Method for all-fiber Q-switching through continuous acoustooptic diffraction
An acousto-optic diffraction and all-fiber technology, which is applied in optics, lasers, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve the problems of low power density of sound waves, low maximum frequency of sound waves, and inaccessibility, and achieves easy realization, realization of sound-optic modulation, The effect of simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
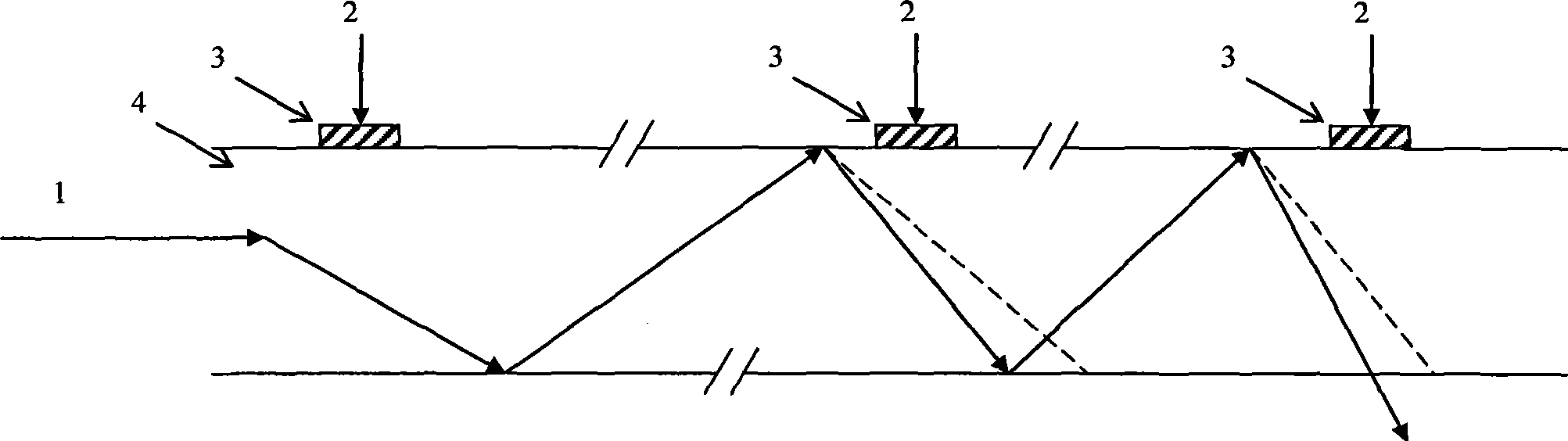
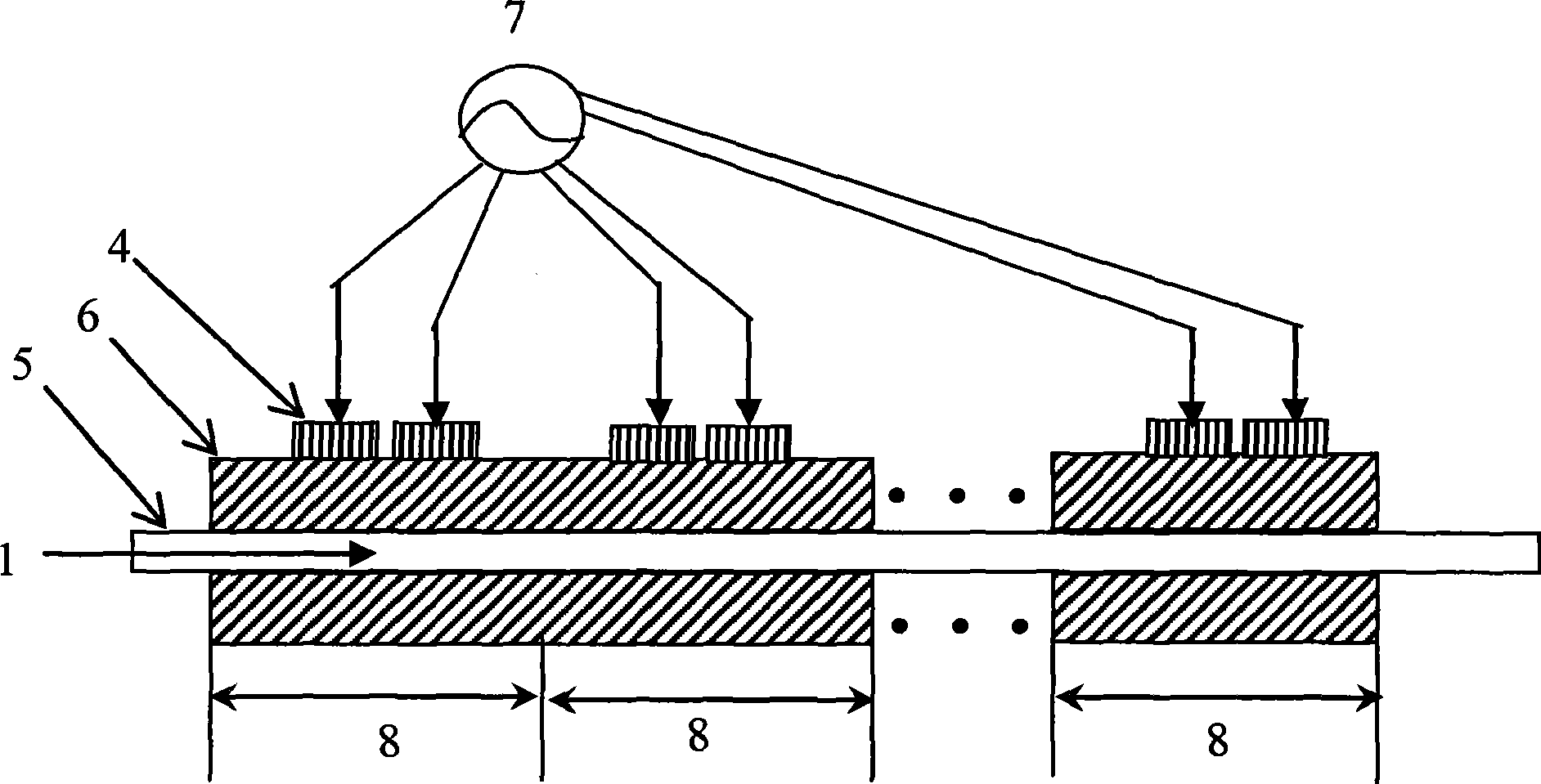
[0027] The continuous acousto-optic diffraction all-fiber Q-switching method provided by the present invention uses multiple sets of piezoelectric transducers to act on the gain fiber of the fiber laser, and each set of piezoelectric transducers has at least two piezoelectric transducers constitute. By changing the phase of the input radio frequency signal of the transducer array in each group of transducers, the output angle of the synthetic sound wave generated by the transducer array is changed to meet the requirement of the Bragg diffraction sound wave incident angle. Each set of piezoelectric transducers can generate sound wave incident angles satisfying Bragg diffraction. After multiple groups of acousto-optic Bragg diffraction, the laser in the gain fiber is separated from the limitation of the numerical aperture, thereby forming a leaky wave, increasing the loss of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com