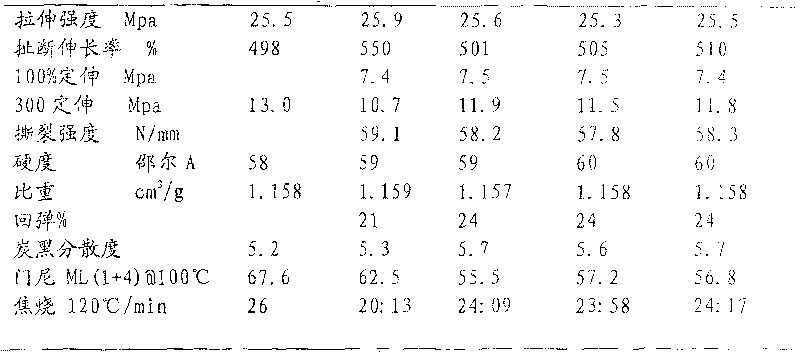Solvent-free method for preparing tackified p-tert-butyl phenolic resin
A technology of p-tert-butylphenol and p-tert-butyl, which is applied in the field of solvent-free preparation of tackified p-tert-butylphenol resin, can solve problems such as environmental pollution and inevitable solvent volatilization damage, and achieve reduced production costs and improved product performance. Improve and avoid the effect of violent gathering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
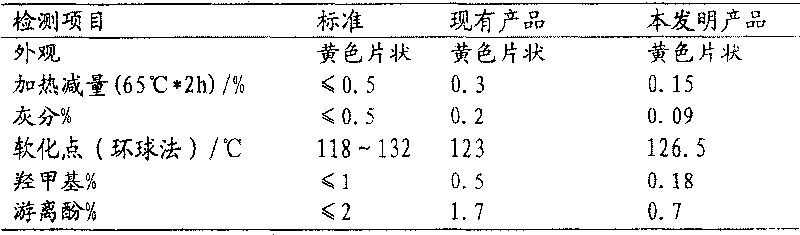
[0041] Add 150g of p-tert-butylphenol and 25g of formaldehyde into a 500mL three-necked flask, slowly heat up and melt, and stop the temperature rise when it reaches 90-95°C. Stir for 15 to 30 minutes, add 8.45 g of catalyst (hydrochloric acid) dropwise under reflux, finish adding in about 1.5 hours, and reflux at 101°C for 3 hours. After the reaction, 0.55 g of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate was added and stirred for 10 to 20 minutes. Heating and dehydration, when the system is 110°C, it becomes transparent, continue to heat up to 170-180°C, add 1.2g of oxalic acid, stir for 10-20 minutes, vacuum dehydration for 20 minutes (vacuum degree > 0.085MPa); stop the reaction, pour out the material, After cooling, a light yellow transparent flaky solid was obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0043] Add 400g of p-tert-butylphenol and 41.6g of formaldehyde into a 1L three-neck flask, slowly heat up and melt, and stop the temperature rise when it reaches 90-95°C. After stirring for 20 minutes, 22.5 g of the catalyst (hydrochloric acid) was added dropwise under reflux, and the addition was completed in about 1.5 hours, followed by reflux at 101° C. for 3 hours. After completion of the reaction, 0.92 g of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate was added, followed by stirring for 10 to 20 minutes. Heat up and dehydrate, when the system is 110°C, it becomes transparent, continue to heat up to 170-180°C, add 2g of oxalic acid, stir for 10-20 minutes, vacuum dehydrate for 20 minutes (vacuum degree > 0.085MPa); stop the reaction, pour out the material, cool A light yellow transparent flaky solid was obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Add 55kg of p-tert-butylphenol and 19kg of formaldehyde into a 200L reactor, slowly heat up and melt until it reaches 90-95°C, then stop the temperature rise. Stir for 15-30 minutes, add 6.5 kg of catalyst (hydrochloric acid) dropwise under reflux, finish adding in about 1.5 hours, and reflux at 101°C for 3 hours. After the reaction was completed, 0.4 kg of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate was added and stirred for 10 to 20 minutes. Heat up and dehydrate, when the system is 110°C, it becomes transparent, continue to heat up to 170-180°C, add 0.9kg oxalic acid, stir for 10-20 minutes, vacuum dehydrate for 25 minutes (vacuum degree > 0.085MPa); stop the reaction, pour out the material, After cooling, a light yellow transparent flaky solid was obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com