Ore coal, melting ironmaking method after direct reduction-flotation-agglomeration
A post-smelting, direct technology, applied in the field of ore, coal-direct reduction-separation-smelting after agglomeration, which can solve the technical indicators that are difficult to meet the requirements of materials, chemical composition, physical properties and metallurgical properties, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
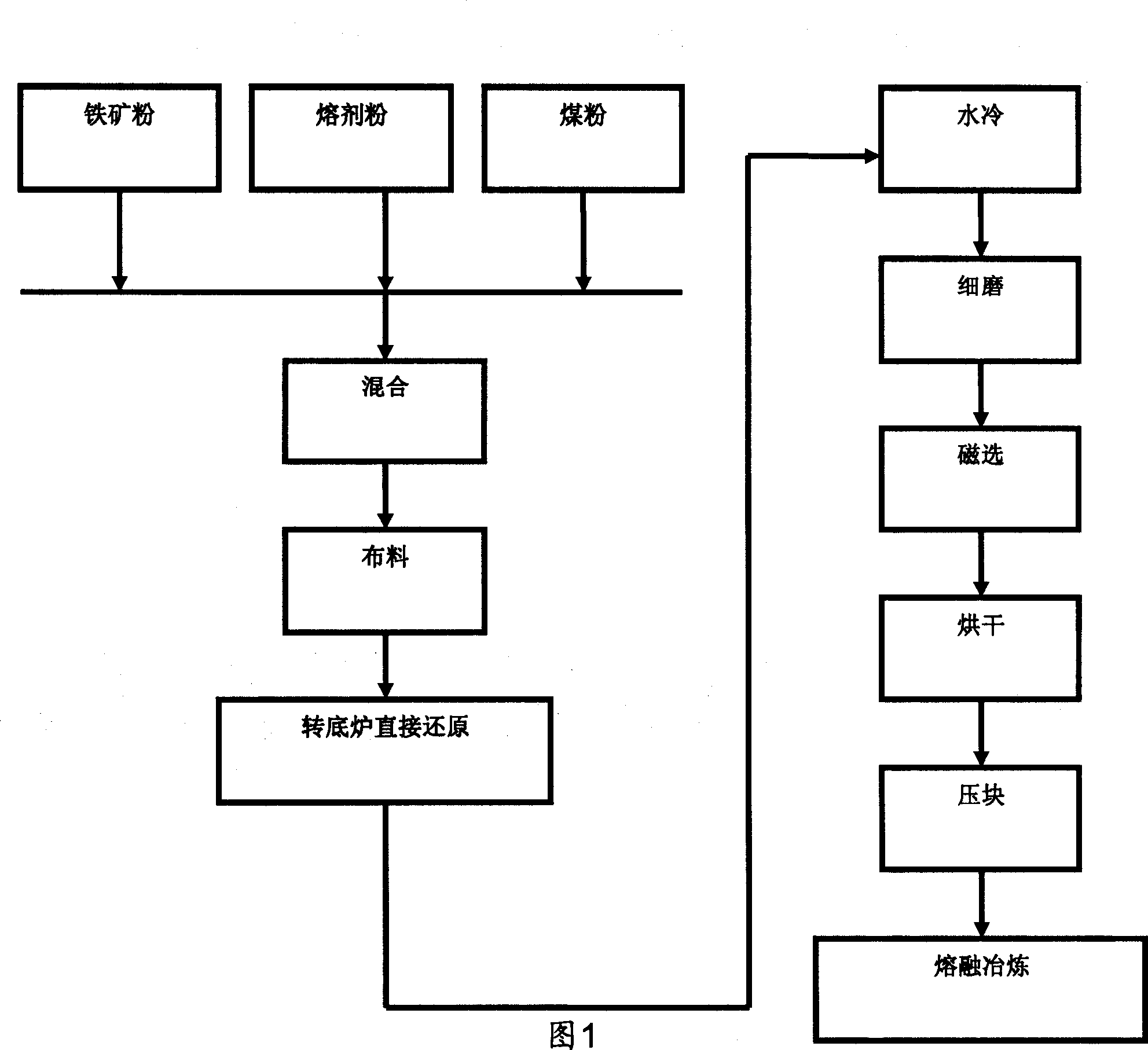
[0013] Ore of the present invention, coal-direct reduction sorting-melting ironmaking method after agglomeration, its preferred specific implementation mode is as shown in Figure 1, comprises steps:
[0014] First prepare the raw materials:
[0015] Coal: Various non-coking coals can be selected, and the particle size of the coal is ≤5mm.
[0016] Iron ore: suitable for ore iron grade 20-60%, ore particle size ≤ 5mm; one or more of the following iron ores can be selected: oolitic hematite, ultrafine grain hematite, limonite , Siderite. Other iron ores can also be used as required.
[0017] Flux: one or more of limestone, magnesia limestone, and dolomite can be selected as flux; flux particle size ≤ 5mm. Other raw materials can also be used as solvents.
[0018] The above three raw materials are mixed in the following parts by weight:
[0019] Coal: 10-30 parts;
[0020] Iron ore: 70-80 parts;
[0021] Flux: 0-20 parts.
[0022] After mixing, the particle diameters of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com