Method for measuring transmissivity relevant frequency spectrum method grain and device thereof
A measurement method and transmittance technology, which are used in transmittance measurement, special data processing applications, complex mathematical operations, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to measure particles above micron level and inability to achieve online measurement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
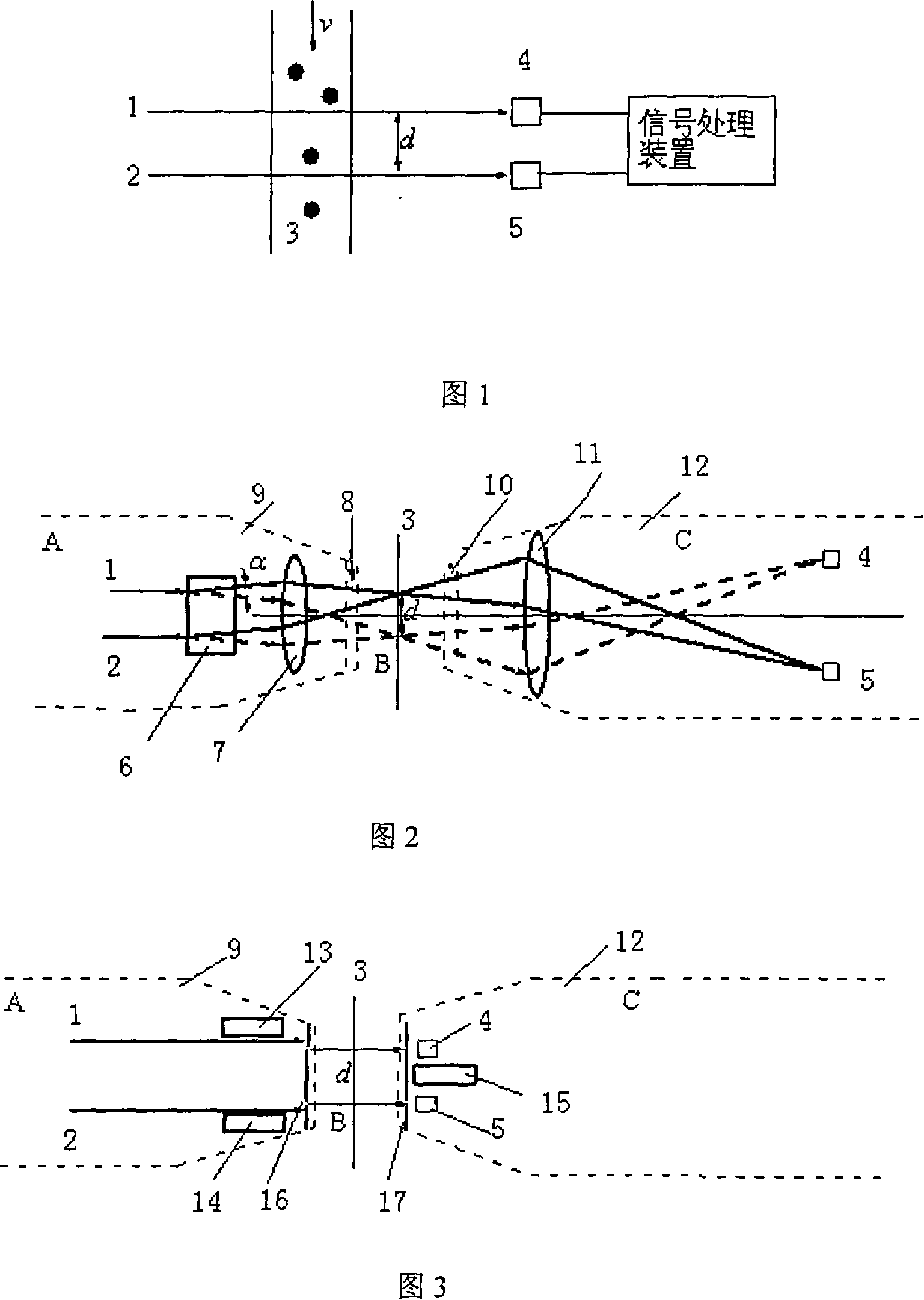
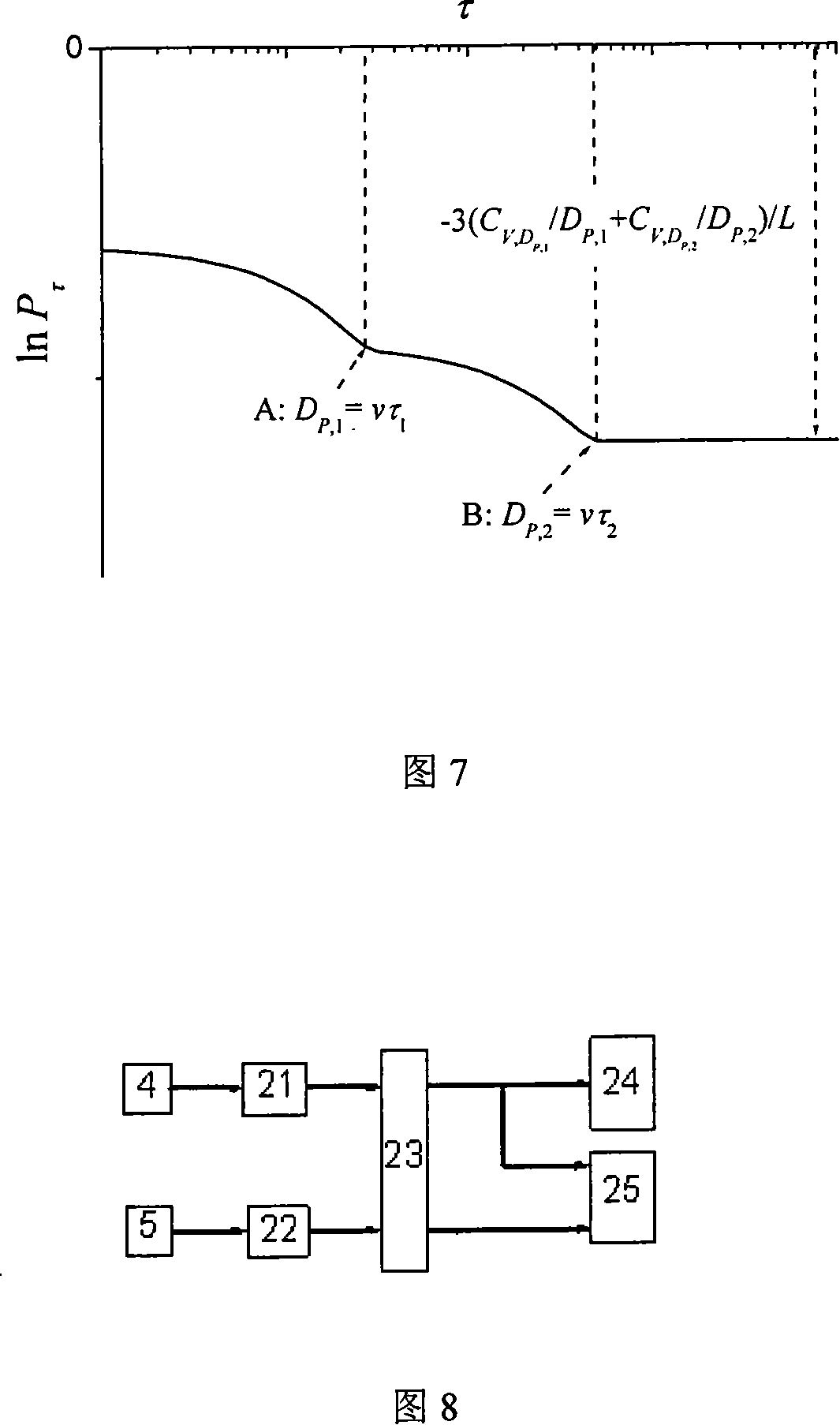
[0056] As shown in Figure 2, the measuring device is composed of a measuring area, a narrow beam generator, a photoelectric signal detector and a signal receiving and processing device. It consists of parallel light beams 1 and 2 emitted by a laser, which are split by a beam splitter 6 and then converged by a convex lens 7 (or lens group). The Rayleigh zone near the focal point results in a narrow beam of approximately parallel light. The transmitted light is two divergent Gaussian beams, which are converged to the respective photodetectors 4 and 5 through the receiving lens 11, which requires high time sensitivity of the measuring device. Air-blown window antifouling devices 8, 10, 9, 12 are respectively arranged at the transmitting end and the signal receiving end as the shells of the transmitting end A and the signal receiving end C respectively. This structure is a probe structure.
Embodiment 2
[0058] As shown in Figure 3, the composition of the measuring device is the same as that of Embodiment 1. The narrow beam generator is composed of a laser that generates parallel beams and one or both of the porous diaphragms or optical fiber groups that are arranged at the optical signal transmitting end and the optical signal receiving end, and the wide beam emitted by the laser A set of porous diaphragms or optical fibers arranged in the direction of propagation results in a set of narrow beams. The parallel light beams 1 and 2 pass through the porous diaphragm 16 at the window and take out the narrow beam group to enter the measurement area 3. The positions of the narrow beams are placed successively along the particle flow direction. After the signal light enters the receiving end C, it irradiates the respective photoelectric signal detectors 4 and 5 through the aperture 17, which requires high time sensitivity of the photoelectric signal detectors. Air-blown window anti...
Embodiment 3
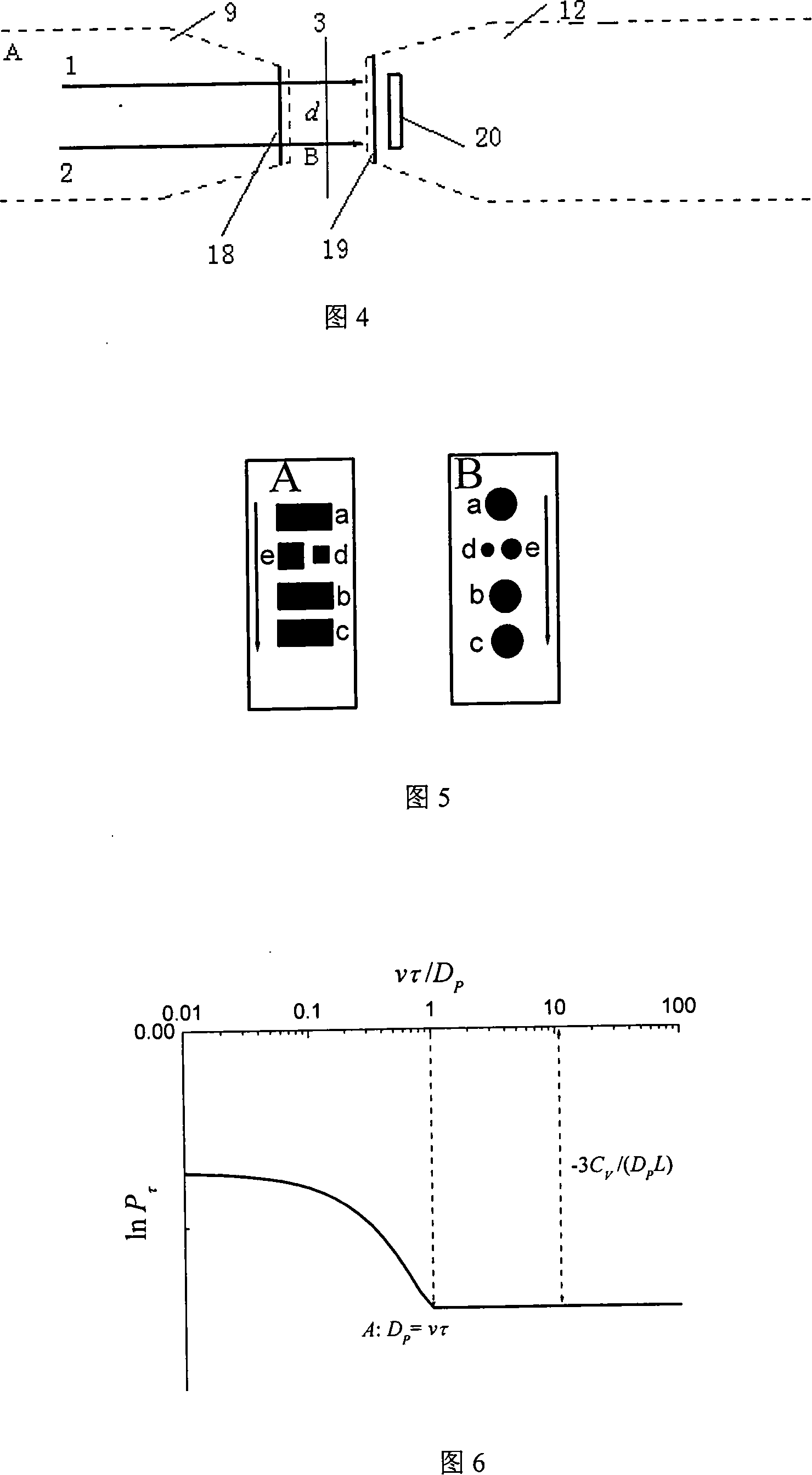
[0060] The measuring device shown in Figure 3 can be made into a probe form or a split-type on-line measuring device, and its composition is also the same as in Embodiments 1 and 2. The narrow beam generator is composed of lasers and microelements that generate parallel beams. The signal detector is composed of parallel light beams 1 and 2 emitted by the laser and directly irradiated to the micro-element photodetector 20 through the measurement area 3. The micro-element photodetector 20 is not only used as a photoelectric signal detection unit, but also as a narrow beam generator. Composition components, 18 and 19 in the figure are air-blown anti-fouling devices, the micro-element photodetector: it is composed of a plurality of photodetection units (made of silicon light film material) with small light-receiving areas, and each unit The shape can be circular or polygonal (such as rectangle, hexagon, etc.), this combination is conducive to the proper placement of the relative po...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com