Method for recovering waste heat during processing of starchy material
A starchy raw material and waste heat recovery technology, applied in the direction of sustainable manufacturing/processing, chemical industry, sugar production, etc., can solve the problems of unrecoverable heat, waste of heat energy, increased production costs, etc., to reduce subsequent concentration costs, reduce The effect of reducing production cost and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
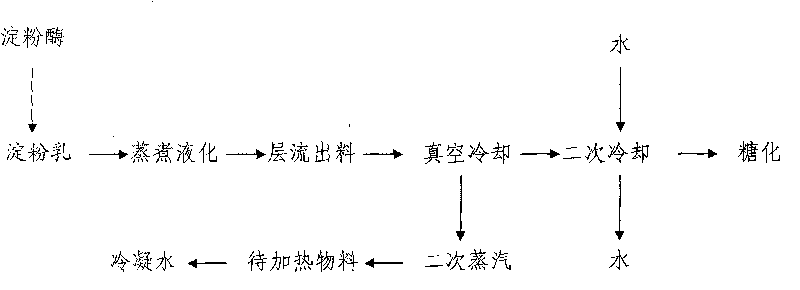
[0027] A method for recovering waste heat during the processing of starchy raw materials, such as figure 1 As shown, after the cooking and liquefied starchy liquefied liquid is kept in laminar flow, the discharge temperature is in the range of 80-95°C, and the discharge is vacuumed and cooled. At this time, the boiling point of the starchy liquefied liquid in the vacuum tank is 60°C , the secondary steam obtained by vacuuming is exchanged with the starch syrup to be evaporated through the heat exchange device to recover waste heat and condensed water.
[0028] Every production of 1t of starch sugar (dry weight) can save about 10 tons of cooling water at 20°C and about 0.25 tons of steam. Has higher economic benefits.
Embodiment 2
[0030] The method for recovery of waste heat as described in Example 1, the difference is that the discharge temperature is between 95-100°C, the boiling point of the starchy liquefaction liquid in the tank is 65°C, and the secondary steam passes through the heat exchange device and is heated The starchy raw materials are heat exchanged to recover waste heat and condensed water.
[0031] Every production of 1t of starch sugar (dry weight) can save about 14 tons of cooling water at 20°C and about 0.5 tons of steam. Has higher economic benefits.
Embodiment 3
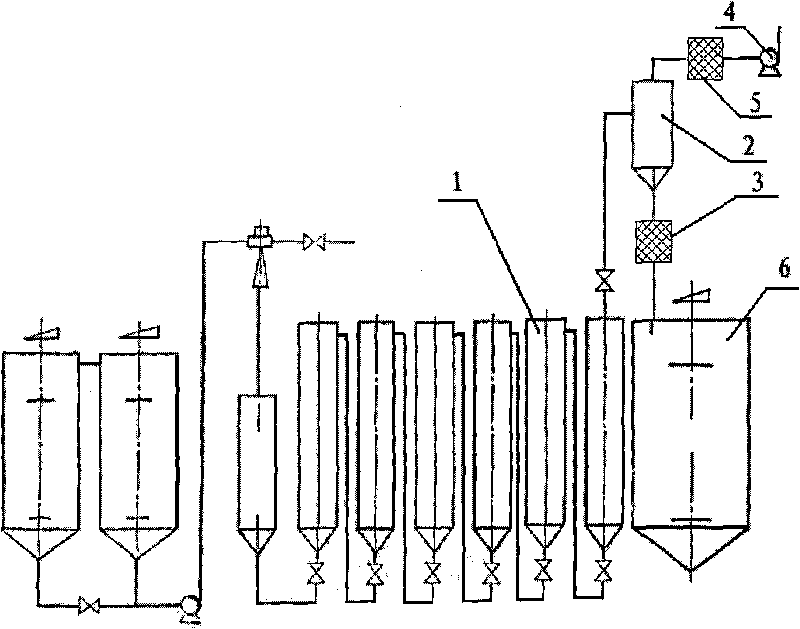
[0033] A special equipment for recovery of waste heat in the process of processing starchy raw materials, such as figure 2 As shown, it is arranged between the laminar flow tank 1 and the saccharification tank 6 of the starch raw material processing equipment, and is located above the saccharification tank 6, including a vacuum tank 2, a heat exchange device 3 and a vacuum pump 4, and the vacuum tank 2 is provided with The feed port, the discharge port and the gas outlet, the feed port of the vacuum tank 2 is connected with the discharge port of the laminar flow tank 1 through a pipeline, the gas outlet of the vacuum tank 2 is connected with the heat exchange device 3, and the heat exchange device 3 is connected with the vacuum pump 4 The discharge port of the vacuum tank 2 is connected with the saccharification tank 6 through a pipeline. A secondary cooling device 5 is arranged between the vacuum tank 2 and the saccharification tank 6, and the secondary cooling device 5 is a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com