Process for obtaining high efficiency human albumin for use in detoxification therapy
A technology for human albumin and albumin, which is applied in the field of obtaining high-capacity human albumin and can solve problems such as complicated processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
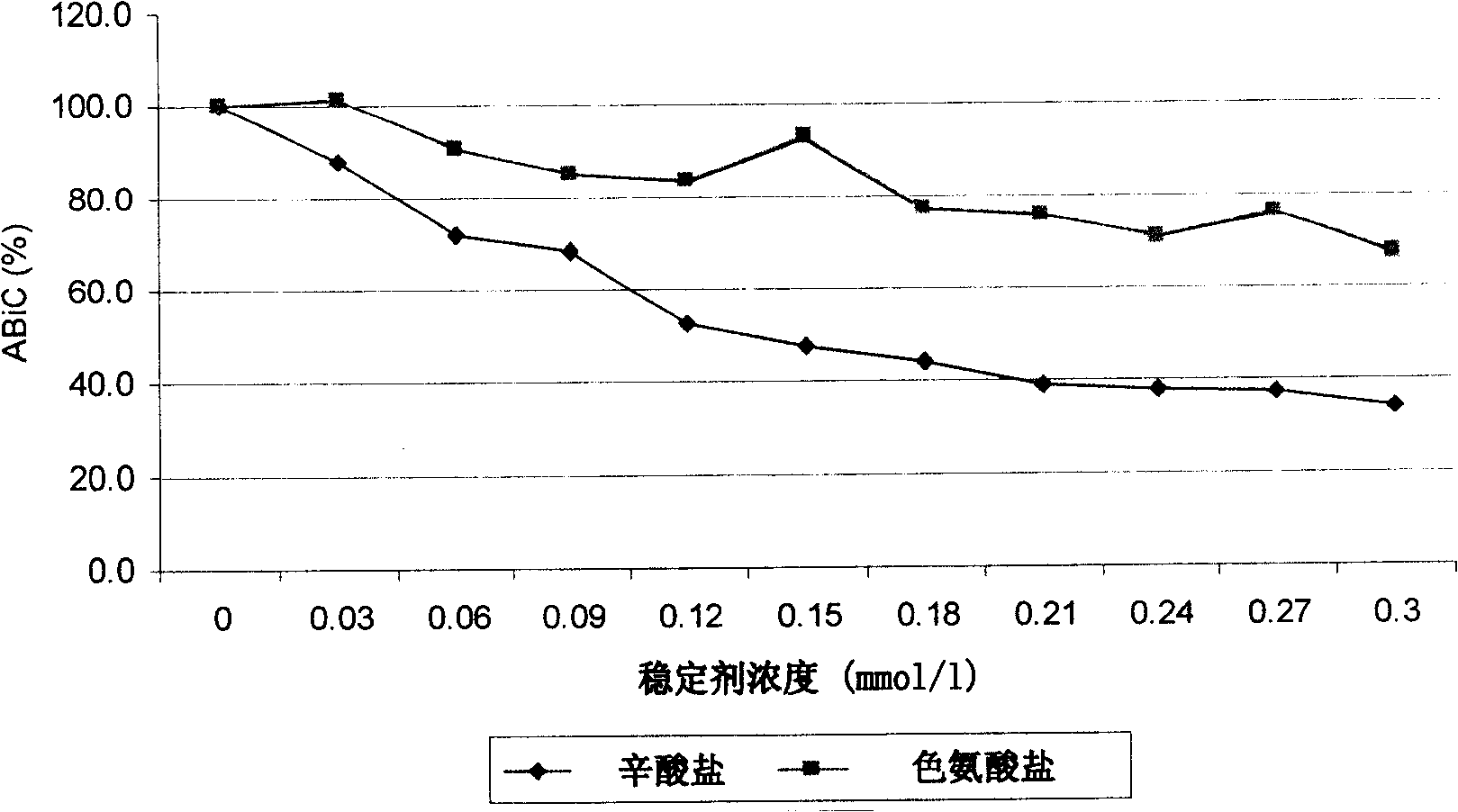
[0071] Example 1: Comparison of the effects of N-acetyltryptophan and sodium caprylate stabilizers on albumin binding capacity (ABiC)
[0072] In order to obtain albumin with a high binding capacity, it was decided to evaluate the extent to which sodium caprylate and N-acetyl tryptophan used to stabilize the commercial formulation affect the binding capacity of unstabilized albumin.
[0073] For this purpose, the ABiC is determined according to the established method, but with albumin without stabilizer as reference. Separate solutions of each excipient (N-acetyl tryptophan and octanoate) were prepared in increasing concentrations. 1 ml of each solution was incubated with 1 ml of albumin without stabilizer (final albumin concentration 1%). Then 1 ml of dansyl sarcosine was added to each mixture and the normal course was followed using the albumin binding volumetric method.
[0074] get the result in figure 1 It was shown that, for the same concentration of excipients, the a...
Embodiment 2
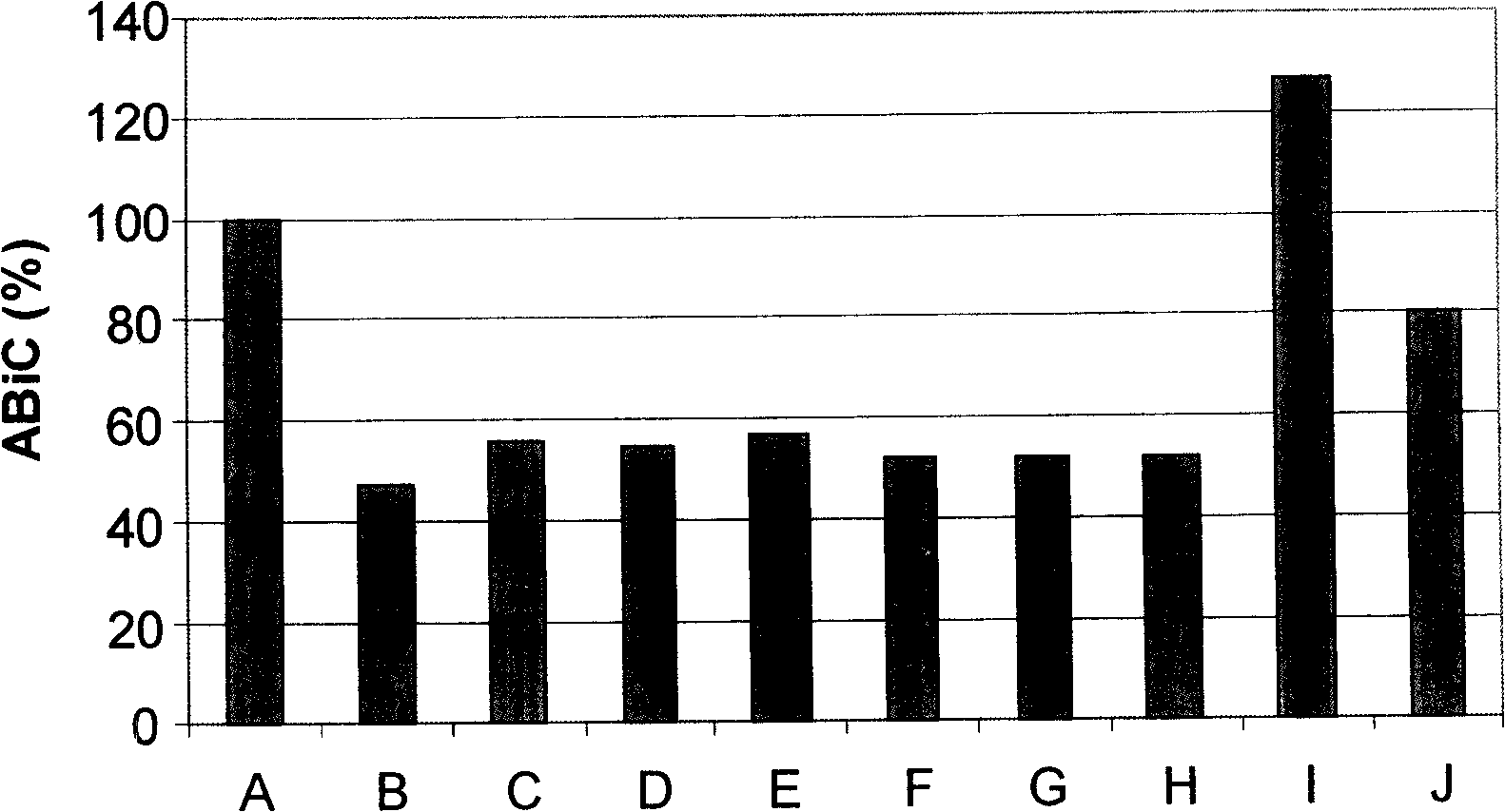
[0075] Example 2: Plasma Albumin Binding Capacity (ABiC) Stabilized with Different Commercially Available Albumin Concentrates and with N-Acetyl Tryptophan Prepared According to the Process Described in the Invention Without Stabilizers and with 0.16 mmol / g Compared with albumin, the results obtained in figure 2 show.
[0076] Taking the binding capacity (100%) shown by native plasma albumin (column A) as reference albumin, we observed The profile of binding capacity was all consistent (48% to 57%) between the different commercially available albumin concentrates of albumin (columns B to G) and compared with only sodium caprylate (0.099 mmol / g albumin) ( 52%) (column H) was consistent with commercially available albumin stabilized. This binding capacity is smaller than that of plasma albumin.
[0077] Albumin obtained according to the invention without stabilizer (127%) (column I) or stabilized at 0.16 mmol / g of N-acetyltryptophan ( 80%) (Column J) A higher binding capaci...
Embodiment 3
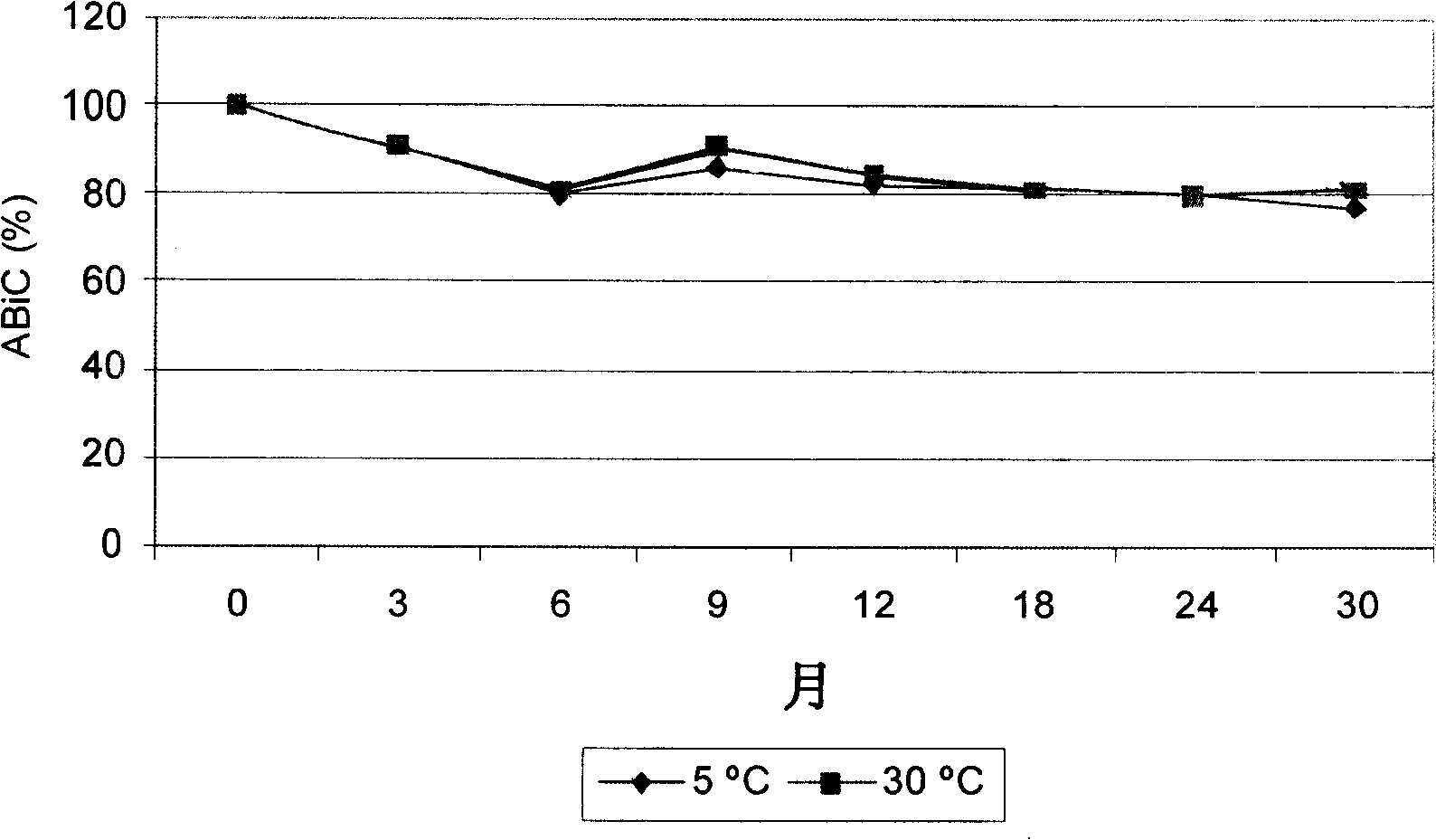
[0079] Example 3: Stability of albumin solutions. The albumin solution with a concentration of 20% obtained by the method described in the present invention is stabilized with 0.15M sodium chloride and a concentration of 0.16mmol N-acetyl tryptophanate / g albumin and in accordance with international level coordination , the current regulations on stability research Q5C "biotechnology / biological products" and Q1A (R2) "stability testing of new drugs, substances and products" conduct research on their stability. image 3 Stability at 20% albumin binding capacity is given. Real-time stability data for the 3 batches of albumin shown showed that the product remained stable. In particular, after at least 30 months of storage at 5°C±3°C and at 30°C±2°C, the binding capacity did not show appreciable changes from the beginning of the study. In fact the fluctuations in binding capacity results observed at 5°C and 30°C occurred in parallel with time and can therefore be attributed to ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com