Pseudo-random code estimation method of direct sequence spread spectrum system
A direct-sequence spread spectrum and pseudo-random code technology, which is applied in the transmission system, multiplexing code generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of not satisfying the estimation of cyclic shift characteristics, affecting the estimation accuracy of pseudo-random code, and high requirements for timing synchronization , to overcome the influence of the principle of time-frequency uncertainty, fast operation speed, and the effect of overcoming estimation errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
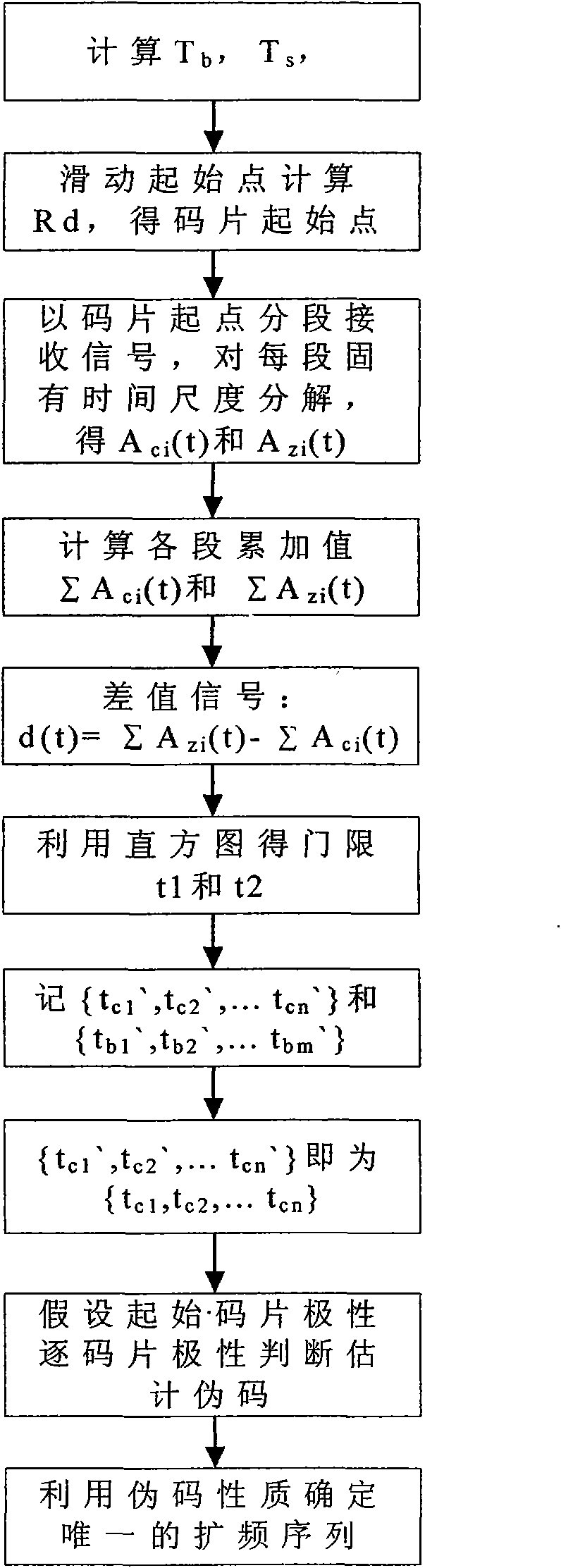
[0027] refer to figure 1 , the steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0028] Step 1, calculate the period T of the spread spectrum pseudo-random code in the received signal s and the symbol period T of the received signal b .
[0029] The period T of the spread spectrum pseudo-random code is obtained from the quadratic spectrum of the received signal r(t) s , its quadratic spectrum S r (e) calculation expression is: S r (e)=|DFT(S r (f))| 2 (1)
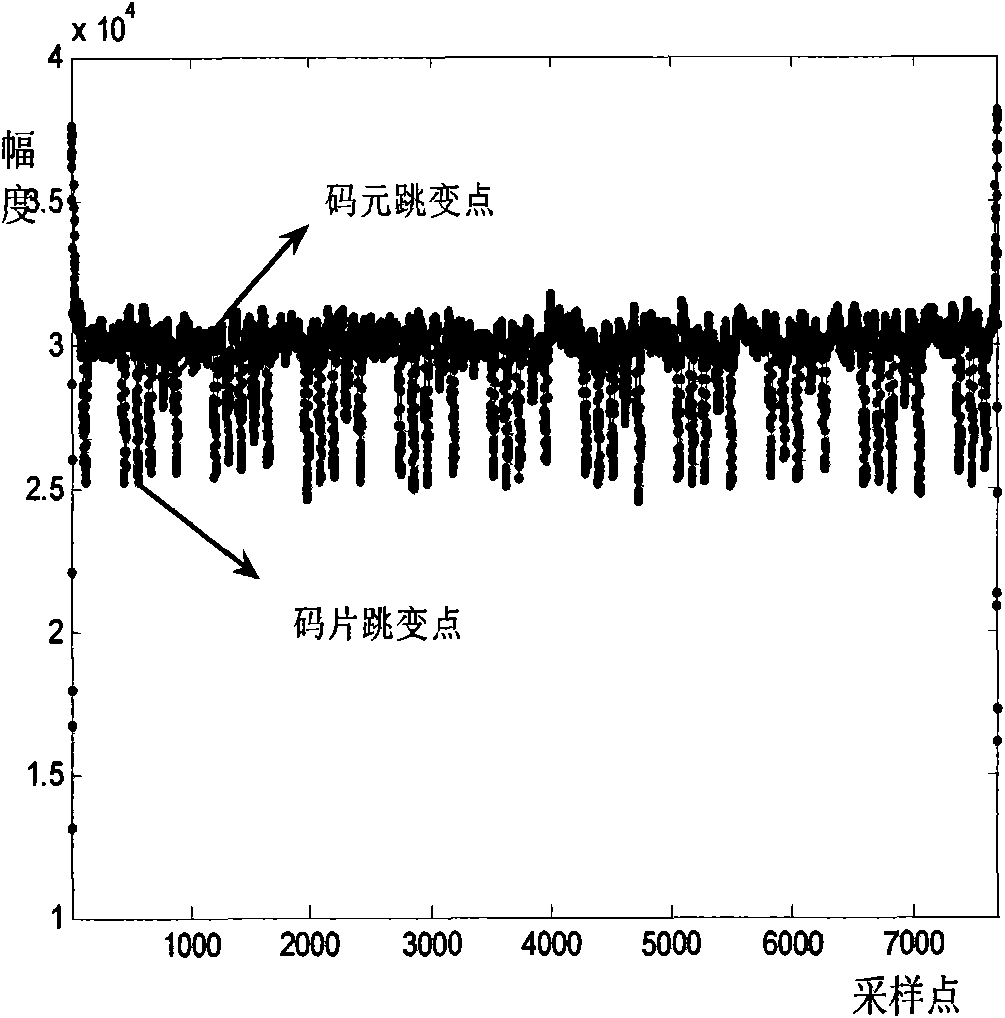
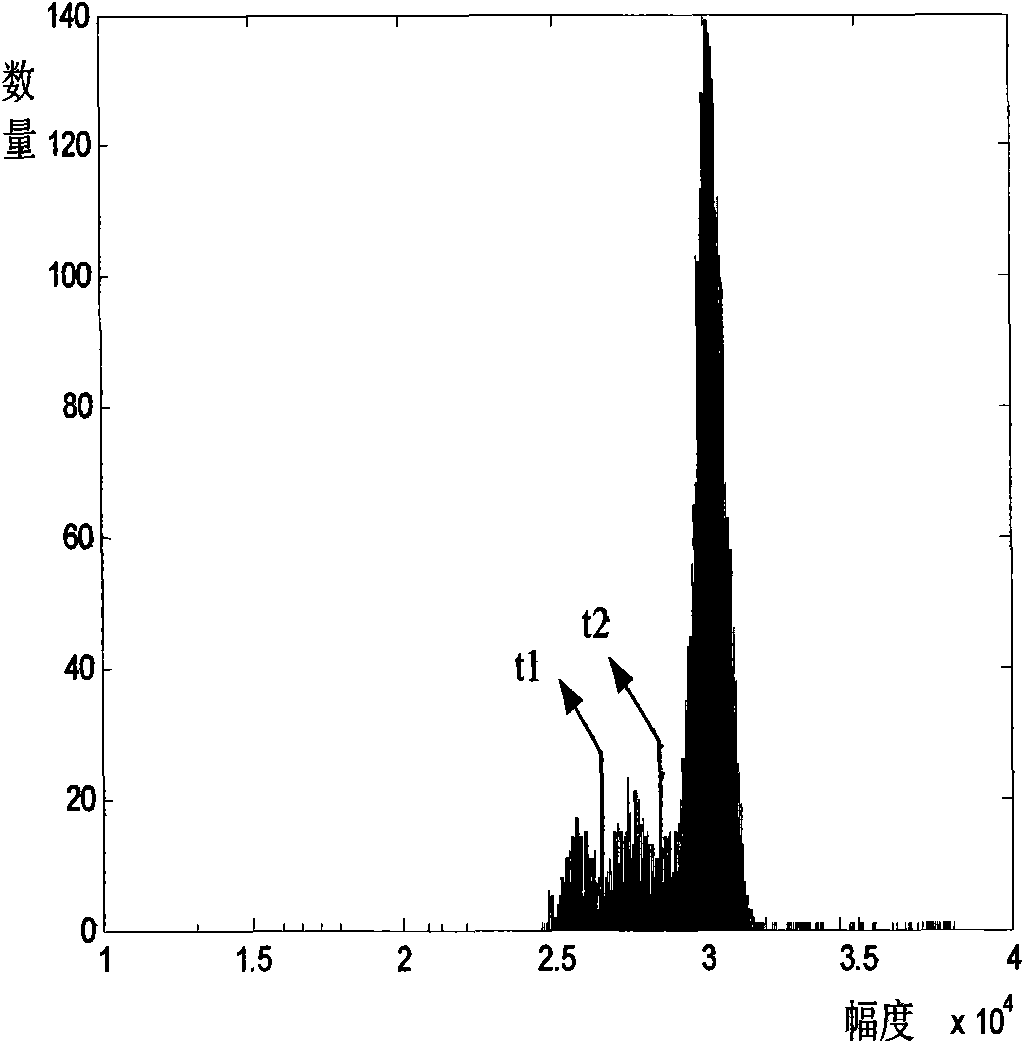
[0030] where S r (f) represents the power spectrum of the received signal, and DFT represents the S r The power spectrum of (f) is Fourier transformed, and the secondary power spectrum of the received signal is defined as S r The square of the modulus after Fourier transform of the power spectrum of (f). Search for the adjacent local maximum of the quadratic spectrum within a certain range, determine the frequency of the quadratic power spectrum corresponding to the local maximum, and calculate its interval T ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com