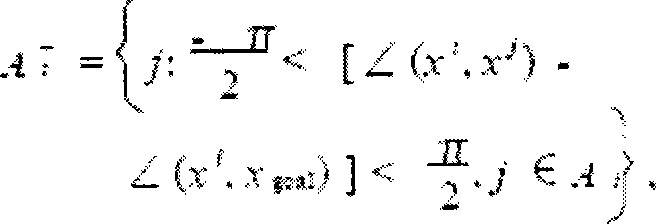A high-efficiency real time group animation frame
A group and frame technology, applied in the field of image data processing and generation, can solve problems such as not easy to generate code of conduct, unreal group behavior, different complex behavior, etc., achieve good scalability, reduce rendering resource consumption, and reduce overhead Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
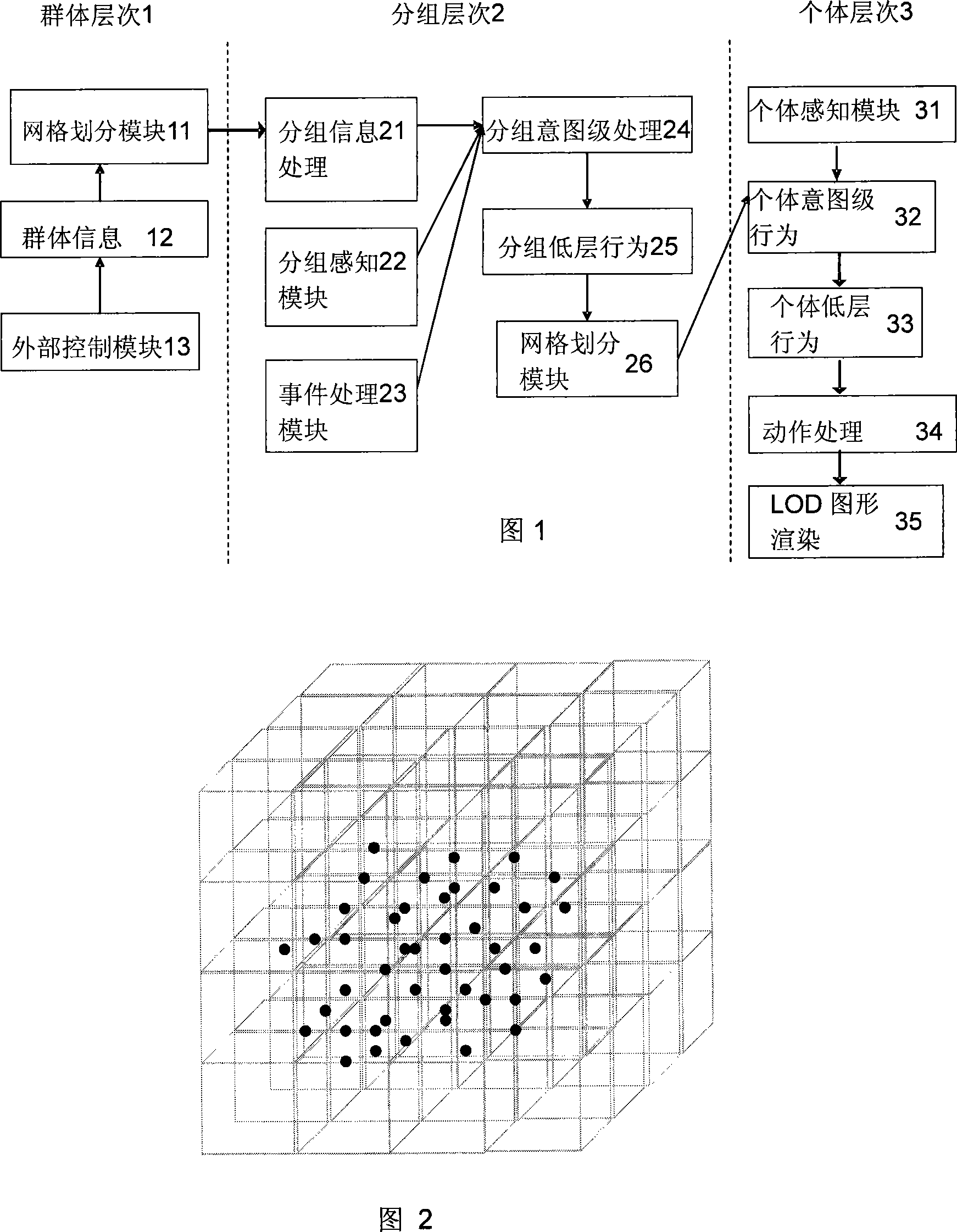
[0079] When the above-mentioned framework is applied to a specific three-dimensional virtual reality scheme: the moving groups are spatially distributed, at this time, the grid division module 26 in the framework divides the group space into a set of "cube regions", as shown in Figure 2 . For convenience, the edges of the large region and the slicing planes that form the faces of the small cube are aligned with the global axis. At the beginning of the movement, individuals are distributed into corresponding "cube regions" based on their initial positions W. The individual checks periodically (not every frame) whether it has entered a new "cube area" when it is moving, and if so, updates its area number. Large regions are used to enclose regions of interest. The number of grid divisions along each axis should be selected moderately, which can not only locate the individual more accurately (more divisions), but also reduce the extra overhead of box switching when the individua...
Embodiment 2
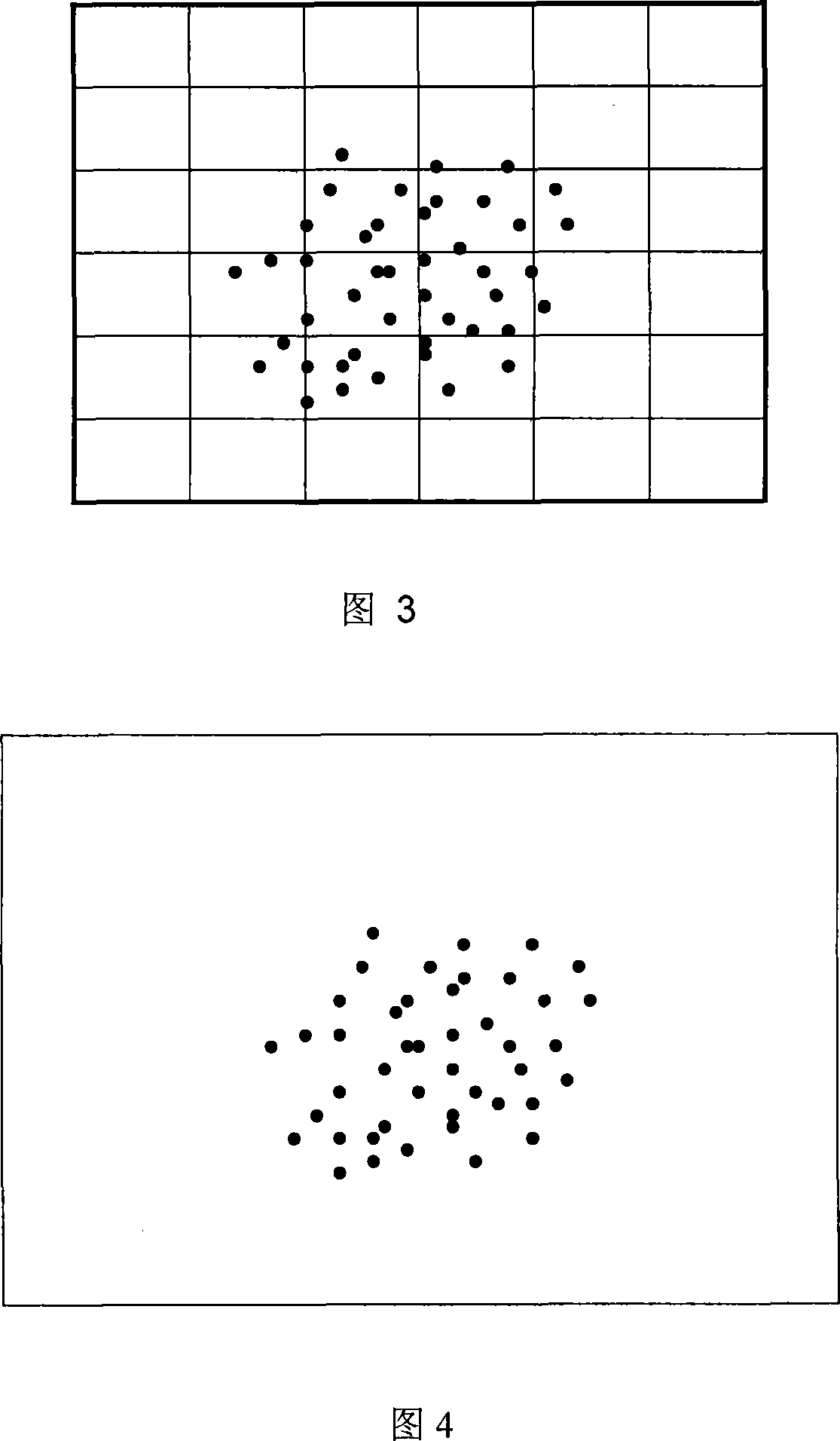
[0081] Apply the above-mentioned framework to the implementation process of real-time schemes for planar and curved surface group animation: in many cases, moving groups are distributed on a flat or curved surface, such as pedestrians on the street, troops in the valley, herds of beasts on the grassland and many more. At this time, the grid division module 26 in the framework divides the group space into a set of "rectangular areas", as shown in FIG. 3 . At the beginning of the movement, individuals are distributed into corresponding "rectangular areas" based on their initial positions W. When the individual is moving, it checks periodically (not every frame) whether it has entered a new "rectangular area", and if so, updates its area number.
Embodiment 3
[0083] As shown in Figure 4, when the above framework is applied to the real-time scheme of planar and curved surface group animation, when the number of rectangles is set to 1*1, this scheme evolves into a single-grid group animation, that is, the usual non-grid , The scheme of using the skybox as the group animation area, as shown in Figure 4. This solution is suitable for operations with a small number of groups and few rendering resources.
[0084] The above three cases are aimed at different application fields. In general, Embodiment 3 is a simplification of Embodiment 2; Embodiment 4 is a simplification of Embodiment 3. The advantage of simplification is that it reduces the computational complexity, and the disadvantage is that it reduces the efficiency. Therefore, during the process of simplification from case 1 to case 3, the programming implementation becomes simpler, the efficiency decreases, and the rendering resource consumption increases.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com