Aluminum fin material for heat exchanger
A technology of heat exchangers and aluminum fins, applied in the field of fin materials, can solve the problems of deodorization performance decline, loss of deodorization performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach 》
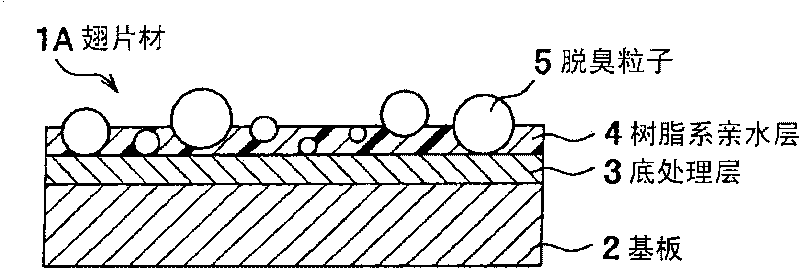
[0020] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view showing a schematic structure of an aluminum fin material for a heat exchanger (hereinafter referred to as a "fin material") according to the first embodiment of the present invention. This fin material 1A has a substrate 2 made of aluminum (Al) or an Al alloy, a primer layer 3 disposed on the substrate 2, and a resin-based hydrophilic layer 4 disposed on the primer layer 3, and the deodorizing particles 5 are coated with resin. The resin-based hydrophilic layer 4 remains exposed on the surface of the resin-based hydrophilic layer 4 .
[0021] Although in figure 1 In the figure, the method in which the primer treatment layer 3 and the resin-based hydrophilic layer 4 are provided on only one side of the substrate 2 is shown, but the primer treatment layer 3 and the resin-based hydrophilic layer 4 may be provided on both surfaces of the substrate 2 . In addition, in order to improve the corrosion resistance of the fin material 1A, a...
no. 2 Embodiment approach 》
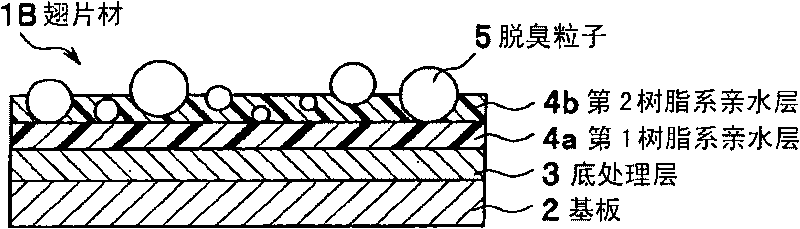
[0045] figure 2 is a cross-sectional view showing a schematic structure of a fin material according to a second embodiment of the present invention. This fin material 1B has a substrate 2, a primer layer 3 provided on the substrate 2, a first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a provided on the primer layer 3, and a first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a provided on the first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a. The second resin-based hydrophilic layer 4b. The deodorizing particles 5 are held by the resin-based hydrophilic layer 4b so as to be exposed on the surface of the second resin-based hydrophilic layer 4b, so that a good deodorizing effect can be obtained from the initial stage. In the fin material 1B, the total film thickness of the first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4 a and the second resin-based hydrophilic layer 4 b is set to 0.05 to 5 μm for the same reason as the fin material 1A described above, preferably 0.2~2μm. The same applies to the fin materials 1C and 1D des...
no. 3 Embodiment approach 》
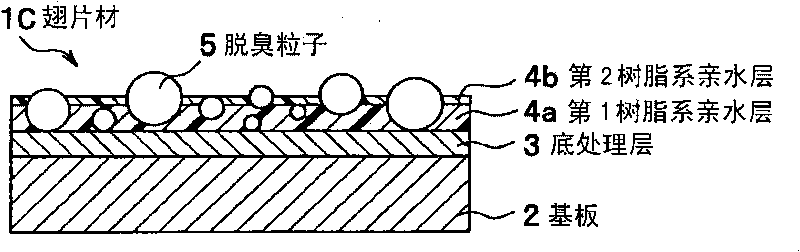
[0048] image 3 It is a cross-sectional view showing a schematic structure of a fin material according to a third embodiment of the present invention. This fin material 1C has a substrate 2, a primer layer 3 provided on the substrate 2, a first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a provided on the primer layer 3, and a first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a provided on the first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a. In the second resin-based hydrophilic layer 4b, the deodorizing particles 5 are held by the first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a so as to be exposed on the surface of the second resin-based hydrophilic layer 4b.
[0049] The substrate 2 , the primer layer 3 , and the deodorizing particles 5 constituting the fin material 1C are the same as those used for the fin material 1A. The first resin-based hydrophilic layer 4a is composed of the above-mentioned poorly soluble hydrophilic resin, and the second resin-based hydrophilic layer 4b is composed of the above-mentioned water...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com