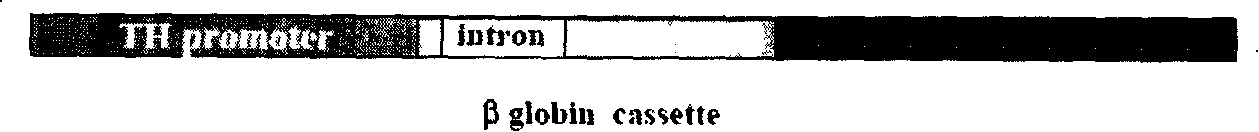Method of building animal model for parkinsonism
A Parkinson's disease and animal model technology, applied in biomedicine, geriatrics, transgenic technology, and neurology in biomedicine, can solve problems such as limiting the application of models, inability to accurately simulate the pathological process of Parkinson's disease, and achieve the goal of exacerbating death Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The BAG5 cDNA of embodiment 1 cloning mouse
[0030] Total RNA was extracted from the brain of 8-week-old C57 / BL6 mice, 5ug RNA was reverse-transcribed in a 20ul system, and 1ul was taken as a template. In the 20ul system, primer 1: 5'ACCTGAATTCGTGAAACTGAACACAGAAGTATG 3'(SEQ ID NO: 3) was used and Primer3: 5'CGATCAAGCCCTGCAGCTCTGTC 3' (SEQ ID NO: 4) to amplify the 5' end of BAG5 cDNA by PCR, using primers Primer2: 5'GACAGAGCTGCAGGGCTTGATCG 3' (SEQ ID NO: 5) and Primer 4: 5'ACCTGAATTCTTA CTTGTCATCGTCGTCCTTGTAGTCATACTCCCACTCGTCCGACTTCATG 3' (SEQID NO: 6) was used to amplify the 3' end of BAG5 cDNA by PCR; then take 1 ul of BAG5 cDNA 5' end PCR product and 1 ul of BAG5 cDNA 3' end PCR product, and use primers Primer1 and Primer 4 to amplify the full-length BAG5 cDNA by PCR . Primer 4 contains the Flag tag sequence (the underlined part in the primer) to facilitate the identification of the protein and distinguish it from the endogenous BAG5 protein; Primer 1 and Primer 4 ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Construction of prTH-globin-BAG5-Flag-hGH plasmid
[0033] Establish a dopaminergic neuron-specific transgenic construct prTH-globin-hGH, which contains (a) the promoter of rat tyrosine hydroxylase (6.8 kb in length, available at Guided expression of enhanced green fluorescent protein in the human dopaminergic cell line SH-SY5Y, see Figure 2a ), (b) part of the globin gene (1.0kb), (c) human growth hormone minigene (providing PolyA tail), see Figure 2b ;
[0034] The BAG5-Flag fragment was excised from the plasmid pBluescript BAG5-Flag with the restriction endonuclease EcoR I, cloned into the EcoR I site in the step 3 transgenic vector-globin gene, identified the direction, and established the dopaminergic neuron-specific process The transgenic construct prTH-globin-BAG5-Flag-hGH expressing BAG5-Flag ( Figure 3a ).
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 BAG5-Flag was introduced into mouse fertilized eggs by microinjection and production of transgenic positive mice
[0036] After the transgenic plasmid prTH-globin-BAG5-Flag-hGH was linearized with the restriction endonuclease Not I (14.7kb), gel recovery and purification ( Figure 3b ). The linearized DNA (about 500 copies) was injected into the male pronucleus of mouse fertilized eggs, and the injected fertilized eggs were transplanted into pseudopregnant mice. About 20 days later, the mice were born. Three weeks after the birth of the mice, the tails were clipped to extract DNA, and two sets of PCR reactions were used to test the primers shown in Table 1 to analyze whether there was integration of the transgene. Two sets of primer names: TH-1 (SEQ ID NO:7) and B5-6 (SEQ ID NO:9), Globin1 (SEQ ID NO:8) and B5-6 (SEQ ID NO:9).
[0037] Table 1
[0038] serial number
Sequence (5'-3' or amino-terminal-carboxyl
base end)
SEQ ID NO ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com