Tuberculosis vaccines comprising antigens expressed during the latent infection phase
A vaccine and antigen technology, applied in bacterial antigen components, antibacterial drugs, depsipeptides, etc., can solve problems such as non-specific protection of disease deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0149] Human recognition of starvation-inducing antigens
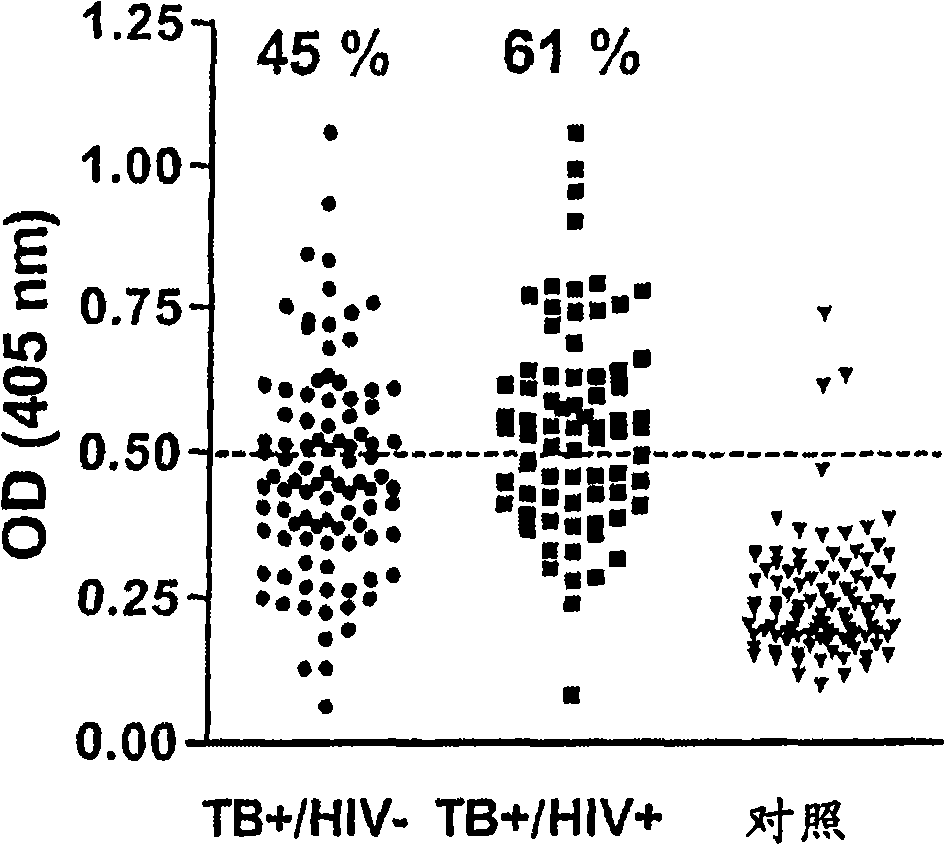
[0150] Human recognition of Rv2660c was assessed in a cohort of pulmonary TB patients from Uganda provided by the WHO Tuberculosis Specimen Bank. Patients with negative and positive HIV infection characteristics were included (N=94 and N=73, respectively). The control group consisted of one hundred healthy Danish-resident donors with estimated BCG coverage greater than 90%.
[0151]Microtiter plates were coated with 1.0 μg / ml (100 μl per well) of Rv2660c protein and incubated with 100x diluted serum samples, developed using peroxidase-conjugated rabbit anti-human Ig and tetramethylbiphenyl as substrates (results in figure 1 shown in ).
[0152] in conclusion
[0153] In this study, the recognition of starvation-inducing proteins was tested. Based on the cutoff determined from the control group with a sensitivity of 97%, it was possible to confirm TB infection in 45% of HIV- cases and 61% of HIV+ cases. The experi...
Embodiment 2
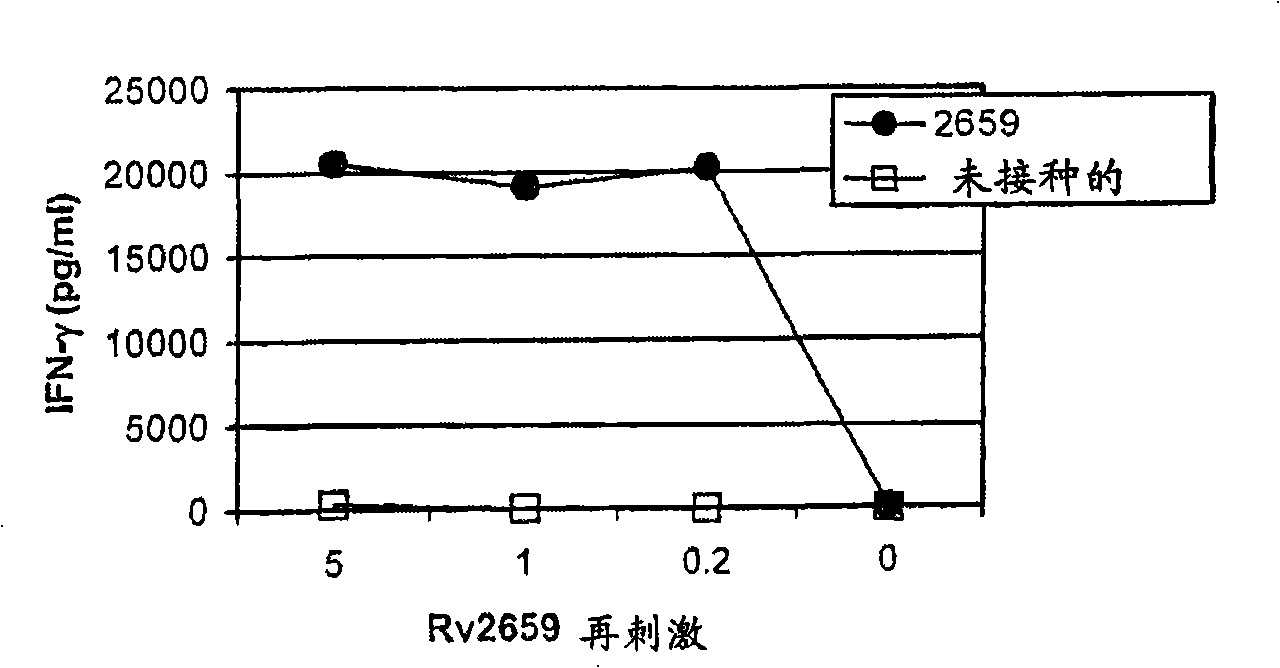
[0155] Prevention of immunogenicity and reactivation of starvation-induced antigen (Rv2659c) by post-exposure administration
[0156] Mice were infected with M. tuberculosis and treated with antibiotics to reduce bacterial burden and entered a latent infection phase with bacterial burden close to detection levels. During the incubation period of infection, the mice were inoculated with Rv2659c-containing adjuvant (such as DDA / MPL) three times every two weeks. One week after the last inoculation, INF-γ secretion of blood cells stimulated with Rv2659c was analyzed by ELISA ( figure 2 ).
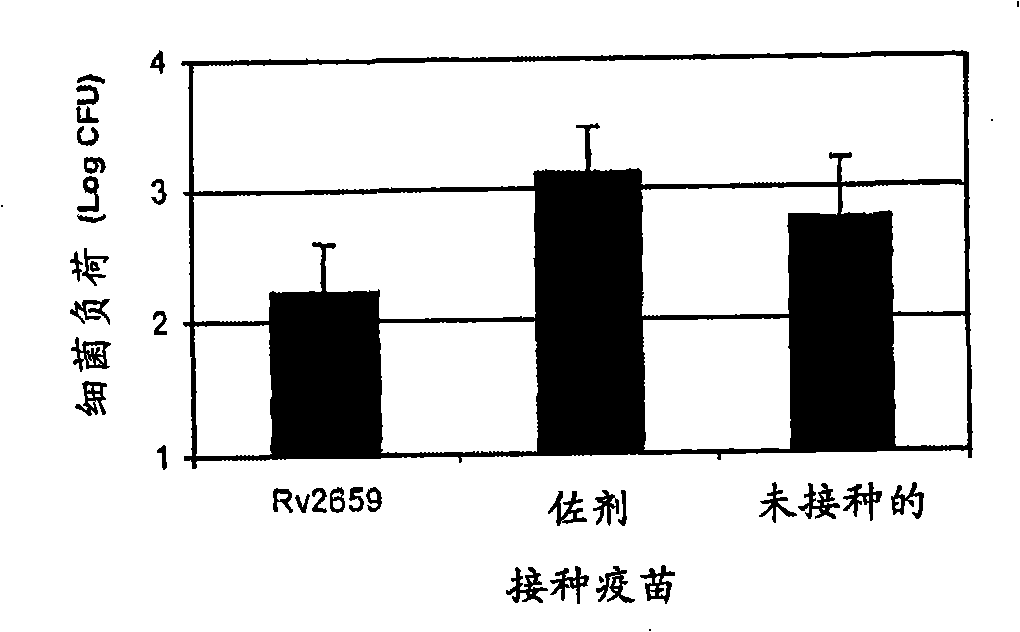
[0157] Ability of the starvation-inducible protein Rv2659c to induce protection against reactivation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
[0158] Groups of mice with latent M. tuberculosis were inoculated subcutaneously three times every two weeks with Rv2659c formulated in an adjuvant such as DDA / MPL, according to relative to unvaccinated (latently infected) mice The protective efficacy was asse...
Embodiment 3
[0162] Immunogenicity and protection against aerosol Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection induced by the starvation-inducible antigen Rv2660c
[0163] Mice were inoculated three times with Rv2660c-containing adjuvant (such as DDA / MPL) every two weeks. One week after the last inoculation, INF-γ secretion after stimulation of blood cells with Rv2660c was analyzed by ELISA ( Figure 4 A). Three weeks after the final inoculation, splenocytes were used to measure IFN-γ secretion after stimulation by Rv2660c ( Figure 4 B), blood cells are used to measure antigen-specific proliferative responses ( Figure 4 C).
[0164] Groups of mice subcutaneously inoculated three times every two weeks with Rv2659c formulated in an adjuvant (such as DDA / MPL) were challenged with an aerosol infection containing M. The reduction in colony forming units (CFU) of the lung relative to uninoculated mice was assessed. Protection was assessed 12 weeks after vaccination. Rv2660c induced an approximat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com