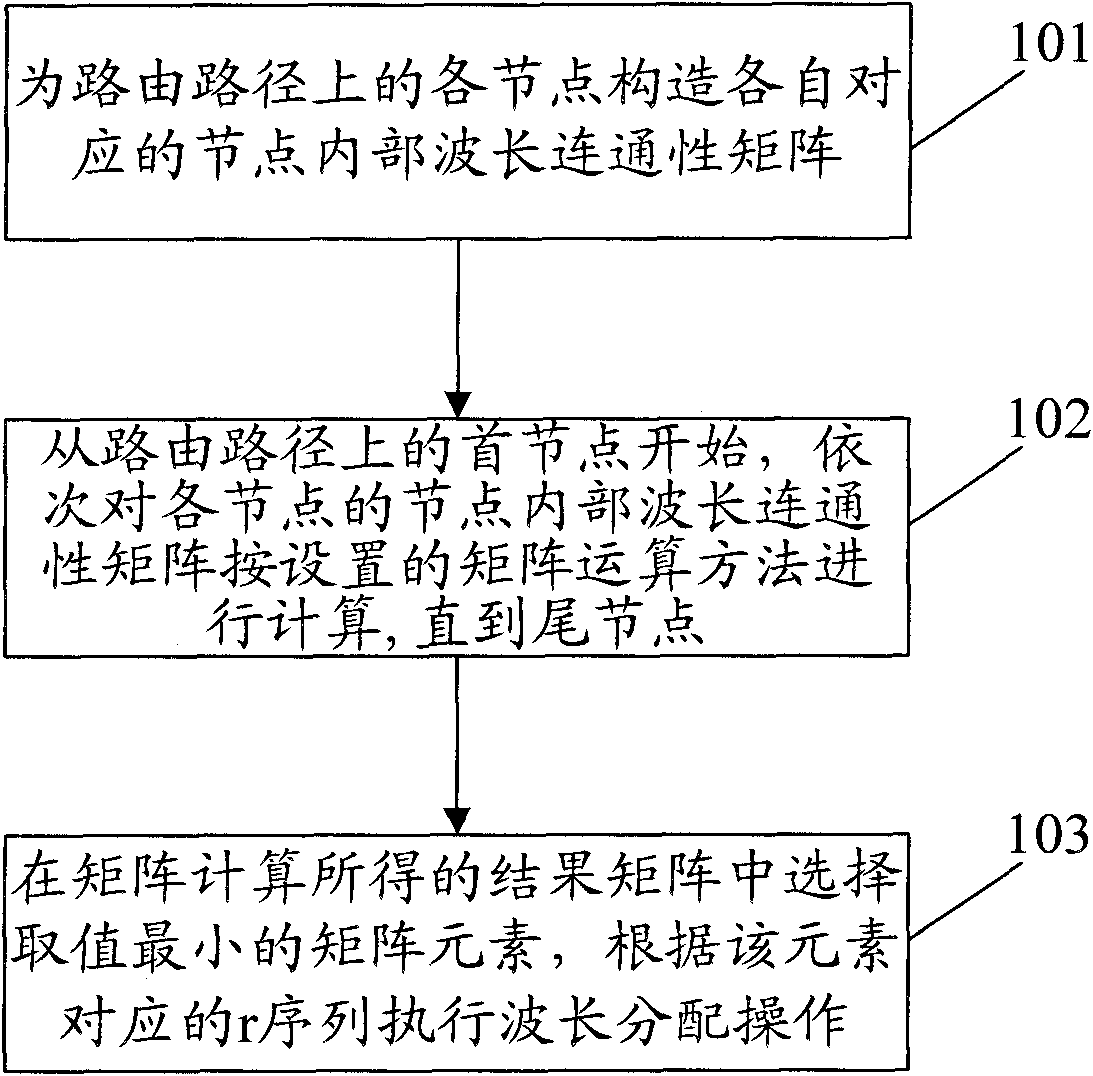
Calculation method and device for wavelength allocation
A wavelength allocation and calculation method technology, which is applied in wavelength division multiplexing systems, electrical components, optical multiplexing systems, etc., can solve the problems of low wavelength allocation calculation efficiency, increased complexity of routing path topology, and wavelength allocation complexity. increase and other issues, to achieve the effect of simple implementation, simple calculation principle, and reduced calculation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
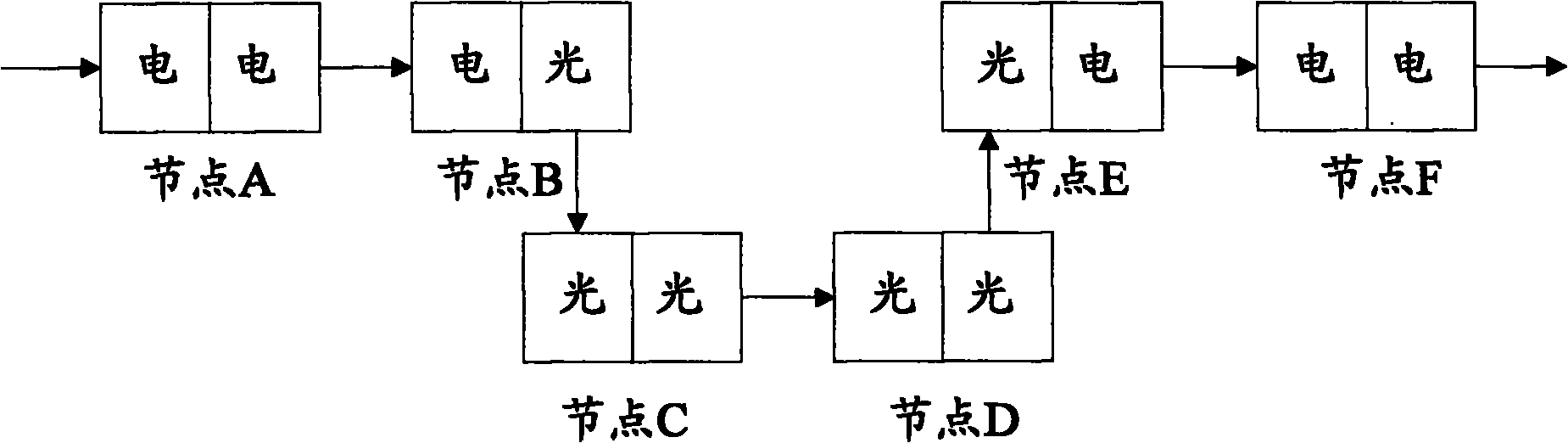
[0068] There are six nodes on the routing path in this embodiment, such as figure 2 As shown, node A, node B, node C, node D, node E and node F are respectively, node A is the first node, which is an electrical and electrical node; node B is an electrical and optical node; node C is an optical-optical node; node D is an optical node Optical node; node E is an optoelectronic node; node F is a tail node, which is an electrical and electrical node.
[0069] The internal wavelength connectivity matrices constructed for node A to node F are: 1*1-order matrix A, 1*n-order matrix B, n*n-order matrix C, n*n-order matrix D, and n*1-order matrix E and 1*1 order matrix F, and then start the matrix operation from node A as follows:
[0070] Perform Δ operation on matrix A(1*1) and matrix B(1*n), set the operation result as matrix B1(1*n), and record the r corresponding to B1(1*n);
[0071] Perform Δ operation on matrix B1(1*n) and matrix C(n*n), set the operation result as matrix C1(1*...
Embodiment 2
[0077] There are only two nodes on the routing path in this embodiment, and let them be respectively figure 2 The node C and node D in the node C is the first node, which is the optical node; the node D is the tail node, which is also the optical node.
[0078] The intra-node wavelength connectivity matrices constructed for node C and node D are respectively: n*n-order matrix C and n*n-order matrix D, and then the matrix operation from node C is performed as follows:
[0079] Perform Δ operation on matrix C(n*n) and matrix D(n*n), set the operation result as matrix D1(n*n), and record the r corresponding to D1(n*n);
[0080] After the above calculation process, the matrix D1(n*n) reflects the wavelength connectivity from the ingress port of the head node C to the egress port of the tail node D. Select the non-∞ element d with the smallest value from the matrix operation result matrix D1 ij , using the recorded and d ij The corresponding r sequence performs wavelength assign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com