Method for inducing human mesenchymal stem cells differentiation to oligoden drocyte
A technology of oligodendrocytes and bone marrow mesenchyme, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, nervous system cells, etc., can solve the problems of complicated separation process, non-autologous transplantation, and high price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Example 1 In vitro culture and expansion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
[0014] hBMSCs (≥70%) were derived from Cambrex, and samples were collected from 38-year-old healthy male youth donors. Primary hBMSCs were inoculated in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and cultured in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator. After 48 hours, rinse twice with PBS to remove unattached cells and replace with new culture medium. When the adherent cells were 90% confluent, they were digested with 0.25% trypsin and subcultured at a ratio of 1:3 to continue to expand and culture.
[0015] The morphological characteristics of the hBMSCs obtained by this method: when the cells are just cultured, a large number of round cells are suspended in the culture dish, and these unattached blood cells can be removed by changing the medium, and the adherent cells are hBMSCs. The initially inoculated hBMSCs are round, large in size, translucent, and strong in refraction; 24 hours after in...
Embodiment 2
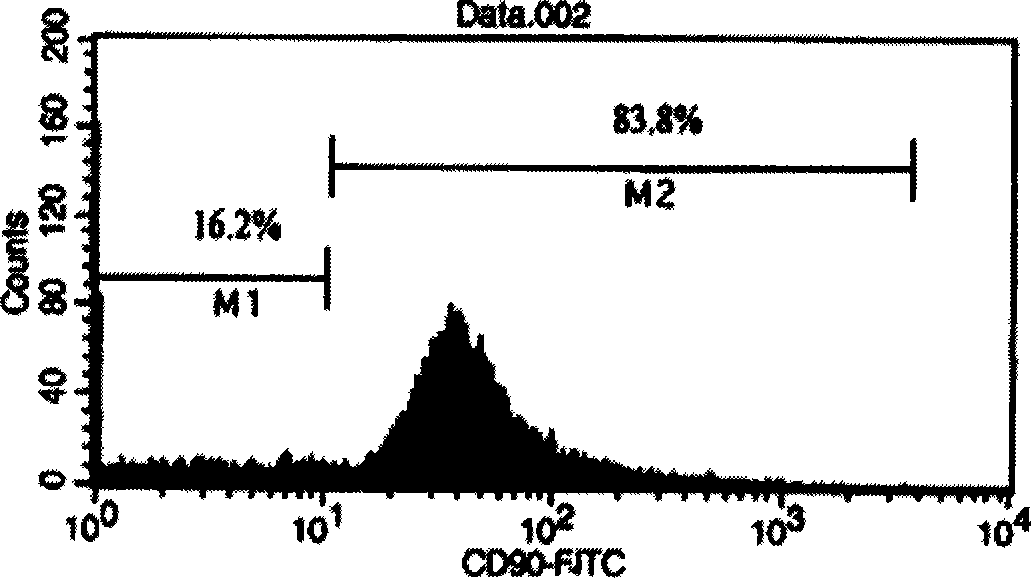
[0016] Example 2 Using Flow Cytometry to Analyze the Characteristics of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells
[0017] When the cells grew to 90% confluence, the cells were collected for flow cytometry detection, and the adherent hMSCs in the plastic dish were digested into single cells with 0.25% EDTA-containing trypsin, washed three times with PBS, counted and adjusted To an appropriate concentration (1×106 / ml), fixed with alcohol, washed three times with PBS; treated with TritonX-100 and hydrogen peroxide; added normal goat serum to block at room temperature for 30 minutes; added CD34, CD45, or CD90 antibodies respectively for 2 hours at room temperature ; Add FITC fluorescent antibody to incubate together, and then use FACS to analyze the number of CD90 positive cells.
[0018] The results showed that flow cytometry analysis was performed when the adherent cells were nearly 90% confluent. The results showed that CD90(+) cells reached 83.8% to 97.7%, with an average of 94.78+...
Embodiment 3
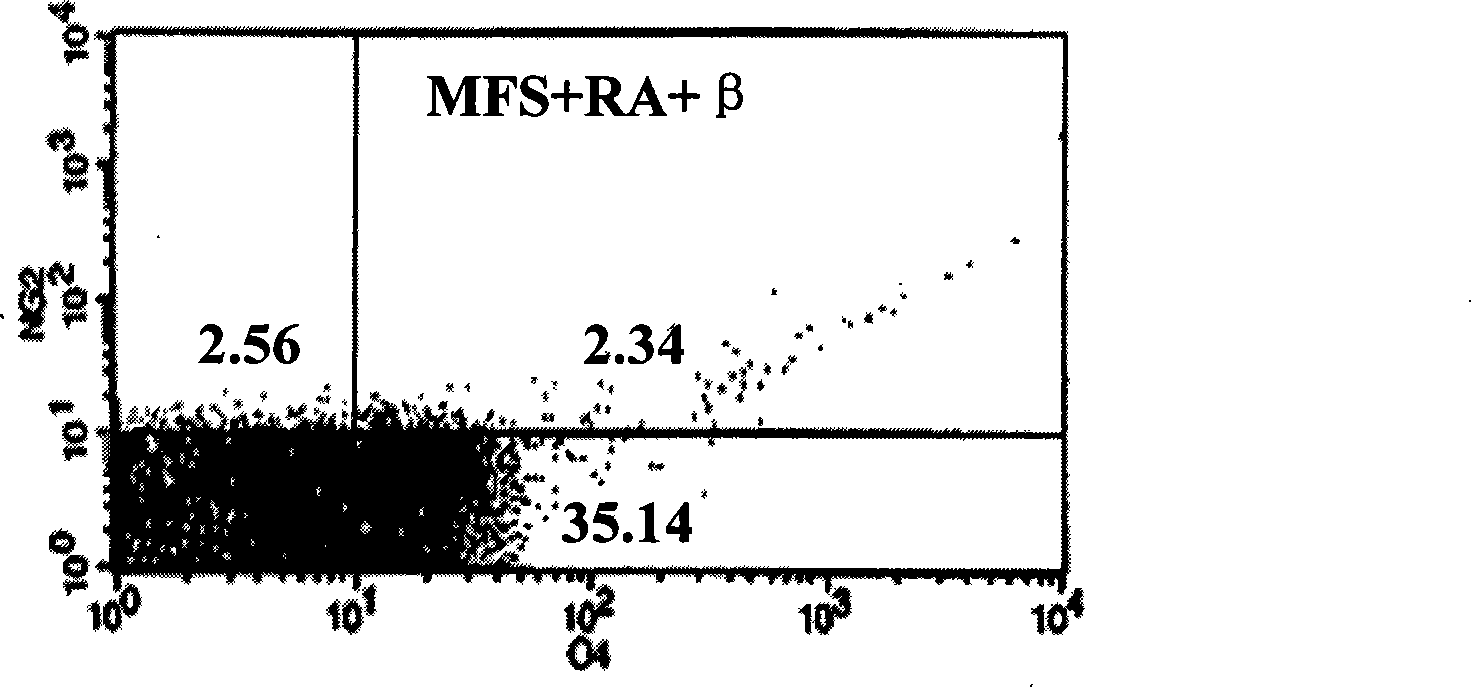
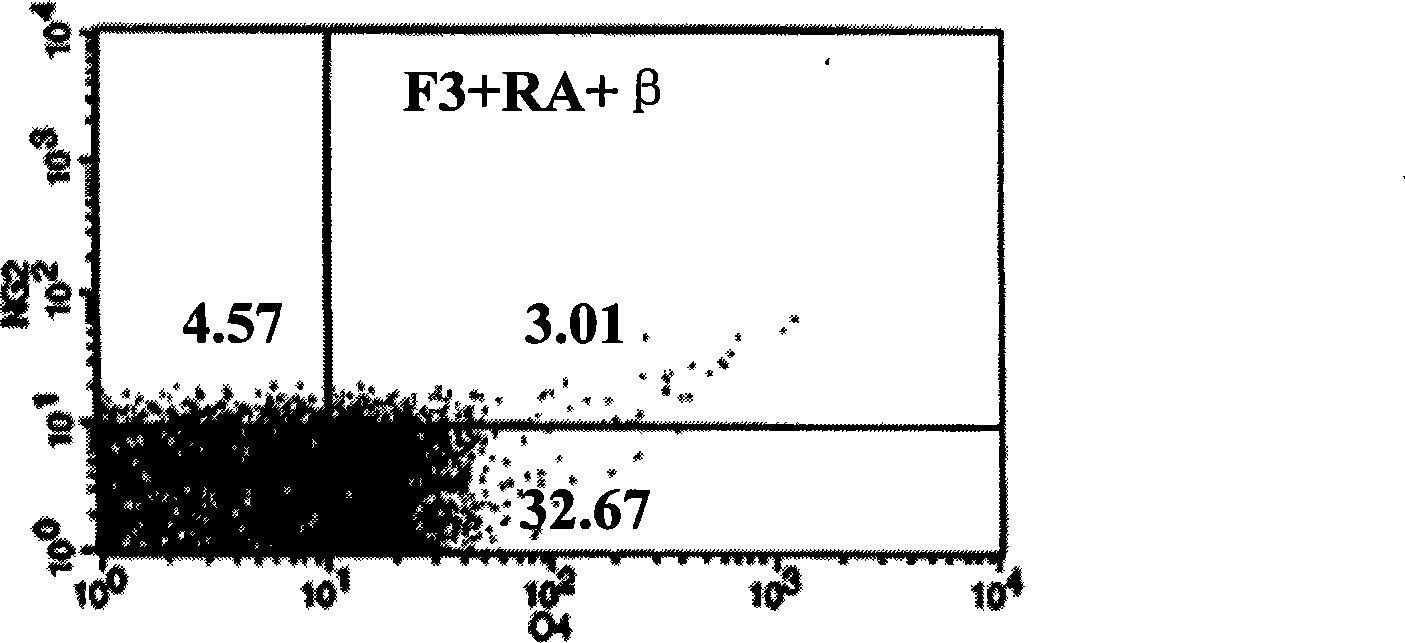
[0019] Example 3 Induction of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into oligodendrocytes in vitro and phenotype identification refer to Dezawa et al. (Dezawa M, Takahashi I, Esaki M, et al. Sciatic nerve regeneration in rats induced by transplantation of in vitro differentiated bone-marrow stromal cells. Eur J Neurosci, 2001, 14: 1771-1776) method of chemically inducing hBMSCs: cells close to confluence were pre-induced with 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME) DMEM for 24 hours; 10% fetal bovine serum DMEM induction solution of RA (RA) for 3 days; then the cells were divided into MFS group (positive control group) and F3 group and continued to culture for 3 days. 10ng / ml basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), 5ng / ml platelet growth factor (PDGF), 200ng / mL heregulin (HRG) DMEM medium; F3 group cells were cultured in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 20nM F3 base.
[0020] The characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced into oligodendrocyt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com