Method for linking monomolecular DNA to single magnetic bead
A linked, single-molecule technology, applied in the field of DNA processing, can solve the problems of cumbersome steps and low efficiency, and achieve the effect of improving sequencing throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
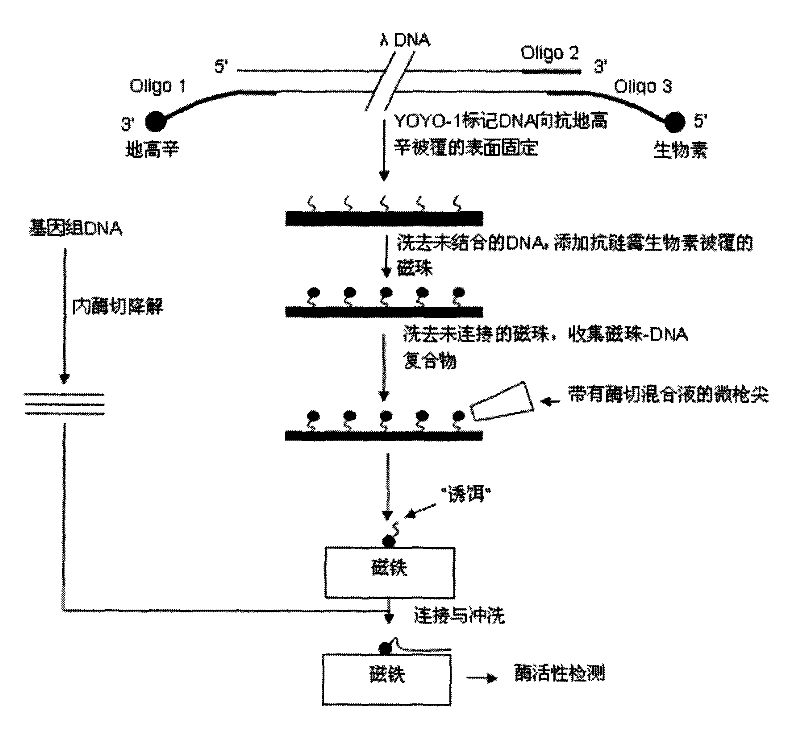
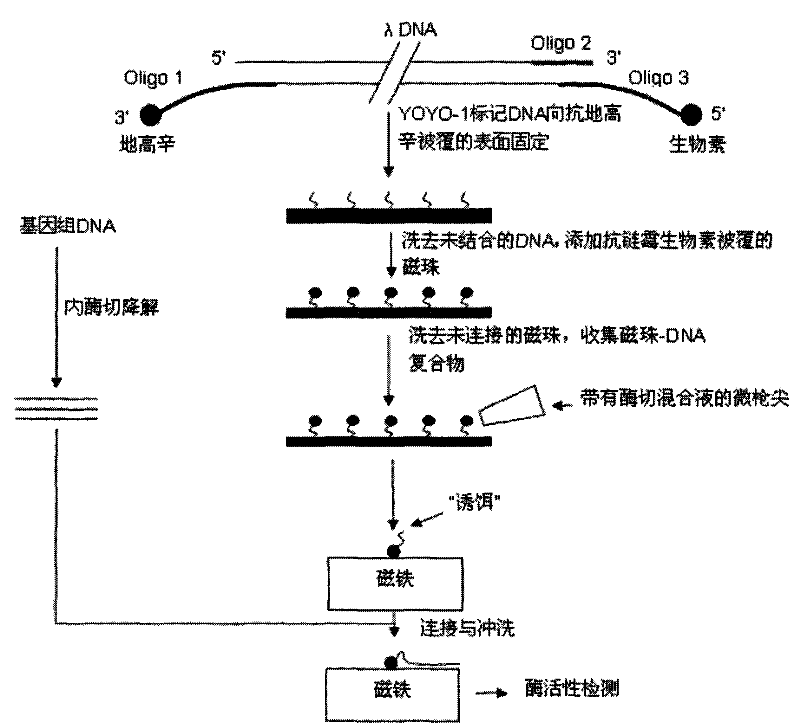
[0020] Step 1, the DNA is fluorescently labeled with YOYO-1, then the 3' end of the DNA is labeled with biotin, and the 5' end is labeled with digoxin;
[0021] Step 2, placing the DNA on the glass whose surface is coated with anti-digoxigenin, so that the 5' end of the DNA reacts with the anti-digoxigenin on the glass surface to immobilize on the surface, and the unfixed DNA molecules are washed away with running water;
[0022] Step 3: Add anti-streptavidin-coated micron or nano-magnetic beads to the glass surface, so that the anti-streptavidin on the magnetic beads reacts with the biotin at the 3' end of the DNA, and washes away the unconnected DNA. free magnetic beads; at this time, the 3' end of the DNA molecule on the glass surface is connected to the glass surface, and the 5' end is connected to the magnetic bead;
[0023] Step 4: Use a micropistol tip to absorb an appropriate amount of DNA endonuclease mixture, and with the assistance of a fluorescent microscope, add t...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Step 1: Fluorescently label the DNA with ethidium bromide, then label its 3' end with biotin, and its 5' end with digoxigenin;
[0031] Step 2: Place the DNA on the glass surface coated with anti-streptavidin, make the 3' end biotin of the DNA react with the anti-streptavidin on the glass surface to immobilize on the surface, wash off the unfixed DNA with running water DNA molecules;
[0032] Step 3: Add anti-digoxigenin-coated micron or nano-magnetic beads to the glass surface, so that the anti-digoxigenin on the magnetic beads reacts with the digoxin at the 5' end of the DNA, and washes away the DNA that is not connected to the DNA. free beads. At this time, the 5' end of the DNA molecule on the glass surface is connected to the glass surface, and the 3' end is connected to the magnetic beads. Only a very small number of magnetic beads are connected to more than one DNA molecule, which can be identified by rotating the magnetic bead with a magnetic bar, because a si...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Step 1, the DNA is fluorescently labeled with Hoechst 33342, then the 3' end is labeled with digoxigenin, and the 5' end is labeled with biotin;
[0039] Step 2: Place the DNA on the glass surface coated with anti-digoxigenin, make the 3' end of the DNA react with the anti-digoxigenin on the glass surface to immobilize on the surface, and wash away the unfixed DNA molecules;
[0040] Step 3: Add anti-streptavidin-coated micron or nano-magnetic beads to the glass surface, so that the anti-streptavidin on the magnetic beads reacts with the biotin at the 5' end of the DNA, and wash with running water to remove the unconnected DNA. free magnetic beads. At this time, the 3' end of the DNA molecule on the surface is connected to the glass surface, and the 5' end is connected to the magnetic beads;
[0041] Step 4: Use a micropistol tip to absorb an appropriate amount of DNA endonuclease mixture, and with the assistance of a fluorescent microscope, add the enzyme digestion m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com