System and method for mask verification using an individual mask error model
A mask error and model simulation technology, applied in the field of optical lithography, can solve problems such as long time and large quantities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
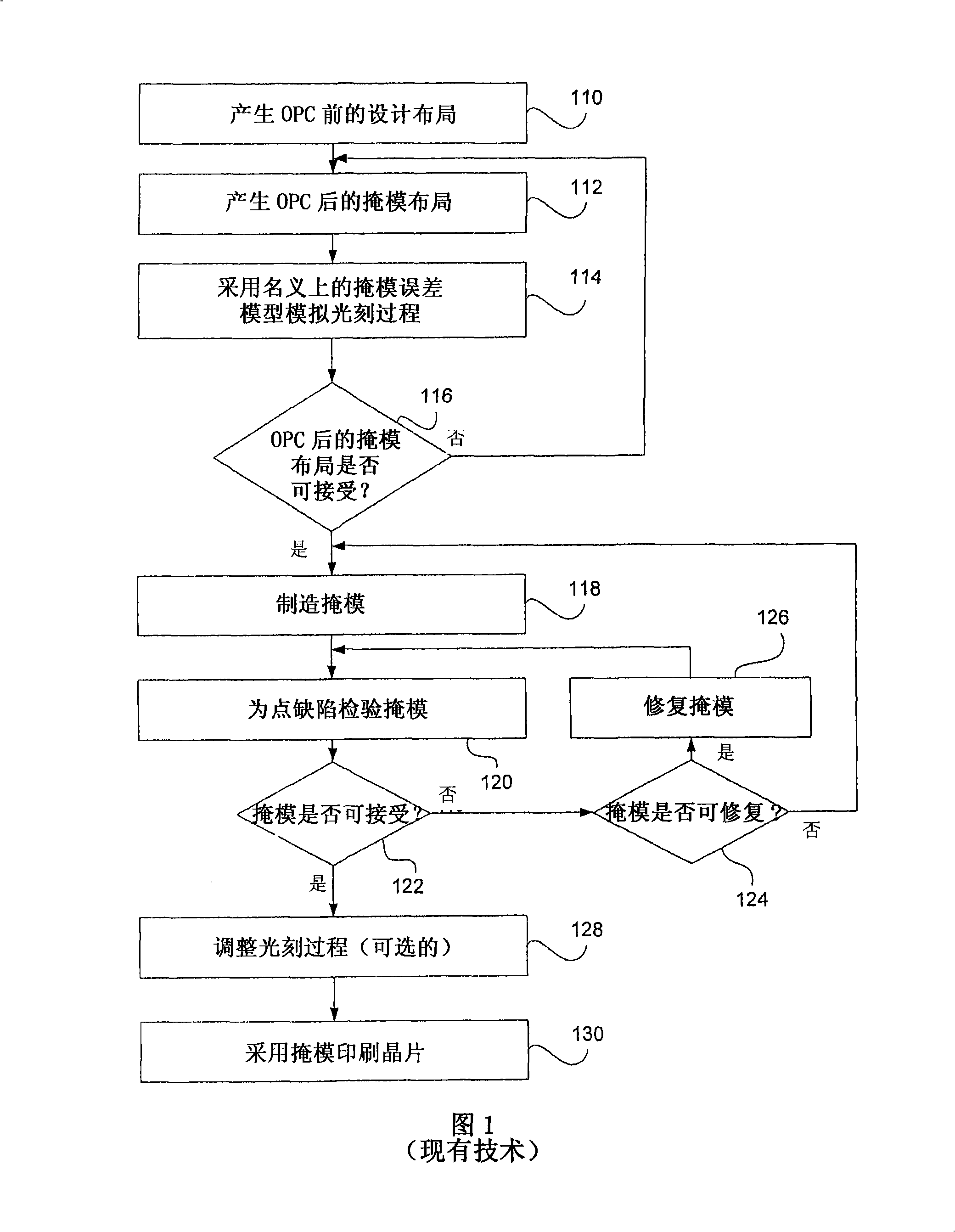
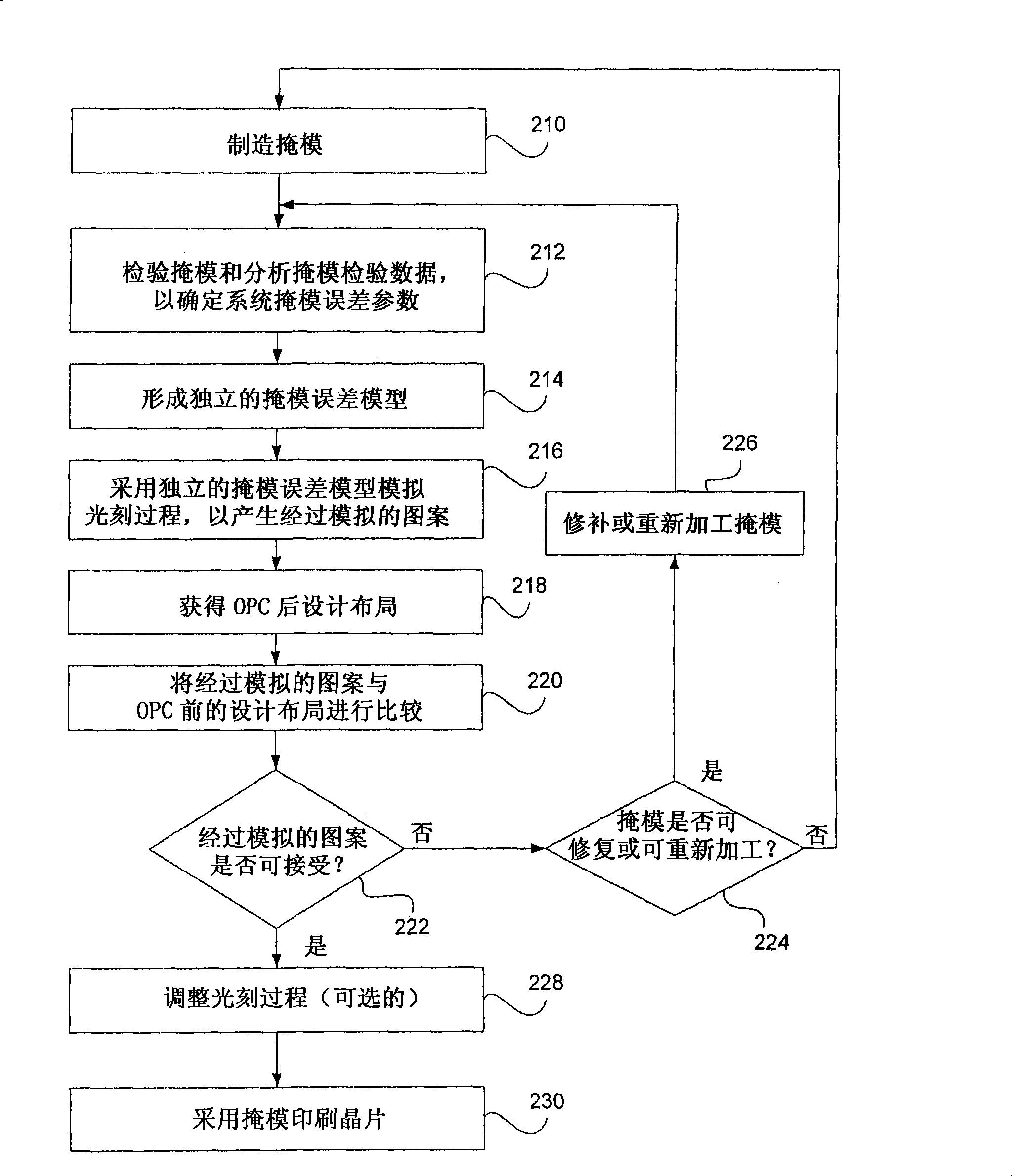
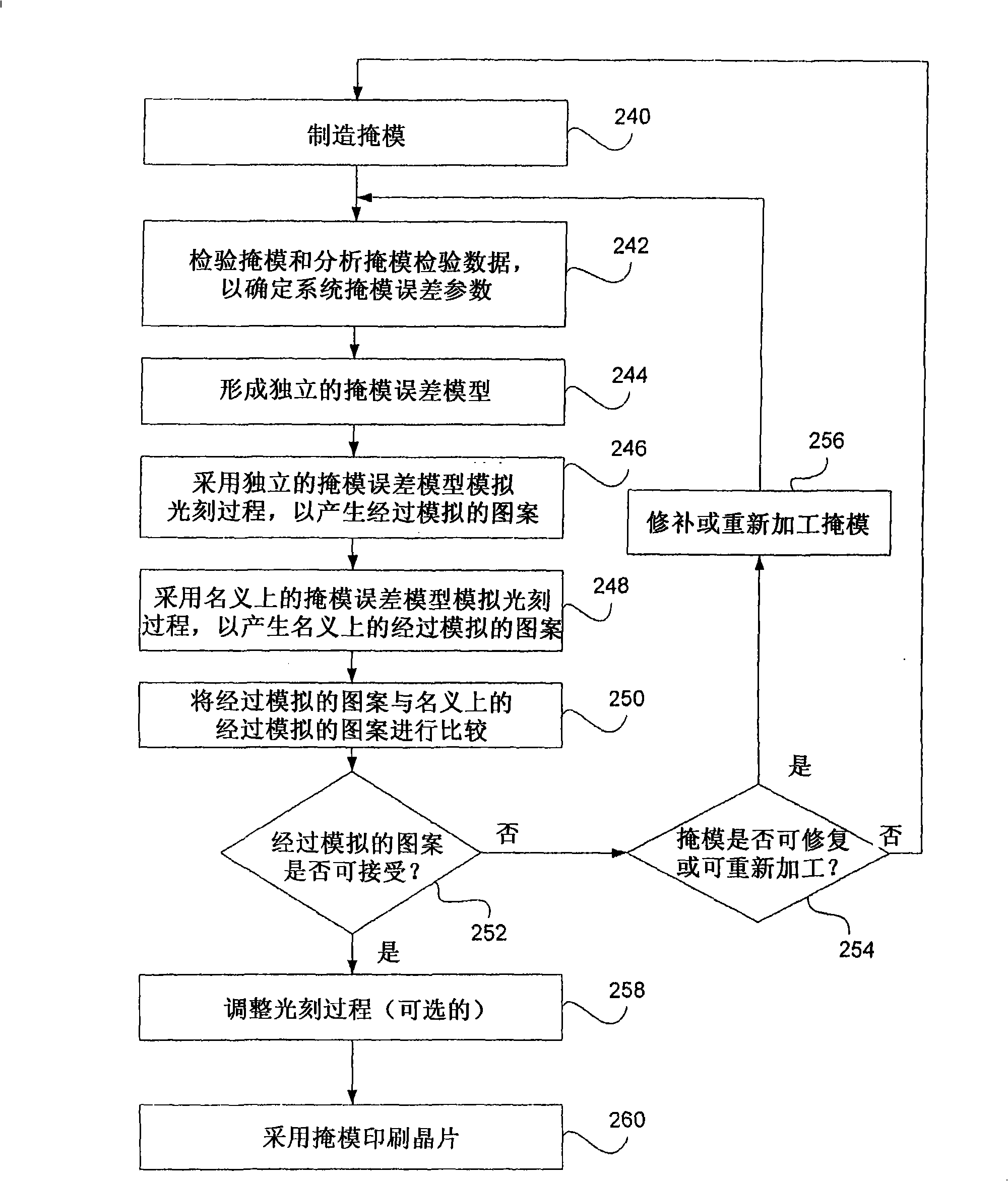
[0038] In practice, due to the defect of the mask manufacturing tool and the change of the mask manufacturing process, the error (or defect, after which the "defect" and "error" can be used interchangeably) is changed from the mask layout after OPC to the actual mask. The pattern transfer process is always introduced into the final manufactured mask. The mask error is the difference between the mask pattern manufactured and the ideal post-OPC mask layout intended to be manufactured on the mask. Generally, mask errors are divided into two categories: random mask errors and systematic mask errors. Random mask errors are errors that cannot be described by models but appear randomly and statistically on the manufactured mask, such as excessive particles and small holes. System mask errors are errors that can be described with a model, where the model depends on the pattern environment (eg, local pattern density, pattern size, pattern spacing, and pattern orientation) and / or pattern po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com