Soft magnetic ribbon, magnetic core, magnetic part and process for producing soft magnetic ribbon
A soft magnetic, thin strip technology, applied in the direction of the magnetic core/yoke, the application of the magnetic film to the substrate, the magnetic layer, etc., to achieve the effect of low magnetic flux density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
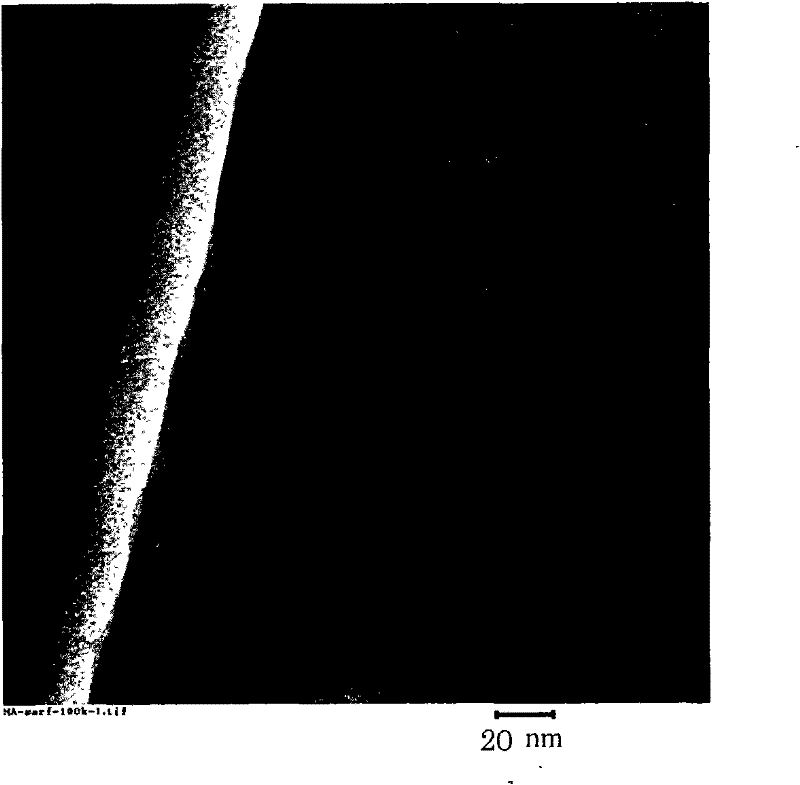
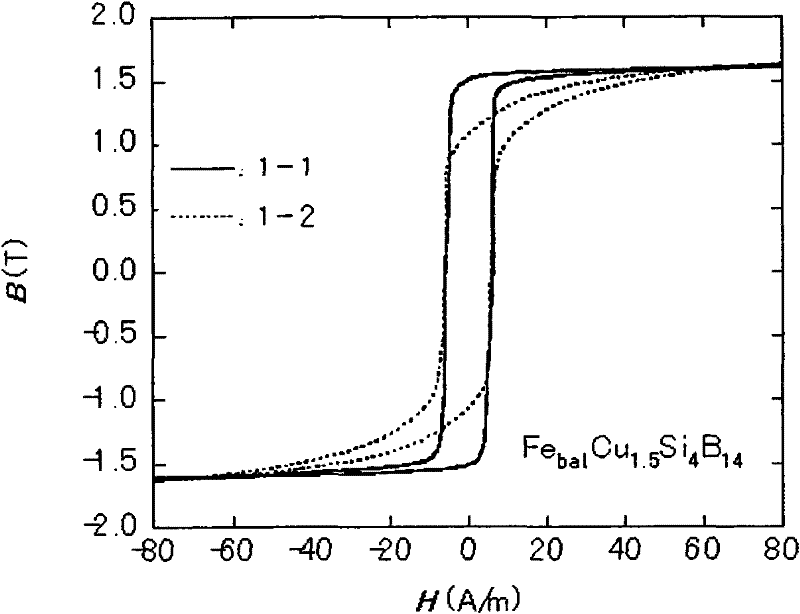
[0060] (Example 1) Thin ribbons each having a width of 5 mm and a thickness of about 20 μm and each having a composition shown in Table 1 were prepared by a melt quenching method using a single roll. Alloy thin strips were prepared by spraying molten alloy heated to 1300°C onto a Cu—Be alloy roll with an outer diameter of 300 mm rotating at a peripheral speed of 32 m / s. As a result of X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation, it was found that thin ribbons contained structures dispersed in an amorphous phase at a volume fraction of less than 30%. The ribbon is annealed such that the average temperature ramp rate above 300°C is above about 200°C / min. The ribbon was kept at a holding temperature of 450° C. for 10 minutes, and then allowed to cool to obtain a soft magnetic ribbon of the present invention. In each sample there was: a crystalline layer about 20 nm thick on the top surface of the ribbon, an amorphous layer about 30 nm thick inside th...
Embodiment 2
[0062] (Example 2) The soft magnetic thin strip prepared in Example 1 was used to measure the apparent power. figure 2 The relationship between the apparent power and the magnetic flux density of the soft magnetic ribbon of the present invention is shown. In addition, Table 2 shows the apparent power S measured under the conditions of 50 Hz and 1.55T, 1.60T and 1.65T, respectively, for the alloy composition of the soft magnetic ribbon of the present invention (Examples 1-1 to 1-4) 1.55 / 50 , S 1.60 / 50 and S 1.65 / 50 The data. For comparison, the data for grain-oriented silicon steel sheets are also shown. In a wide region of magnetic flux density of about 1.55T to 1.7T, the apparent power properties of the soft magnetic ribbon of the present invention are better than those of Fe-based amorphous materials and grain-oriented silicon steel sheets. These results combined with the results of Example 1 show that the soft magnetic ribbon of the present invention has particularly e...
Embodiment 3
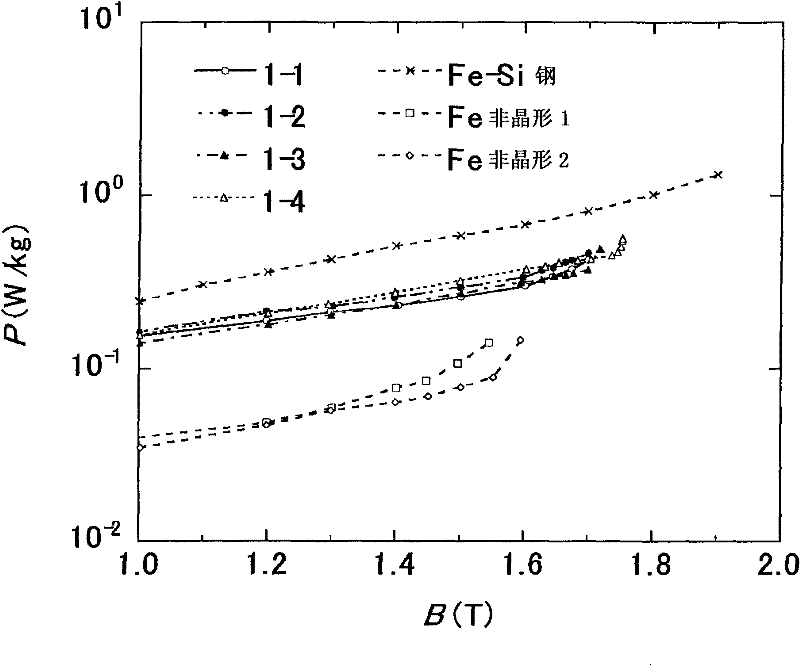
[0064] (Example 3) The soft magnetic strip prepared in Example 1 was used to measure iron loss at frequencies of 400 Hz and 1 kHz. Table 3 shows the iron loss P at 1.0T and 400Hz, and 0.5T and 1kHz of the soft magnetic strip and grain-oriented silicon steel sheet of the present invention, respectively. 1.0 / 400 and P 0.5 / 1k . The difference in iron loss between the material of the invention and the grain-oriented silicon steel plate increases with frequency, indicating that the material of the invention is suitable for high-frequency applications. also, image 3 The results of the magnetic flux density dependence of the iron loss measured by using the soft magnetic thin strips in Examples 1 to 4 for each frequency are shown.
[0065] name composition (characteristics) Amorphous layer presence or absence P 1.0 / 400 (W / kg) P 0.5 / 1k (W / kg) Example 1-1 Fe bal. Cu 1.4 Si 5 B 13 have 2.6 3.6 Example 1-2 Fe bal. Cu 1.4 Si 4 B...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com