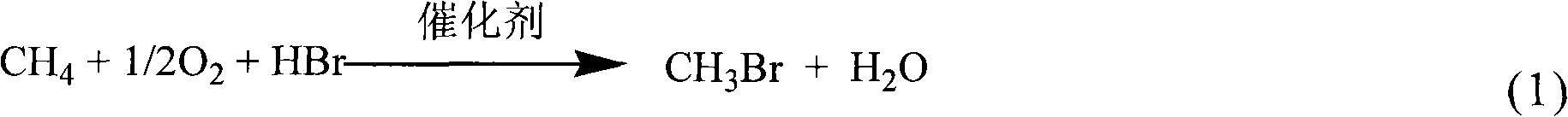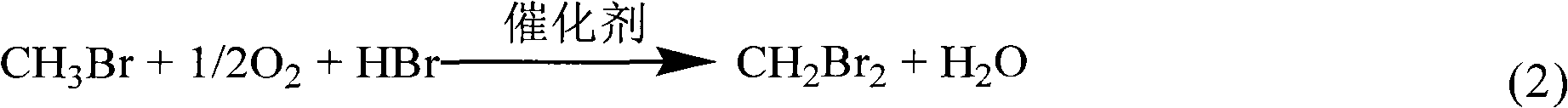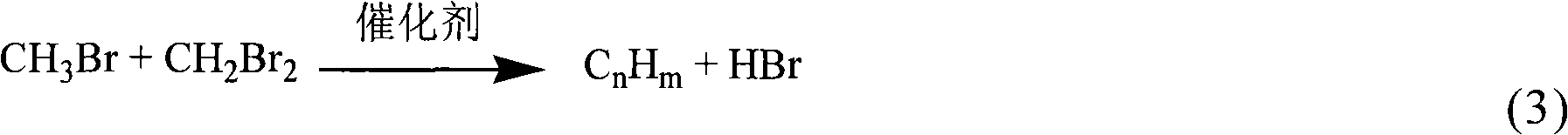Method for preparing methyl bromide, high-carbon hydrocarbon, methanol or dimethyl ether by bromine oxidation of methane
A high-carbon hydrocarbon and catalyst technology, applied in the field of methane bromination oxidation, can solve the problems of aggravating the greenhouse effect and wasting limited carbon resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] Example 1: Low CH 4 / O 2 Feed ratio case, adding a single CO 2 bromination reaction of methane
[0126] Under the same reaction conditions as in Comparative Example 1, a certain amount of CO was added before the feed gas entered the reactor. 2 , CO 2 Commercial finished CO desorbed by industrial decarbonization processes from outside the reaction 2 . After the reaction was stable for 2 hours, samples were taken to analyze the content of components in the tail gas.
[0127] When a certain amount of CO is added before the feed gas enters the reactor 2 Afterwards, methane conversion, methyl bromide yield, dibromomethane yield, CO yield, CO 2 The yields are shown in Table 1.
[0128] CO 2 The yield of the added CO 2 Does not participate in the reaction calculation, that is, the CO in the mixed gas at the outlet of the first-stage reactor 2 The amount of CO added to the first-stage reactor 2 The ratio of the difference between the amount of the product and the am...
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2: Low CH 4 / O 2 Oxidation of methane with a single addition of CO at the feed ratio
[0133] Under the same reaction conditions as in Comparative Example 1, a certain amount of CO was added before the feed gas entered the reactor, and the CO came from the commercial finished product CO obtained through the industrial steam reforming process outside the reaction. After the reaction was stable for 2 hours, samples were taken to analyze the content of components in the tail gas.
[0134] When a certain amount of CO is added before the feed gas enters the reactor, the yield of CO is calculated based on the fact that the added CO does not participate in the reaction, that is, the amount of CO at the outlet of the first-stage reactor is equal to the amount of CO added in the first-stage reactor The ratio of the difference in the amount of the amount to the amount of methane in the raw material, and the yield of other products refers to the ratio of the amount of th...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Example 3: Low CH 4 / O 2 In the case of feed ratio, adding carbon oxides (CO and CO 2 ) methane bromination oxidation reaction
[0139] Operated under the same reaction conditions as in Comparative Example 1. Introduce 5mL / min of CO into the first stage reactor 2 And a certain amount of CO, where CO comes from the commercial finished CO obtained from the industrial steam reforming process outside the reaction, CO 2 Commercial finished CO desorbed by industrial decarbonization processes from outside the reaction 2 . Repeat the previous reaction operation. After the reaction was stable for 2 hours, samples were taken to analyze the content of components in the tail gas.
[0140] When a certain amount of CO and CO are added before the feed gas enters the reactor 2 Afterwards, methane conversion, methyl bromide yield, dibromomethane yield, CO yield, CO 2 The yields are shown in Table 3.
[0141] CO 2 The yield of the added CO 2 Does not participate in the reacti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com