Armature core, motor and axial gap electrical rotating machine using same and method for making same
A technology of armature iron core and axial gap, applied in the field of armature iron core, can solve the problem of difficulty in using a rotating motor, etc., and achieve the effects of preventing rust on the gap surface, reducing iron loss, and simple processing procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] Below, use Figure 1 to Figure 6 An example of the present invention will be described.
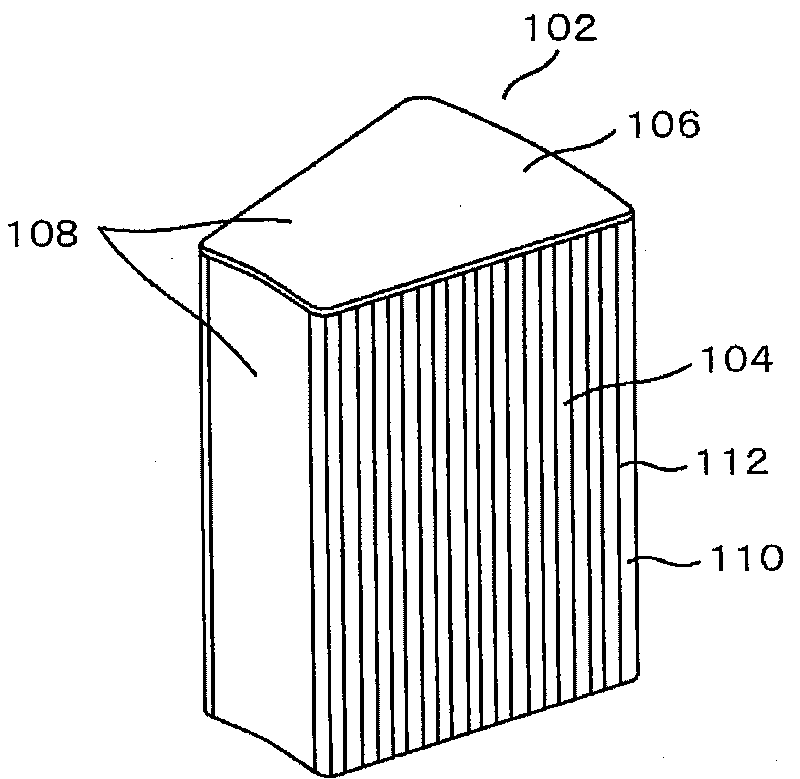
[0117] figure 1 An overall view of the amorphous core 102 as the first embodiment of the present invention is shown.
[0118] The core portion 104 of the amorphous core 102 uses a strip-shaped (foil strip) amorphous metal (amorphous metal) 110 as an iron base, and an insulating resin material (hereinafter referred to as resin) 112 is interposed therebetween. In a laminated structure, strip-shaped amorphous metals 110 are respectively fixed with resin.
[0119] In addition, the core portion 104 is fan-shaped when viewed from above and below.
[0120] In the gap surface 106 in the vertical direction of the core part 104, the layer of the resin part 108 made of a very thin resin of 0.3 mm to 0.5 mm is used to prevent the gap surface 106 from rusting. The directional surface and the outer surface are also formed with a layer of the resin part 108 based on the resin to prevent rust. ...
Embodiment 2
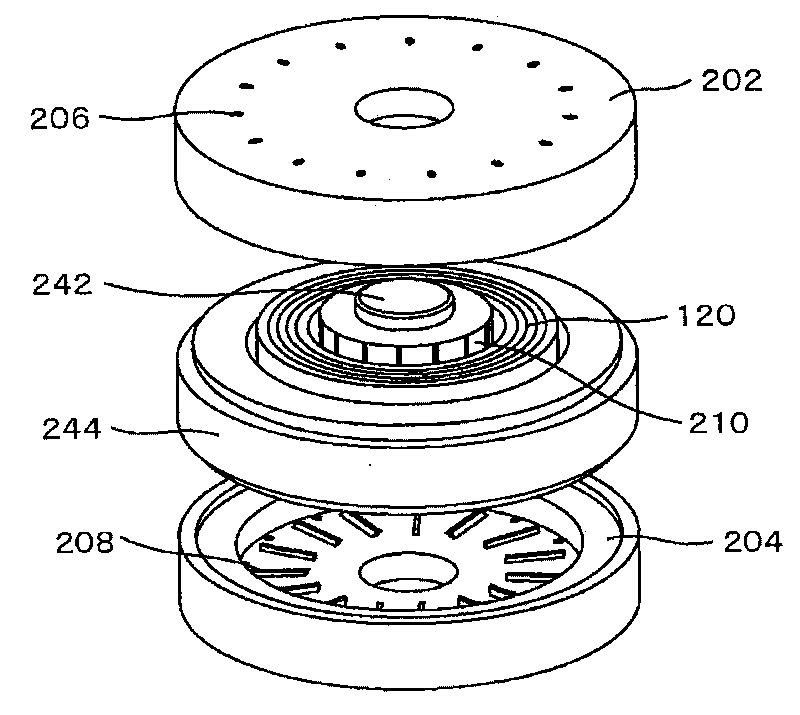
[0131] Figure 6 It is a diagram showing an axial gap motor using the amorphous core 102 of the first embodiment. A motor using the amorphous core of this embodiment includes: a stator 304 having a plurality of stator amorphous cores 102 and stator windings 160; and rotors 302, 304 having substantially rhombic ferrite magnets 310. The two rotors 302, 304 have a structure sandwiching the stator 304. In the motor of this embodiment, the stator has 9 poles and the magnet has 6 poles. However, the number of poles of the armature and the number of magnet poles can also be other. combination. In addition, depending on circumstances, the rotor in this embodiment may be set to the fixed side and the stator side may be rotated.
[0132] Figure 7 The detailed shapes of the ferrite magnet 310, the amorphous core 102, and the winding 160 are shown. Figure 7 showing the view from above Figure 6 shape of the motor. In order to reduce the cogging torque, the magnet 310 is provided w...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Figure 12 is a partial cross-sectional perspective view of the rotating electric machine of Embodiment 3, Figure 13 It is an exploded perspective view in which the components of the electric rotating machine according to the third embodiment are developed along the rotor axial direction. Figure 14 It is a structural view of the core holding member which comprises the stator of the electric rotating machine of Example 3, (a) is a perspective view, (b) is a top view.
[0144] Such as Figure 12 As shown, this axial gap type rotating electric machine 501 (hereinafter simply referred to as "rotating electric machine 501") includes a stator 402 and two sides of the rotor shaft 401 in the axial direction of the stator 402 that are arranged opposite to each other with a predetermined gap (gap). A pair of rotors 403A, 403B are accommodated in the casing 404, and the two outer surfaces of the rotor shaft 401 in the axial direction ( Figure 12 The upper and lower outer sur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com