Hot extrusion production technique for improving plastisity of magnesium alloy sectional material
A production process, hot extrusion technology, applied in metal extrusion, metal extrusion control equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve problems affecting product processing and mechanical properties, high local temperature, destructive plasticity, etc., to achieve convenience Calculate and apply the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
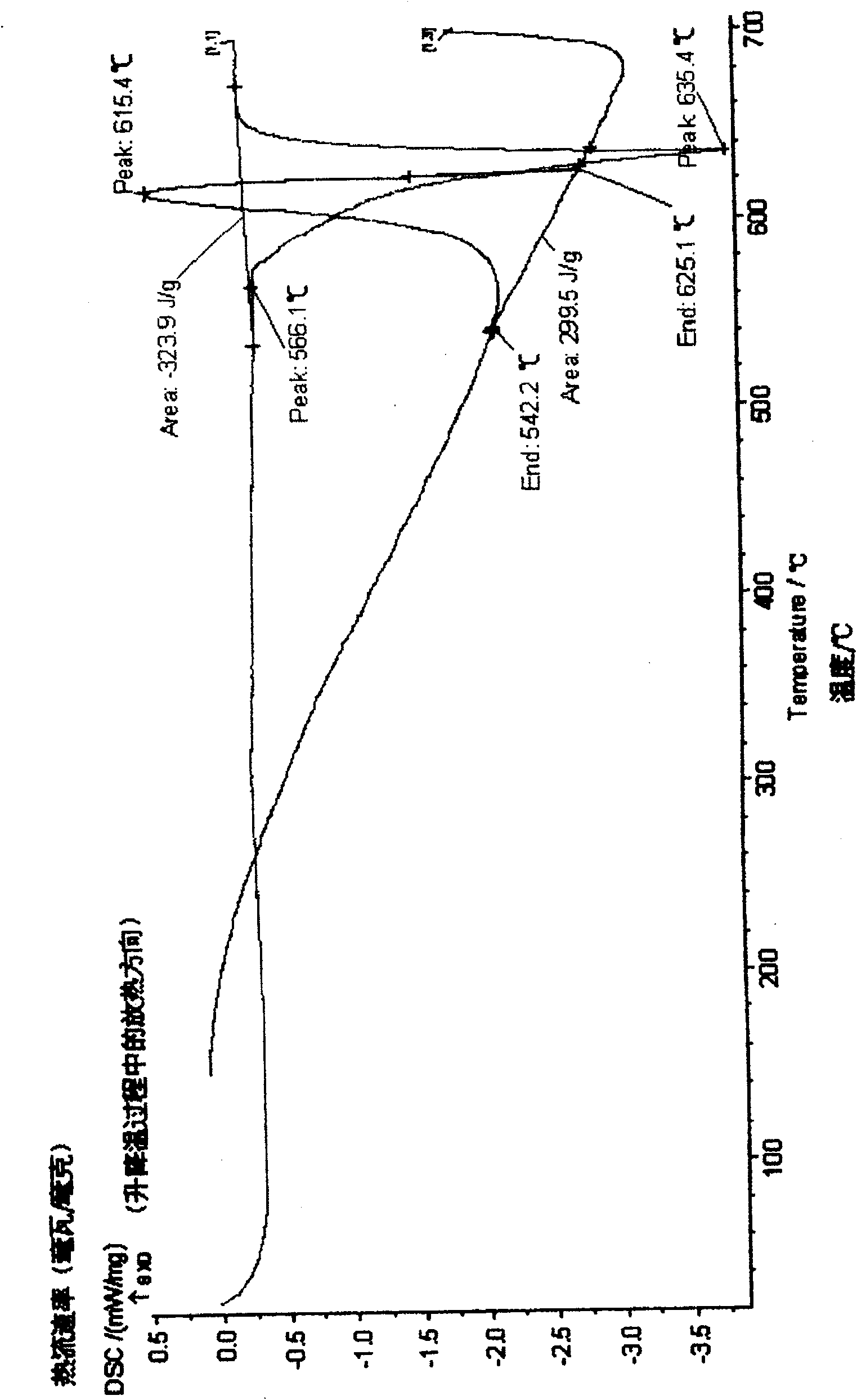
[0036] Put the ZM21 magnesium alloy billet into the heating furnace when the furnace temperature is less than 250°C, use the conventional heating rate to raise the temperature to 350°C with the furnace, and keep the constant temperature. The temperature of the furnace is raised to 430°C, and the constant temperature is maintained, and the billet is continuously subjected to the second-stage homogenization annealing at the constant temperature for 5 hours. The temperature rise rate from the first stage to the second stage with the furnace temperature rise can be ignored because of the basis of the homogenization annealing of the first stage.
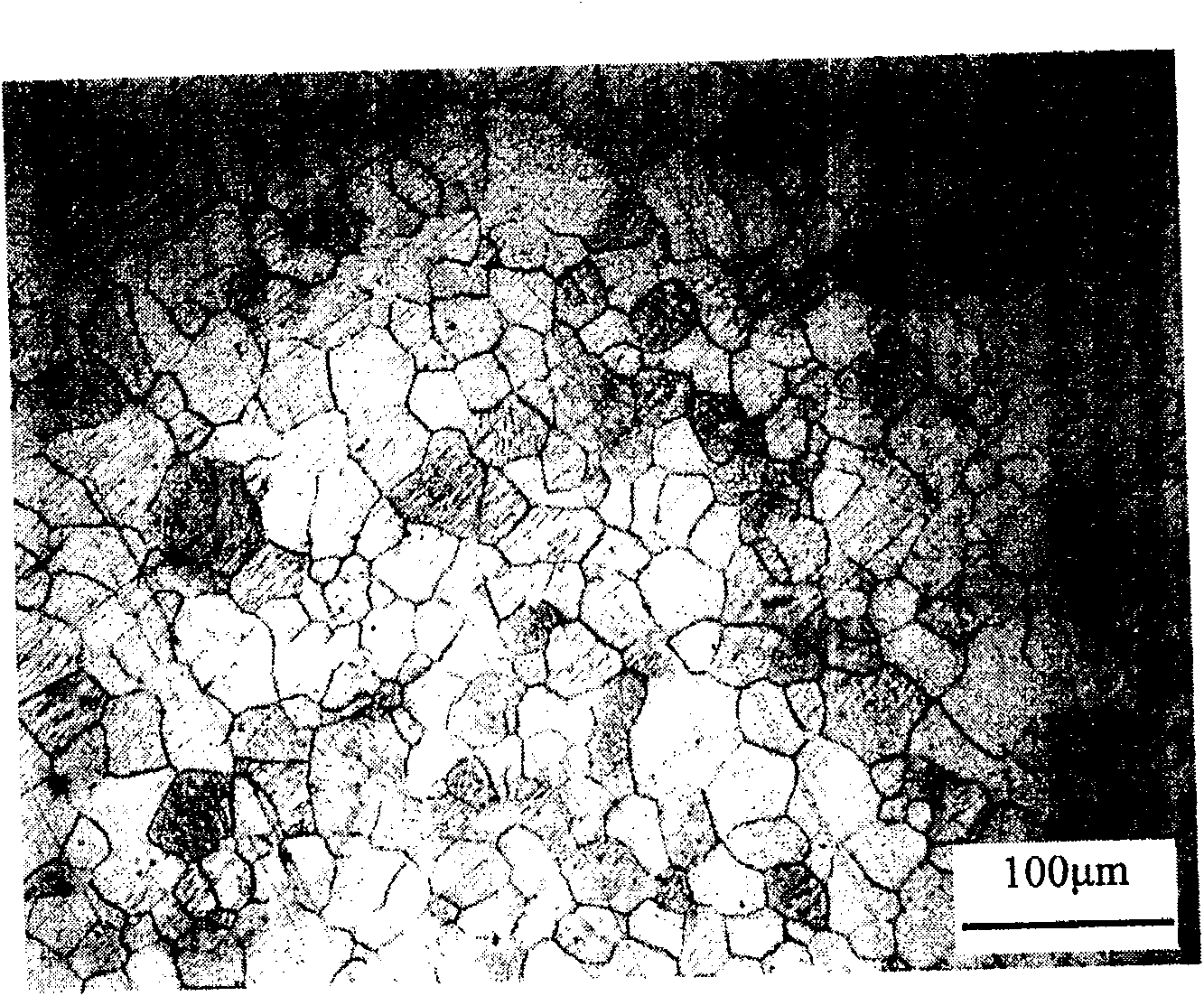
[0037] After the billet is annealed, it is air-cooled and then loaded into the extruder for hot extrusion deformation.
[0038] When extruding a bar with a cross-sectional area of 11.6 square millimeters (12 millimeters in diameter), a 500-ton extruder is used for extrusion deformation. The inner diameter of the extrusion cylinder is 85...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Put the ZM21 magnesium alloy billet into the heating furnace when the furnace temperature is less than 250°C, use the conventional heating rate to raise the temperature to 350°C with the furnace, and keep the constant temperature. The temperature of the furnace is raised to 430°C, and the constant temperature is maintained, and the billet is continuously subjected to the second-stage homogenization annealing at the constant temperature for 5 hours. The temperature rise rate from the first stage to the second stage with the furnace temperature rise can be ignored because of the basis of the homogenization annealing in the first stage.
[0041] After the billet is annealed, it is air-cooled and then loaded into the extruder for hot extrusion deformation.
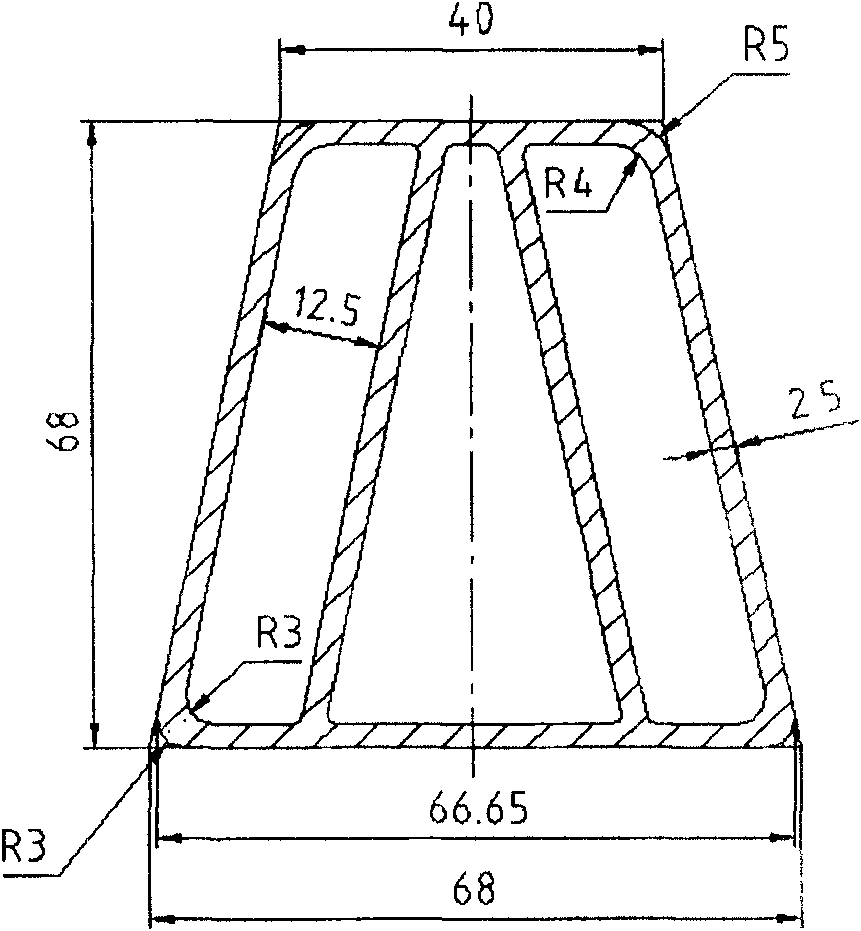
[0042] Extrusion section shape as image 3 For the profile shown in the profile, a 2,500-ton extruder is used for extrusion deformation. The inner diameter of the extrusion cylinder is 200 mm, and the extrusion ratio i...
Embodiment 3
[0044]The AZ61 magnesium alloy blank is loaded into the heating furnace when the furnace temperature is <250°C, and the blank is loaded into the heating furnace when the furnace temperature is <250°C. The conventional heating rate is used to raise the temperature to 300°C with the furnace, and the constant temperature is maintained. The blank is heated at a constant temperature. The first stage of homogenization annealing for 6 hours, and then the temperature of the furnace is raised to 420°C, and the temperature is kept constant. The billet continues to perform the second stage of homogenization annealing at constant temperature for 5 hours. The temperature rise rate from the first stage to the second stage with the furnace temperature rise can be ignored because of the basis of the homogenization annealing in the first stage.
[0045] After the billet is annealed, it is air-cooled and then loaded into the extruder for hot extrusion deformation.
[0046] When extruding a bar ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com