Three-dimensional crimp fibre
A technology of three-dimensional crimping and crimping fibers, which is applied in the field of three-dimensional crimping fibers, which can solve the problems of high apparent viscosity, contamination of filaments, and inability to spin, and achieve good crimping performance, spinnability, and good uniformity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Raw material composition: the first component is polycaprolactam; the second component is polycaprolactam / carbon black; the viscosity η ratio of the two is 1.2.
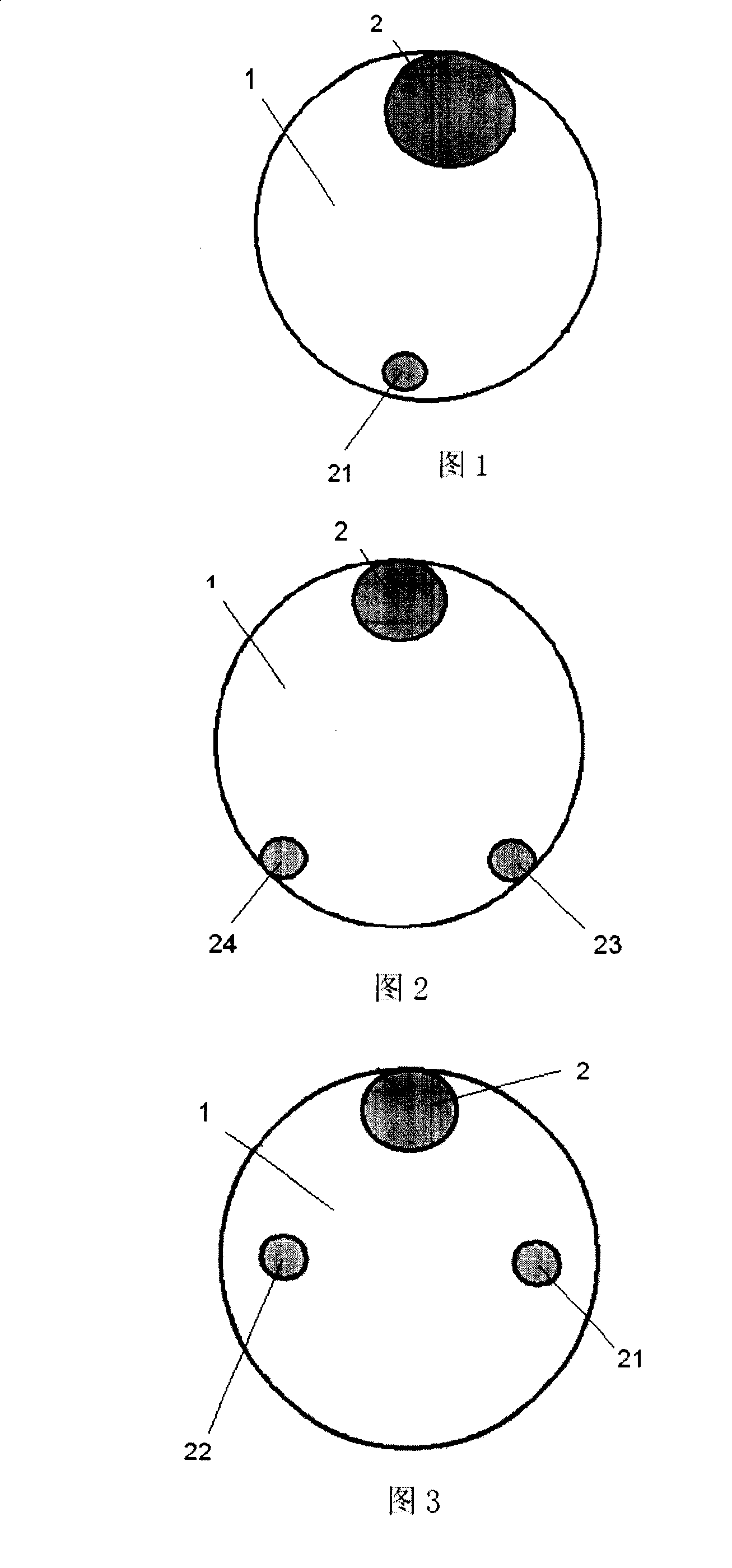
[0033] Preparation process: The second component is mixed with a co-rotating twin-screw extruder to make a blended chip, and then spun with the first component using a two-component spinning machine; the first component and the second component raw materials The two components are fed into the screw extruder respectively. After the two components are compounded in the channel of the distribution plate, they are sprayed out from the guide hole of the spinneret to form a tape with special functions after spinning, drawing, shaping, winding and other processes. There are three-dimensional crimped composite fibers, and the cross-sectional shape of the fibers is shown in Figure 3.
[0034] In accompanying drawing 3, 1 represents the zone that the first polymer component forms, and 2, 21, 22 represent the independent ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Raw material composition: the first component is polyethylene terephthalate; the second component is polyethylene terephthalate / aluminum oxide, and the viscosity η ratio of the two is 1.5.
[0038] Preparation process: The second component is mixed with a co-rotating twin-screw extruder to make a blended chip, and then spun with the first component using a two-component spinning machine. The first component of the raw material, the second component Add the two components to the screw extruder respectively, after the two components are compounded in the channel of the distribution plate, they are sprayed out from the guide hole of the spinneret to form, and after spinning, drawing, shaping, winding and other processes, they are made into a far-infrared function A composite fiber with three-dimensional crimp; the cross-sectional shape of the fiber is shown in Figure 2.
[0039] Among the accompanying drawings 2, 1 represents the region formed by the first polymer componen...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Raw material composition: the first component is polypropylene; the second component is polypropylene / tourmaline, and the viscosity η ratio of the two is 1.3.
[0043] Preparation process: use a compound spinning machine to spin, and use a screw extruder to inject the first component and the second component of the raw material respectively. After the two components are compounded in the channel of the distribution plate, they are sprayed out from the spinneret guide hole. After spinning, drawing, shaping, winding and other processes, the finished product is obtained. The cross-sectional shape of the fiber is shown in Figure 1.
[0044] Among the accompanying drawings 1, 1 represents the region formed by the first polymer component, the second polymer component region represented by 2 is connected with a part of the first polymer component region, and the other parts are the edges of the fiber, and the second polymer component region represented by 21 The region of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Curvature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curvature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crimp elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com