Optical means for detecting i-motif conformation of DNA
An optical method, conformational technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, fluorescence/phosphorescence, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of long time required, achieve high selectivity and sensitivity, shorten detection time, The effect of simplifying the detection steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Take 2.5 μL of C-probe solution with a concentration of 100 μM and add it to 2.5 μL of solutions with pH values of 5.0, 6.8, 7.0 and 8.5, react at room temperature for 10 minutes, and then add PMNT solution of equal charge (1 mM PMNT solution 5 μL), observe the color change of the solution, and then measure the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum. At the same time, take any sequence of nc-probe solutions for negative control experiments.
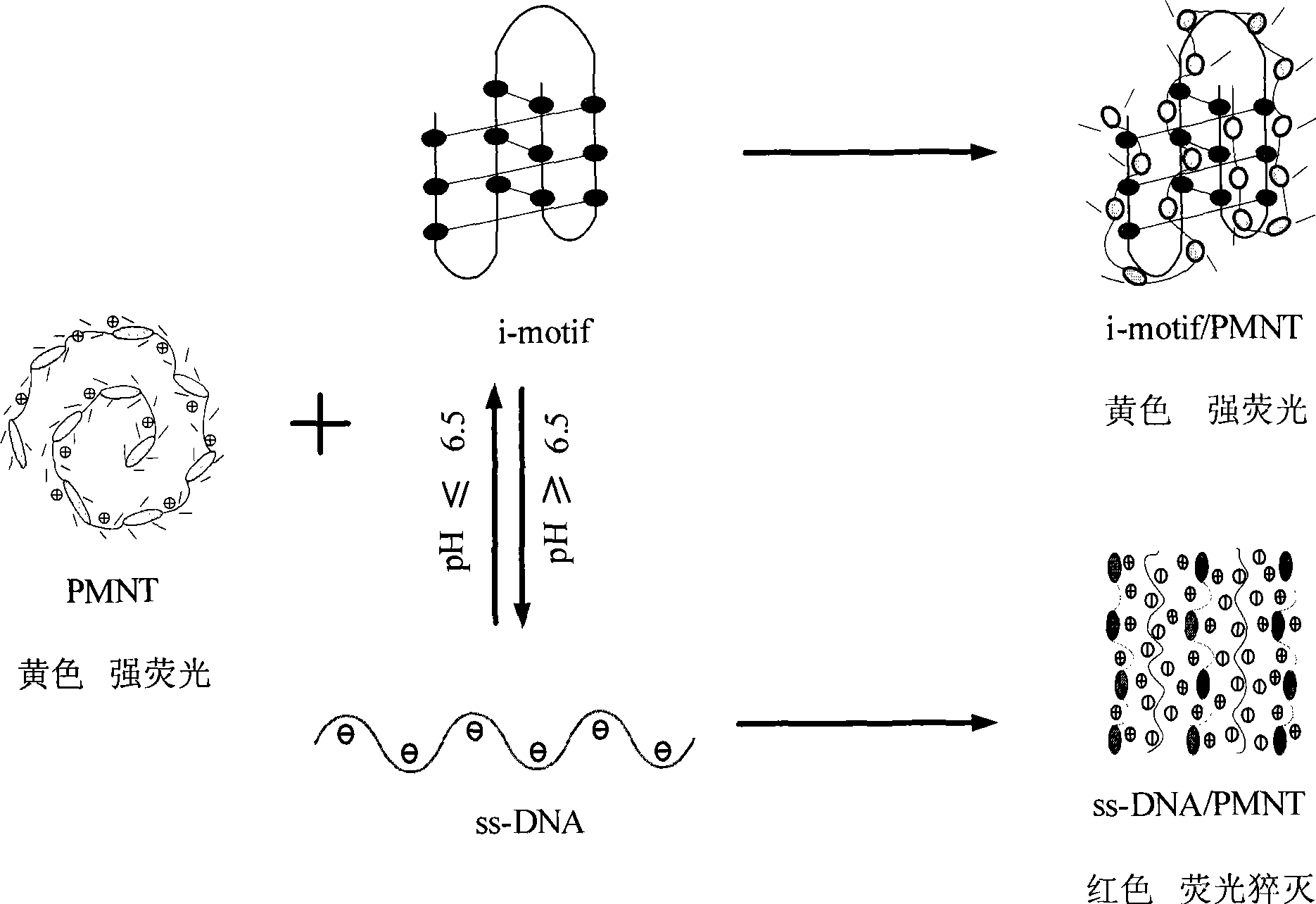
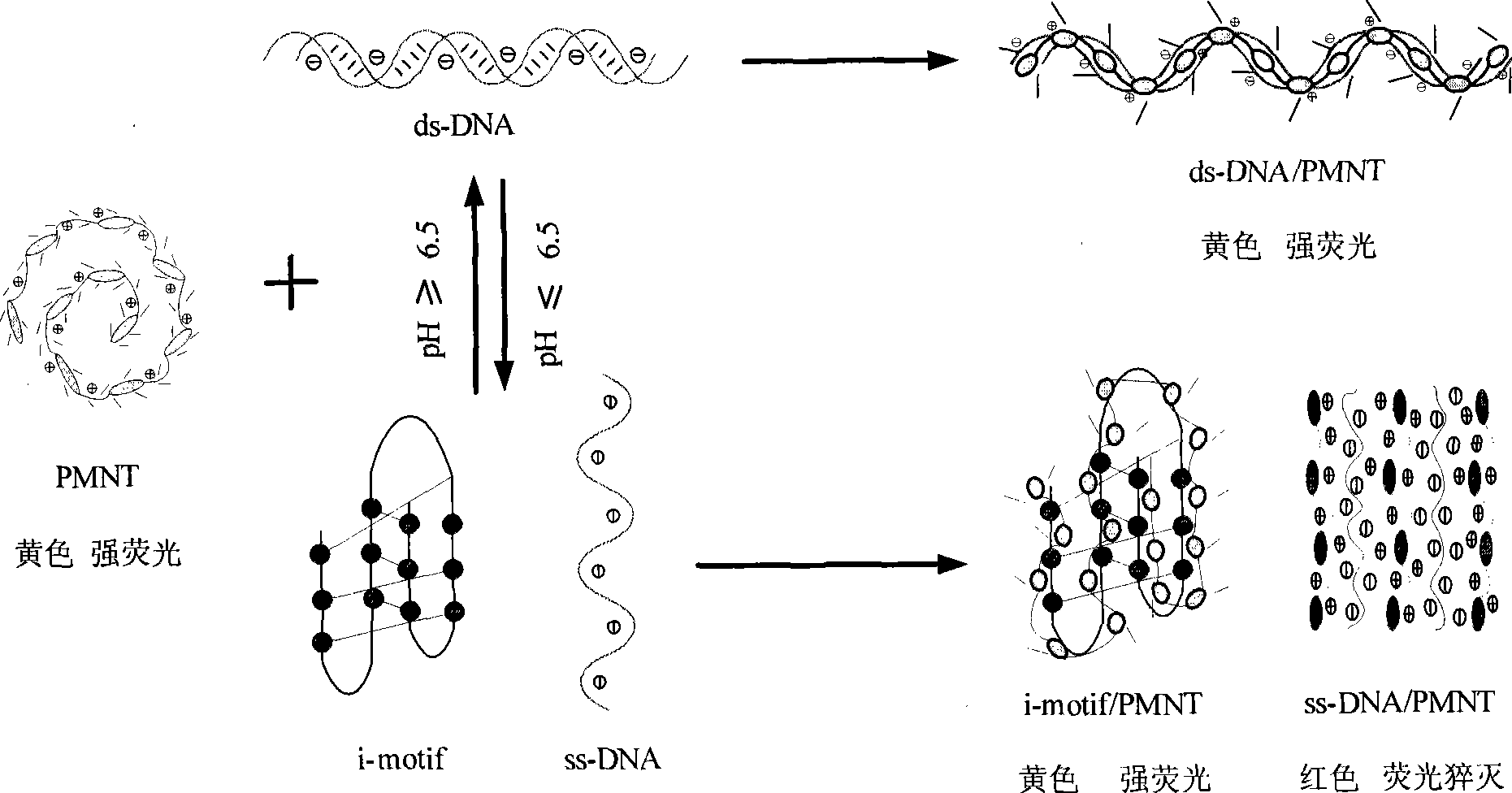
[0038] The results showed that when the specific C-probe was used for detection, the color in the pH 5.0 solution was yellow, while in the other three solutions, the color was orange-red. This is due to the fact that residue C of DNA is protonated to form a semi-protonated C-C in a weakly acidic environment at pH 5.0 + base pair, thus forming a stable i-motif structure, which turns yellow when electrostatically combined with positively charged PMNT. In a neutral alkaline environment with a pH greater than or equal to 6.8, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Take 2.5 μL of C-probe solution with a concentration of 100 μM and add it to 2.5 μL of the solution whose pH was adjusted with HCl and NaOH. Then add an isoelectric PMNT solution (5 μL of 1 mM PMNT solution) to it, and observe the color change of the solution, so as to investigate the influence on the detection of structural transformation in a strong acid or strong alkali environment.
[0042] The results showed that in the environment with pH less than 6.5 such as pH 1, 3 and 5, the color of the solution was yellow due to the formation of i-motif structure, while in the environment with pH greater than 6.5 such as pH 7, 9, 11 and 13 , the color of the solution is red because the i-motif structure cannot be formed. It shows that the detection of conformational changes of C-rich DNA can also be carried out in more acidic or alkaline environments.
Embodiment 3
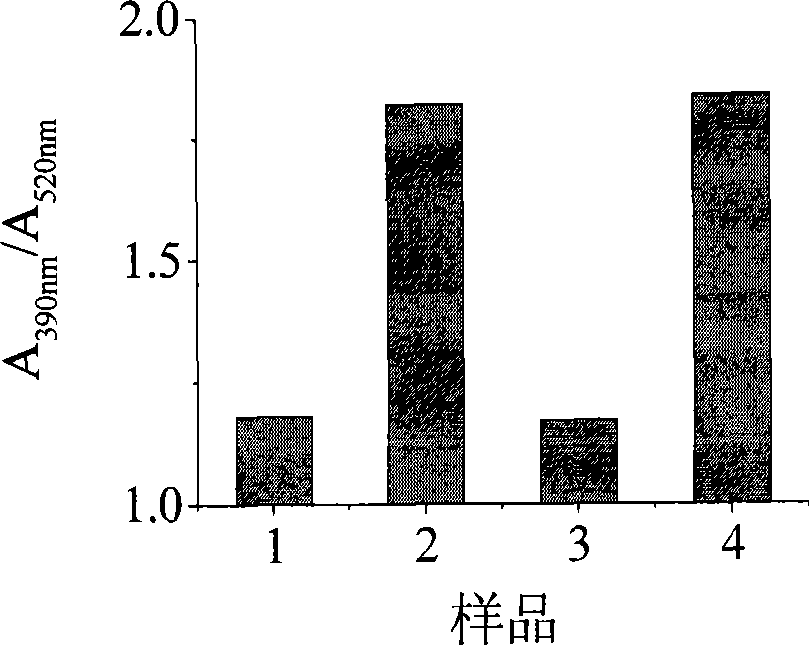
[0044] Experiments were carried out according to the conditions in Example 1, and the reversibility of the method of the present invention for conformational transition detection was analyzed. First, the specific probe C-probe solution (sample 1) was added to the pH 8.0 solution. Since the four-chain structure cannot be formed, the color is red after adding the conjugated polymer. Then add a certain amount of strong acid solution (1M HCl) therein to make the system change to pH 5.0, the system is weakly acidic (sample 2), the DNA forms a four-stranded i-motfi structure, and the color turns yellow. After the color is stable, add 1M NaOH to make the solution pH become 8.0 (sample 3) again, and the color turns red again, then according to the above method, the solution pH becomes 5.0 (sample 4) again, repeat the experiment, and finally detect each The UV-Vis absorption spectrum of the solution.
[0045] see results image 3 . When the pH of the system is acidic, the color of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com