Hepatitis B virus complete-genome polymerase chimera and its construction process and application
A hepatitis B virus, whole genome technology, applied in the field of hepatitis B virus whole genome polymerase chimera and its construction, can solve the problem of failing to find the significance and replication characteristics of the P gene
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
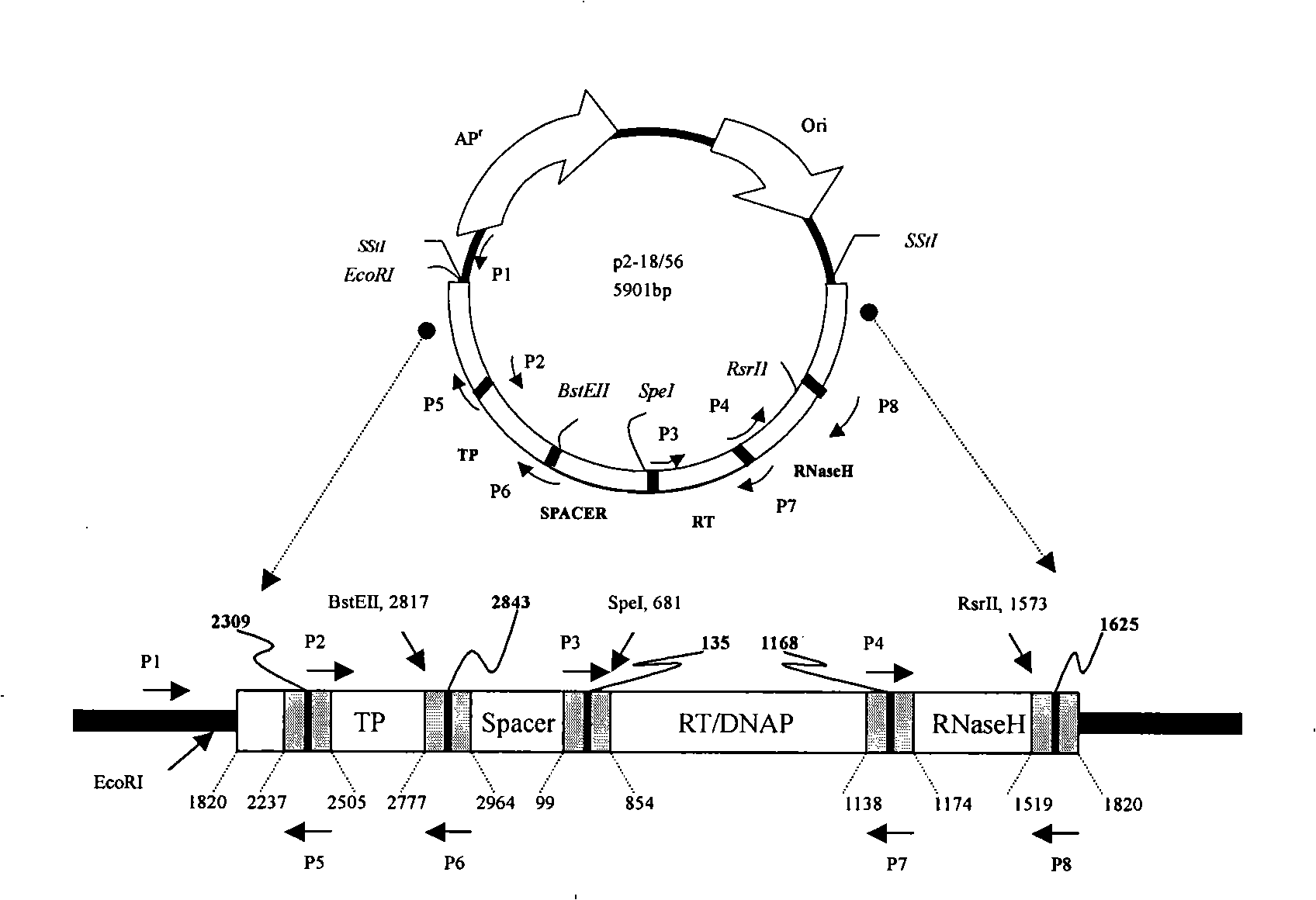
[0024] Since the genome sequence of each HBV strain is not the same, we can only select strains with similar sequences or suitable restriction sites, or strains that can undergo fusion PCR after PCR amplification to replace the P gene and its fragments. The following is an example of the steps and results of the replacement design of the P gene and its fragments from a high-replication strain to a low-replication strain.
[0025] Select two HBV high (#56) and low (#2-18) replication strain genomes from the serum of Chinese hepatitis B patients to obtain the SP fragment of the P gene, and replace the SP of #2-18 with the SP of #56. Two HBV strains from two chronic hepatitis B patients, both of genotype B and serotype adw2, were cloned for the whole genome and transfected into HepG2 liver cancer cell lines to confirm that they were high replication type#56 and low replication type# 2-18. After measuring the nucleotide sequence of the whole gene, it was found that there were 42 ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Primers were designed to amplify the TP fragment in the polymerase gene, and the TP fragment of #56 was replaced and cloned into #2-18 to form a chimera.
[0029] The primers designed in this experiment are P1, P2, P5, P6. Among them, P1 is the pUC universal reverse primer, and P2, P5, and P6 are HBV specific primers. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0030] P1: 5'AGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGA 3'
[0031] P2: 5'AGACCACCAAATGCCCCTATC 3' (2299-2319nt)
[0032] P5: 5'GATAGGGGCATTTGGTGGTCT 3' (2299-2319nt)
[0033] P6: 5'CTGAGTTGGCTTTGAATGCAGG 3' (2948-2971nt)
[0034] Chimera construction strategy:
[0035] P1 and P5 use p2-18 (pUC19 recombinant vector containing low replication strain #2-18) as template to amplify about 580bp fragment, P2 and P6 use p56 (containing high replication strain #56 pUC19 recombinant vector) as template, A fragment of about 580bp was amplified. The two amplified fragments were slowly annealed through the complementary P2 and P5 sequences,...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Construction of chimeric genomes replacing #2-18 holopolymerase (P) genes with #56 holopolymerase (P) genes
[0039] On the basis of the above 2-18TP, the entire polymerase gene of #56 was replaced and cloned into #2-18 to form a chimera.
[0040] Plasmid p2-18TP was double digested with BstEII and RsrII, and a large fragment of 4.0 Kb was recovered. The fragment had removed 2-18 Spacer, RT, and RNaseH, and only contained 2-18 TP. p56 was digested with the same double enzymes, and a fragment of about 2.0Kb was recovered, containing only #56Spacer, RT, RNaseH but not 56d1TP. Connect the above two recovered fragments and convert DH 5α bacteria and screened. The #2-18 chimera containing the full polymerase gene of #56 was confirmed by enzyme digestion and sequence determination (referred to as 2-18P)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com