Novel sintered neodymium-iron-boron permanent-magnet material and manufacture method thereof
A rare earth permanent magnet, NdFeB technology, applied in the field of magnetic materials, can solve the problems of not clearly specifying the optimal composition range of Ho, not specifying Ho, not mentioning the role of Ho and reasonable composition range, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
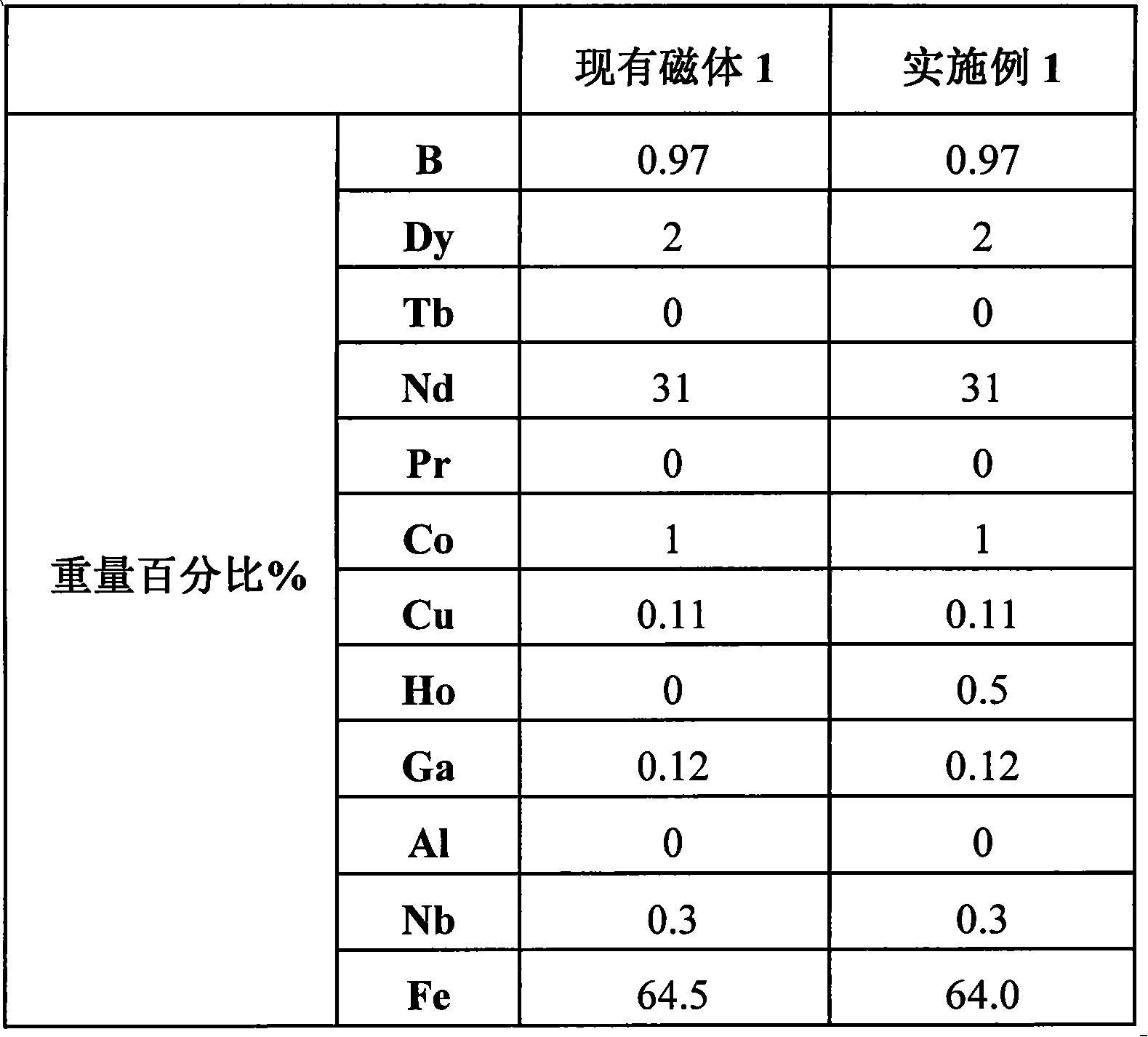
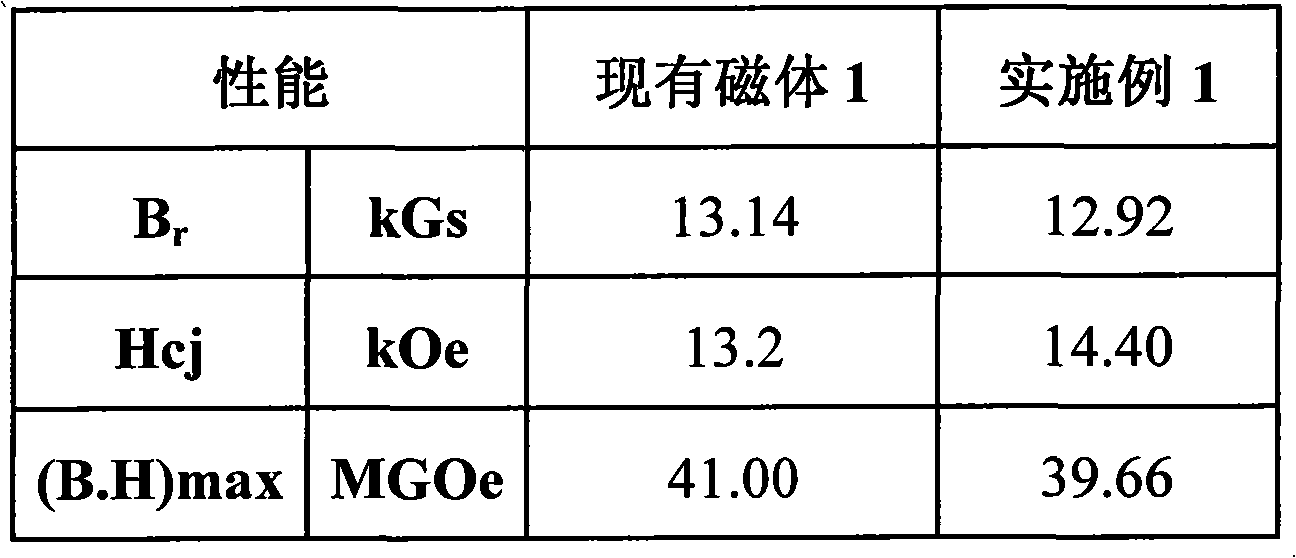
[0045] A kind of neodymium iron boron rare earth permanent magnet material containing Ho, according to the batching described in following table 1:
[0046] Table 1
[0047]
[0048] Then adopt following steps to prepare NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet material:
[0049] (1) Melting-casting: the raw materials are formed into molten alloy liquid by vacuum melting method, and then the molten alloy liquid is cast and cooled into a book-shaped alloy ingot with a thickness of about 40 mm;
[0050] (2) Pulverization: the ingot is pulverized into powder by the hydrogen crushing method, the average particle size is <1mm, and then, the powder is made into a fine powder by jet milling method, and the average particle size is 3-6 μm powder;
[0051] (3) Forming: the powder is pressed into a compact by molding;
[0052] (4) Sintering: sintering the compact in a vacuum sintering furnace at 1075°C for 4 hours;
[0053] (5) Tempering: Tempering the sintered compact in a vacuum sinter...
Embodiment 2
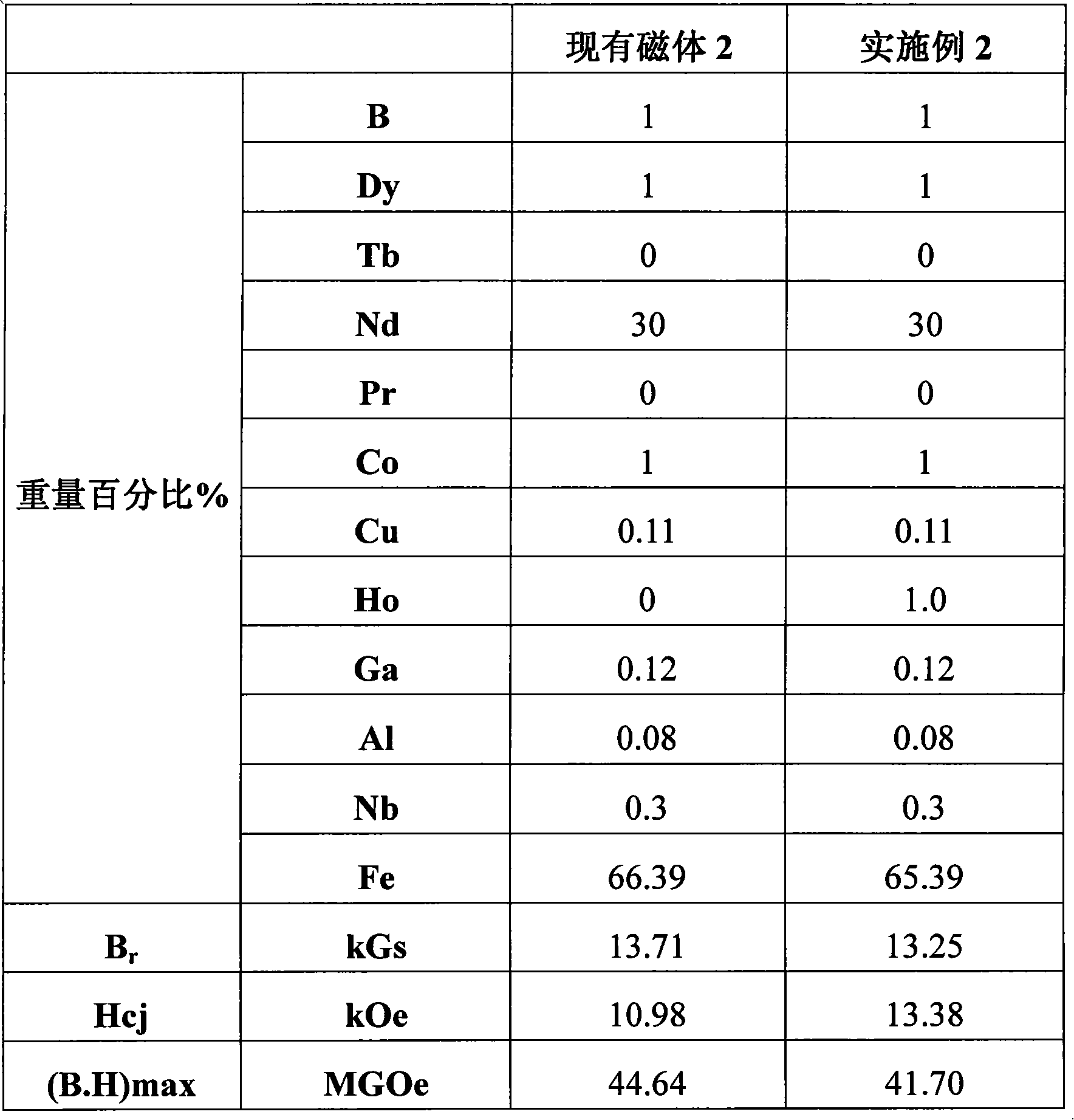
[0059] The smelting step adopts vacuum smelting, and the thickness of the alloy ingot is about 10mm; the ingot is crushed into powder by mechanical coarse crushing method, the average particle size is <1mm, and then, the fine powder is made by jet milling method, the average particle size is 3~ 6 μm powder; forming: molded and cooled isostatic pressing; sintering: the formed blank is sintered in a vacuum sintering furnace at 1085°C for 3 hours; finally tempered at 500°C for 2 hours, and the remaining steps are the same as in Example 1 , to obtain NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet materials. The results are shown in Table 3:
[0060] table 3
[0061]
[0062] By comparison, it can be found that the Hcj of the magnet of Example 2 with Ho added is 2.4 kOe higher than that of the existing magnet 2 without Ho added.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The smelting process adopts vacuum melting, and the alloy ingot with a thickness of about 25mm is used; the solution heat treatment process (1095°C) is used between the casting and crushing processes; the ingot is crushed into powder by hydrogen crushing method, and the average particle size is <1mm, and then, The jet mill is used to grind powder into fine powder with an average particle size of 3-6 μm; forming: forming by molding; the temperature of the vacuum sintering furnace is 1085 ° C, the tempering temperature is 600 ° C, and the rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1 to obtain neodymium iron Boron rare earth permanent magnet material. The results are shown in Table 4:
[0065] Table 4
[0066]
[0067] By comparison, it can be found that the Hcj of the magnet of Example 3 with Ho added is 3.6 kOe higher than that of the existing magnet 3 without Ho added.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com