Semiconductor device with surge current protection and method of making the same
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as inapplicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
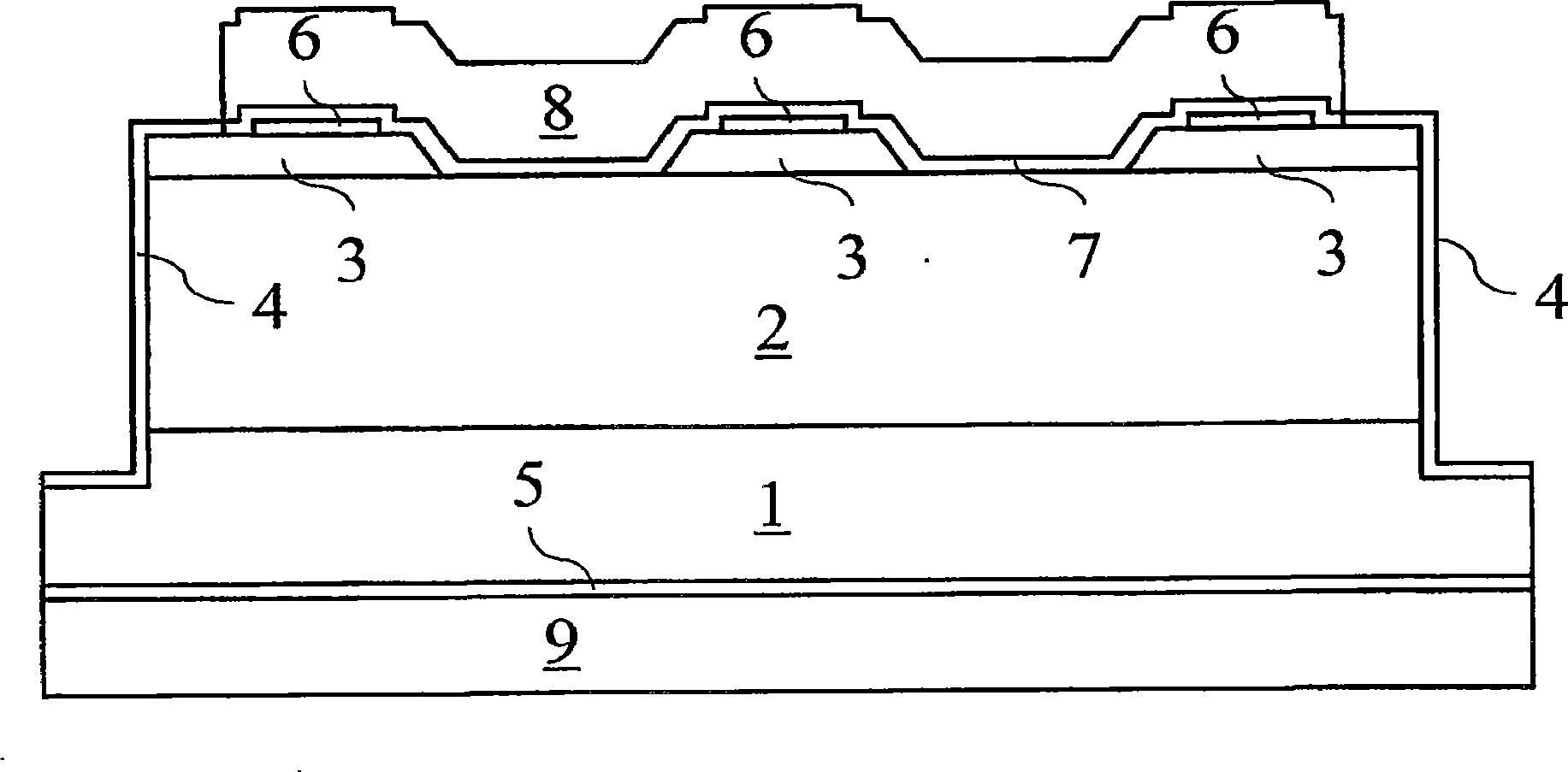
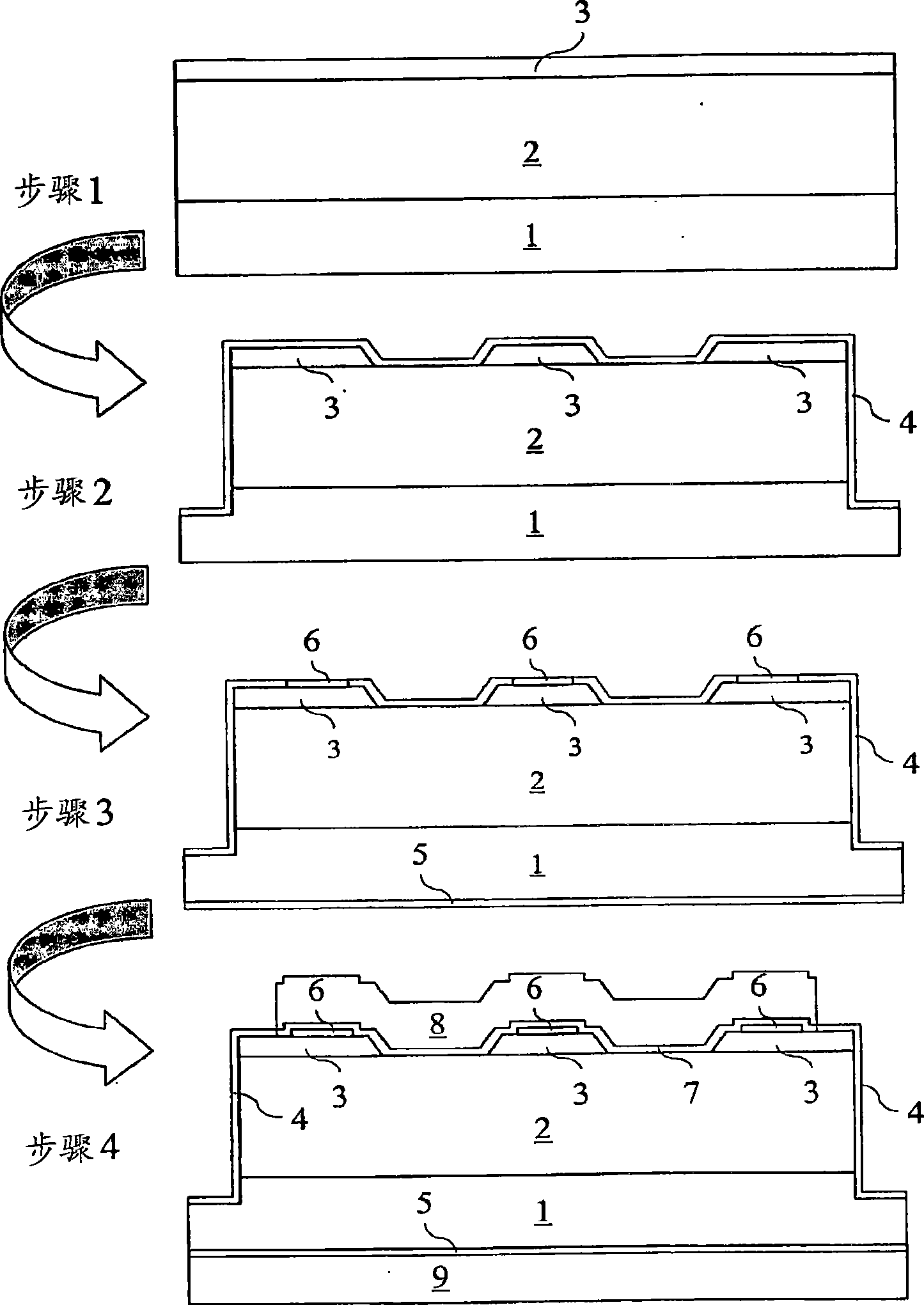
[0046] According to one embodiment, the device includes a monolithically integrated Schottky barrier diode and a p-type / intrinsic / n-type (PiN) junction diode connected in parallel. figure 1Exemplary devices are shown. Under normal operating conditions, the device acts as a Schottky barrier diode with most of the current flowing through the Schottky contact. However, under surge current conditions, the current mainly flows through the p-n junction due to the significant decrease in drift resistance due to conductance modulation at larger current densities. This phenomenon can be explained by the following mathematical formula, which calculates the forward current density J F The specific resistance of the base region of the PiN diode (Reference 6):
[0047] R ( J F ) = t q · μ n ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Doping concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Doping concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com