Method for electrochemically machining titanium alloy large-scale blades
A processing method and large-size technology, applied in the field of electrolytic machining of large-size titanium alloy blades, to achieve the effects of mature technology, shortened process, and small pressure loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Prepare a compressor rotor blade, the material is TC4, the electrolytic processing area is 960cm 2 .
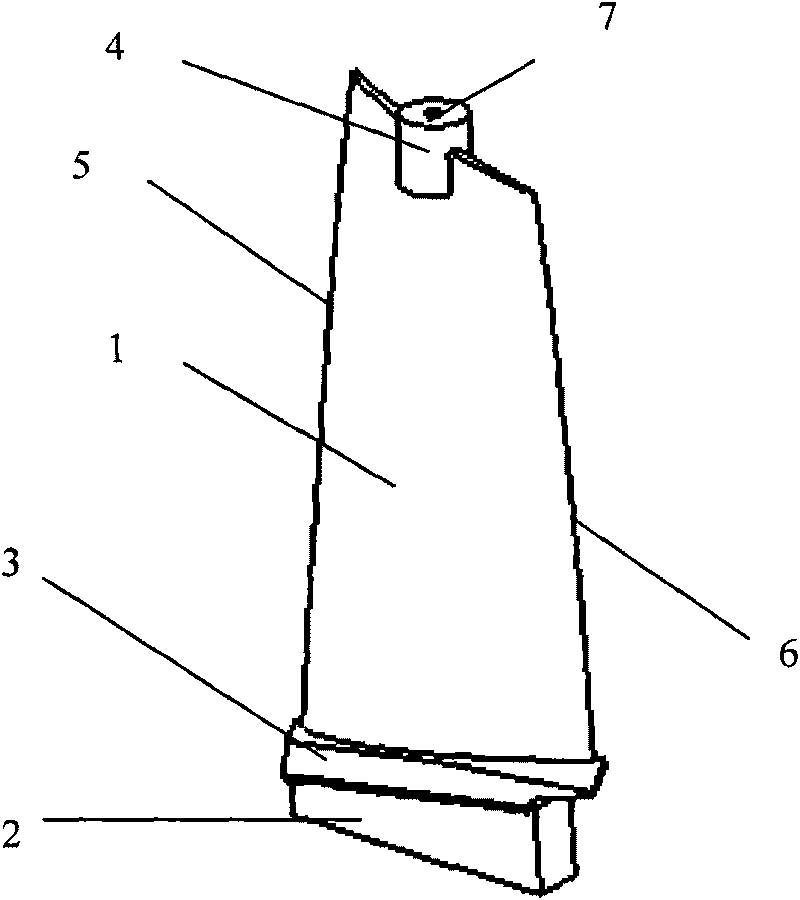
[0039] The structure of the blade blank is as figure 2 As shown, it includes the airfoil part, the mortise 3 and the boss 2, the two sides of the airfoil part are the blade back 1 and the blade basin respectively, the two sides are the air inlet edge 5 and the exhaust edge 6 respectively, and the top is provided with The round table 4 has a center hole 7 processed on the round table 4, which is the 60°A-type center hole described in GB145-85, and the size is as follows Figure 6 As shown. Boss 2 is a cube with the same width and length as the bottom surface of tenon 3, and the same length as the bottom surface of tenon 3, with a height of 40mm; the top surface of boss 2 is connected with tenon 3, and the The opposite bottom surface is the conductive surface; the side of the boss 2 on the same side as the blade back 1 is the blade back side, the side on the same side...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The blade material is TC6, and the electrolytic processing area is 880cm 2 .
[0047] The structure of the blade blank is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the height of the boss is 30mm.
[0048] The material of the blade basin electrode and the blade back electrode is 1Cr18Ni9Ti, the cathode width is 2.5mm larger than the blade blank width, the dimensional accuracy grade is IT8, and the working surface roughness value is Ra 0.8μm.
[0049] The machine tool used is the same as in Example 1, and the installation method of the blade blank in the working box is the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the pressing force of the tip is 3500N, and the width of the electrolyte inlet is 3 times the thickness of the blade.
[0050] The electrolytic machining method is the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the machining parameters are: initial gap 0.9mm, electrode feed speed 0.3mm / min, delay time before machining 4s, delay time after machining 4s,...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The blade material is TC11, and the electrolytic processing area is 770cm 2 .
[0054] The structure of the blade blank is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the height of the boss is 20 mm.
[0055] The material of the blade pot electrode and the blade back electrode is 1Cr18Ni9Ti, the cathode width is 2.5 mm larger than the blade blank width, the dimensional accuracy grade is IT8, and the working surface roughness value is Ra 0.4 μm.
[0056] The machine tool used is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the installation method of the blade blank in the working box is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the pressing force of the tip is 3000N, and the width of the electrolyte inlet is 2.5 times the thickness of the blade.
[0057] The electrolytic machining method is the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the machining parameters are: initial gap 0.8mm, electrode feed speed 0.4mm / min, delay time before machining 5s, delay time after mach...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com