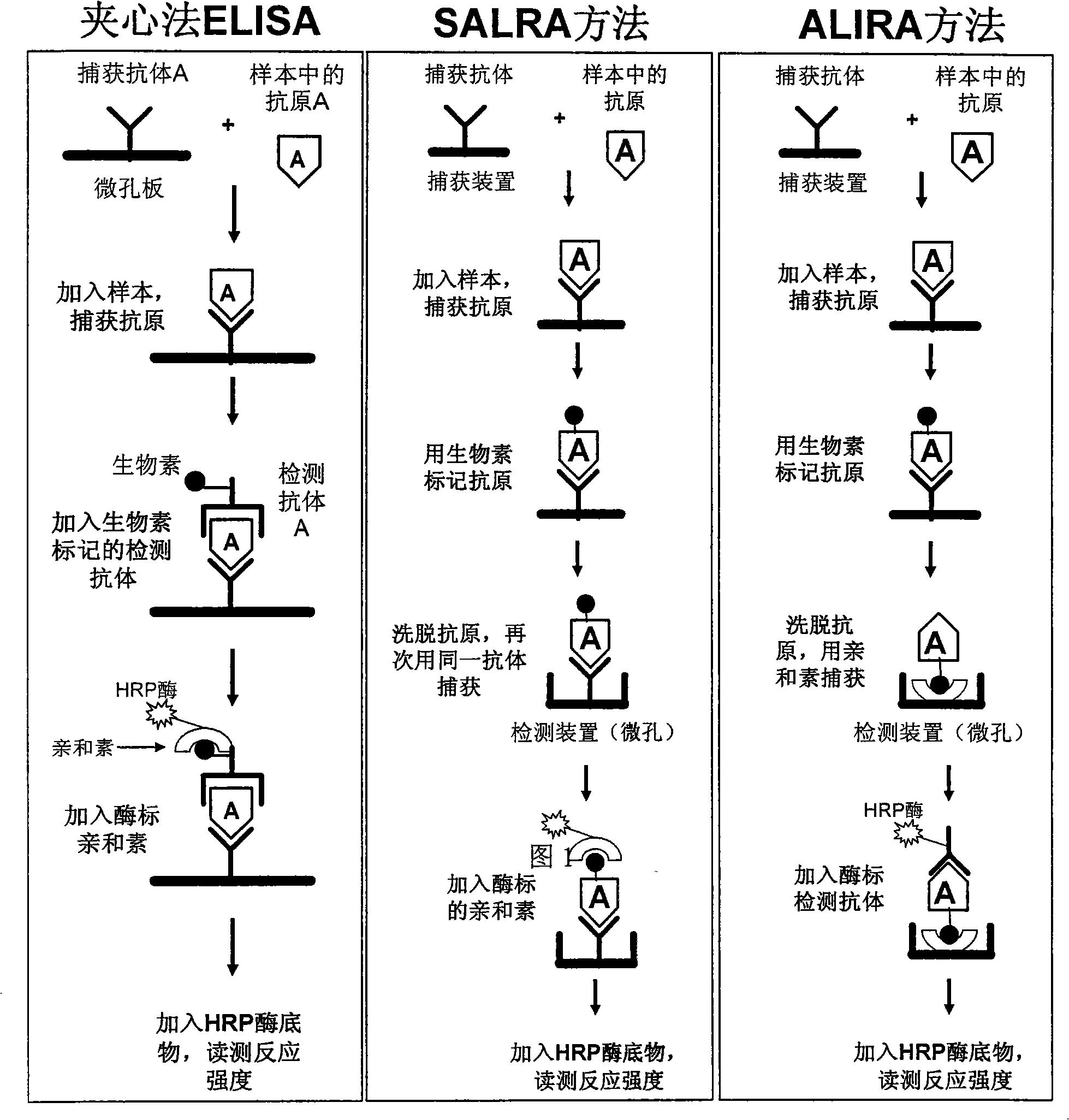
Novel method for quantitatively determining analyte by scavenger with single specificity
A quantitative detection method and analyte technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of interference with specific analyte labeling efficiency, failure to distinguish from specific analytes or non-specific substances, and reduce antibody binding.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
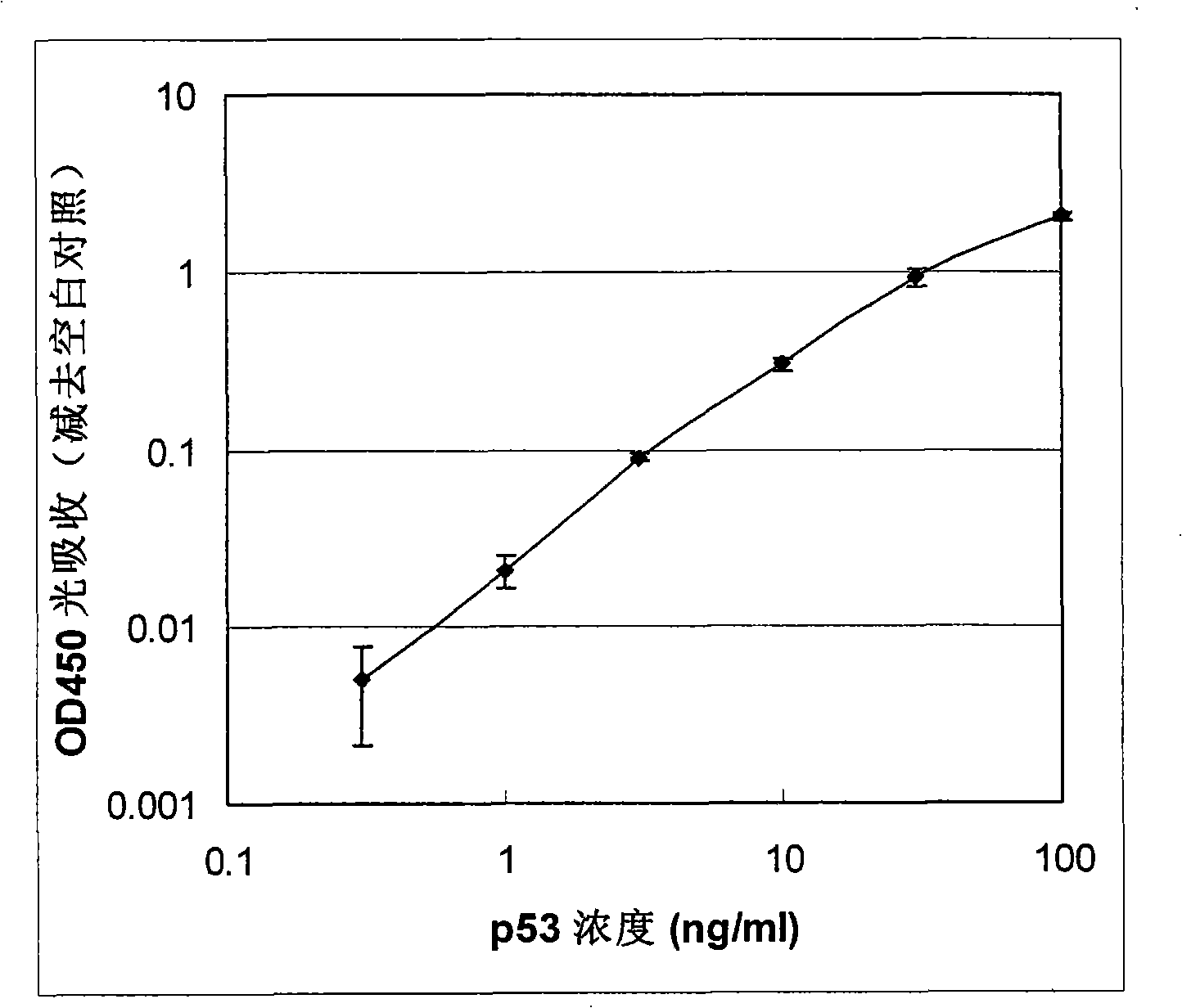
[0061] Embodiment 1: Use HRP as reporter molecule to detect human p53 protein
[0062] In this example, the antigen protein to be tested is human p53 protein which has tumor suppressive function and promotes cell apoptosis, and both the capture device and the detection device are 96-well microplates. The microwells of the capture device are coated with anti-p53 monoclonal antibody, and the detection device is coated with streptavidin. The detection antibody is the same anti-p53 monoclonal antibody labeled with fluorescein, here the reporter molecule is fluorescein.
[0063] (1) Capture antigenic protein:
[0064] a. Coating capture antibody: Take two 96-well microplates (flat bottom, highly binding to protein), one is used as a capture device to capture the antigen in the sample, add 100 μl concentration of 2 μg / ml (diluted in Coating buffer, 0.05M sodium bicarbonate buffer, pH 9.6) anti-p53 monoclonal antibody (CalBiochem, USA), was added to two longitudinal rows of 16 micr...
Embodiment 2
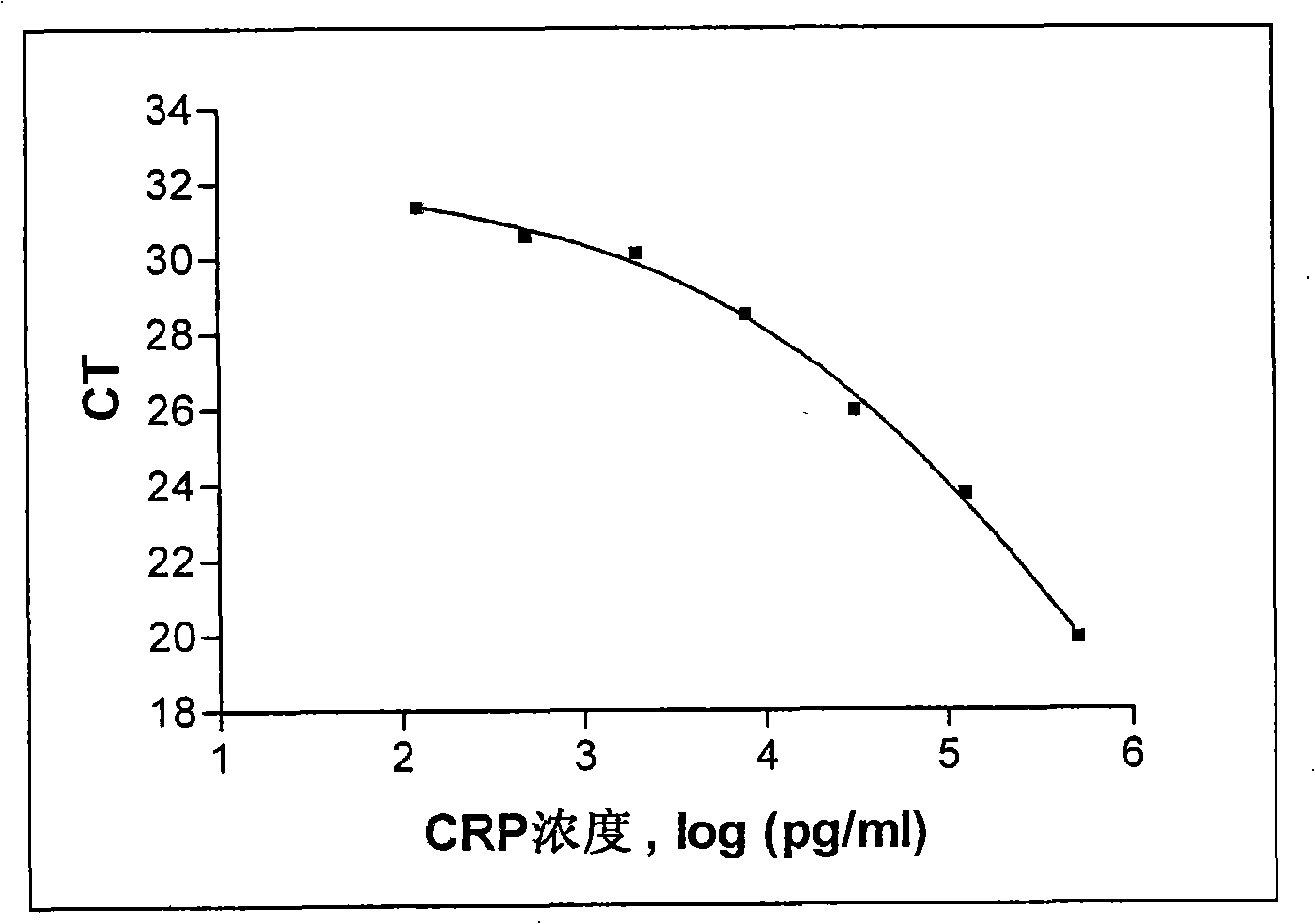
[0077] Example 2: Detection of human C-reactive protein with oligonucleotides as reporter
[0078] In this embodiment, the antigenic protein to be tested is human C-reactive protein (C-reactive protein, CRP), which plays an important role in the immune response, and both the capture device and the detection device are 96-well microplates. The microwells of the capture device are coated with anti-CRP monoclonal antibody, and the detection device is coated with streptavidin. The detection antibody was the same anti-CRP monoclonal antibody labeled with an oligonucleotide (60 bases long), where the reporter molecule was the oligonucleotide.
[0079] (1) Capture antigenic protein:
[0080] a. Coating capture antibody: Take two 96-well microplates (flat bottom, highly binding to protein), one is used as a capture device to capture the antigen in the sample, add 100 μl concentration of 2 μg / ml (diluted in Coating buffer, 0.05M sodium bicarbonate buffer, pH 9.6) anti-CRP monoclonal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com