Nesting mixed flow constructed wetland
A technology of constructed wetland and mixed flow, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., and can solve problems such as limited application, large footprint, and single rules of constructed wetlands. Achieve the effects of convenient operation and maintenance, saving floor space, low investment and operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
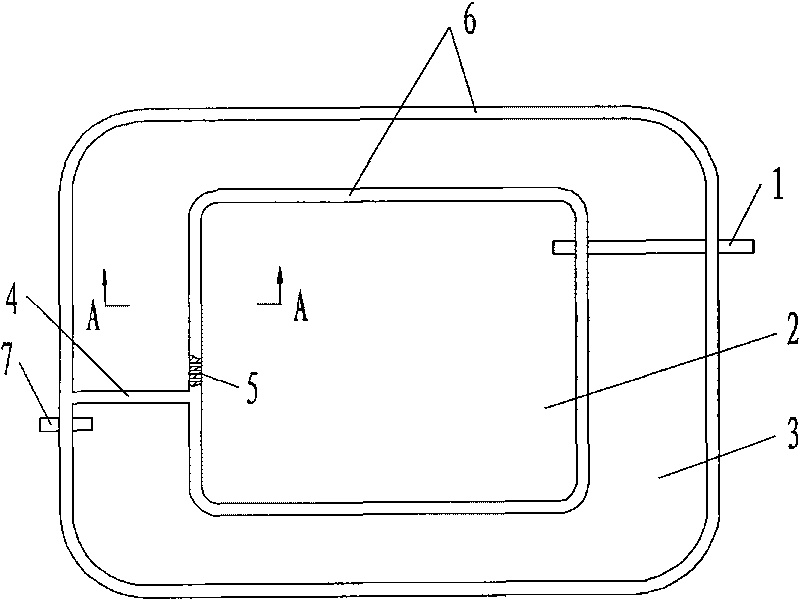
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment is a nested mixed flow artificial wetland formed by nesting and connecting the internal horizontal subsurface flow wetland 2 and the external surface flow wetland 3 in series. The external surface flow wetland 3 is in a ring shape, and the internal horizontal subsurface flow wetland 2. It can be set into a square or a rectangle according to local conditions, and the internal and external wetlands are connected through the perforated plate 5 to form a "pond-island" landscaping mode. The inner horizontal subsurface flow wetland 2 is provided with a water inlet pipe 1 , and the outer surface flow wetland 3 is provided with a water outlet pipe 7 . The water outlet pipe 7 on the outer surface wetland 3 is provided with a partition plate 4, which separates the water outlet pipe 7 from the perforated plate 5, and makes the sewage flow circularly along the pool body. Such as figure 2 As shown, the lower part of the matrix layer of t...
Embodiment 2
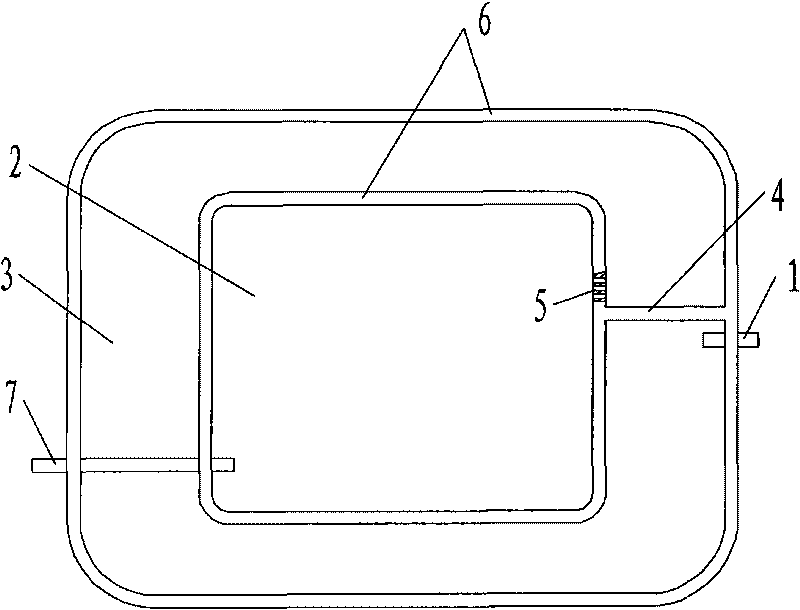
[0026] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment is a nested mixed-flow artificial wetland formed by nesting and connecting the internal surface flow wetland 3 and the external horizontal subsurface flow wetland 2 in series, forming a "garden-pond" landscaping mode. The outer horizontal subsurface flow wetland 2 is provided with a water inlet pipe 1 , and the inner surface flow wetland 3 is provided with a water outlet pipe 7 . Other configurations are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0027] During operation, the sewage directly enters the gravel layer 8 of the horizontal subsurface flow wetland 2 through the water inlet pipe 1, and flows circularly along the pool body. The preliminarily purified sewage enters the surface flow wetland 3 through the perforated plate 5, undergoes further treatment, and is finally discharged through the outlet pipe 7.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment is a nested mixed-flow artificial wetland formed by nesting and connecting the external surface flow wetland 3 and the internal vertical subsurface flow wetland 13 in series, forming a "pond-pagoda" landscaping mode. The inner vertical subsurface flow wetland 13 is provided with a water inlet pipe 1 , and the outer surface flow wetland 3 is provided with a water outlet pipe 7 .
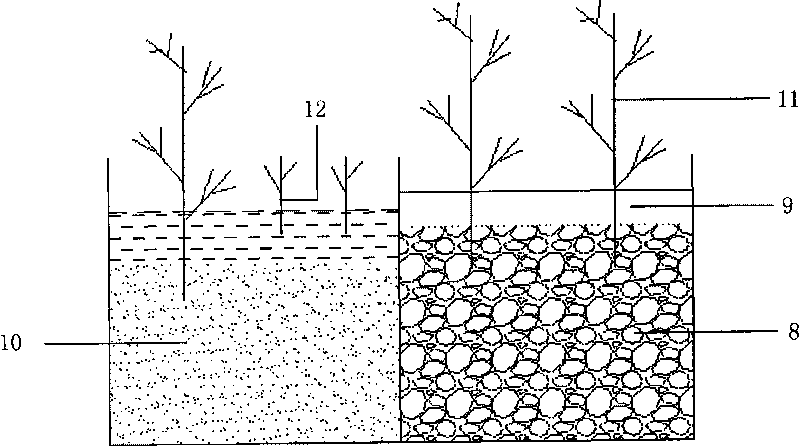
[0030] The lower part of the matrix layer of the vertical subsurface wetland 13 is filled with a mixture of blast furnace slag, coal ash and gravel with good phosphorus removal effect, and its thickness is 90cm-105cm; The matrix layer of 3 is all the mixture 10 of pastoral soil and yellow sand, about 55cm~70cm thick. Other configurations are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0031] When the system is running, the sewage enters the pastoral soil layer of the vertical underflow wetland 13 through the water inlet pipe 1, enters the gravel layer through in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com