Method for extracting geoscience spatial information based on generalized self-similarity principle
A self-similarity, spatial information technology, applied in the field of geospatial information, can solve the problems of geospatial information processing and extraction accuracy and precision reduction, and achieve the effects of reducing boundary effects, high extraction precision, and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
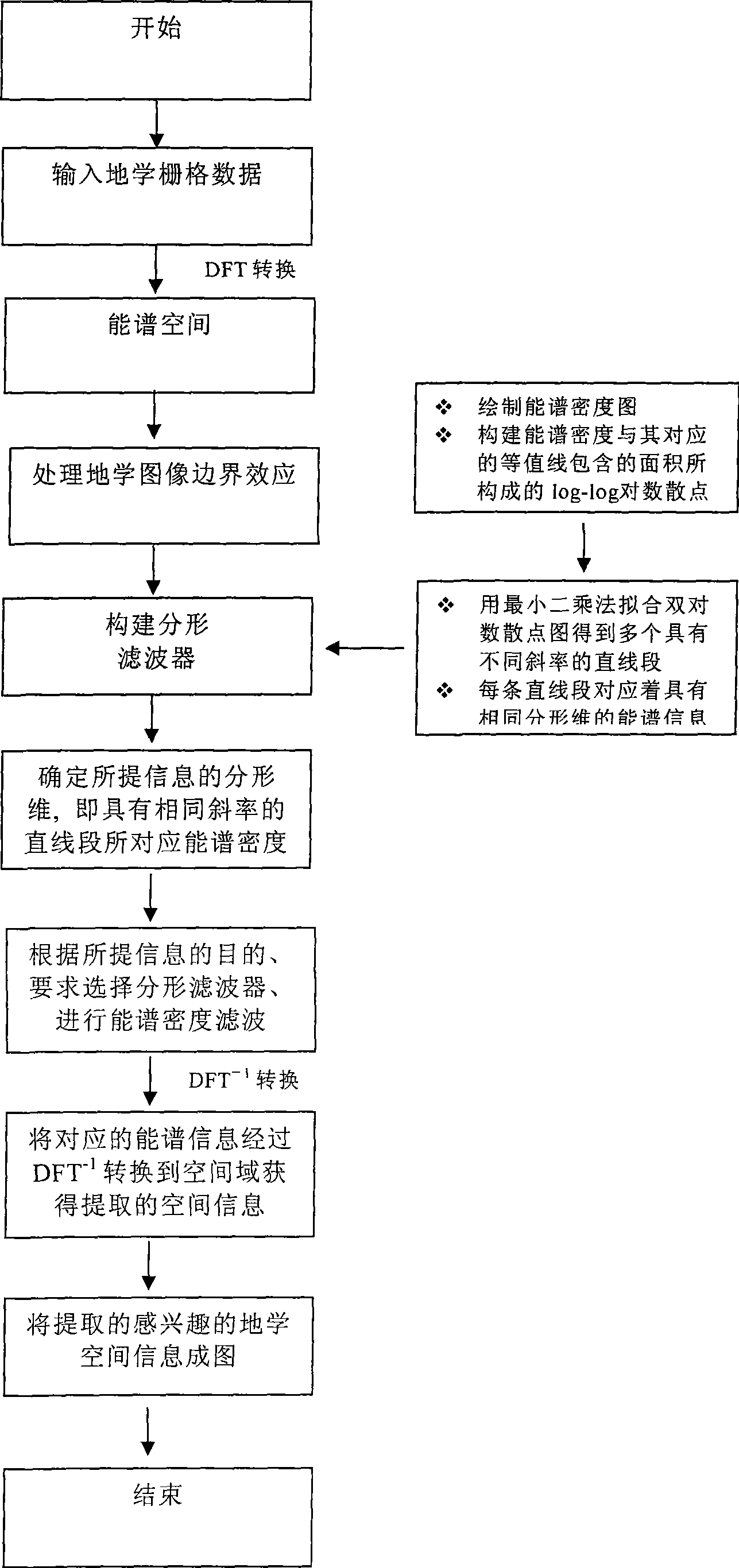
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, the specific implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0034] The first step is to preprocess the data and convert the geospatial data to be processed into raster data;
[0035] First, prepare the data, select the geoscience data to be analyzed, and convert the collected geoscience data, such as point data, image data (TIF, JPG, BMP) and other file formats, to the raster data file format through interpolation and format conversion. These methods It is available in some commonly used commercial GIS software, such as ArcGIS. E.g, figure 2 It is a raster data image obtained by sampling and interpolation of lake sediments of the metallic element arsenic, named AS_IDW.
[0036] In the second step, the Fourier transform is used to transform the raster data into the energy spectral density space, while reducing the influence of the boundary effect caused by the Fourier transform.
[0037] In this step, Fourier transform is applied...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com