Very thin hard steel sheet and method for producing the same
An extremely thin, hard technology used in toolmaking, metal rolling, furnace types, etc., to solve problems such as not paying special attention to uniform elongation, and not addressing fracture or necking surface properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
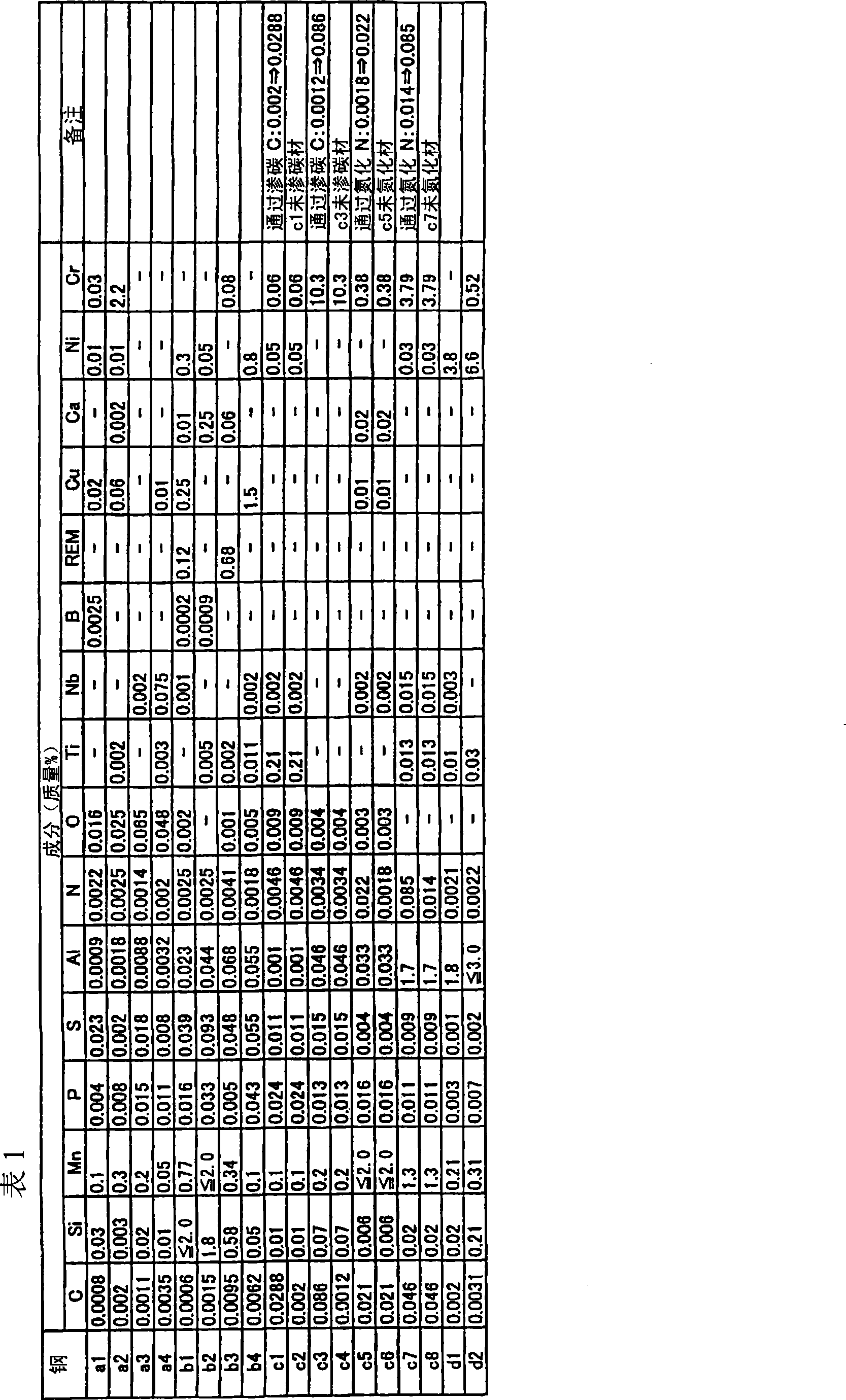
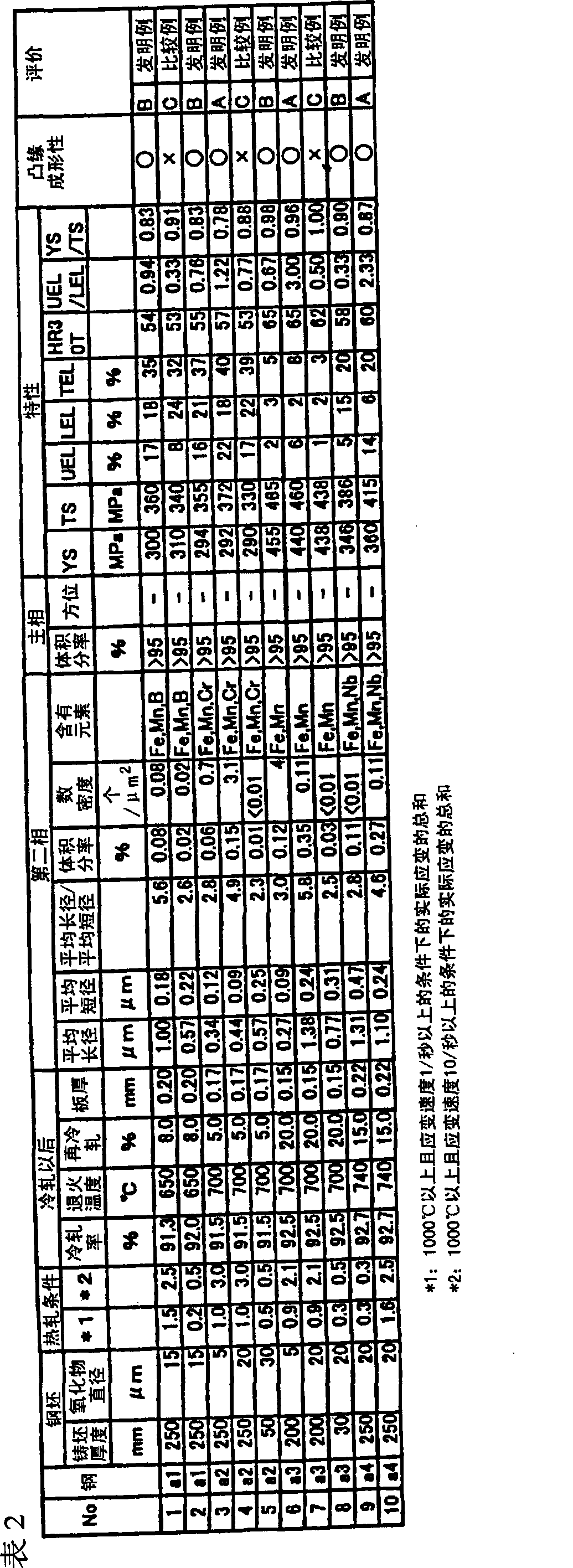
[0109] Table 2 shows the experimental results when the second phase was defined as an oxide. The form of oxides is mainly controlled by the size of oxides depending on casting conditions and the amount of elongation depending on hot rolling conditions. The "number density" of oxides was determined by observation with SEM. It was confirmed that favorable uniform elongation was obtained by controlling the state of oxides within the range of the present invention.
Embodiment 2
[0111] Table 3 shows the experimental results when the second phase was defined as sulfide. The form of the sulfide is mainly controlled by the size of the sulfide depending on the casting conditions and the amount of elongation depending on the hot rolling conditions. The "number density" of the sulfide was determined by cross-sectional observation using TEM. It was confirmed that good uniform elongation was obtained by controlling the state of the sulfide within the range of the present invention.
Embodiment 3
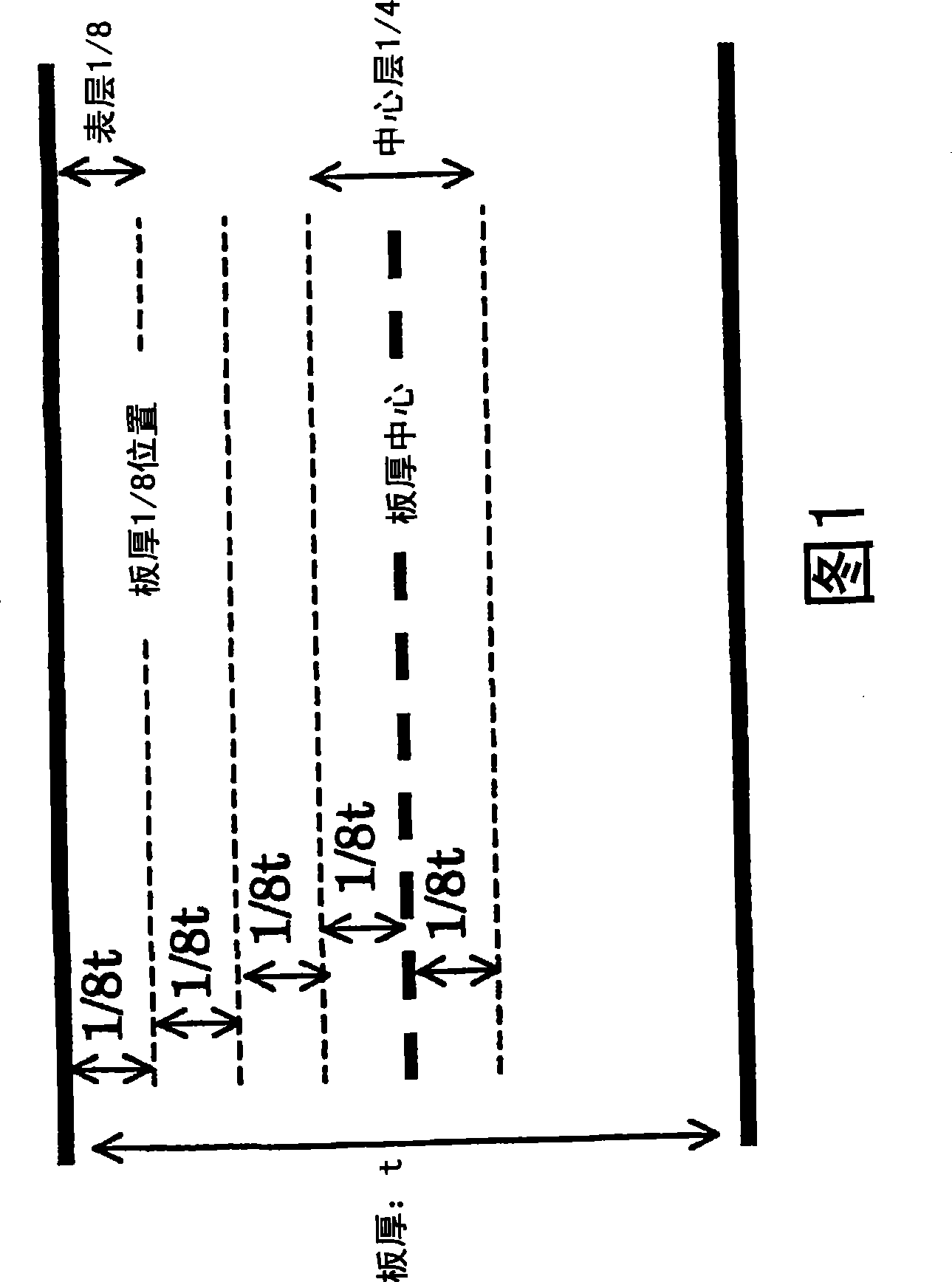
[0113] Table 4 shows the experimental results when the second phase was defined as carbide or nitride. The morphology of carbides or nitrides is mainly controlled by carburizing or nitriding conditions. The "roughly machined thin steel material" in this embodiment is a steel plate subjected to recrystallization annealing at 700°C. As a comparative material, a steel sheet that has not been carburized or nitrided but has a hardness equivalent to that of a carburized or nitrided steel sheet by re-cold rolling also shows its characteristics. Carbide or nitride was observed at the 1 / 8th position of the plate thickness and the center of the plate thickness. The "number density" of carbides or nitrides is determined by SEM observation of residues when electrolysis is performed on the surface layer 1 / 8 of the plate thickness or the center layer 1 / 4 of the plate thickness. The "volume fraction" and "number density" of the second phase in Table 4, and the values of the main phase ar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com