Method and device for improving flow character of gas liquid bubble column with row tubes
A technology of flow characteristics and bubble towers, applied in chemical methods, chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, etc. for reacting liquid and gaseous media, and can solve the difficulty of enlarging the ratio of empty towers in reactors with heat exchange tubes , no flow measurement data support, serious gas-liquid backmixing and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing the difficulty of amplification, improving reaction performance, and reducing gas-liquid backmixing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
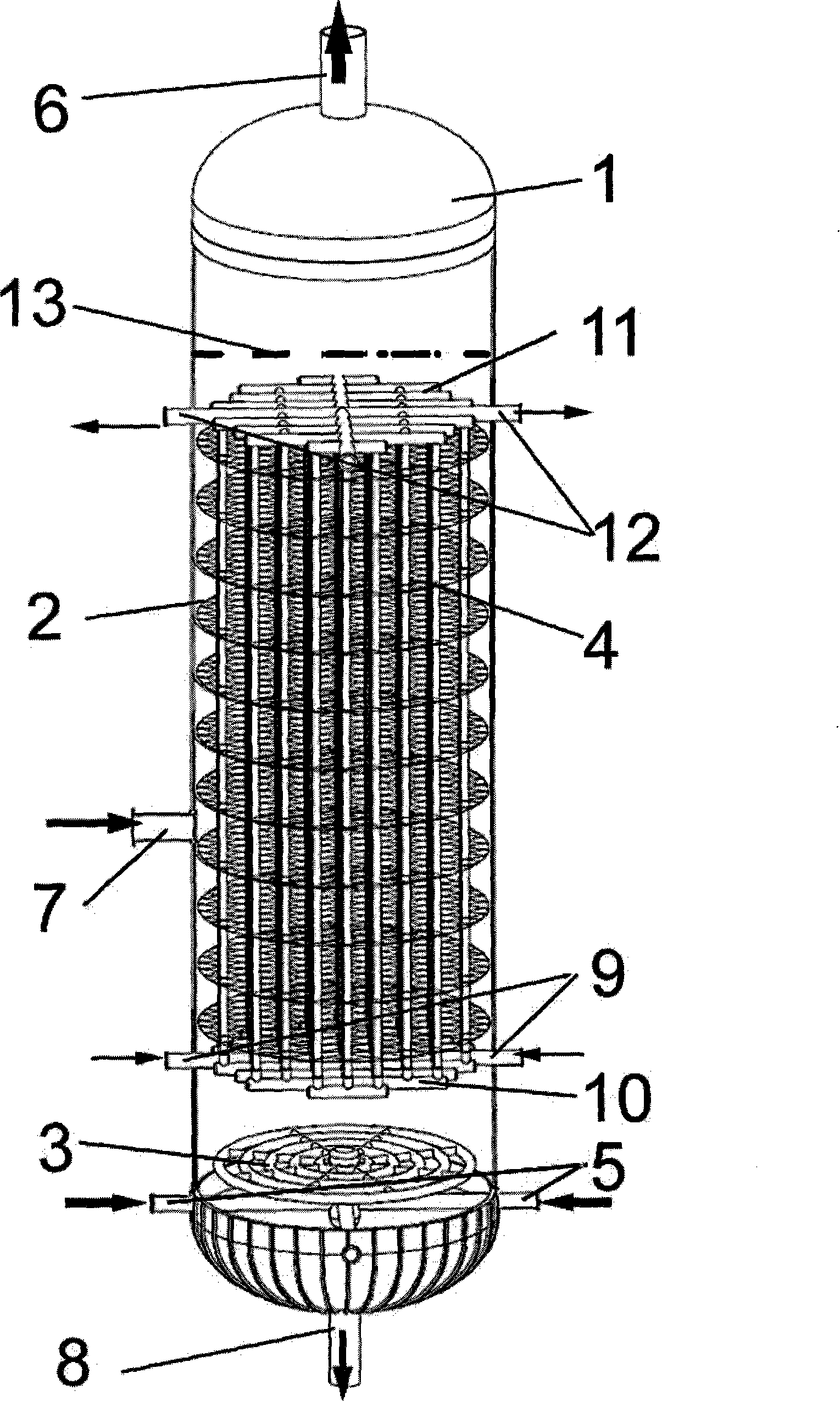
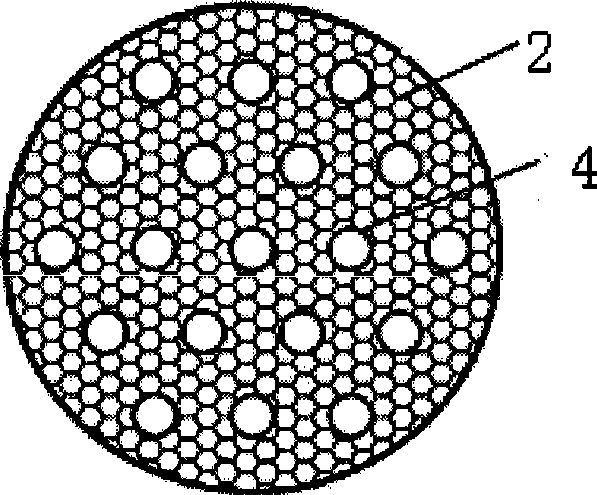
[0037] Slurry bed cold model experimental device, with a diameter of 500mm and a liquid level height of 4000mm, with a perforated plate gas distributor installed at the bottom. A number of galvanized iron vertical heat exchange tubes with a length of 4000mm and a diameter of 25mm are evenly arranged from the top of the gas distributor to the liquid level. The fully developed flow zone in the middle section of the tower is evenly arranged with 10 floors, such as figure 2 The grid-type damping member shown has a rhombus-shaped mesh, and each layer of damping net is evenly arranged on the entire cross-section of the tower, and the vertical heat exchange tube bundles vertically pass through the 10-layer grid-type damping member. The specific structural parameters of tube bundles and damping grids are listed in Table 1, where the damping area density A R (m 2 / m 3 ) is the total cross-sectional area of the latitude and longitude of the multi-layer grid / the slurry volume surro...
Embodiment 2
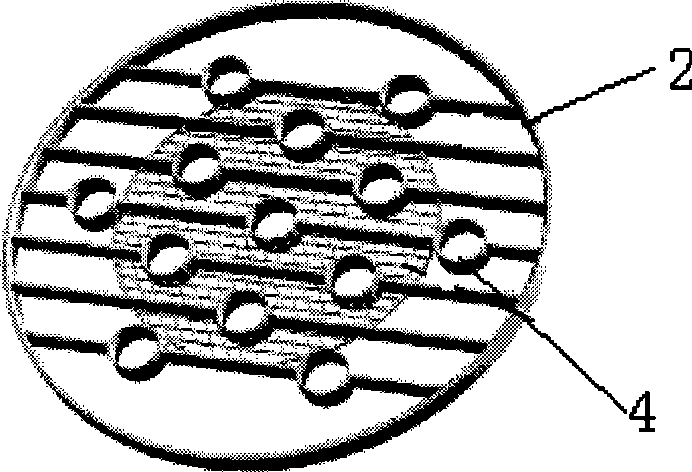
[0064] In addition to the damping area density, the radial distribution of the damping area density is also an important parameter to characterize the performance of the grid-type damping internal member. In order to investigate the influence of different damping area density distributions on the flow velocity, this example compares two grid distributions: one is to arrange the damping grid evenly on the entire tower cross section, and the other is to arrange the damping grid only in the central area of the tower mesh, with no damped mesh in the peripheral region. Still using the same dense array of tubes as in Example 1 (the number of tubes N=40), and the small hole grid with the same parameters and number of layers (the parameters of the tubes and grids are listed in the last row of Table 1). Different from Embodiment 1, the diameter of each layer grid in this example is only half of the tower diameter (250mm), and it is arranged in the central area of the tower. In the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com