Laser cloud-detection radar signal self-adaptive identification method based on least mean square algorithm
A recognition method, laser technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problem of low signal-to-noise ratio of the returned signal, achieve high resolution, suppress system and background noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
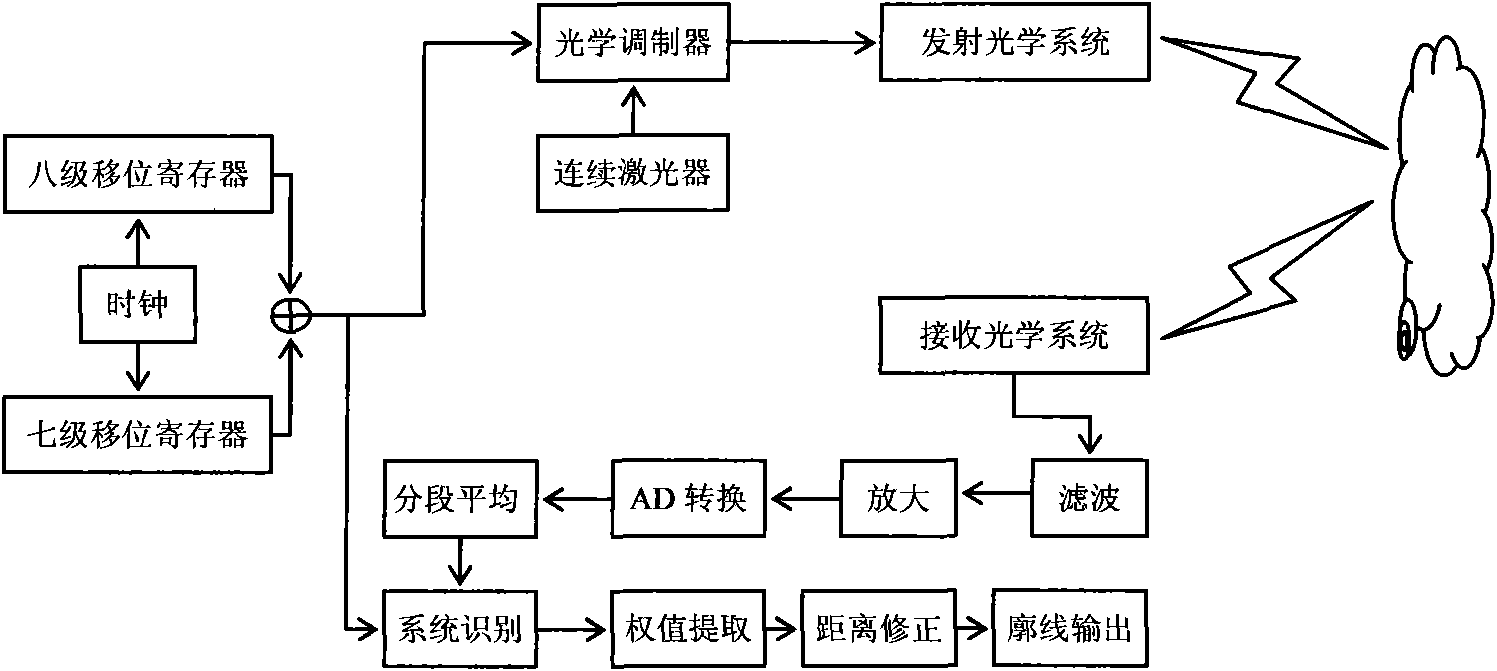
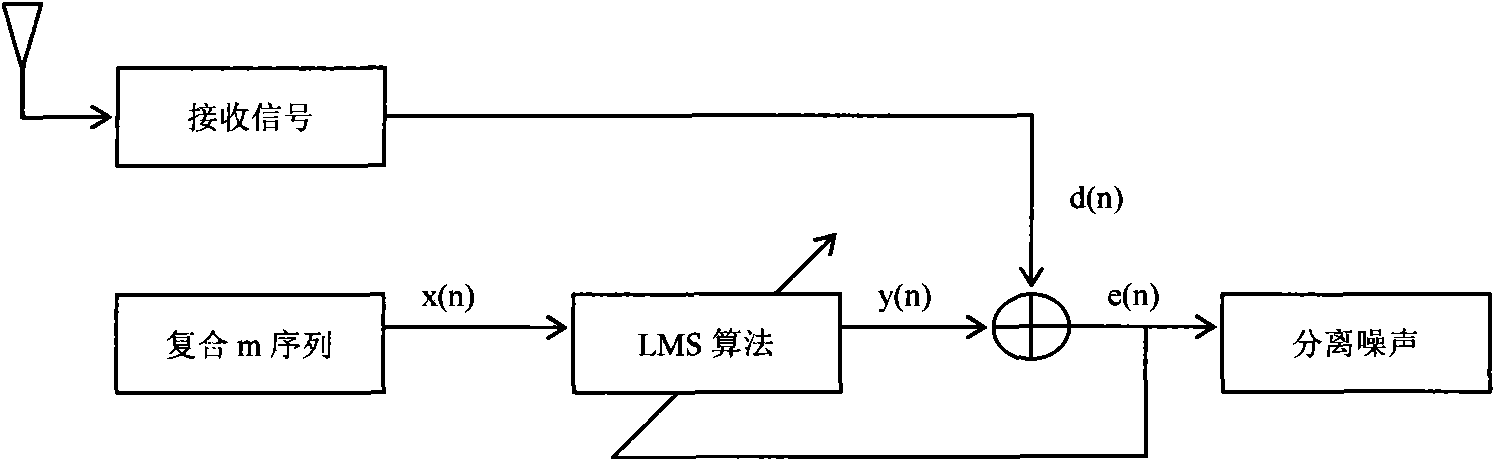
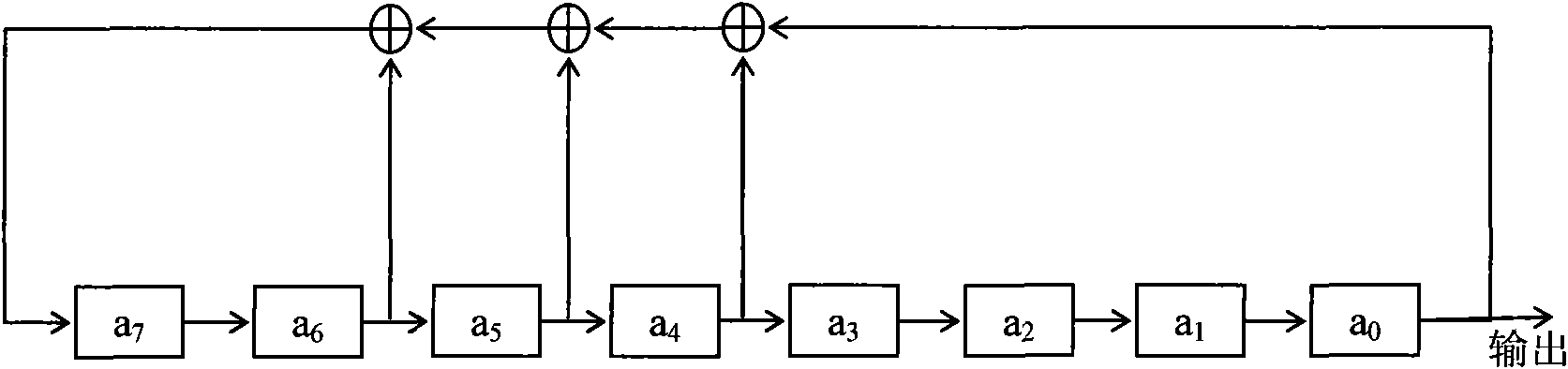
[0031] 1. Principle introduction
[0032] Assuming that the signal modulated by the pseudo-noise sequence emitted by the laser is s(t), it is polluted by various signals and interference noise in the space during the propagation process, and then the signal plus noise scattered into the receiving detector by the clouds in the air is:
[0033] R(t)=s d (t-τ d )+n(t)+s c (t-τ c )
[0034] In the formula: s c (t-τ c ) represents the continuous signal scattered back (the continuous envelope part of the ideal signal in the following schematic diagram, which is usually used to describe fog or aerosol information), and also includes the multipath delay of the useful signal itself and artificial interference signals (enemy interference), n(t) is all additive white Gaussian noise in the channel (such as background light, circuit noise, etc.), s d (t-τ d ) is a sudden change signal (the two impacts of the ideal signal in the following schematic diagram, which are usually used to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com