Disinsection method using pest taxis to crops
A crop and pest technology, applied in the field of insecticidal field, can solve the problem of no insecticidal technical solution, and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of excessive pesticide residues, improving quality and added value, and reducing the dependence of pesticides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
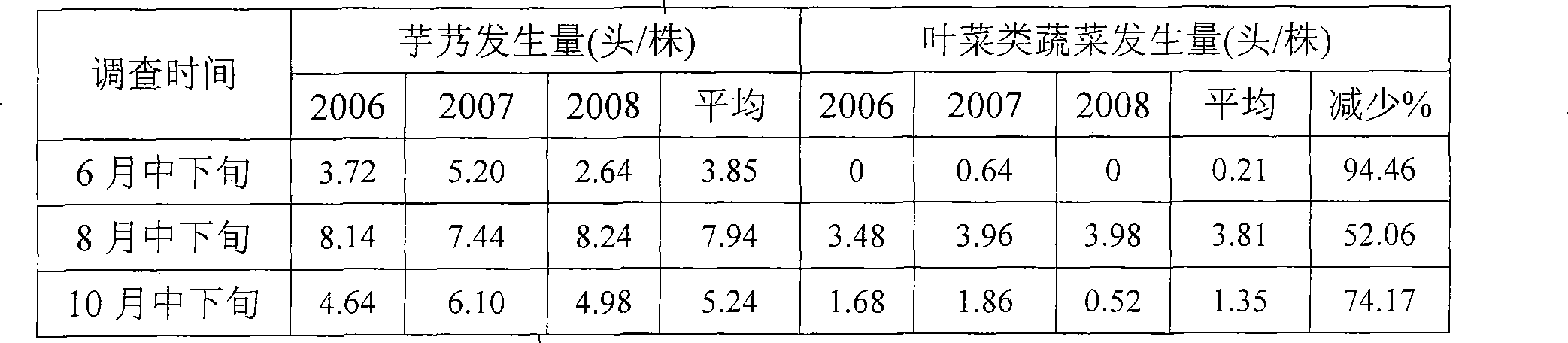
[0015] Example 1: Field surveys found that vegetable pests such as Prodenia litura (Fabricius) and diamondback moth (Plutellaxylostella Curtis) have relatively different feeding tropisms to different crops, especially when there are different crops in the same area. Sometimes, the adults of pests often choose to lay eggs on crops with strong feeding tendency, which leads to large differences in the occurrence of pests on different crops, as shown in the following table:
[0016] Table 1 Comparison of occurrence of Spodoptera litura larvae in different crops
[0017]
[0018] (The survey points are selected in the area where the two crops are adjacent to each other and planted in an area of more than 2,000 square meters. Five points are used for sampling, evenly distributed, and 10 plants are investigated at each point.)
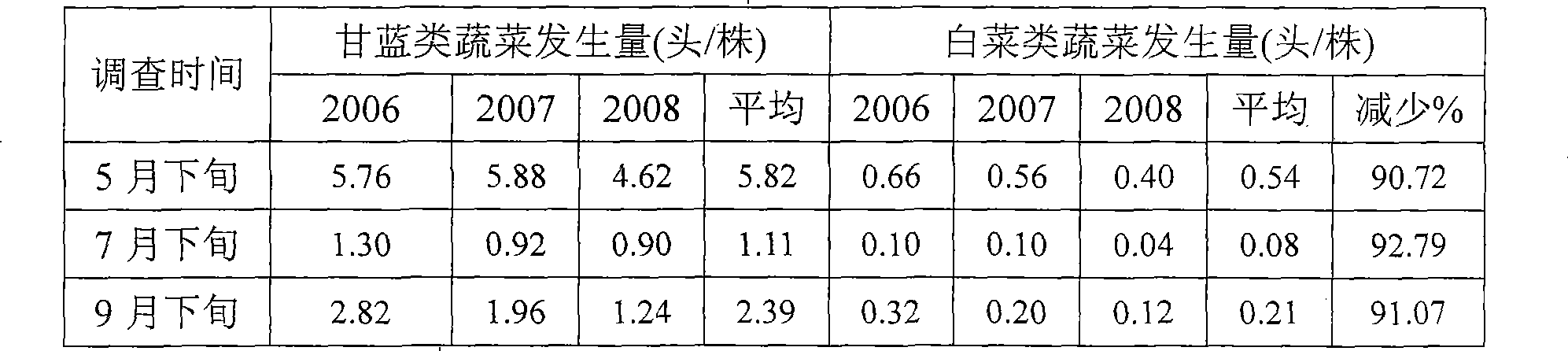
[0019] Table 2 Comparison of occurrence of Plutella xylostella larvae in different crops
[0020]
[0021] (The survey points are selected in the ar...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: The implementation method for the control of Spodoptera litura is: every 15-20 borders of leafy vegetables are interplanted with 1 border taro (Colocasia esculenta Schott.), and the intercropping ratio is 15-20:1. The method of field application is: from the middle and late October of each year to the middle and late June of the following year, it is only necessary to investigate the occurrence of Spodoptera litura on the taro, and to kill the pests intensively after the pests are found, without using them on leafy vegetables. Use of pesticides for prevention and control: From early July to early October every year, use pesticides on taro every 5 to 7 days, and use pesticides on leafy vegetables every 10 to 14 days or according to the occurrence of insect pests; the amount of pesticides in the field can be reduced by 40% throughout the year. %, reduce the risk of pesticide residues in leafy vegetables exceeding the standard, and realize efficient and safe cont...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Embodiment 3: The implementation method for the prevention and treatment of diamondback moth is: for every 4-6 furrow cabbage class (Brassica chinensis L.) vegetables interplant 1 furrow cabbage class (Brassica oleracea L.var.capitata Linn.) vegetables, the intercropping ratio is 4~6:1. The method of field application is: every 5 to 7 days during the period of high pest incidence from early May to late June every year on cabbage vegetables, and every 10 to 14 days or according to the occurrence of pests on cabbage vegetables; By the end of April of the following year, according to the occurrence of pests, pesticides are mainly used for control on cabbage vegetables, which can reduce the amount of pesticides in the field by more than 30% throughout the year, reduce the risk of pesticide residues in vegetables exceeding the standard, and achieve efficient and safe control of diamondback moth.
[0025] As a supplement: For the prevention and control of Spodoptera litura (F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com