Solid-liquid separator
A solid-liquid separation and adding device technology, which is applied in the direction of liquid separation, separation method, grease/oily substance/floating matter removal device, etc., can solve the problems of difficult waste, large amount of sludge, etc., to reduce the amount of medicine, The effect of reducing the amount of sludge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
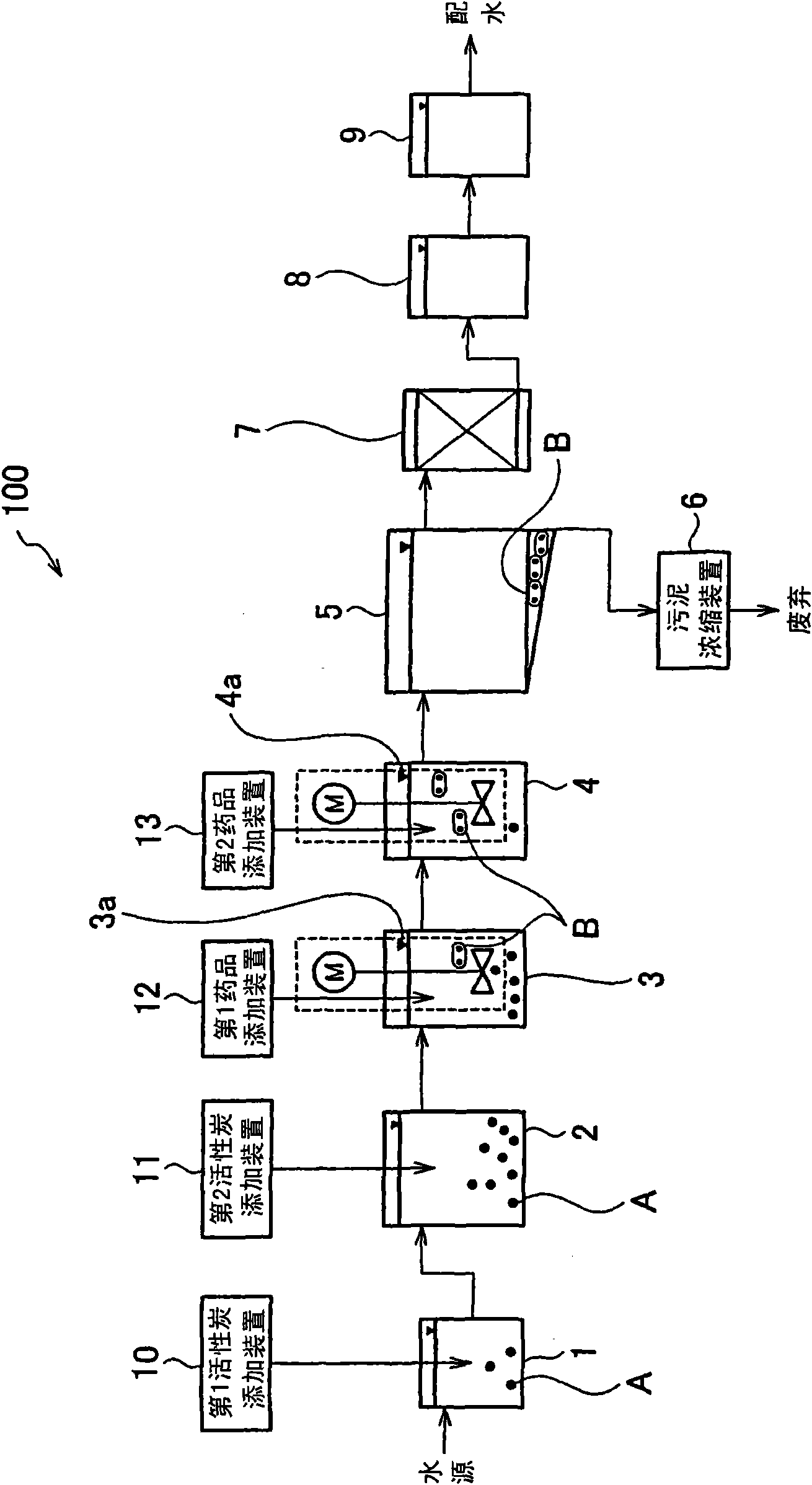
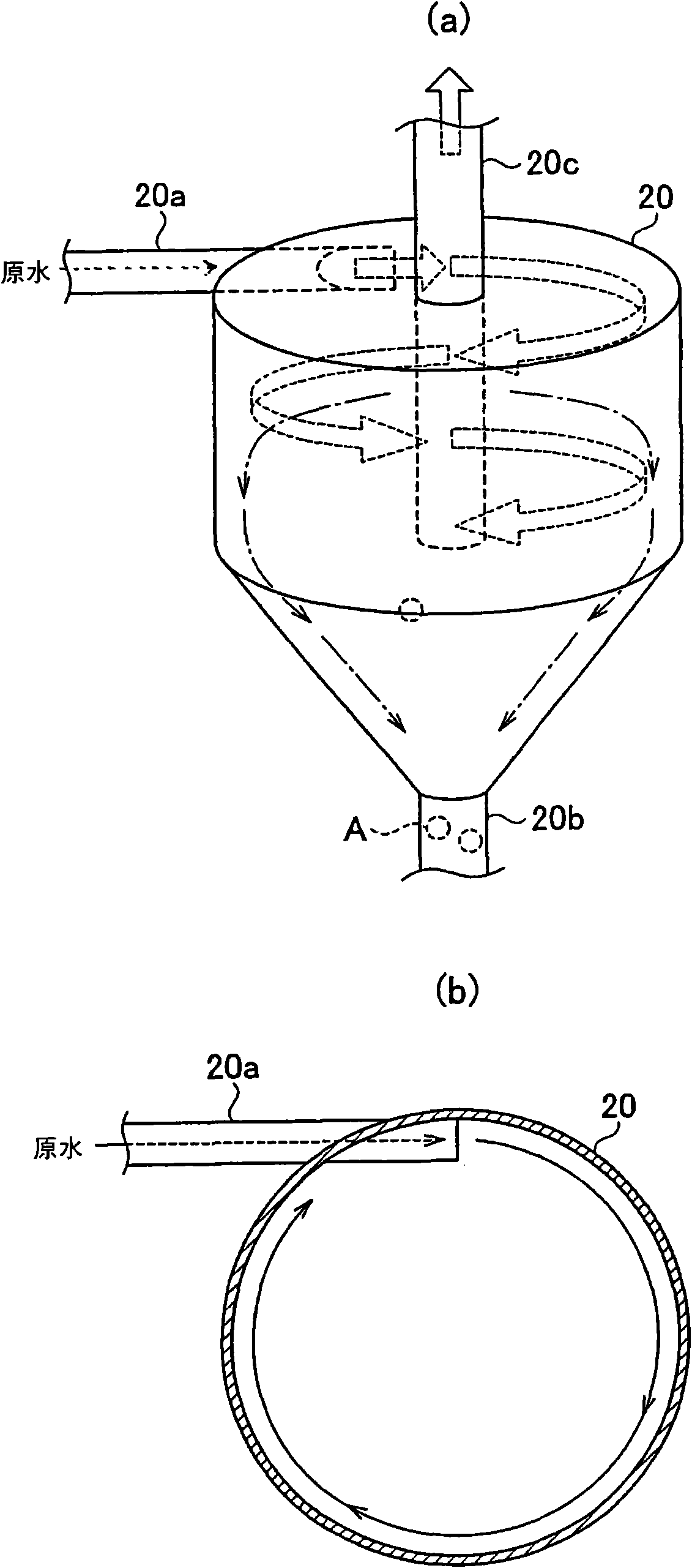
[0037] use figure 2 The water treatment system 101 provided with the solid-liquid separator 51 of the first embodiment will be described. The solid-liquid separator 51 of the first embodiment includes an activated carbon adding device 10 for adding activated carbon A to raw water to be treated, and a liquid cyclone 20 for separating activated carbon A adsorbing suspended matter in the raw water from the raw water.
[0038] Such as figure 2As shown, the water treatment system 101 is that, in addition to the solid-liquid separation device 51 equipped with the activated carbon addition device 10 and the liquid cyclone 20, it also has: a water intake well 1, which stores the raw water taken from water sources such as rivers, and adds Activated carbon A; collecting well 2, the raw water separated from activated carbon A is supplied from the liquid cyclone 20; the rapid stirring tank 3 is supplied with raw water from the collecting well 2; the first drug adding device 12, the coa...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
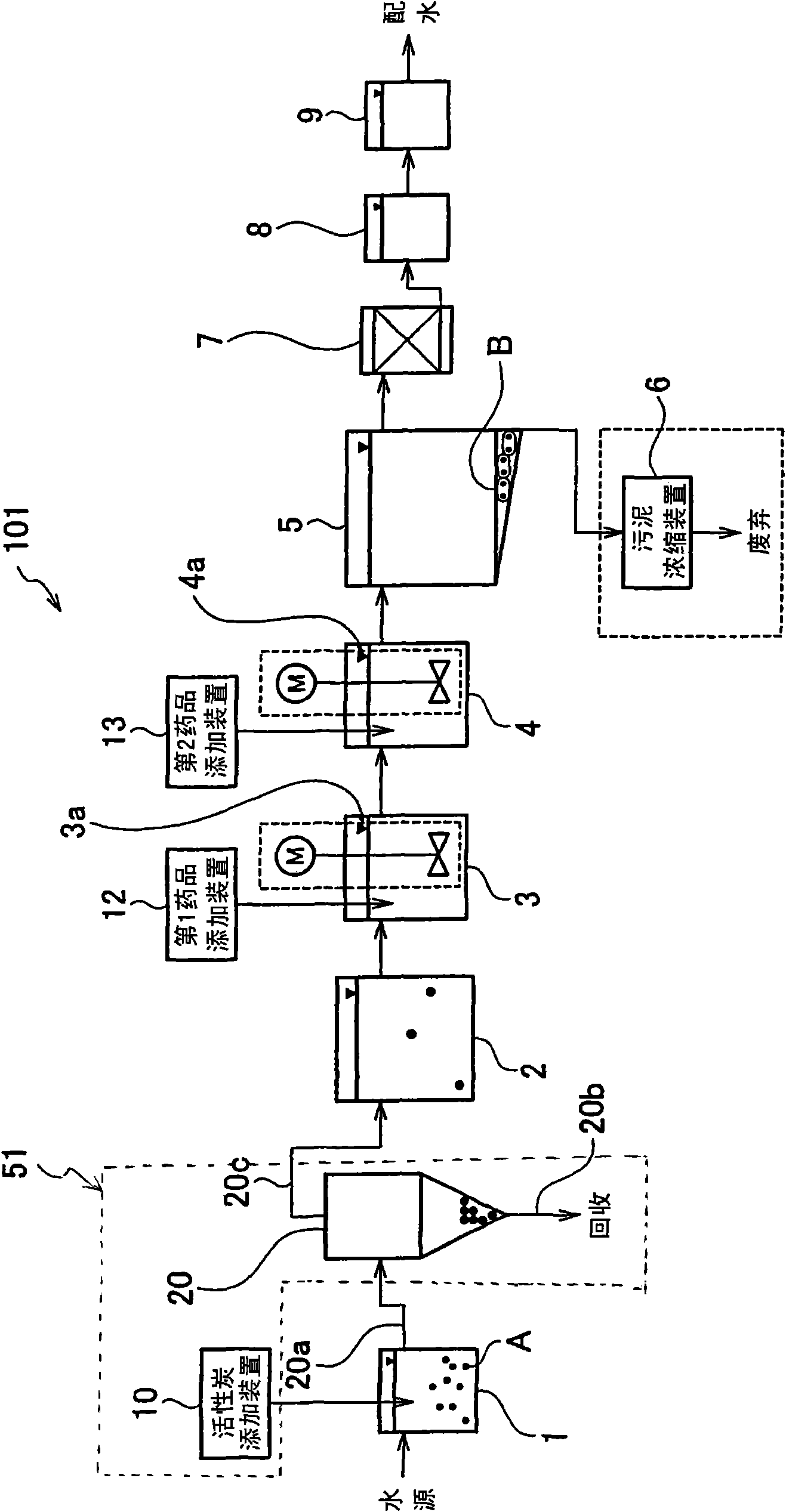
[0054] use Figure 4 The water treatment system 102 provided with the solid-liquid separator 52 of the second embodiment will be described. Figure 4 The solid-liquid separator 52 of the second embodiment shown and the use figure 2 Compared with the solid-liquid separation device 51 of the first embodiment described above, the difference is that the solid-liquid separation device 52 of the second embodiment has two activated carbon adding devices 10, 11, and has two liquid cyclones 20, twenty one. Here, the device for adding activated carbon to the water intake well 1 is referred to as the first activated carbon adding device 10 , and the device for adding activated carbon A to the water collection well 2 is referred to as the second activated carbon adding device 11 . Furthermore, the liquid cyclone in the rear stage of the water intake well 1 is the first liquid cyclone 20 , and the liquid cyclone in the rear stage of the water collection well 2 is the second liquid cyclo...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0068] use Figure 7 The water treatment system 105 provided with the solid-liquid separator 55 of the third embodiment will be described. Figure 7 The solid-liquid separation device 55 of the third embodiment shown and the use Figure 4 Compared with the water treatment system 102 of the second embodiment 52 described above, the difference is that the solid-liquid separation device 55 of the third embodiment is that the activated carbon discharge pipe 20b that discharges activated carbon from the first liquid cyclone 20 is a circulation pipe. The activated carbon discharge pipe 21b that discharges activated carbon from the second liquid cyclone 21 is connected to the second activated carbon addition device 11 as a circulation line. In addition, in the water treatment system 105 , after the coagulation and sedimentation in the coagulation and sedimentation tank 5 , the same as the water treatment system 101 , the sand filter 7 , the chlorine disinfection device 8 and the wat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com