Process for preparing detergent builder zeolite - A from kimberlite tailings
A technology of tailings and zeolite, applied in the direction of detergent compounding agent, detergent composition, chemical instruments and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
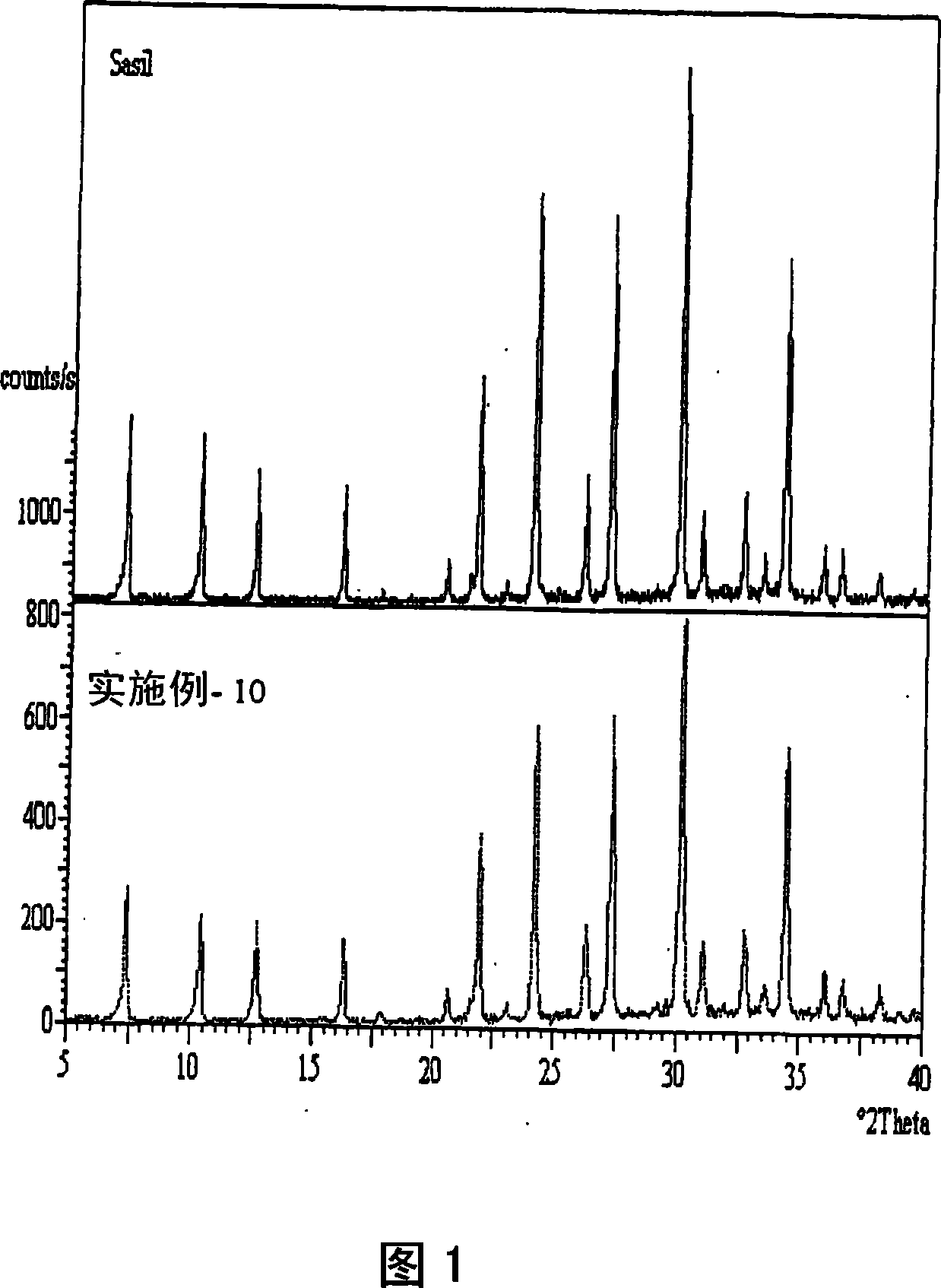
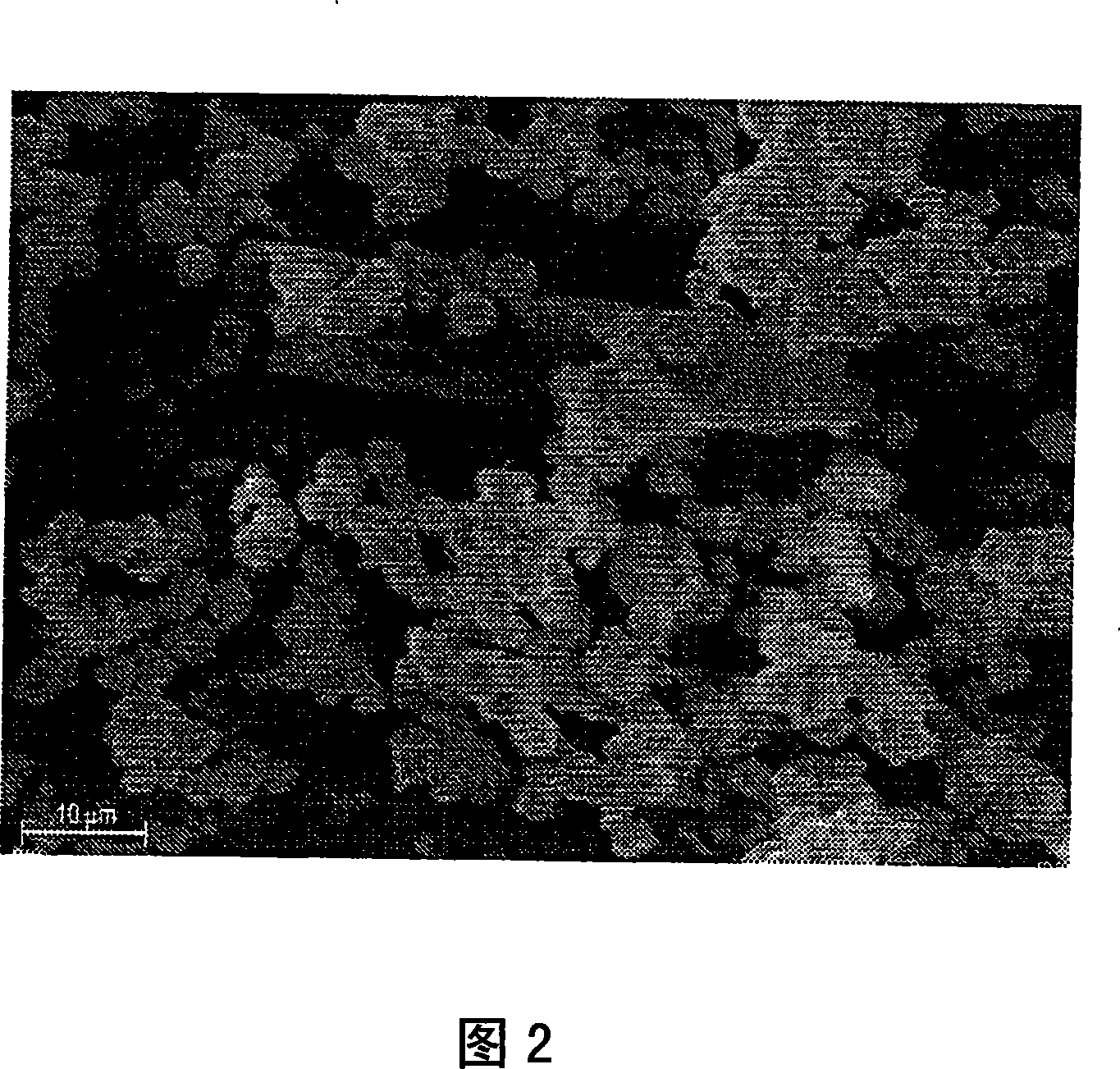
[0109] Under reflux conditions and continuous stirring, 500 g of kimberlite tailings were digested in a round bottom flask with 100 g of NaOH and 1280 g of tap water at boiling temperature for 5 hours. After the digestion is complete, the sodium silicate is isolated by filtration. To prepare the sodium aluminate solution, 7.9 g of NaOH and 6.3 g of aluminum trihydrate were dissolved in 17.4 g of water under continuous stirring and heating. For gel formation, 62 g of sodium silicate (with 2.93% Na 2 O and 7.75% SiO 2 ) into a stainless steel container, and the sodium aluminate solution was added to the container at a controlled rate at ambient temperature with stirring. It was then transferred to a closed reactor and crystallized at 95°C for 2.5 hours. After crystallization, the product slurry was filtered and washed with deionized water until the pH of the filtrate was ~10.5. The wet cake was dried in an oven at 110°C for 6 hours. X-ray diffraction analysis of this produc...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Under reflux conditions and continuous stirring, 500 g of kimberlite tailings were digested in a round bottom flask with 100 g of NaOH and 1280 g of tap water at boiling temperature for 5 hours. After the digestion is complete, the sodium silicate is isolated by filtration. To prepare the sodium aluminate solution, 7.9 g of NaOH and 6.3 g of aluminum trihydrate were dissolved in 17.4 g of water under continuous stirring and heating. For gel formation, 62 g of sodium silicate (with 2.93% Na 2 O and 7.75% SiO 2 ) into a stainless steel container, and the sodium aluminate solution was added to the container at a controlled rate at ambient temperature with stirring. It was then transferred to a closed reactor and crystallized at 95°C for 1.0 hour. After crystallization, the product slurry was filtered and washed with deionized water until the pH of the filtrate was ~10.5. The wet cake was dried in an oven at 110°C for 6 hours. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that t...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Under reflux conditions and continuous stirring, 72 g of kimberlite tailings were digested in a round bottom flask with 20 g of NaOH and 200 g of tap water at boiling temperature for 5 hours. After the digestion is complete, the sodium silicate is isolated by filtration. To prepare the sodium aluminate solution, 7.44 g of NaOH and 6.28 g of aluminum trihydrate were dissolved in 54.46 g of water under continuous stirring and heating. For gel formation, 25.20 g of sodium silicate (with 8.62% Na 2 O and 19.05% SiO 2 ) into a stainless steel container, and the sodium aluminate solution was added to this container at a controlled rate at ambient temperature with stirring. After preparation of the gel, 100 mg of Zeolite-A was added as seed crystals. It was then transferred to a closed reactor and crystallized at 95°C for 1.0 hour. After crystallization, the product slurry was filtered and washed with deionized water until the pH of the filtrate was ~10.5. The wet cake wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com