High-brightness controllable pseudo-thermal light source based on liquid crystal light valve modulation
A technology of liquid crystal light valve and pseudothermal light source, which is applied in the field of high-brightness controllable pseudothermal light source, can solve the problems of poor repeatability, difficult precise calibration, large mechanical changes of ground glass sheets, etc., and achieve the effect of small energy loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the embodiments and accompanying drawings, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
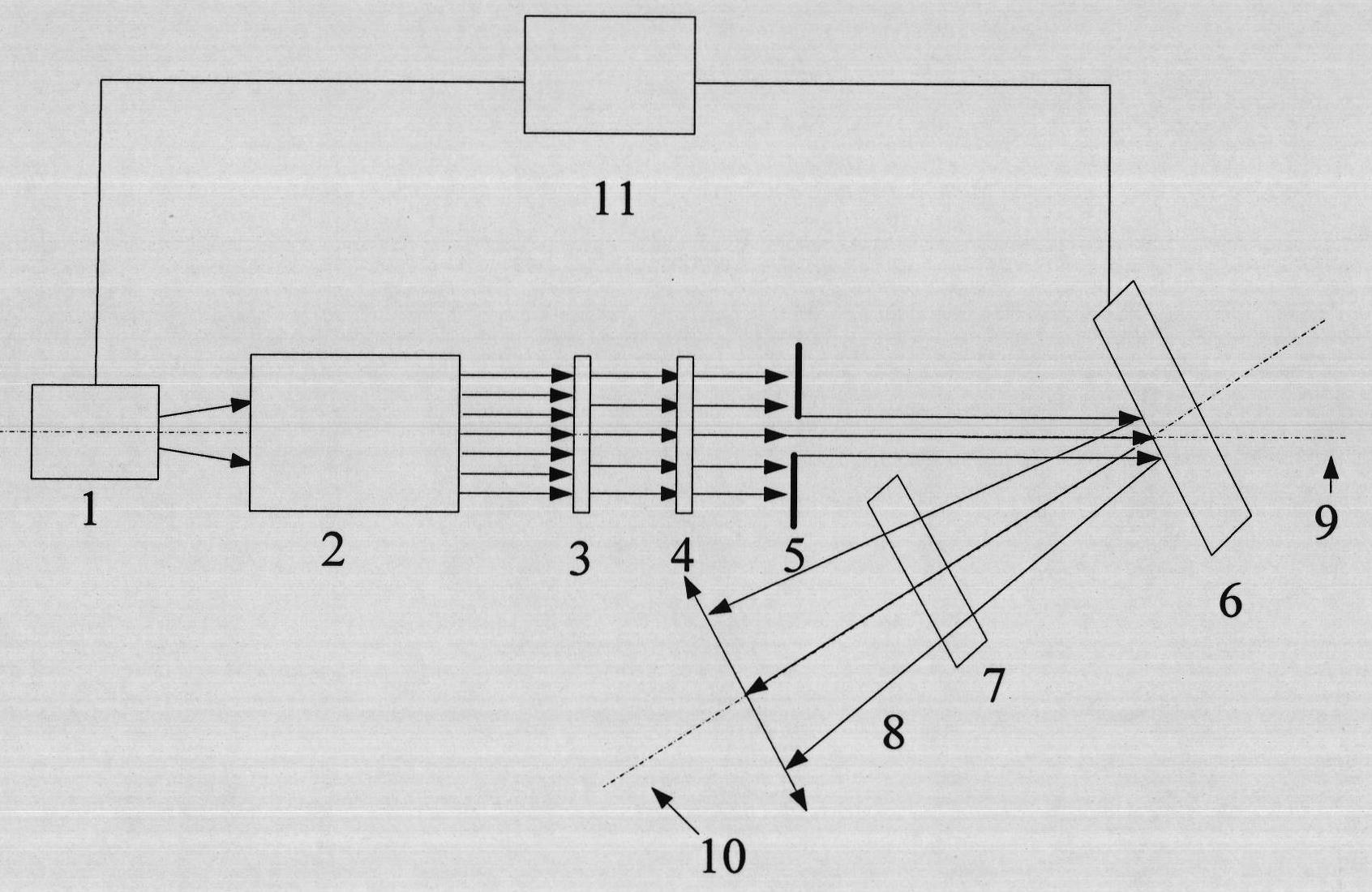
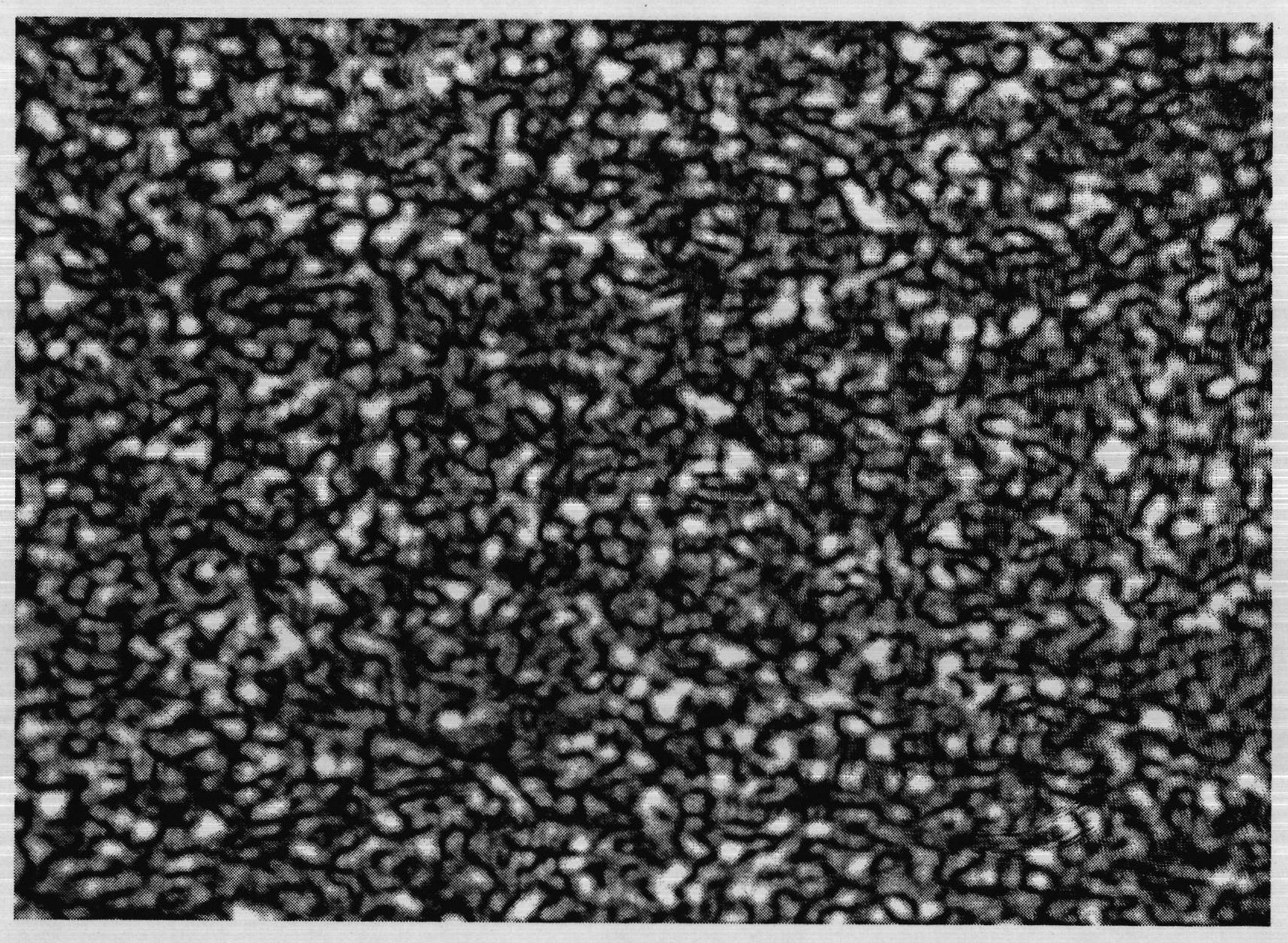
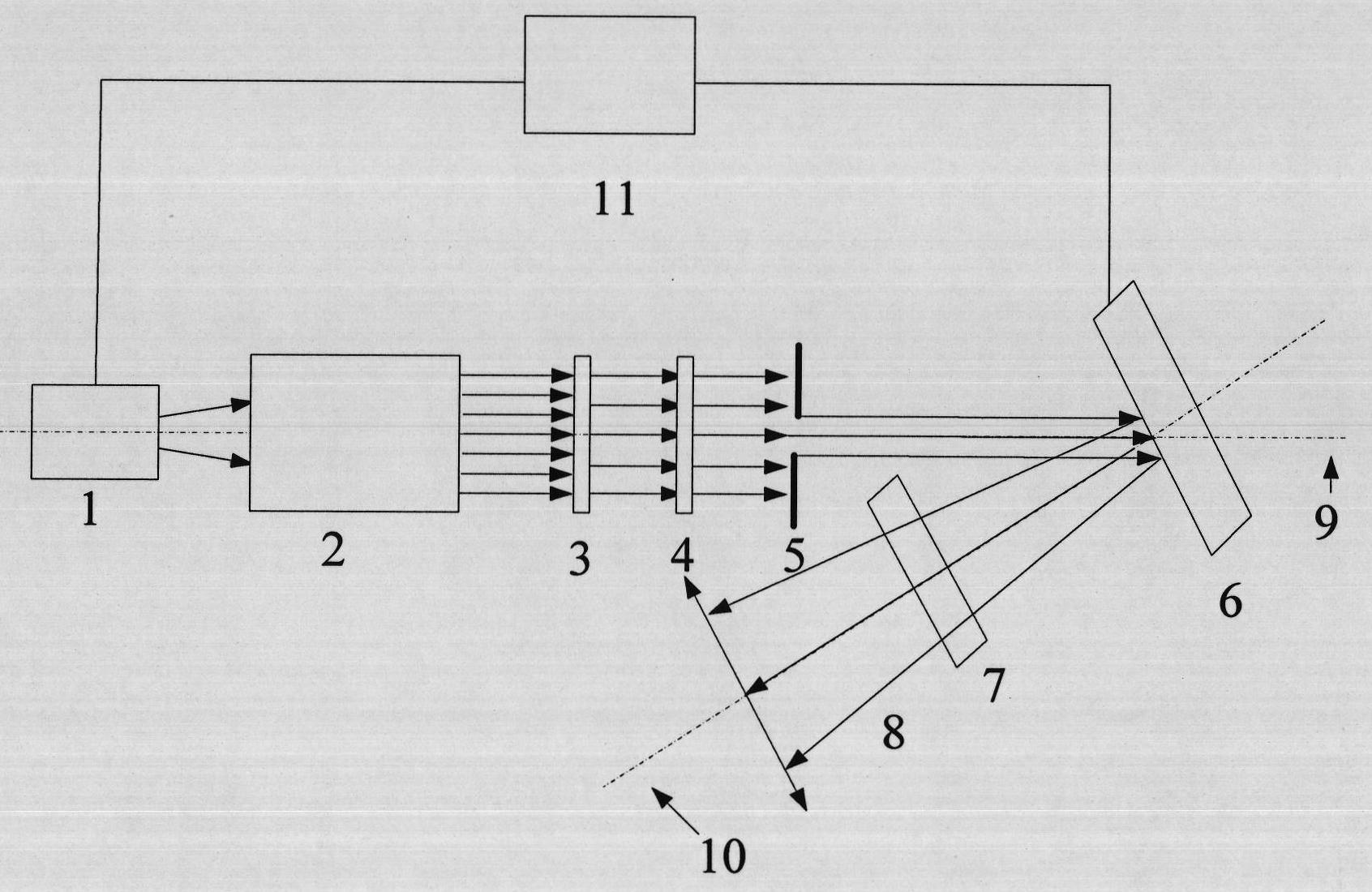
[0025] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a structural block diagram of the high-brightness controllable pseudothermal light source device based on the liquid crystal light valve modulation method of the present invention, which is also an embodiment of the present invention. It can be seen from the figure that the high-brightness controllable pseudothermal light source based on the liquid crystal light valve modulation of the present invention consists of Including pulsed laser 1, adjustable beam expander collimation system 2, polarizer 3, first analyzer 4, adjustable aperture stop 5, liquid crystal light valve 6, second analyzer 7 and liquid crystal light valve control System 11, the pulsed laser 1, the adjustable beam expander collimation system 2, the polarizer 3, the first...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com