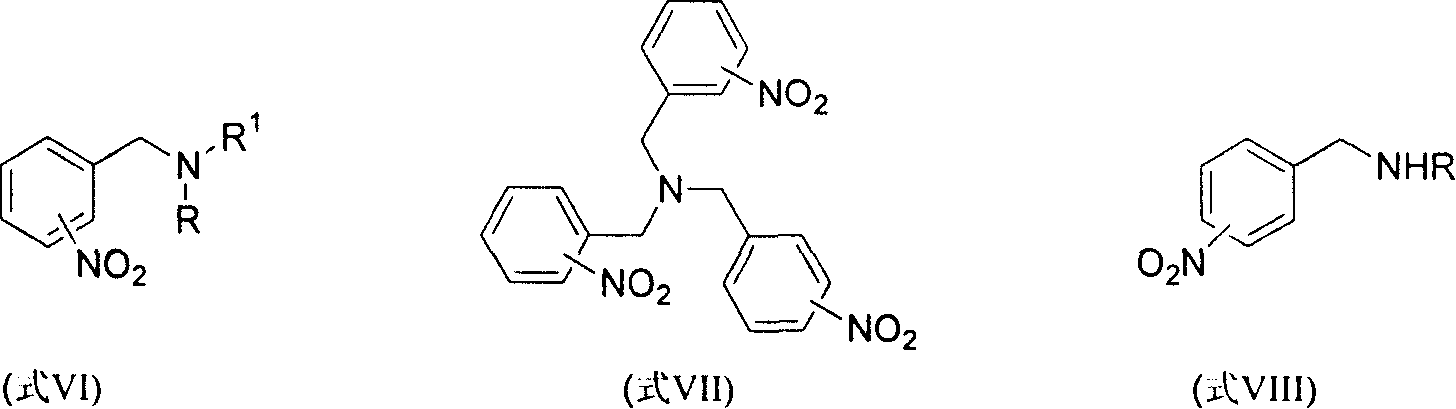
Method for reducing nitroxylbenzyl amine compound to amino-benzylamine hydrochloride
A technology of aminobenzylamine hydrochloride and nitrobenzylamine is applied in the field of reducing nitrobenzylamine compounds to aminobenzylamine hydrochloride, and achieves the effects of broad application prospects, mild reaction conditions and convenient post-processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
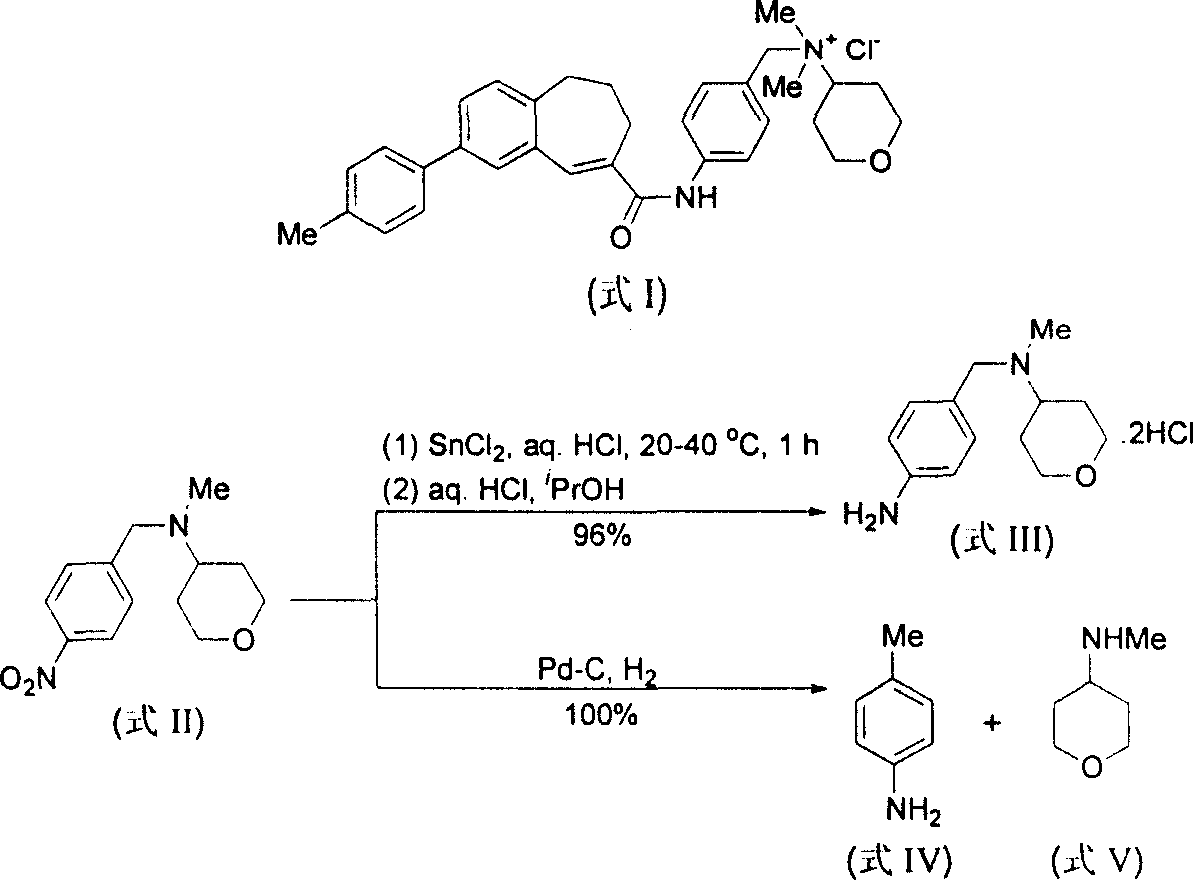
[0052] Embodiment 1, use CHCl 3 Preparation of 4-amino-N,N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a) as a source of HCl
[0053] At 25° C., 4-nitro-N, N-dimethylbenzylamine (formula VI / a, 450 mg, 2.5 mmol), 10% Pd / C (45 mg, 10% by weight) and CHCl 3 (2 mL) in methanol (30 mL) was hydrogenated at atmospheric pressure for 2 h, and the Pd / C catalyst was filtered off. The filtrate was distilled off of methanol under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product of yellow crystals. The yellow crystals were then washed with a small amount of ether to remove any non-salt-forming material. Finally by MeOH / Et 2 O was recrystallized to give pale yellow crystalline compound 4-amino-N,N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a, 510 mg, 91%).
[0054] m.p.198-200℃(MeOH / Et 2 O);
[0055] 13 C NMR (CD 3 OH): δ133.7, 133.0, 130.5, 123.7, 60.1, 42.0;
[0056] Elemental analysis (C 9 h 16 N 2 Cl 2 ): C, 48.44; H, 7.23; N, 12.55; Found: C, 48.20; H, 7.24; N, 12.32.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2, use concentrated hydrochloric acid as the source of HCl to prepare 4-amino-N, N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a)
[0058] At 25° C., 4-nitro-N, N-dimethylbenzylamine (formula VI / a, 450 mg, 2.5 mmol), 10% Pd / C (45 mg, 10% by weight) and 37% concentrated hydrochloric acid ( A suspension of 1 mL containing about 8 mmol of HCl) in methanol (30 mL) was hydrogenated at atmospheric pressure for 15 minutes, and hydrogen uptake ceased completely. The Pd / C catalyst was filtered off, and the filtrate was evaporated to remove methanol under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product of yellow crystals. The yellow crystals were then washed with a small amount of ether to remove any non-salt-forming material. Finally by MeOH / Et 2 O was recrystallized to give pale yellow crystalline compound 4-amino-N,N-dimethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / a, 550 mg, 98%). The physical data are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, preparation 4-amino-N, N-diethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (formula IX / b)
[0060] Under the same conditions as in Example 2, the reaction was carried out with 4-nitro-N,N-diethylbenzylamine (formula VI / b), and hydrogen absorption was completely stopped after 15 minutes. The crude product was obtained from MeOH / Et 2 Recrystallization from O gave pale yellow crystalline compound 4-amino-N,N-diethylbenzylamine dihydrochloride (Formula IX / b, 100%).
[0061] m.p.180-182℃(MeOH / Et 2 O);
[0062] 13 C NMR (CD 3 OH): δ150.0, 132.2, 117.3, 115.1, 56.2, 46.4, 8.1;
[0063] Elemental analysis (C 11 h 20 N 2 Cl 2 ): C, 52.60; H, 8.03; N, 11.15; Found: C, 52.48; H, 8.03; N, 11.17.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com