Biological target molecule detection method based on multivalent capture and output signal amplification
A technology for biological targets and output signals, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as low exosome capture efficiency and detection sensitivity, poor chain reaction hybridization efficiency, and cumbersome experimental steps. , to maintain its own stability, improve hybridization efficiency, and simplify detection steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Detection of exosomes based on single-step multivalent capture and amplification
[0074] 1. Recognition probe design: design 4 probes A, B, C, and D that make up the nucleic acid framework, wherein A, B, C, and D contain sequences that hybridize with each other to form the nucleic acid framework structure FNAs / apt;
[0075] According to the detection of epithelial cell adhesion molecules on the surface of the target breast cancer-associated exosome membrane, A includes the nucleic acid aptamer sequence Aapt that can specifically recognize and bind epithelial cell adhesion molecules, and B includes Ba, where the full or partial sequence of Ba can Crossed with Aapt. DNA three-dimensional nanostructures such as nucleic acid frameworks have a certain ability to resist enzymatic degradation in complex biological environments, which is conducive to improving the stability of the carried recognition probes in complex biological samples and improving the ability to recognize a...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Based on single-step multivalent capture of exosomes and amplified fluorescent signal detection
[0094] The design of the detection probe: the modification of biotin on H2 was changed to the modification of fluorescent group, and the rest of the sequences were kept the same.
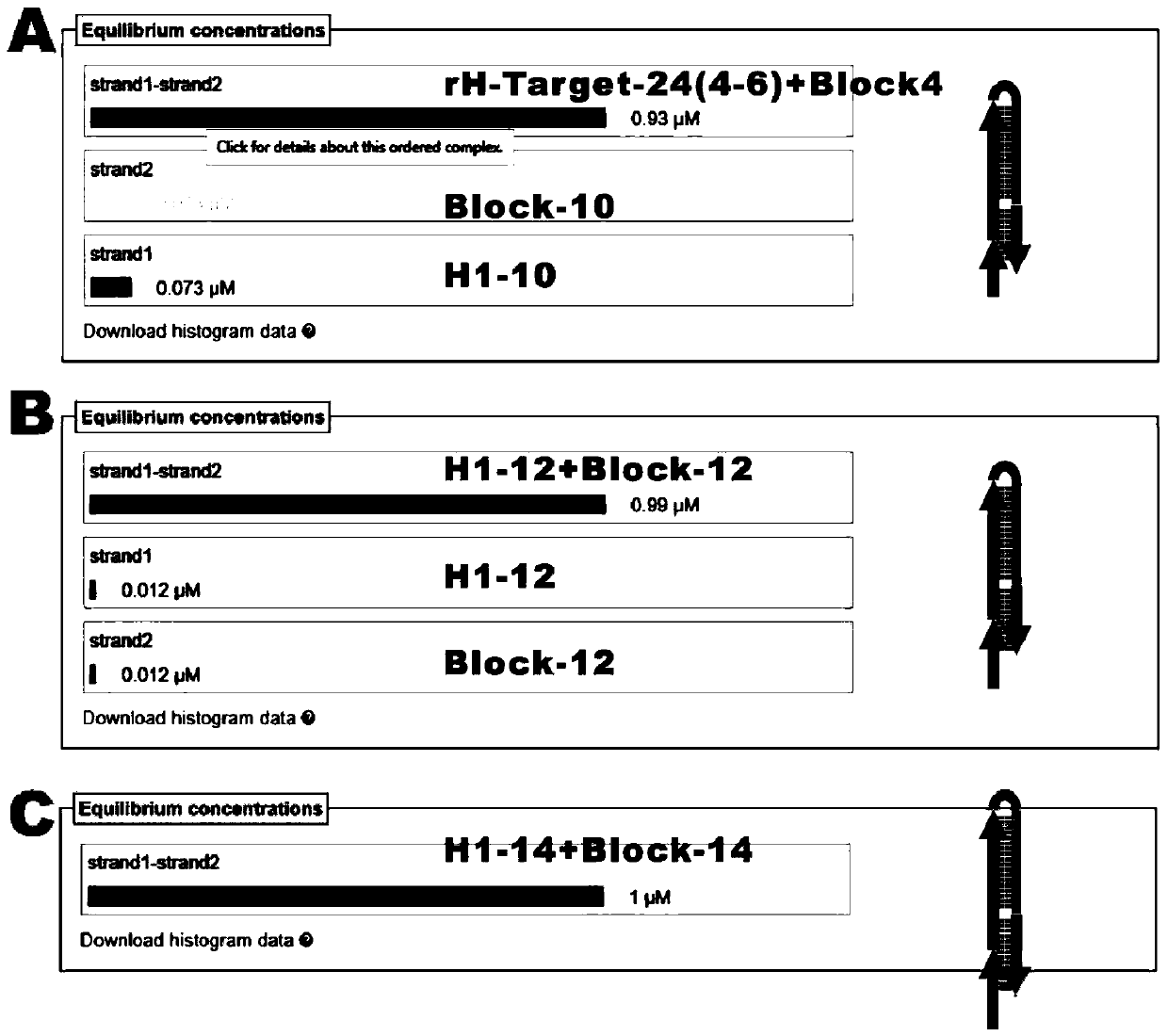
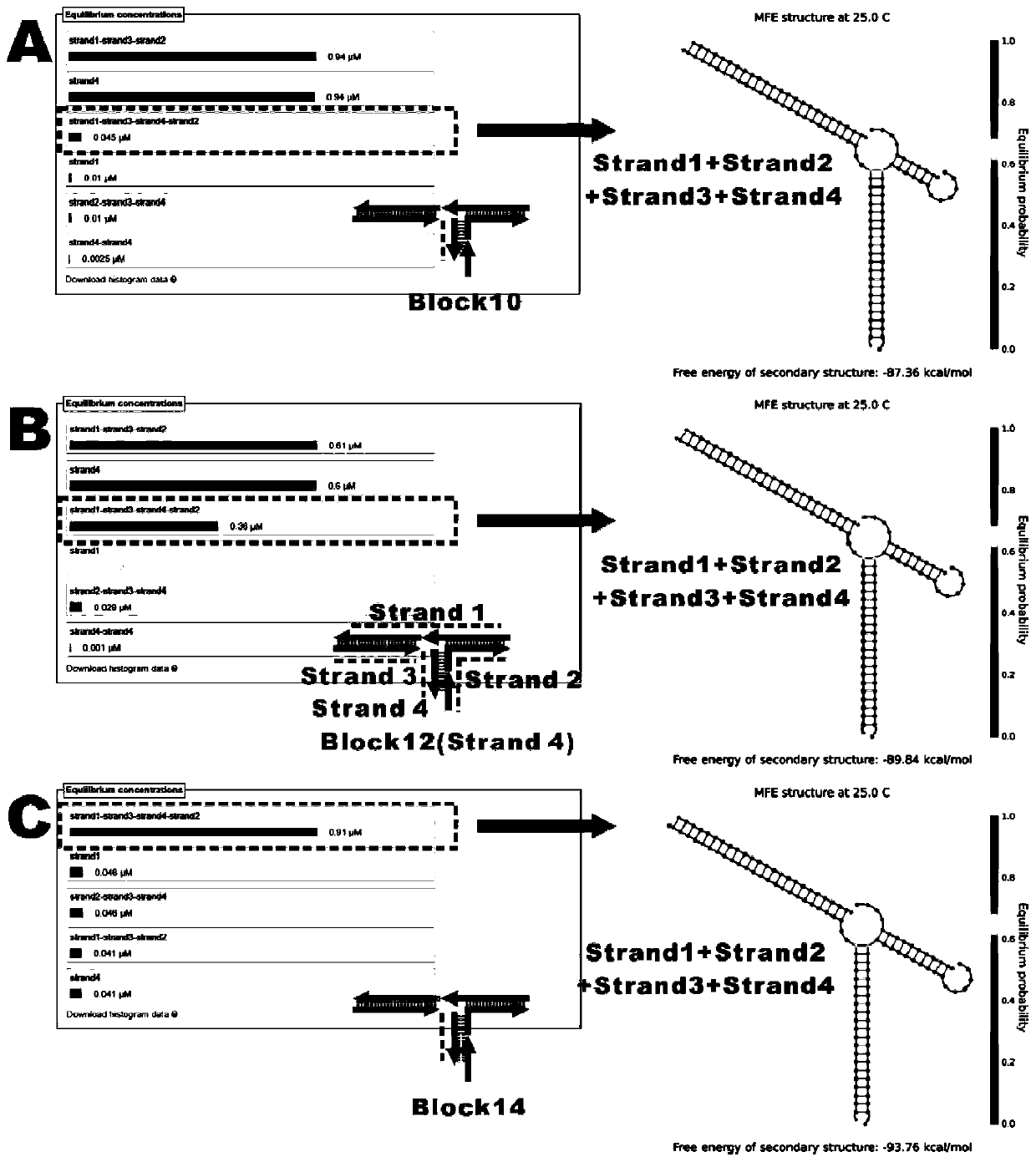
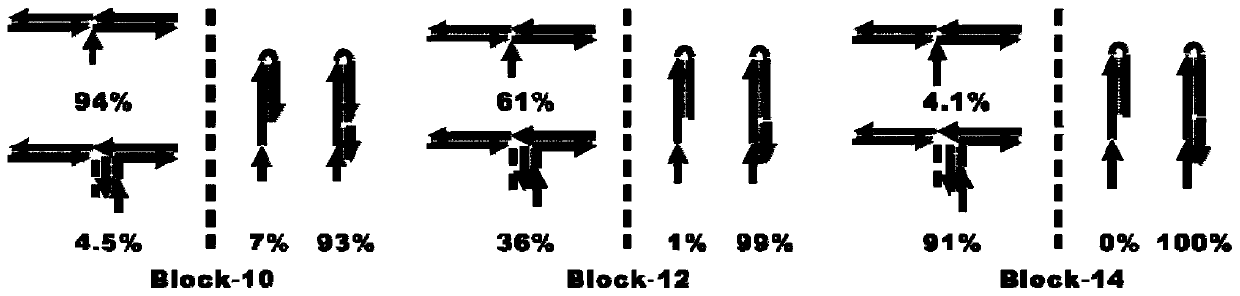
[0095] Figure 10 It is a flow chart of the principle of single-step multivalent capture of exosomes and fluorescence amplification detection, using fluorescence imaging to verify target recognition, multivalent capture and signal amplification output in one step. FNAs / apt with a concentration of 100nM (final concentration), H1 and H2-biotin were added to 10 10 In a target exosome (total volume 100 μL), after the chain hybridization reaction is initiated, each chain product has a multi-branched single-chain structure. With the aid of the blocker probe, a single-step multivalent The exosomes were captured, and the gold flakes were imaged by a fluorescence microscope to output corresponding fluor...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Single-step multivalent capture and amplified detection of exosomes in serum
[0099] When detecting exosomes in serum, DNase in serum will degrade the recognition probe and reduce the detection efficiency of biological targets. The stability of needles and the efficiency of binding to exosomes. In addition, the efficiency of the hybridization chain reaction is reduced due to the interference of a large number of non-target biomolecules and the reduced concentration of salt ions required for hybridization. In order to improve the hybridization chain reaction efficiency in serum, 25 μL 2*SPSC buffer solution was added to 75 μL serum. There is a large amount of albumin in the serum, which can play a blocking role, prevent the adsorption of horseradish peroxidase on the electrode interface, and reduce the background signal. comparable detection sensitivity.
[0100] Figure 12 The result is that the number of exosomes in the serum is directly proportional to the output...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com