Patents
Literature
43 results about "Dynamic speckle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
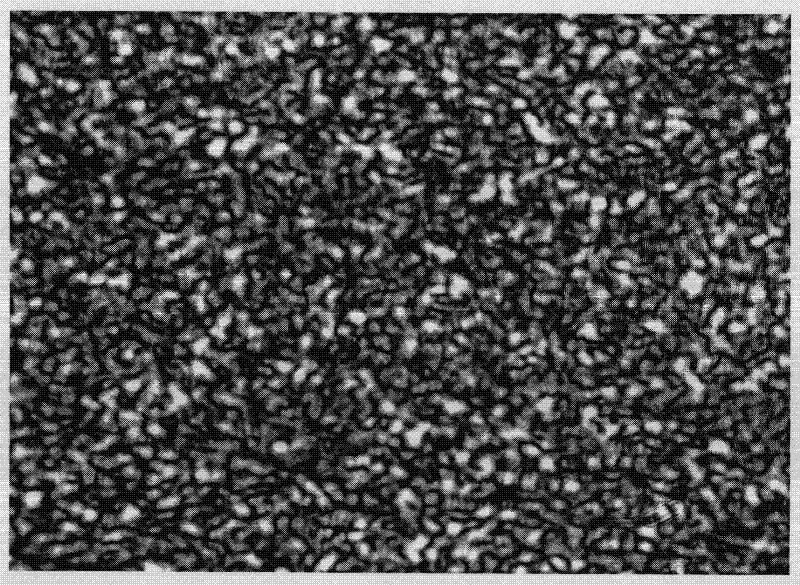
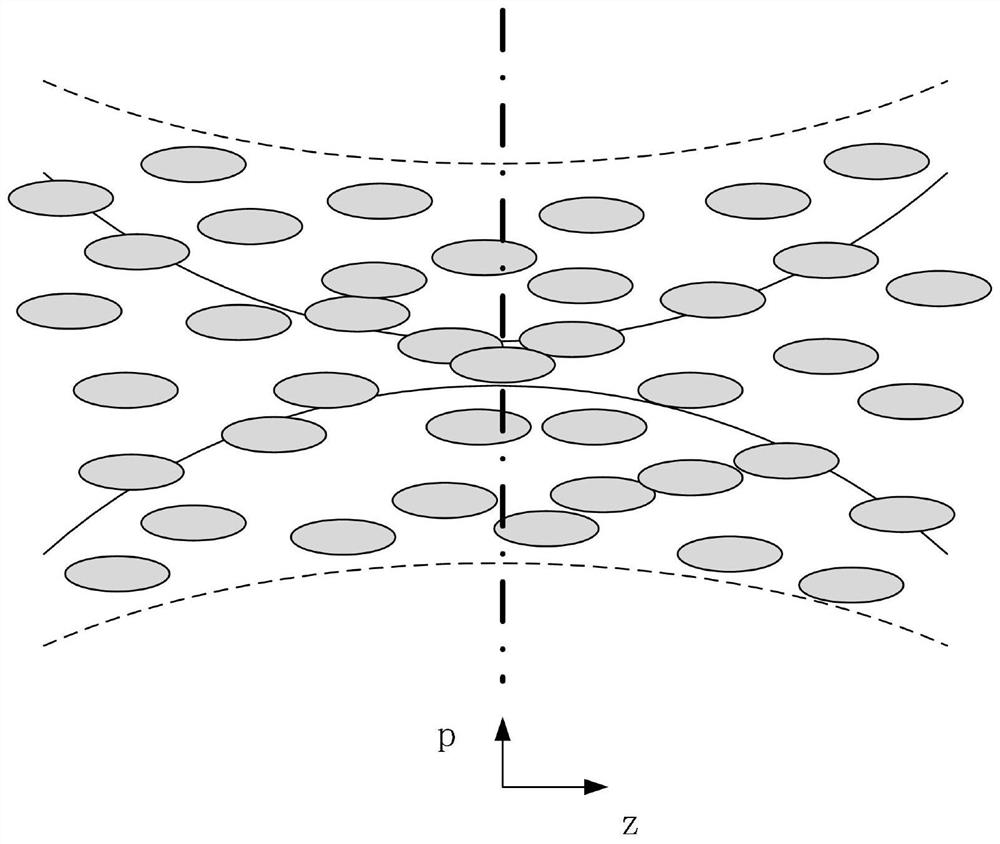
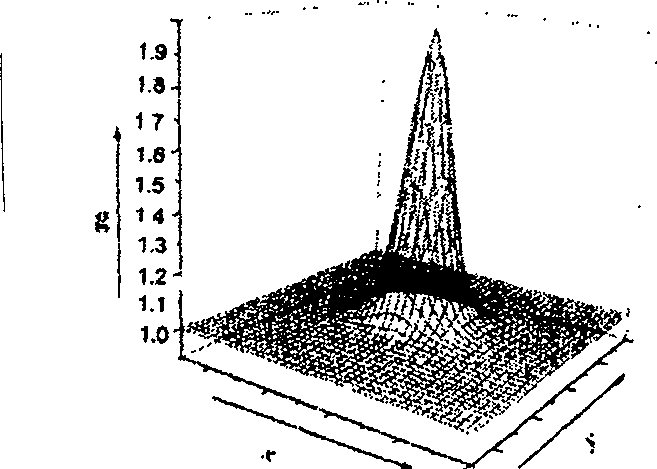
In physics, dynamic speckle is a result of the temporal evolution of a speckle pattern where variations in the scattering elements responsible for the formation of the interference pattern in the static situation produce the changes that are seen in the speckle pattern, where its grains change their intensity (grey level) as well as their shape along time. One easy to observe example is milk: place some milk in a teaspoon and observe the surface in direct sunlight. You will see a "dancing" pattern of coloured points. Where the milk dries on the spoon at the edge, the speckle is seen to be static. This is direct evidence of the thermal motion of atoms, which cause the Brownian motion of the colloidal particles in the milk, which in turn results in the dynamic speckle visible to the naked eye.
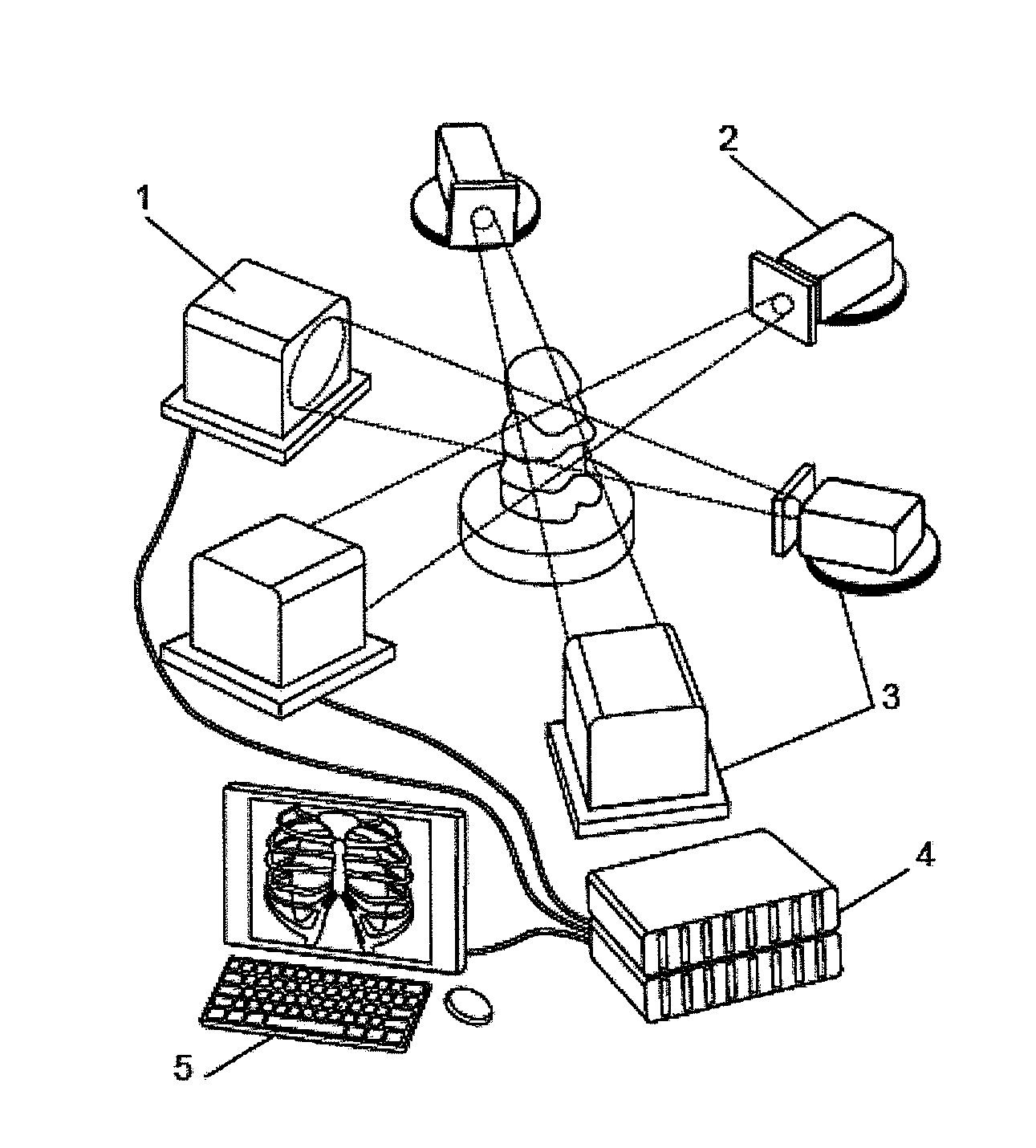
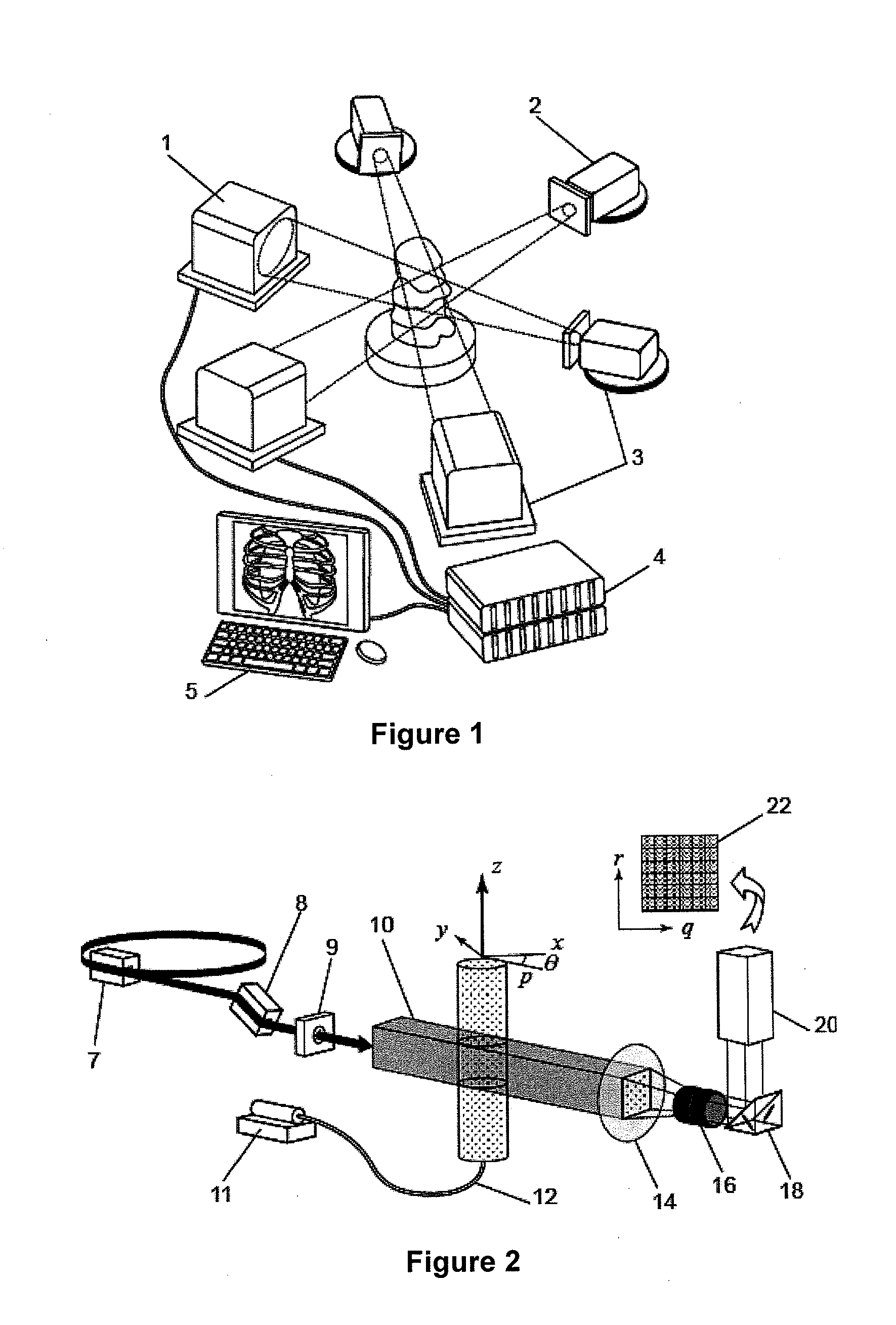
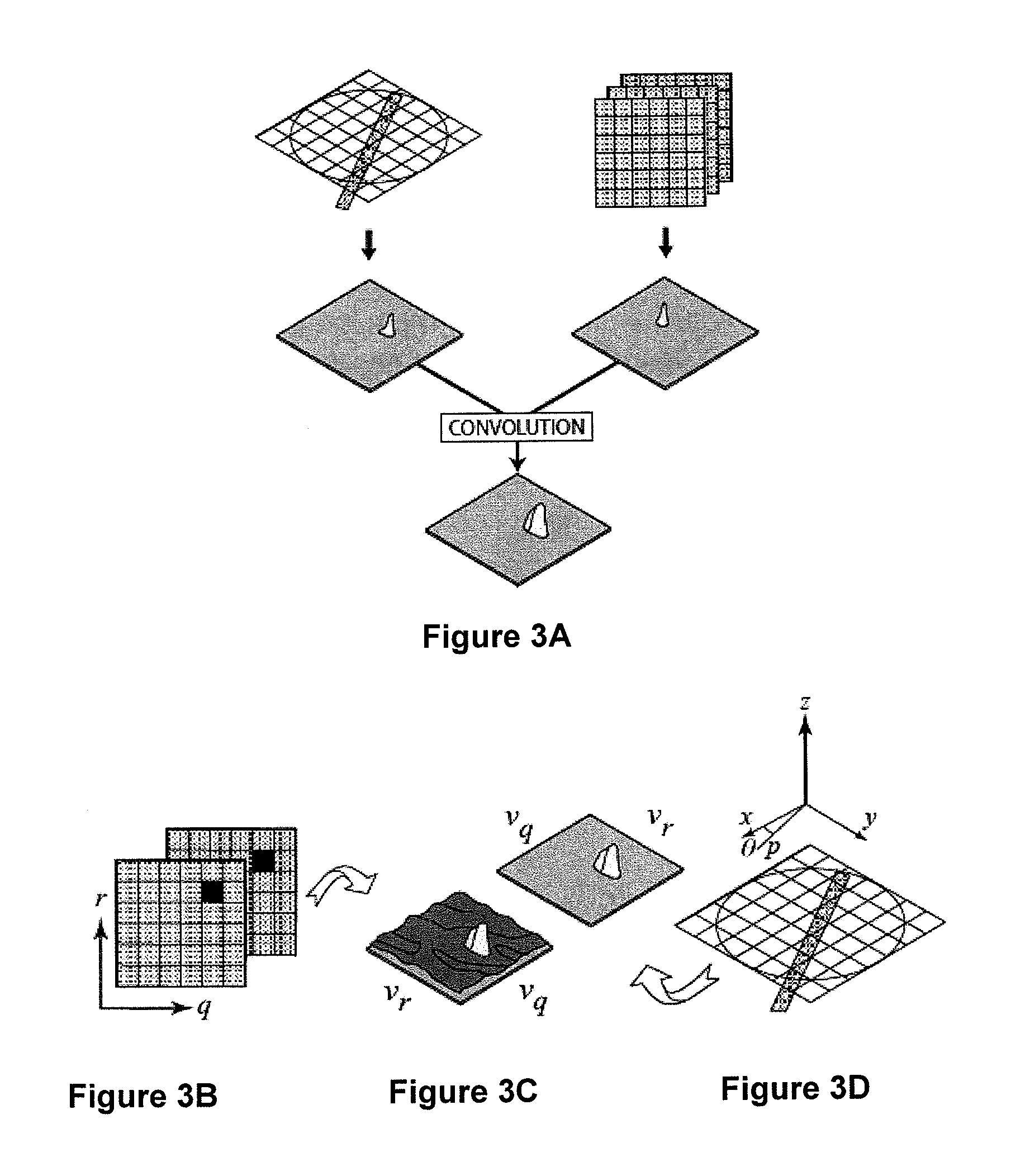
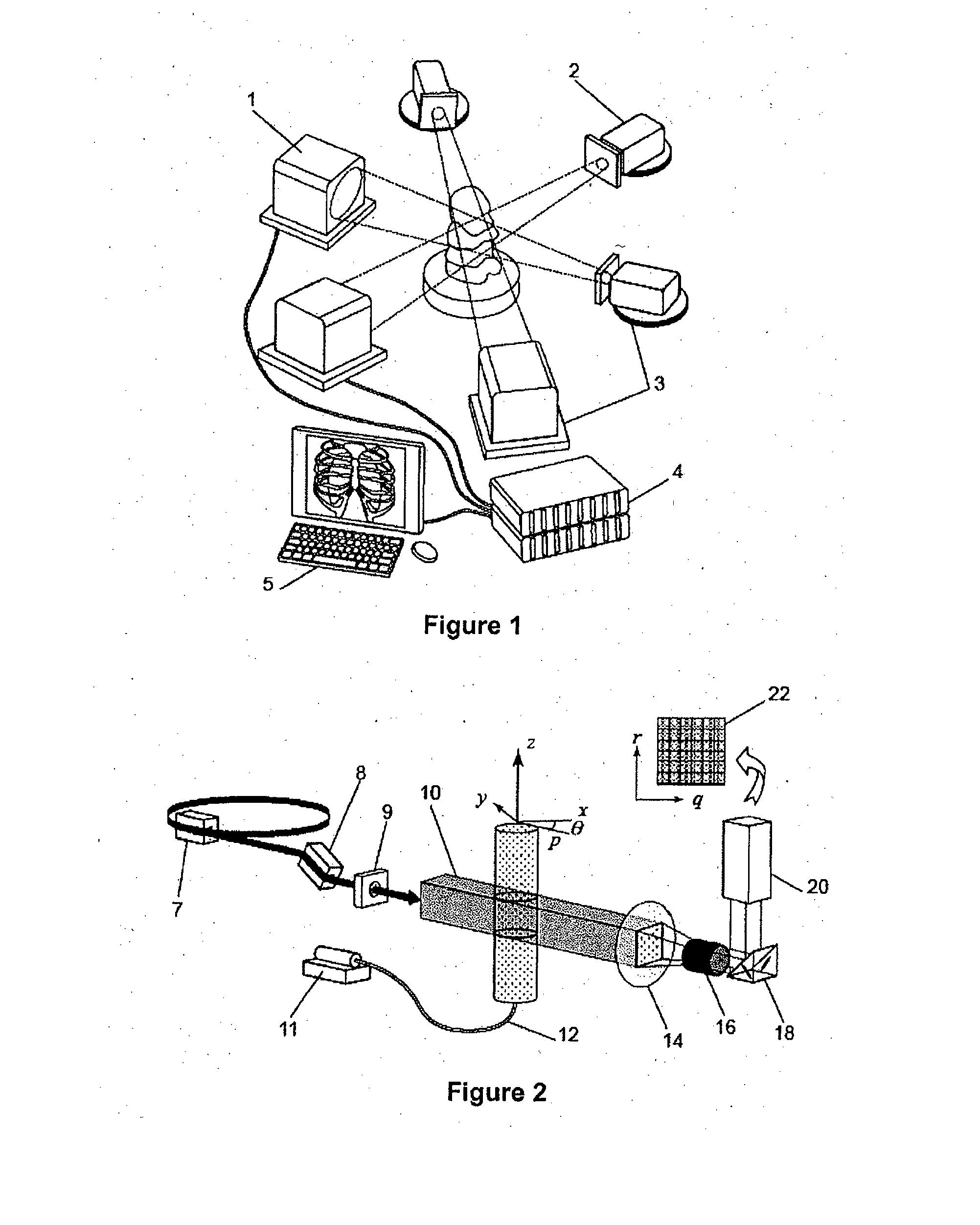
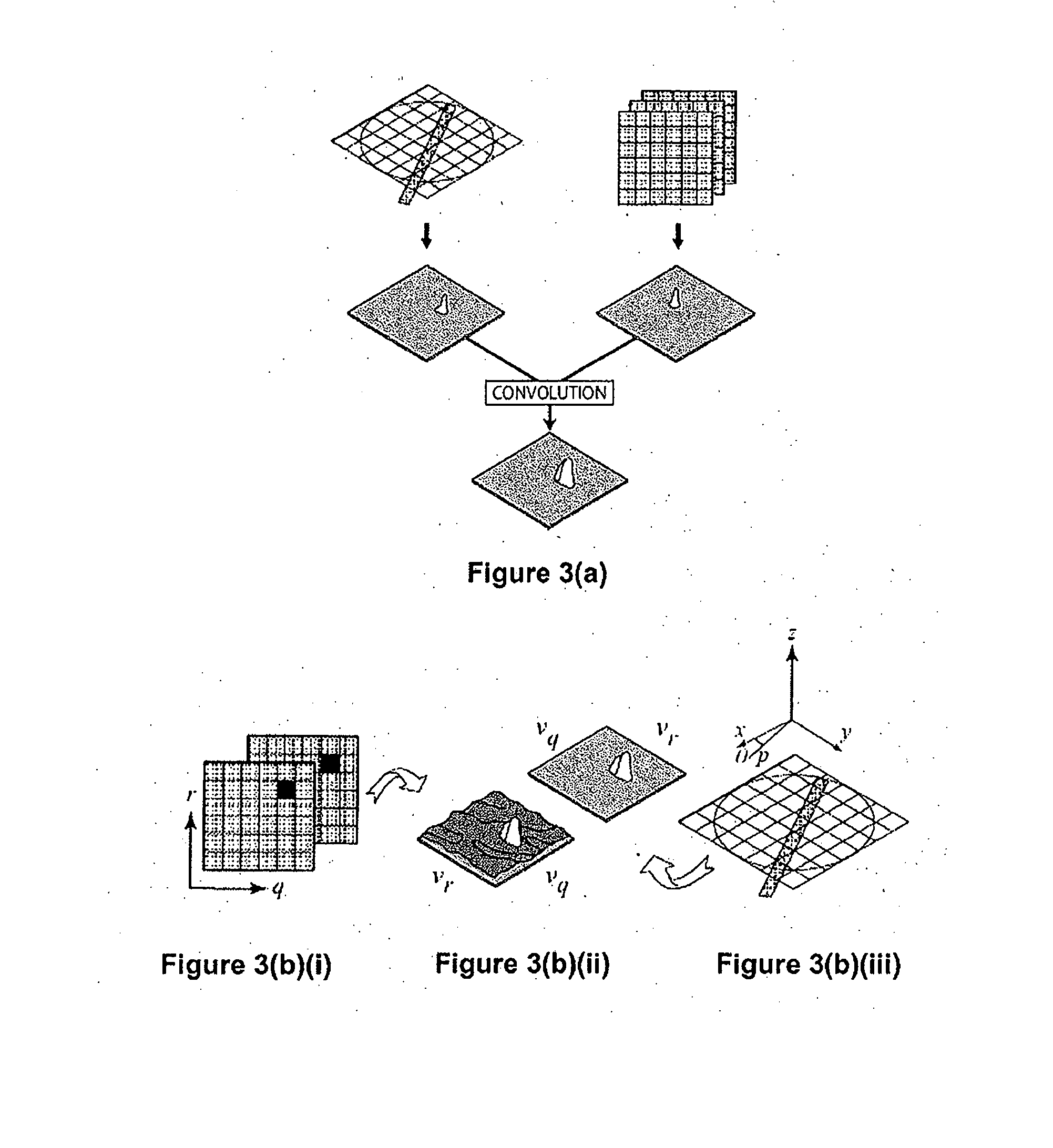
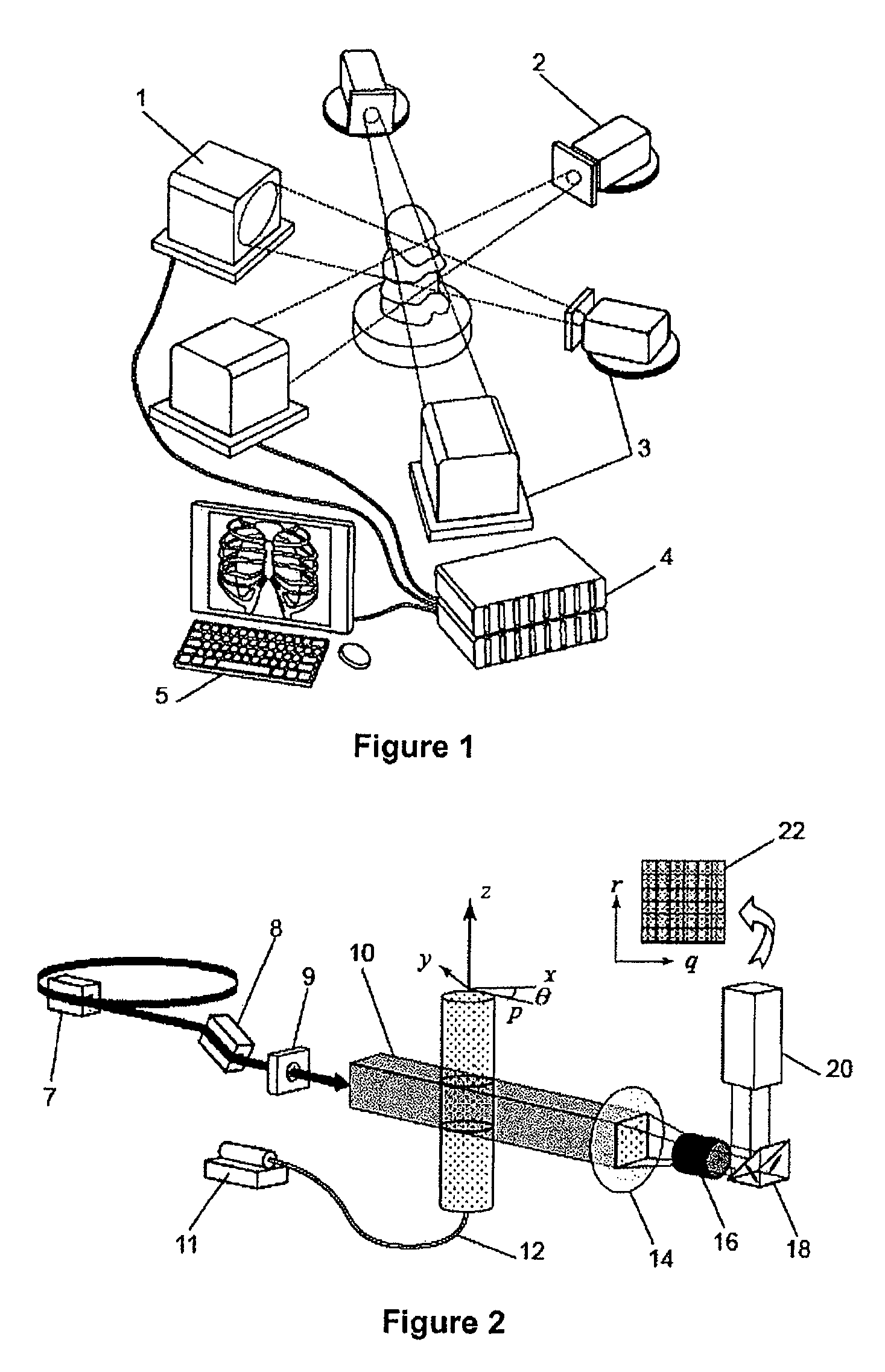
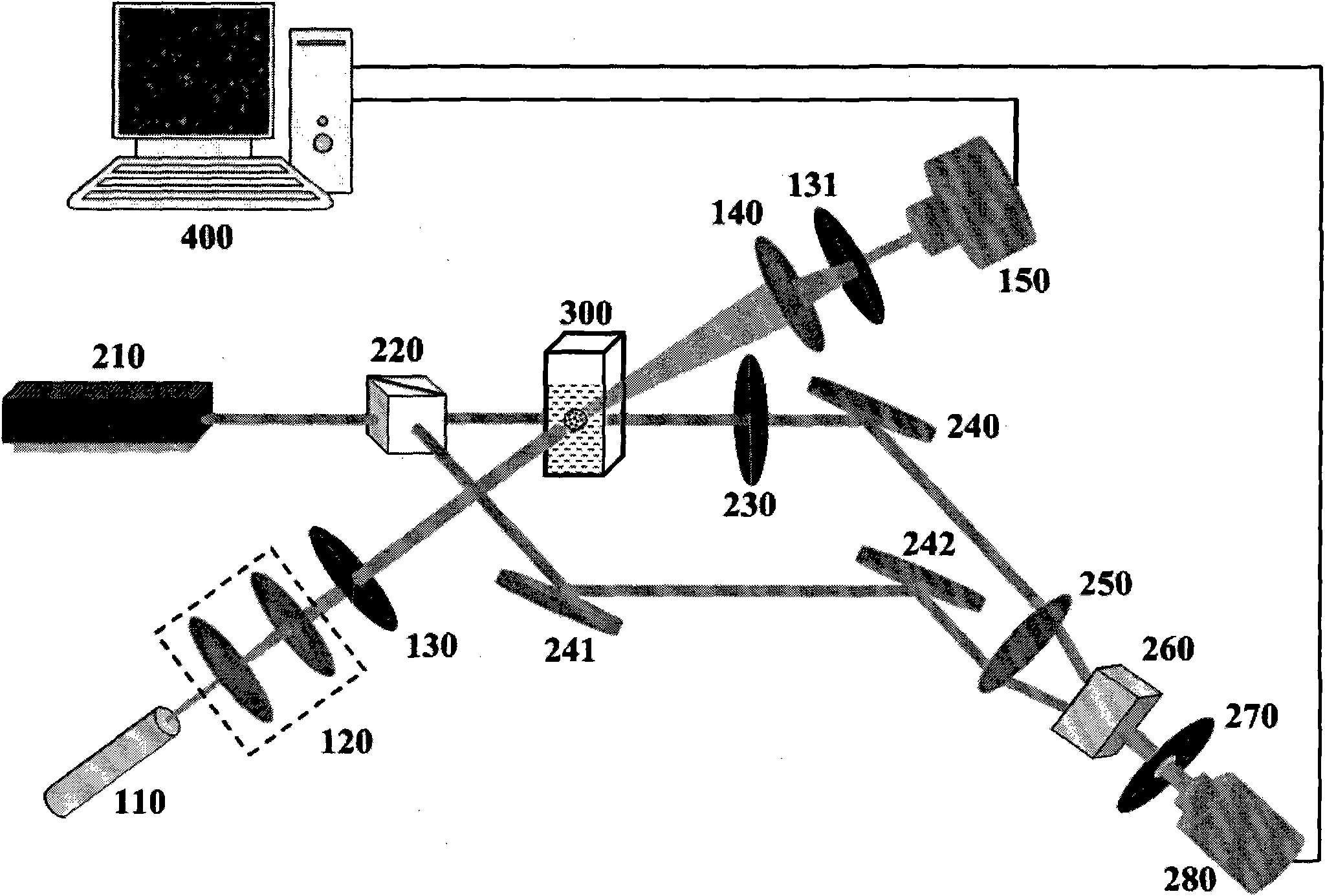
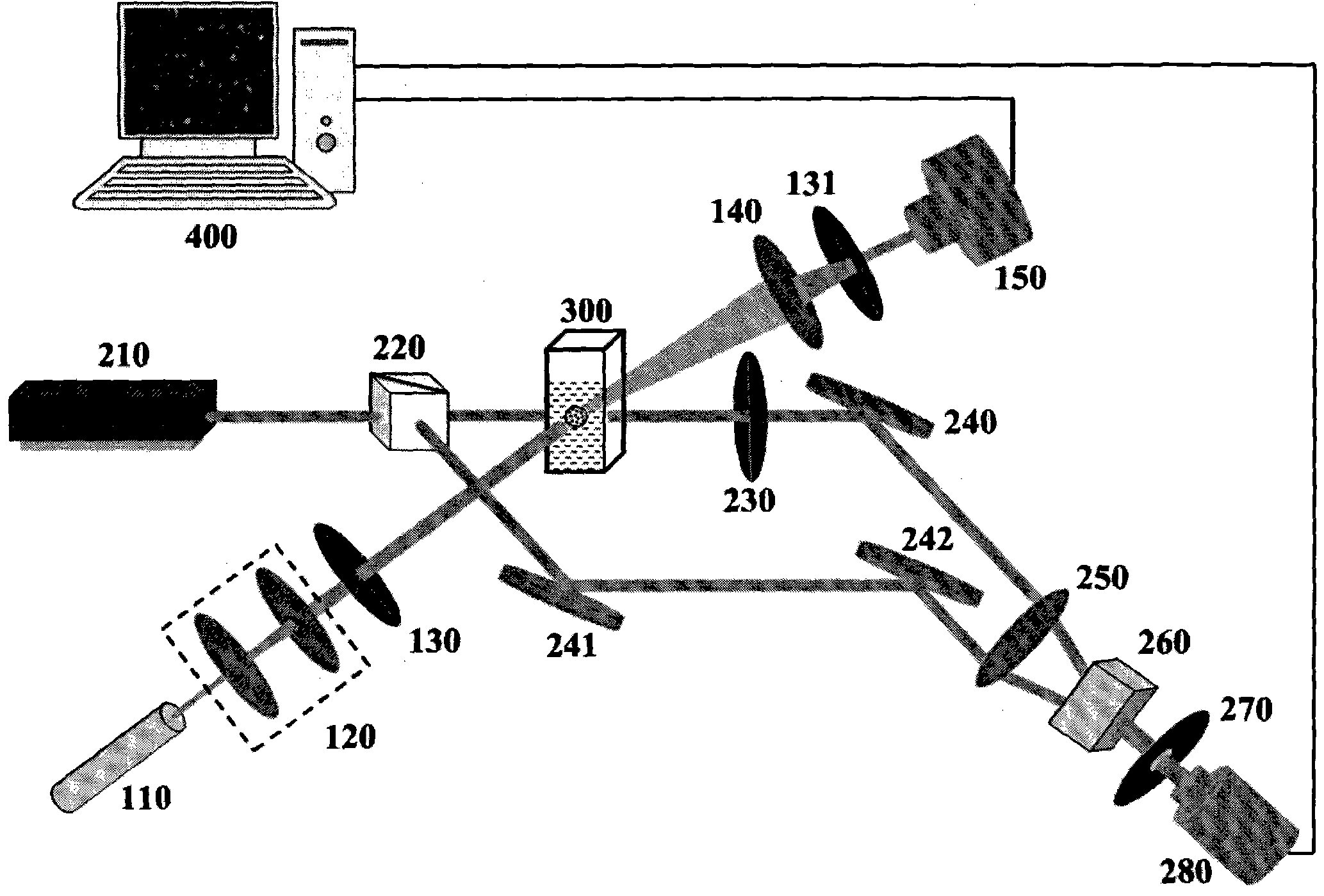
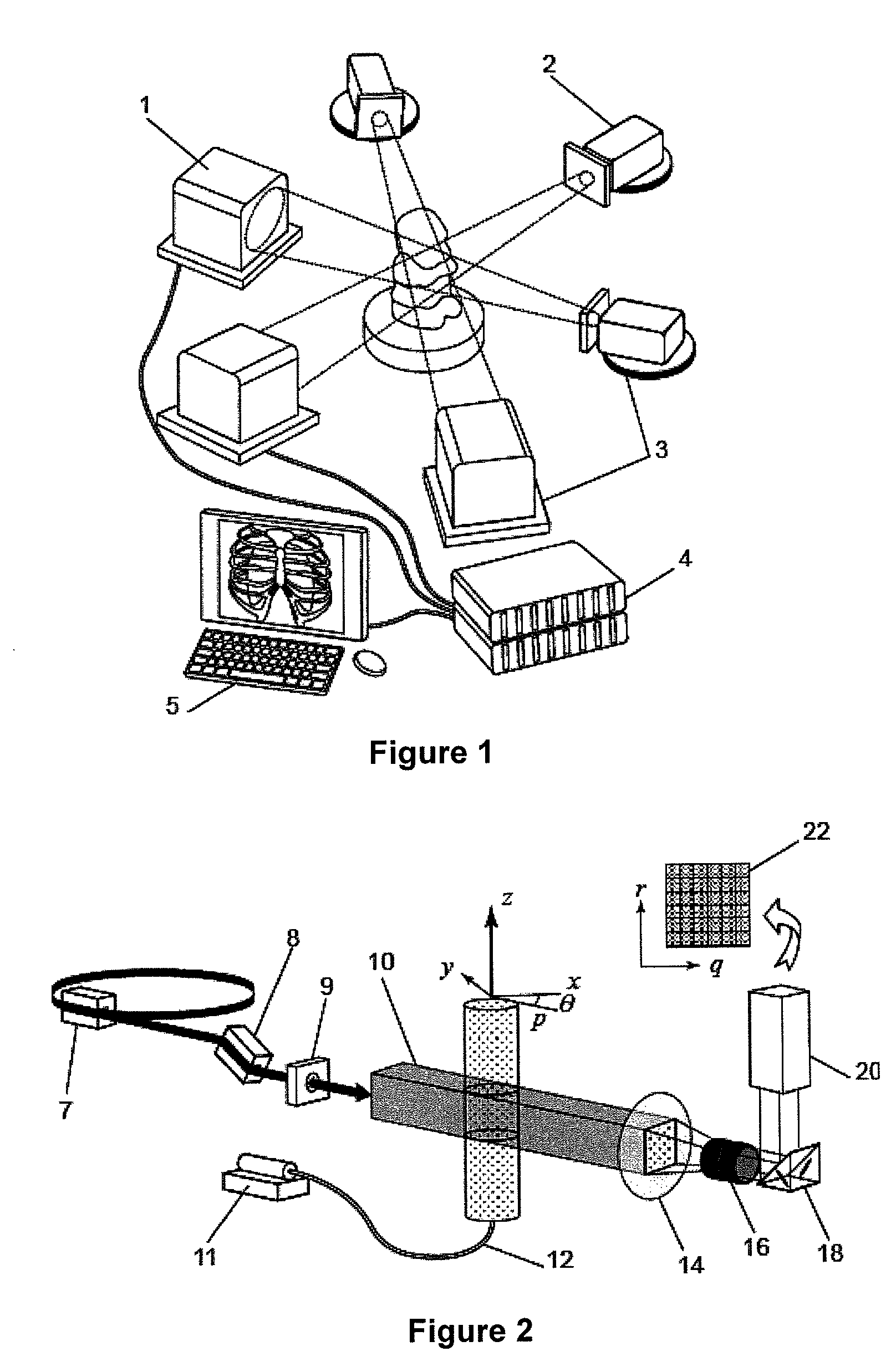
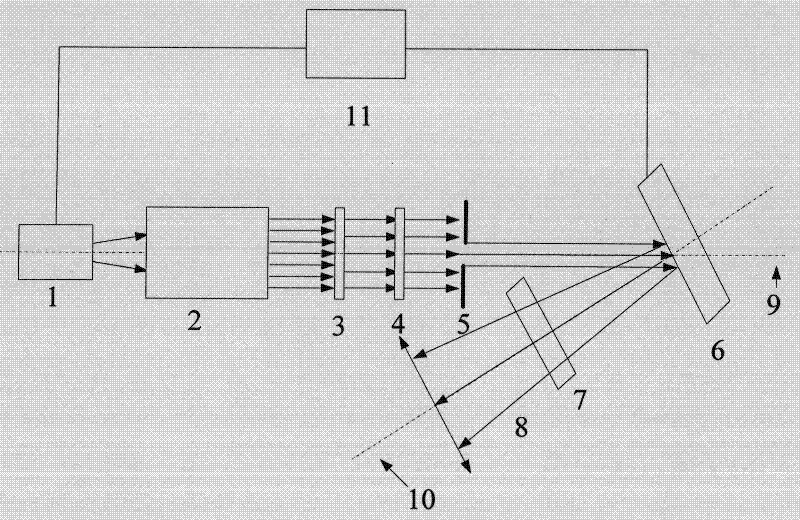
Partical image velocimetry suitable for x-ray projection imaging
ActiveUS20130070062A1Enhance the imageImprove overall utilizationTelevision system detailsTomographyX-rayDynamic speckle
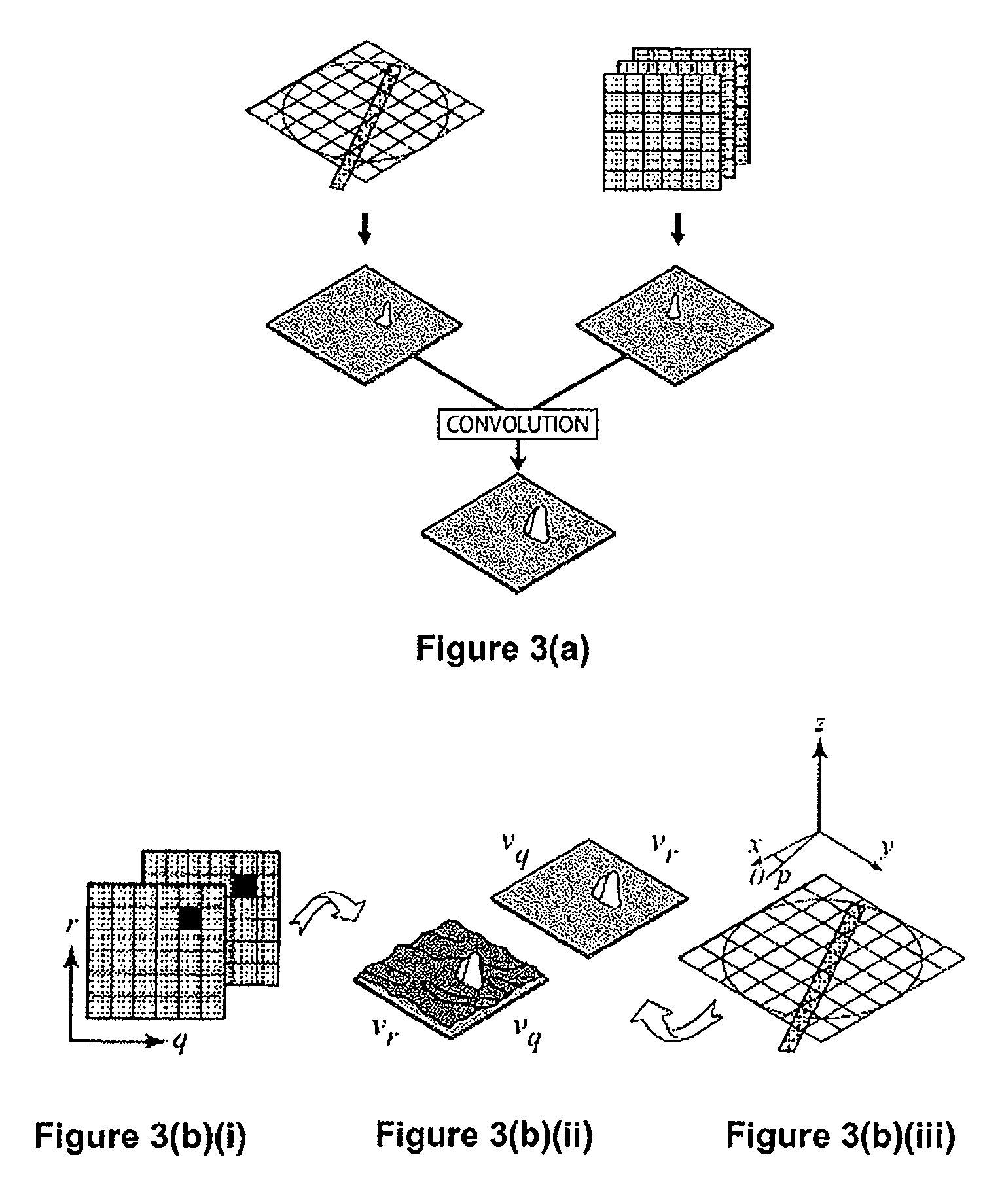
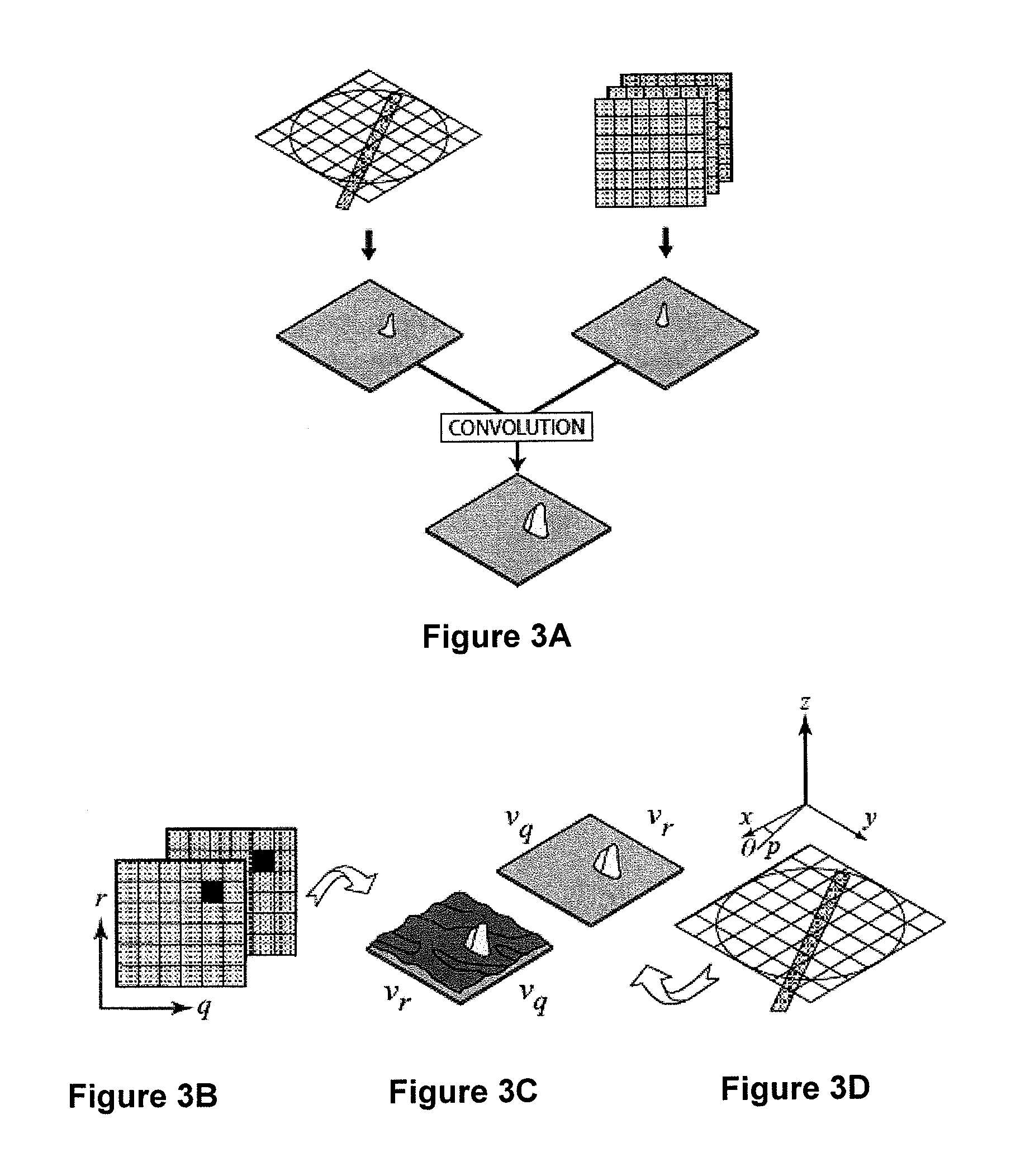
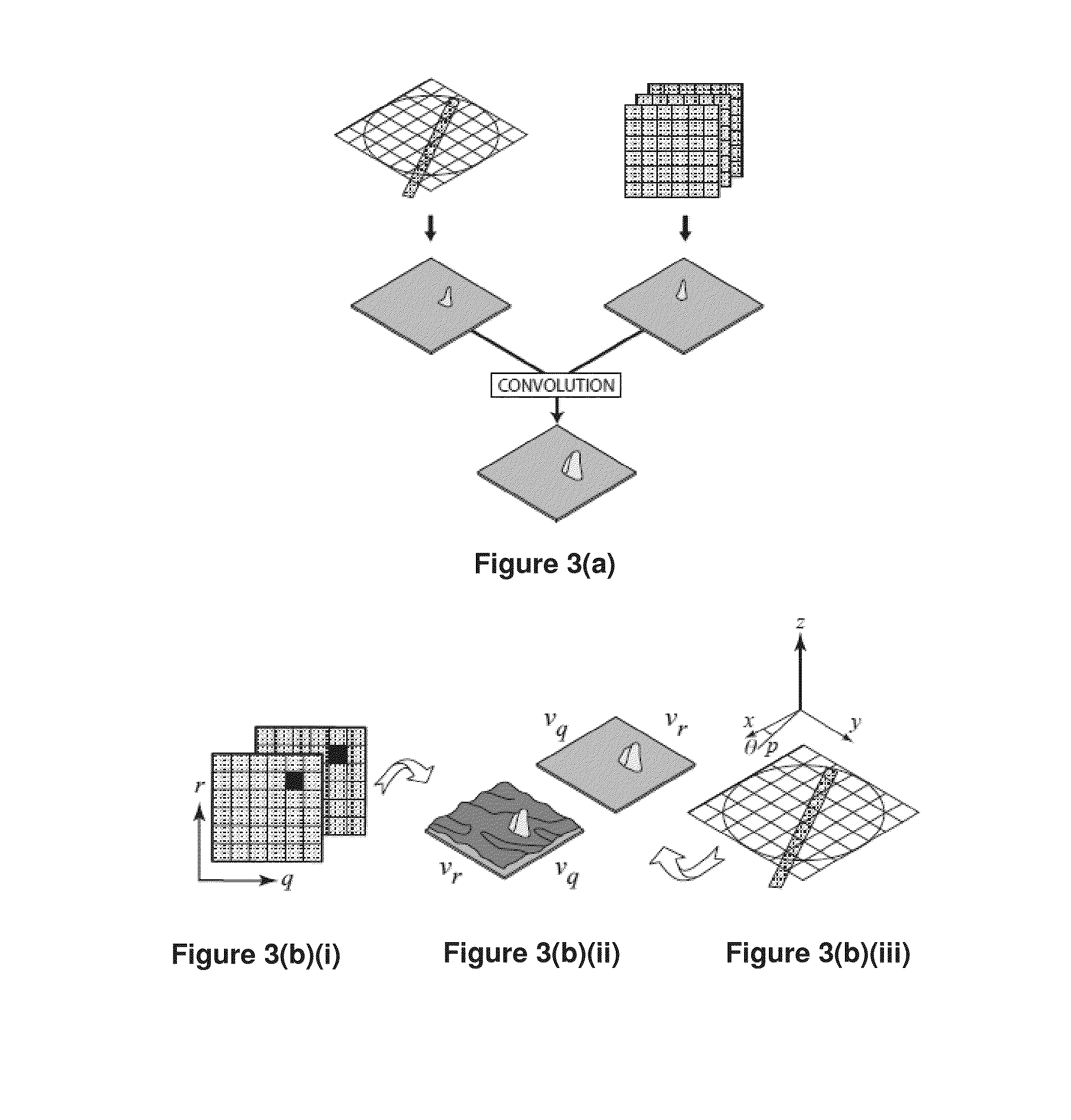
A 2D or 3D velocity field is reconstructed from a cross-correlation analysis of image pairs of a sample, without first reconstructing images of the sample spatial structure. The method can be implemented via computer tomographic x-ray particle image velocimetry, using multiple projection angles, with phase contrast images forming dynamic speckle patterns. Estimated cross-correlations may be generated via convolution of a measured autocorrelation function with a velocity probability density function, and the velocity coefficients iteratively optimised to minimise the error between the estimated cross-correlations and the measured cross-correlations. The method may be applied to measure blood flow, and the motion of tissue and organs such as heart and lungs.
Owner:4DX LTD
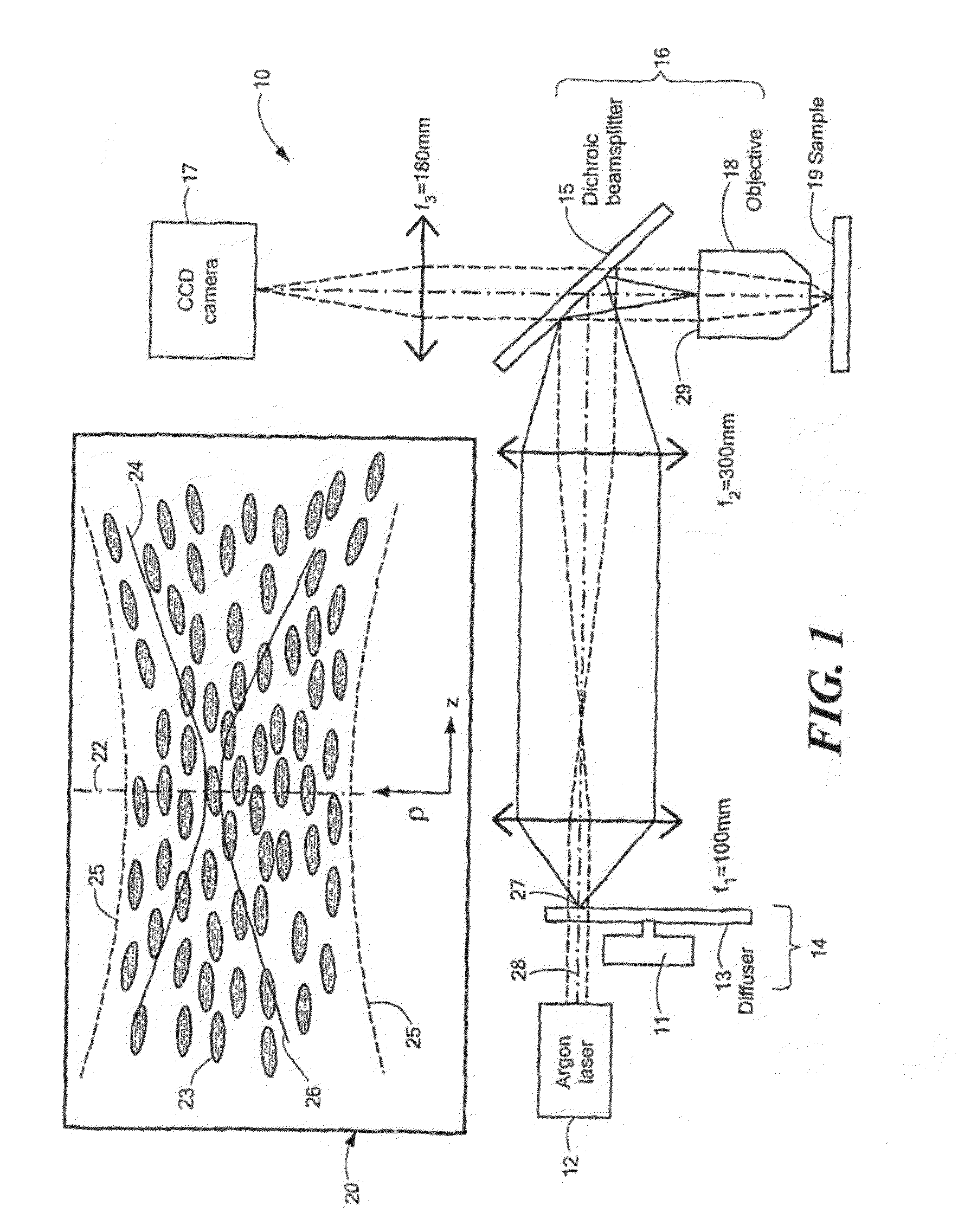
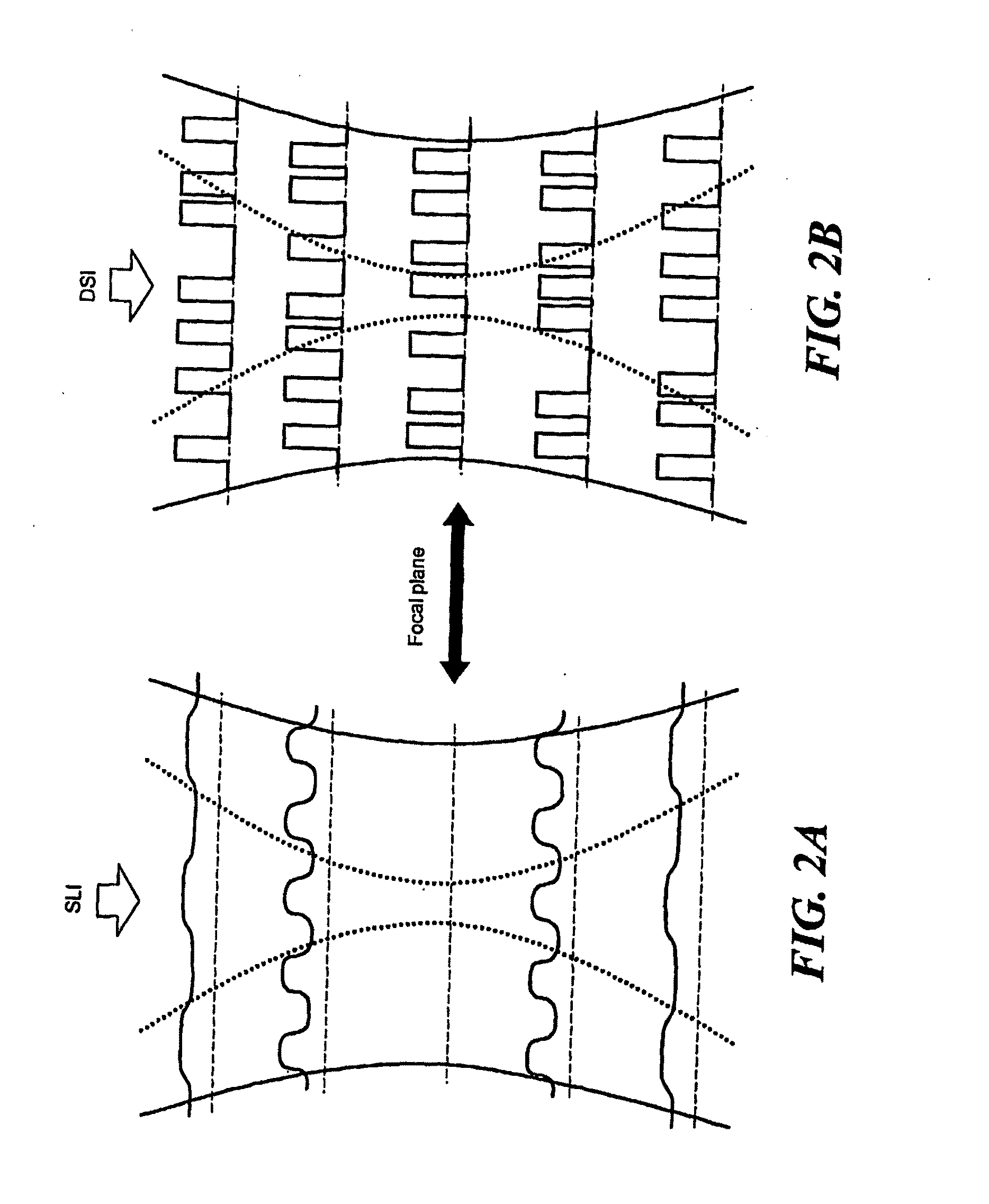
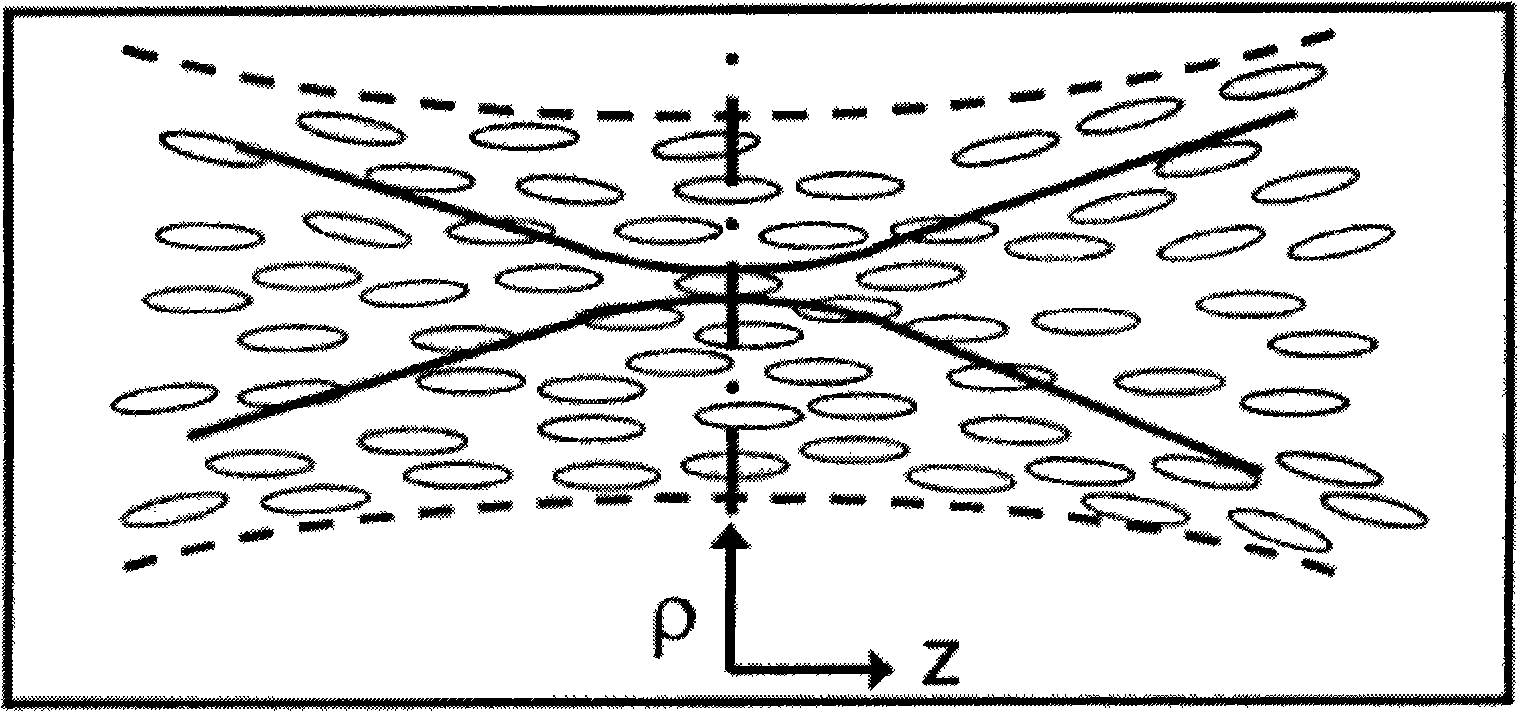
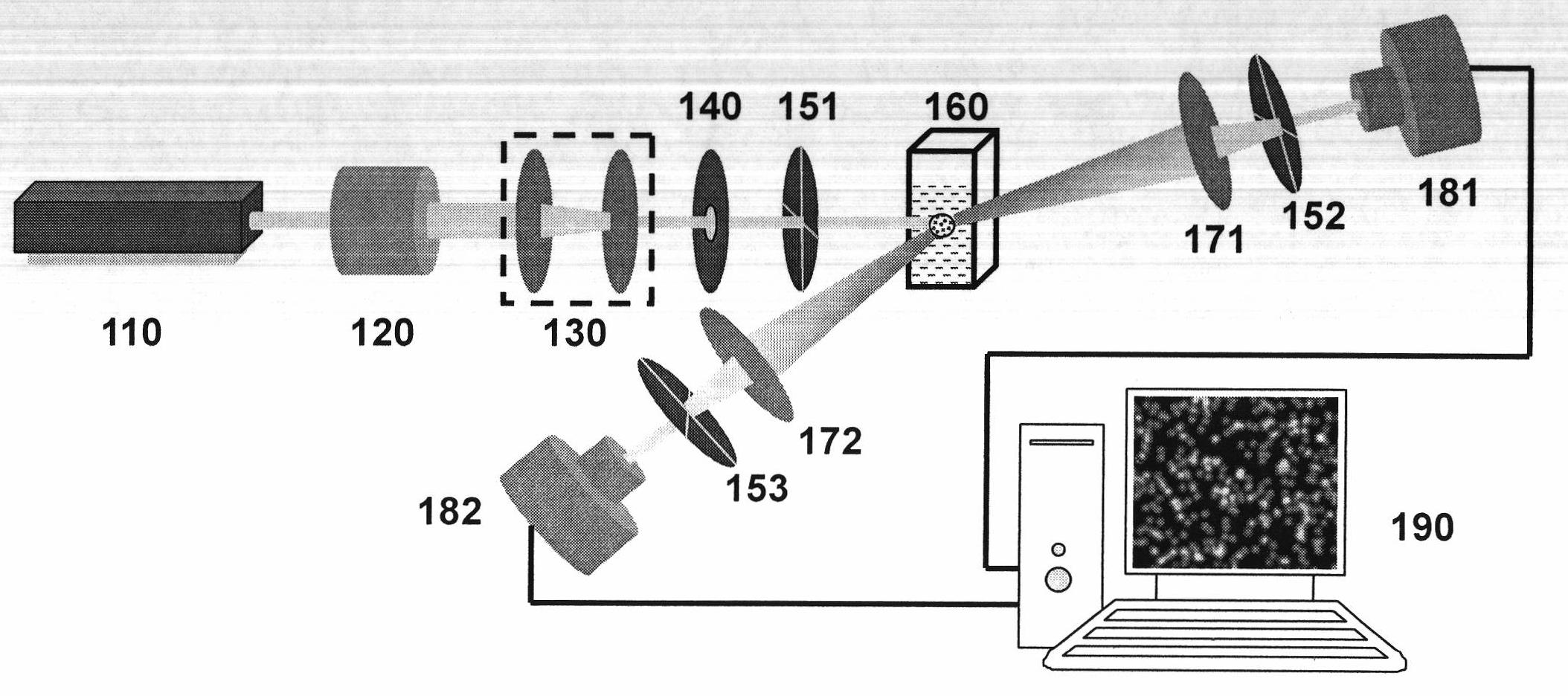
Imaging System Using Dynamic Speckle Illumination
InactiveUS20100224796A1Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsImage recordingSignal light
A versatile, imaging system that uses dynamic speckle illumination (DSI) is disclosed. The DSI microscope includes at least one light source for producing light to illuminate a target object in an object plane; an image recording device for recording a sequence of images of the target object; imaging optics for transmitting signal light from the target object as the sequence of images from the target object to the image recording device; and a dynamic speckle generating system for illuminating the target object with dynamic speckle.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
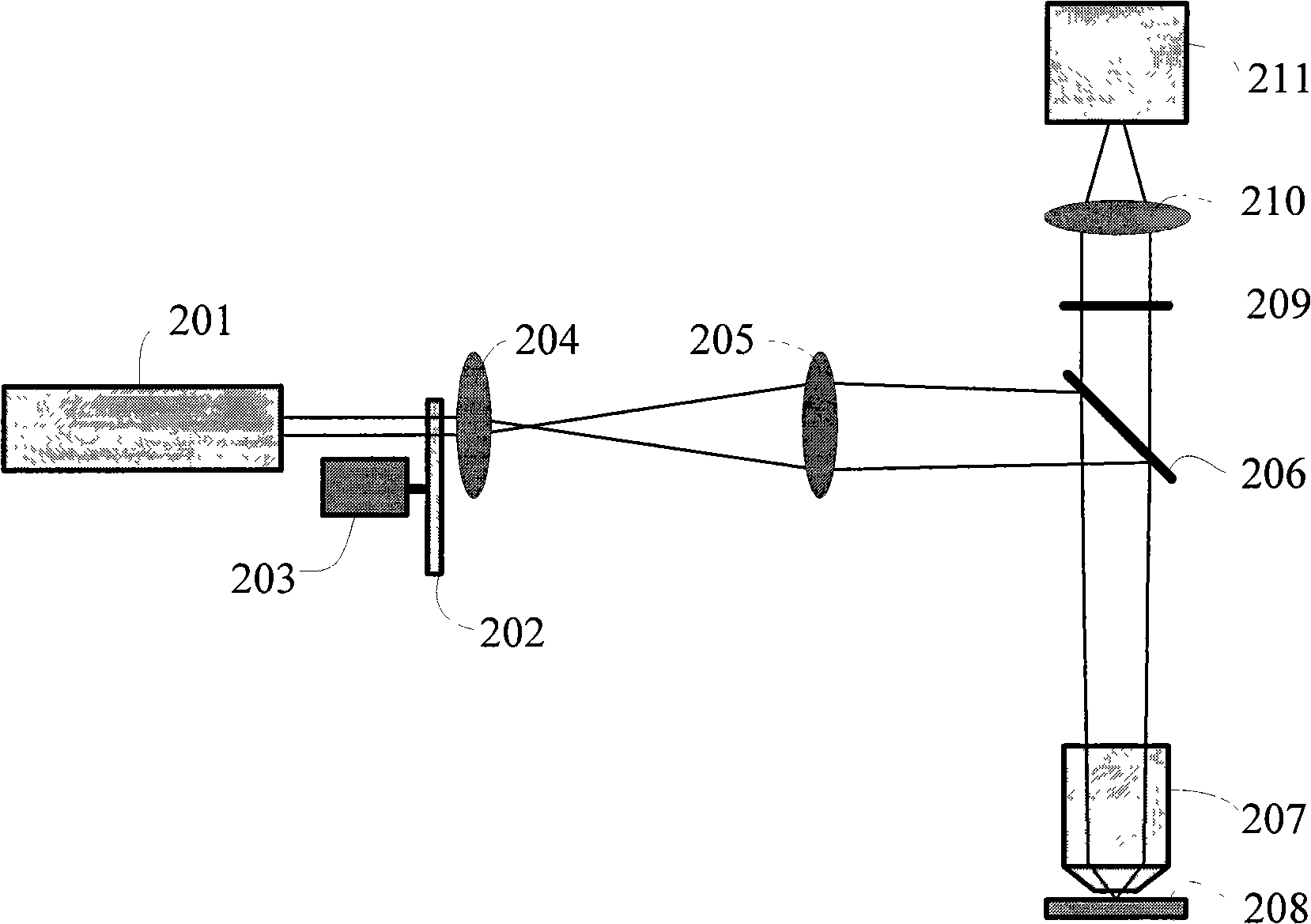
Method and apparatus realizing quasi confocal fluorescent microscopic with dynamic speckle illumination
InactiveCN101303302AGood value for moneySimple structureScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageEffect light
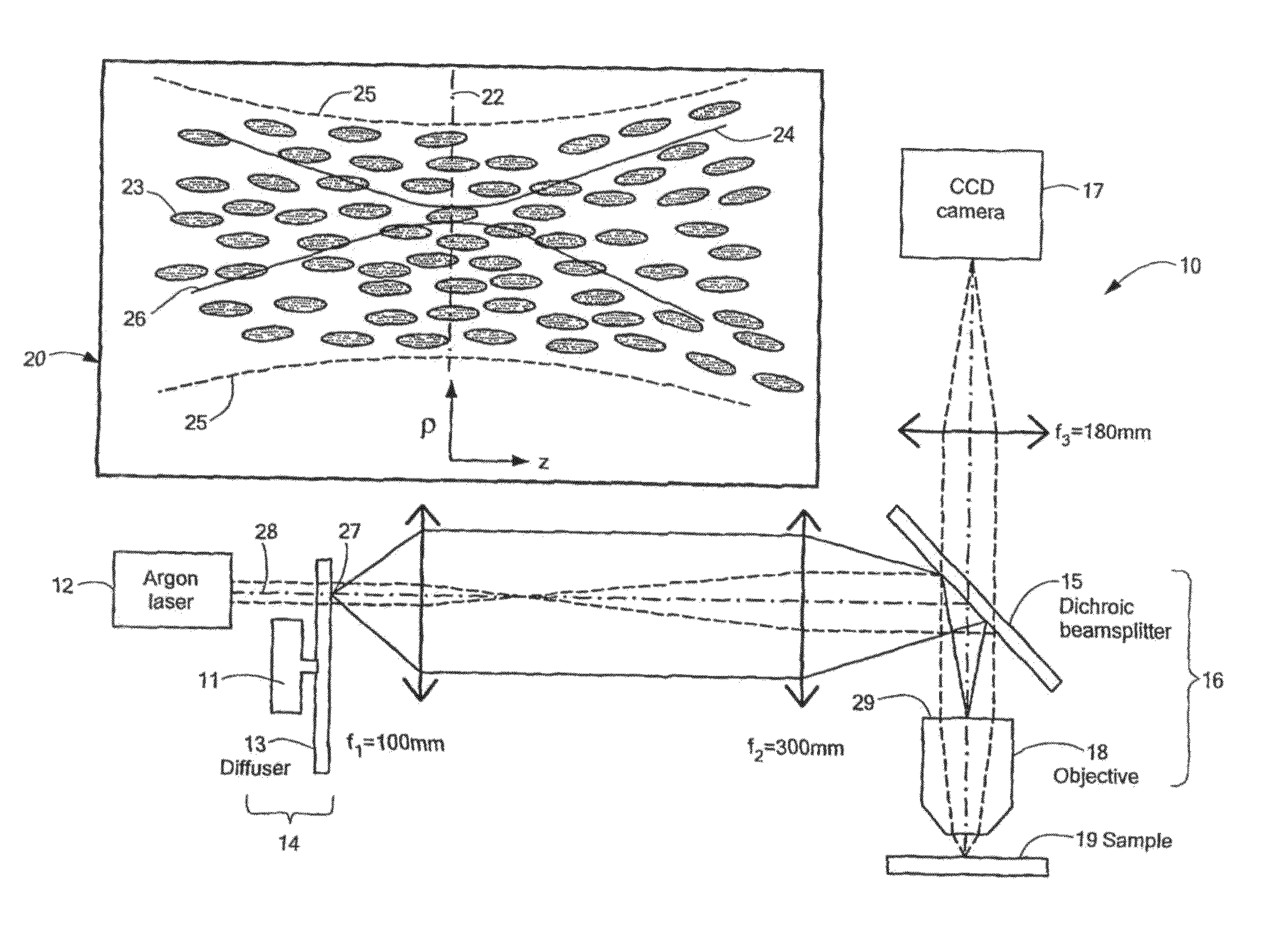
The present invention relates to a novel method and a novel device, incorporating dynamic speckle lighting with a conventional wide field fluorescence microscope organically to implement approximately confocal fluorescence microscopy (i.e., quasi-confocal fluorescence microscopy). The present invention employs an argon ion laser as the light source; the exciting light passes through a scattering object, a relay light path system for expanding and shaping, and then is coupled to the fluorescence microscope and focused to the sample. The stepping and revolution of the scattering object is controlled with a computer to produce a dynamic speckle pattern on the sample. The received fluorescent images are processed to obtain high-resolution spatial chromatographic images under no need to scan condition. The method can be used to obtain high-resolution three-dimensional chromatographic and microscopic image information of biological tissue samples in a non-intrusive manner. The device has simple structure, high cost-performance ratio, and is favorable for post data processing, easy to operate and apply; therefore, the device and method have a wide market application prospect and great significance for clinical diagnosis and life science research.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Laser speckle optical path and laser projection light source system
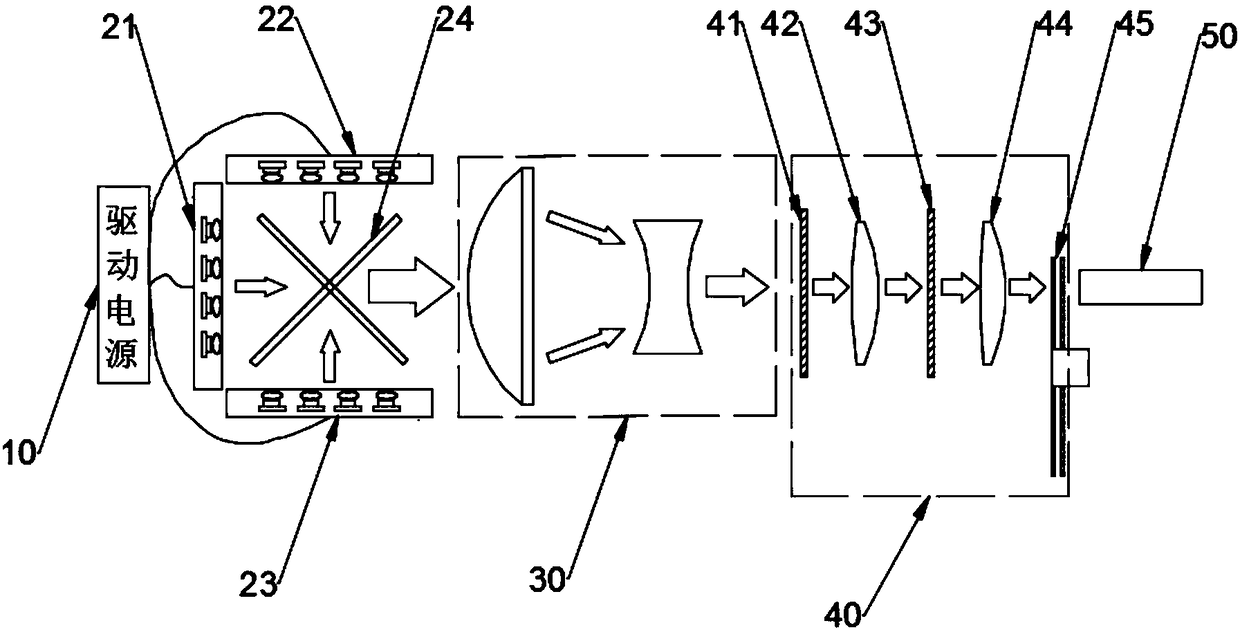
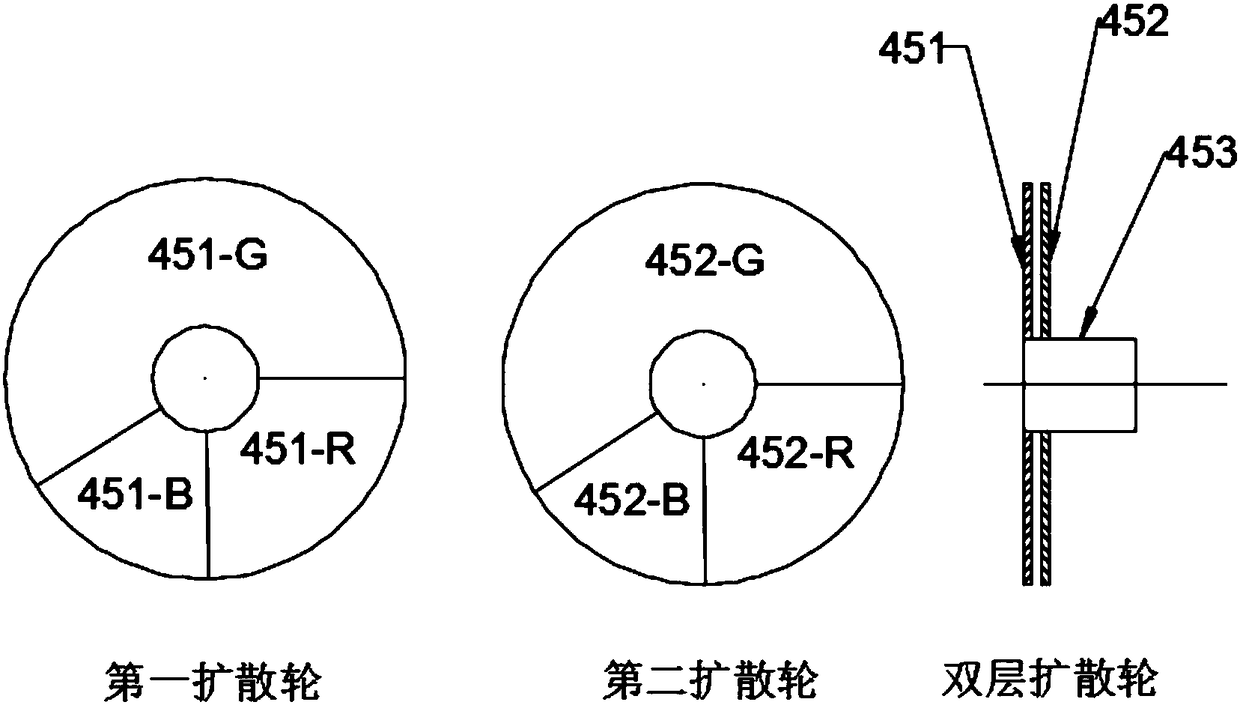
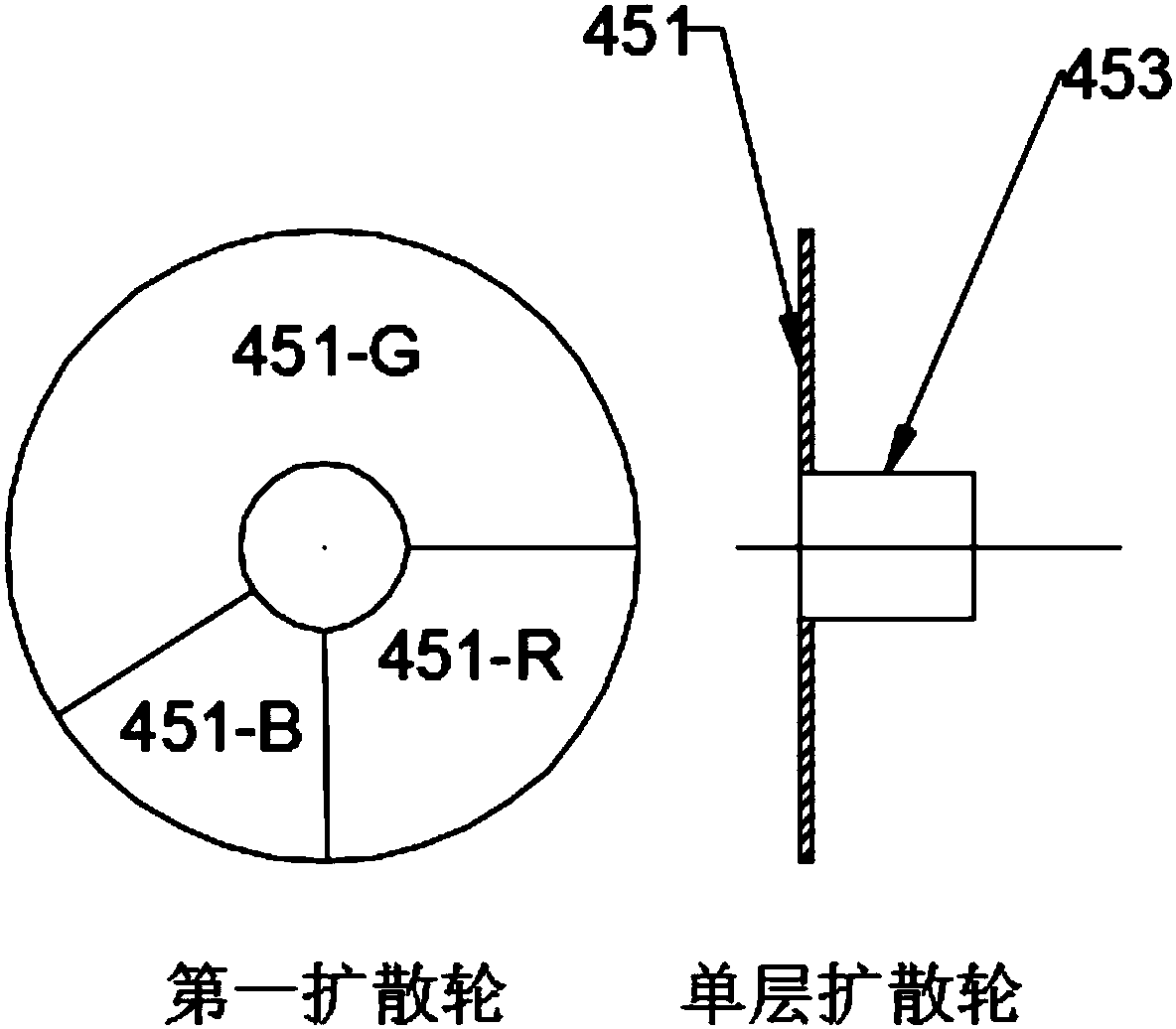
The invention discloses a laser speckle optical path and a laser projection light source system, and relates to the technical field of laser display. The system comprises a diffusion assembly and a lens assembly used for collimation and spotlight, the diffusion assembly is composed of at least two diffusion parts, wherein one of the diffusion parts is a dynamic speckle device, the other diffusionparts are static speckle devices, and the movement mode of the dynamic speckle device is cyclical rotation; and the lens assembly is arranged among the diffusion parts. The laser speckle optical pathand the laser projection light source system have the advantages that better speckle and facula homogenization functions can be achieved through the combined use of the dynamic diffusion assembly andstatic diffusion assemblies; the laser beams are diverged and collimated repeatedly to greatly reduce the spatial coherence of the laser beams, thereby effectively solving the problem of speckle; thelaser speckle optical path is simple in structure and small is size, and can be integrated easily in a laser display system to make the structure of an x ray machine more compact.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Particle image velocimetry suitable for x-ray projection imaging
ActiveUS20120237104A1Enhance the imageImprove overall utilizationImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayDynamic speckle
A 2D or 3D velocity field is reconstructed from a cross-correlation analysis of image pairs of a sample, without first reconstructing images of the sample spatial structure. The method can be implemented via computer tomographic X-ray particle image velocimetry, using multiple projection angles, with phase contrast images forming dynamic speckle patterns. Estimated cross-correlations may be generated via convolution of a measured autocorrelation function with a velocity probability density function, and the velocity coefficients iteratively optimised to minimise the error between the estimated cross-correlations and the measured cross-correlations. The method may be applied to measure blood flow, and the motion of tissue and organs such as heart and lungs.
Owner:4DX LTD
Particle image velocimetry suitable for X-ray projection imaging
ActiveUS9036887B2Improve overall utilizationImage enhancementImage analysisCross correlation analysisImage formation
A 2D or 3D velocity field is reconstructed from a cross-correlation analysis of image pairs of a sample, without first reconstructing images of the sample spatial structure. The method can be implemented via computer tomographic X-ray particle image velocimetry, using multiple projection angles, with phase contrast images forming dynamic speckle patterns. Estimated cross-correlations may be generated via convolution of a measured autocorrelation function with a velocity probability density function, and the velocity coefficients iteratively optimized to minimize the error between the estimated cross-correlations and the measured cross-correlations. The method may be applied to measure blood flow, and the motion of tissue and organs such as heart and lungs.
Owner:4DX LTD
Frequency domain laser speckle imaging based blood flow velocity measuring method
ActiveCN104173038AImprove measurement accuracyEliminate static noiseDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDynamic speckleSpeckle imaging
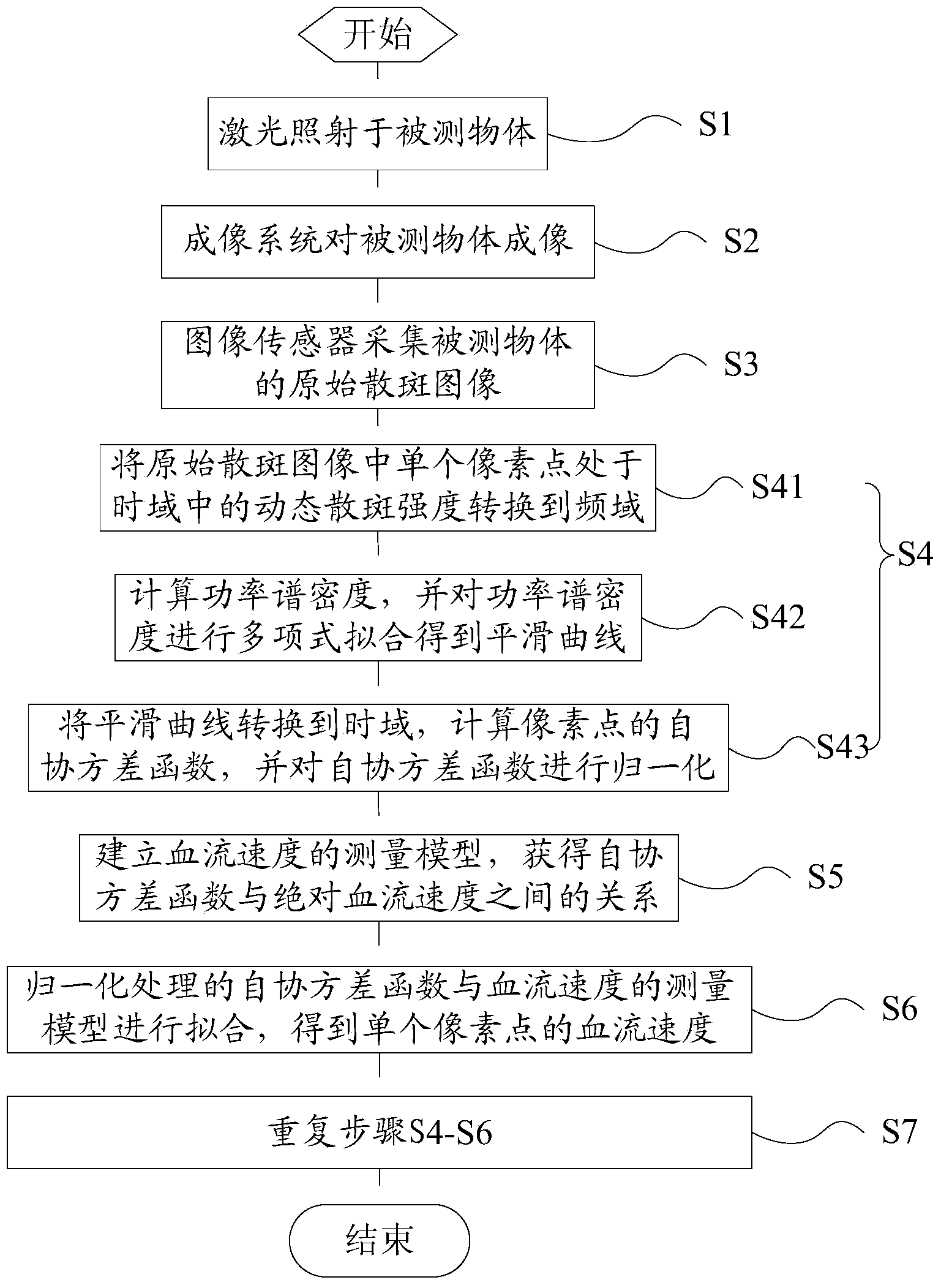
The invention discloses a frequency domain laser speckle imaging based blood flow velocity measuring method. The frequency domain laser speckle imaging based blood flow velocity measuring method comprises the following steps of illuminating laser beams on a measured object, imaging the measured object through an imaging system, collecting an original speckle image of the measured object through an image sensor, transferring dynamic speckle intensity with single pixel points being in a time domain of the collected original speckle image into a frequency domain, calculating the power spectral density, performing polynomial fitting on the power spectral density to obtain a smooth curve, transferring the smooth curve into the time domain through Fourier transform, calculating an autocovariance function of the pixel points and performing normalization, establishing a blood velocity measuring model, obtaining a relationship between the covariance function and the blood velocity and finally performing fitting to obtain a blood velocity value. The frequency domain laser speckle imaging based blood flow velocity measuring method has the advantages of not only eliminating static noise, improving the blood velocity measuring accuracy, avoiding influences from imaging environmental factors such as intensity and illumination angles and improving the measuring stability.
Owner:亿慈(上海)智能科技有限公司
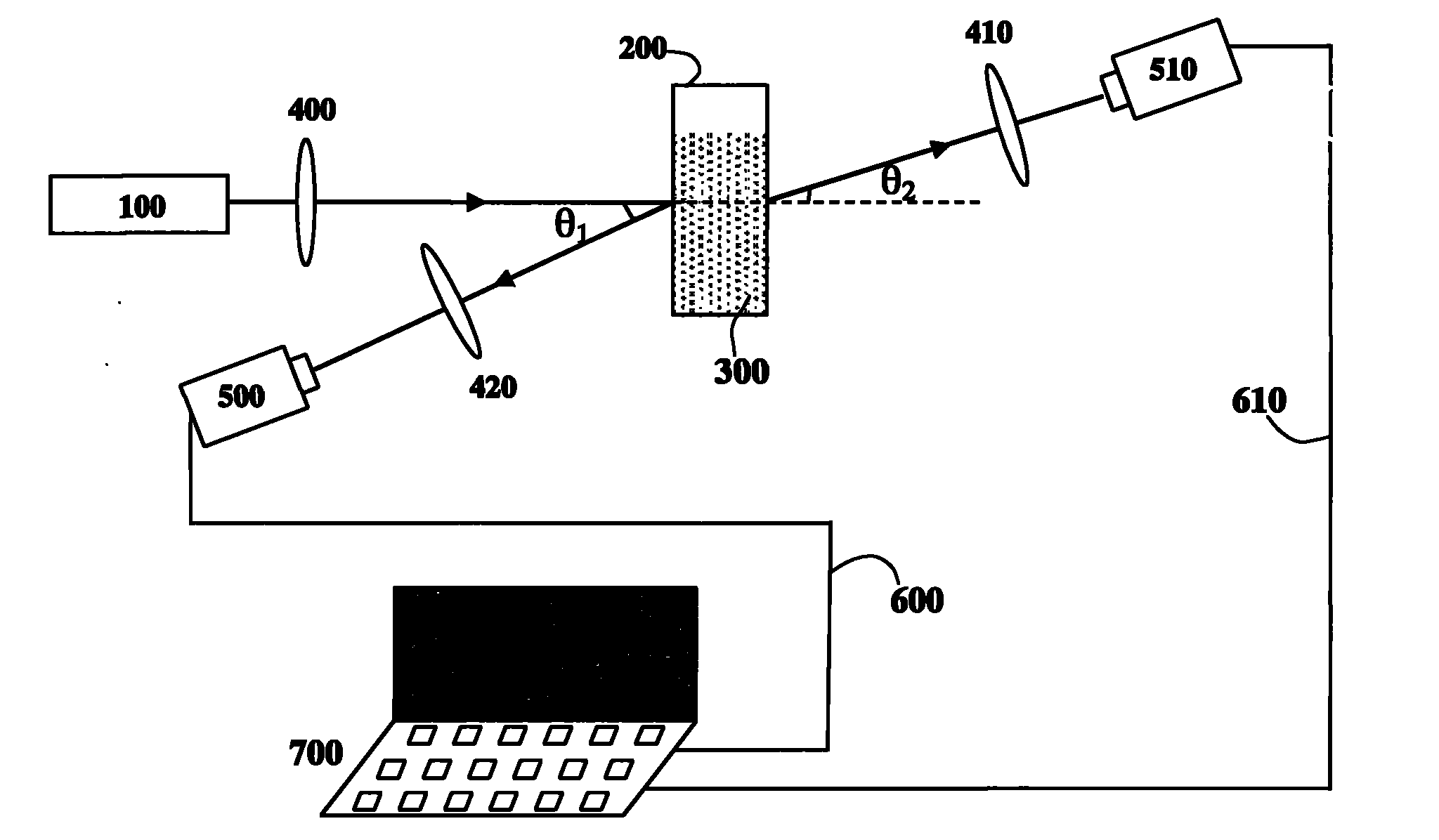
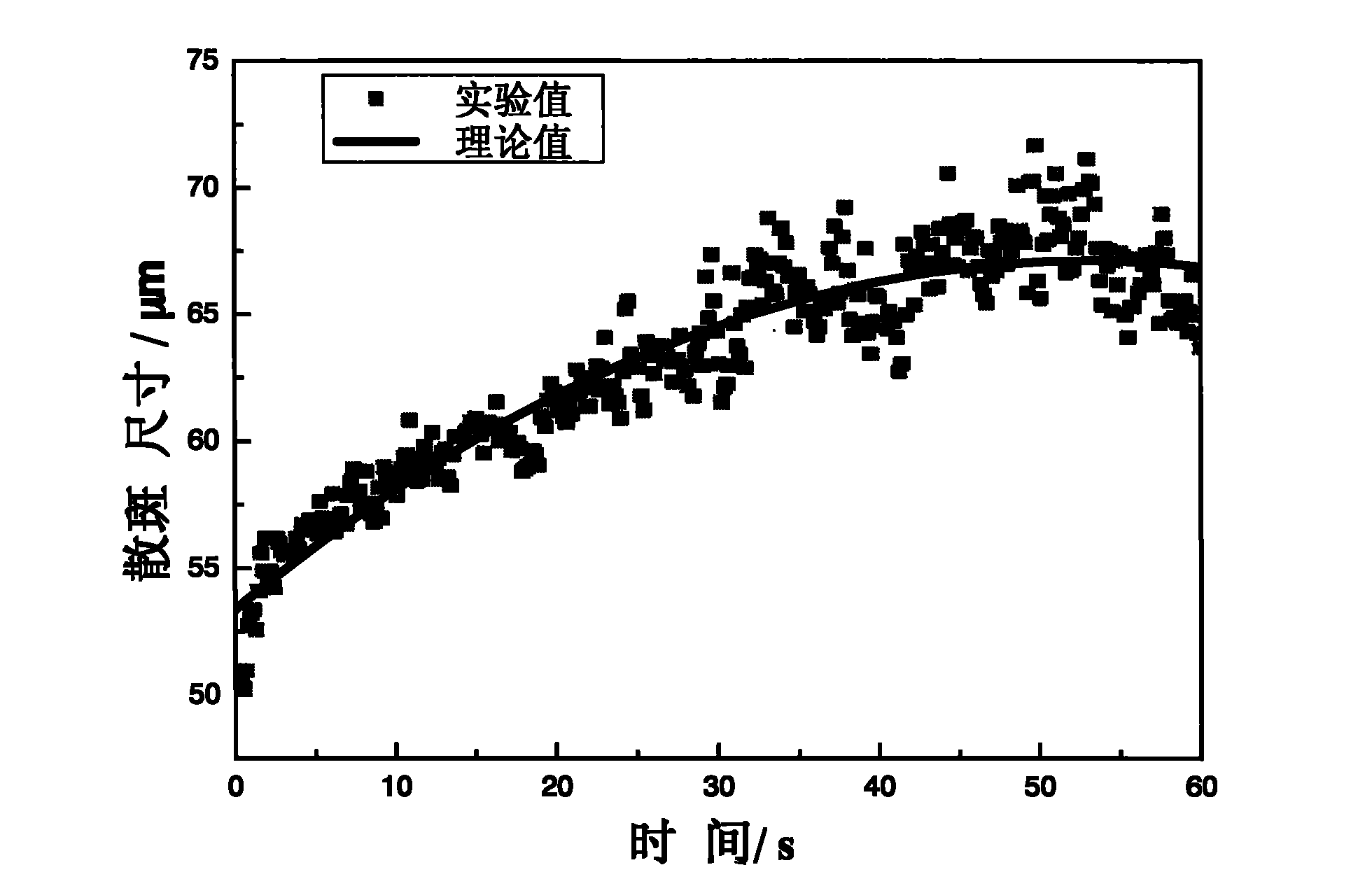
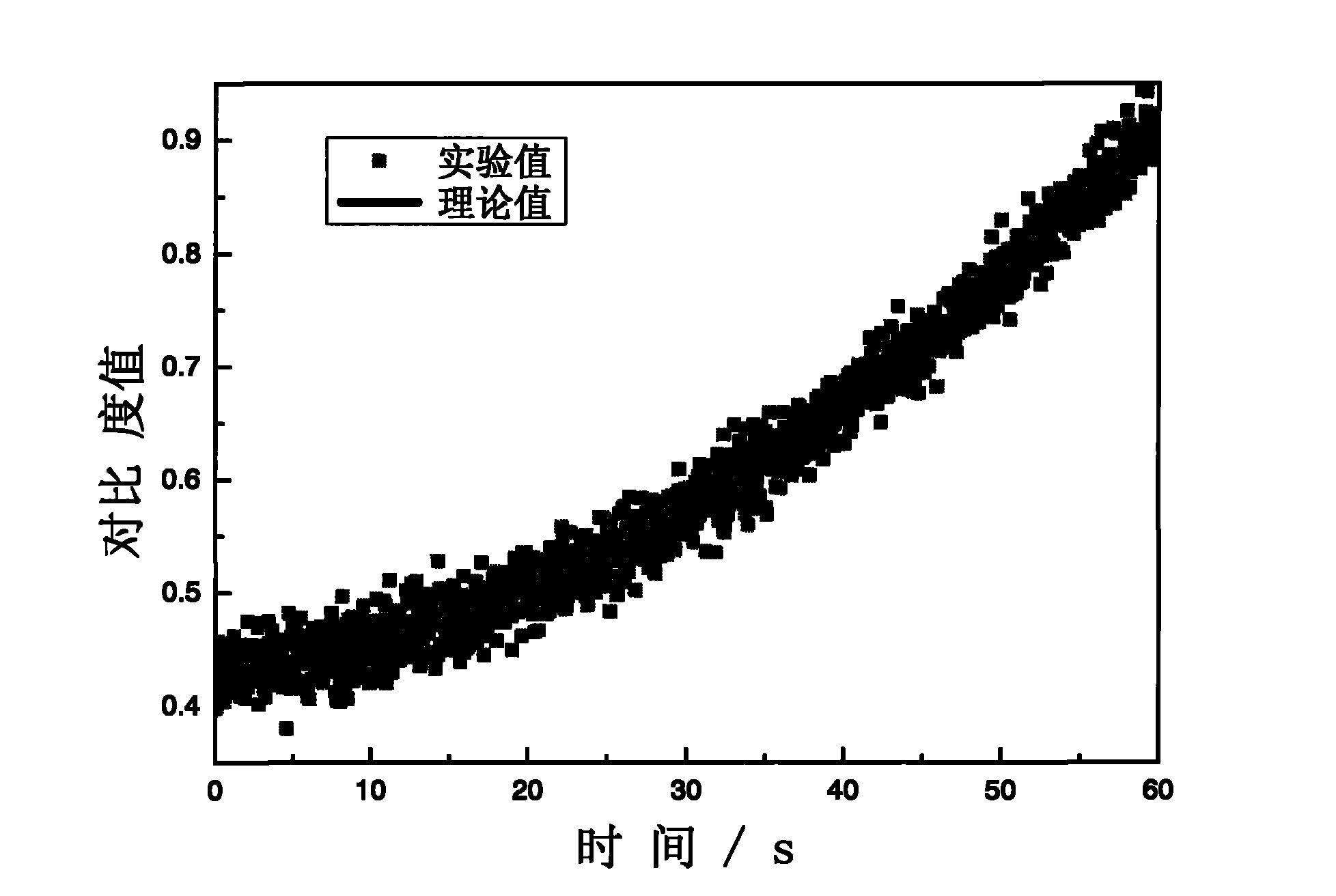
Dynamic speckle measurement method for particle size and concentration change of turbid medium
InactiveCN101788448AParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisForward scatterComputational physics
The invention discloses a dynamic speckle measurement method for the particle size and concentration change of turbid medium. The invention adopts the principle that when laser irradiates on turbid medium solution with dynamic change, dynamic speckles are formed in a forward scattering field and a backward scattering field, and the speckle size and contrast value of a dynamic speckle picture is in direct proportion with the particle size in the turbid media and in inverse proportion with concentration. Therefore, the particle size and concentration change in the turbid medium can be dynamically monitored in a real time mode by calculating the change of speckle size and contrast value of a dynamic speckle picture sequence. The method is a non-invasive type detection method, has the characteristics of simple operation and wide application range, and can be widely applied in the fields of medical biology, atmospheric environmental monitoring, underwater exploration, and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
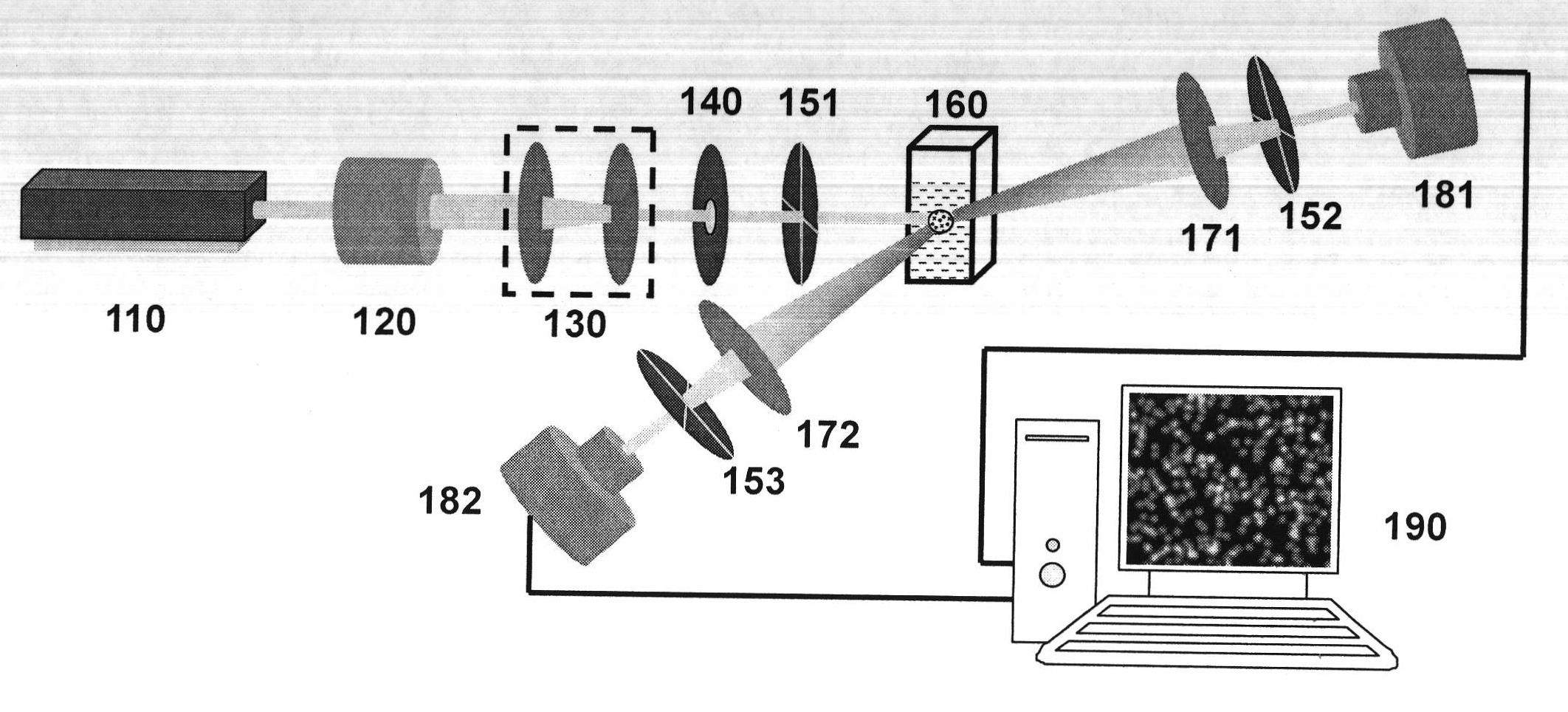
Device and method for measuring particulate motion of turbid media by using dynamic speckle method
InactiveCN102175580AEliminate the effects of measurement accuracyMeasuring DynamicsMaterial analysisParticulatesForward scatter
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring particulate motion of turbid media by using a dynamic speckle method. The device comprises a laser beam shaping contracting part, a forward scattering speckle field measuring part, a backward scattering speckle field measuring part, and a computer control and processing system. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing the device to record a forward scattering speckle field and a backward scattering speckle field generated by the particulate motion of turbid media and store the fields into the computer; according to the particle light scattering theory, choosing the forward scattering speckle field or backward scattering speckle field data; and analyzing the motion characteristic of the particulate, by utilizing a speckle chart characteristic value. The method is characterized by real time, dynamic and accuracy and can be widely applied to the fields such as medicaments, biology, life science, and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Complete and high-resolution test method for motion characteristics of particles in turbid media
InactiveCN101980000AReal-time detectionContinuous detectionScattering properties measurementsApplicability domainTemporal resolution
The invention discloses a complete and high-resolution test method for the motion characteristics of particles in turbid media. The method comprises the following steps of: performing continuous, complete and real-time detection on the motion characteristics of the particles in the process of 'solution-colloid-sediment' of the turbid media by combining the resolution relation between the characteristic value of a speckle pattern and particle motion and utilizing a dynamic speckle test light path according to the particle light scattering theory; simultaneously, performing transient study on different critical points of the particle motion in the process by using a femtosecond laser test light path to perform the analysis of high spatial and temporal resolution on transient dynamics of the particles in the turbid media; and combining the two steps to realize the complete test with high spatial and temporal resolution characteristic on motion images of the particles in the process of 'solution-colloid-sediment' of the turbid media finally. The method is a non-contact, high-accuracy and real-time online detection method, has the characteristics that the operation is simple and the application range is wide, and can be widely used in the fields of medical science, pharmacy, chemical production and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Partical image velocimetry suitable for X-ray projection imaging
ActiveUS9025849B2Improve overall utilizationMinimize exposureTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionX-rayDynamic speckle
A 2D or 3D velocity field is reconstructed from a cross-correlation analysis of image pairs of a sample, without first reconstructing images of the sample spatial structure. The method can be implemented via computer tomographic x-ray particle image velocimetry, using multiple projection angles, with phase contrast images forming dynamic speckle patterns. Estimated cross-correlations may be generated via convolution of a measured autocorrelation function with a velocity probability density function, and the velocity coefficients iteratively optimized to minimize the error between the estimated cross-correlations and the measured cross-correlations. The method may be applied to measure blood flow, and the motion of tissue and organs such as heart and lungs.
Owner:4DX LTD
Method for eliminating laser display speckles and laser source
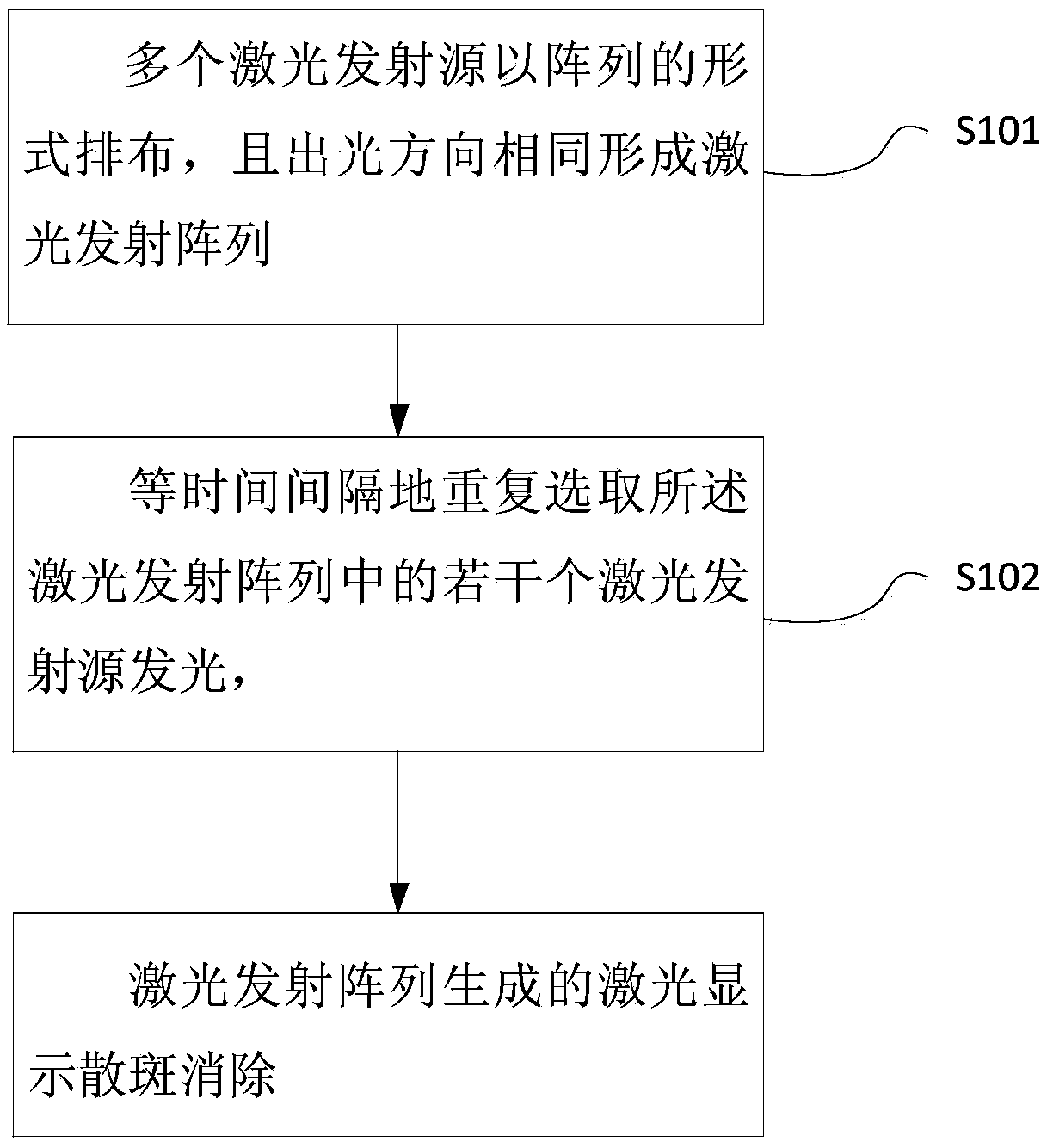
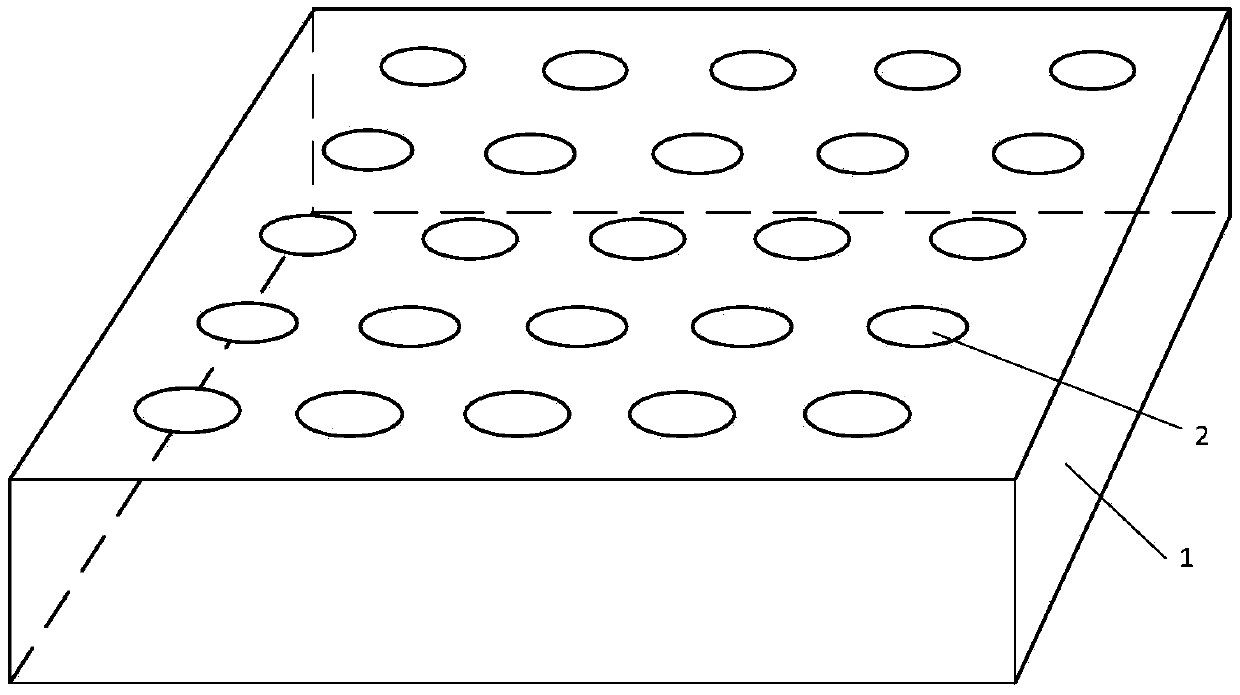
InactiveCN105372827AIncrease profitDecoherenceSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsOptical energyDynamic speckle
The invention relates to the technical field of laser display and discloses a method for eliminating laser display speckles and a laser source. The method comprises steps of: arranging multiple laser emission sources in an array, wherein the multiple laser emission sources have the same light emission direction and form a laser emission array; repeatedly enabling, at equal time intervals, a plurality of laser emission sources in the laser emission array to emit laser until the laser display speckles generated by the laser emission array are eliminated, wherein the number of the selected laser emission sources is a preset value, and the number of the selected laser emission sources at each time is not completely same. The method enables multiple laser emission sources in the laser emission array to emit laser in turns so as to eliminate the time coherence of the laser emission sources and continuously superpose the dynamic speckles, thereby gradually reducing the contrast of the speckles and finally eliminating the speckles. In addition, other optical devices are not arranged in an optical path so that the utilization rate of optical energy is increased and laser display quality is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
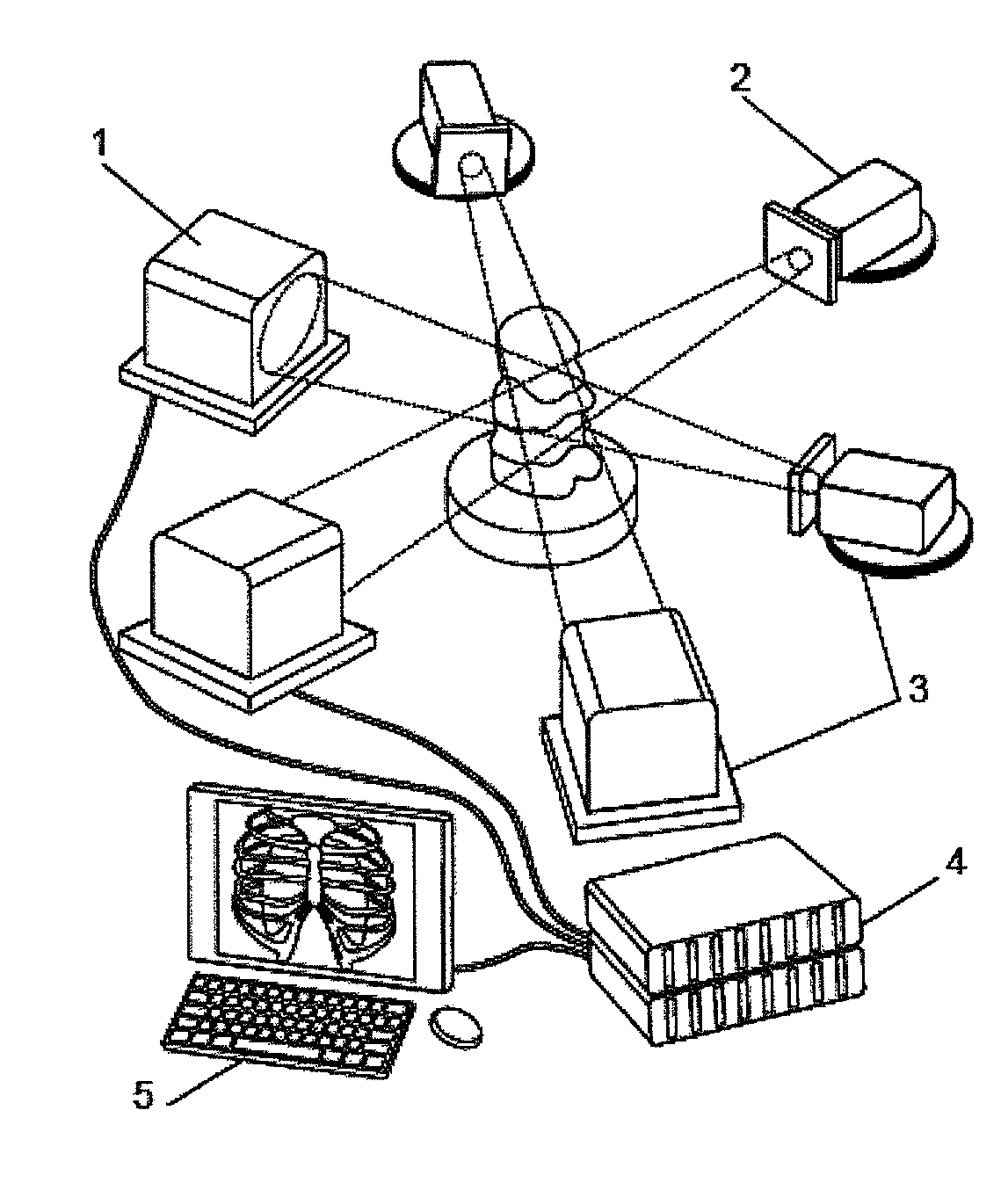
Vision measurement device of sheet forming limit curve
InactiveCN103969134AHigh precisionQuickly get measurement resultsInvestigating material ductilityMeasurement deviceEngineering
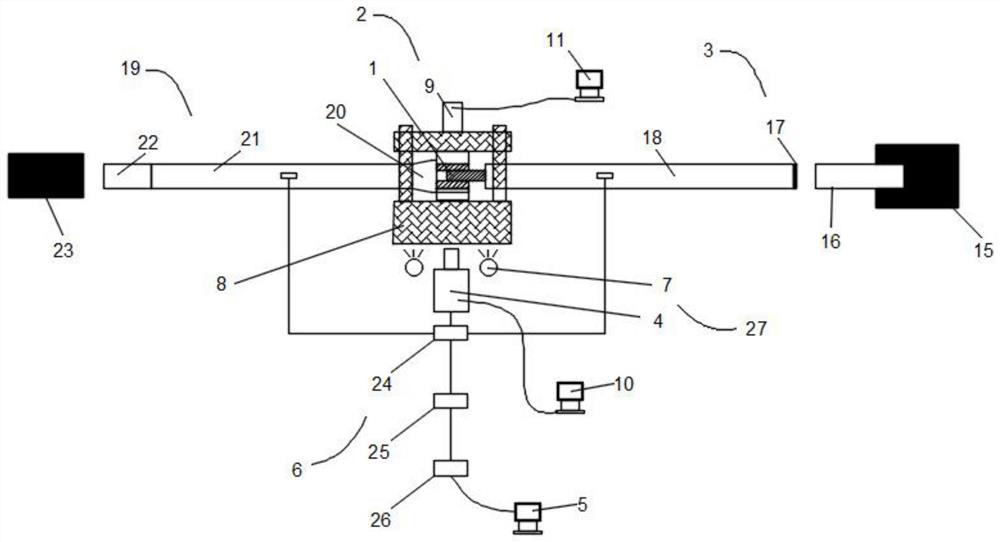
The invention discloses a vision measurement device of a sheet forming limit curve. The vision measurement device comprises a dynamic speckle strain measurement system and a cupping forming tester, wherein the dynamic speckle strain measurement system comprises a binocular stereoscopic measuring head (1); and the cupping forming tester comprises a measuring head bracket (2), an integrated rack (3), a cupping forming stamping device (4) and a built-in punching machine. The vision measurement device can perform high-precision measurement to obtain high-precision material data, can rapidly obtain the measurement results and is low in cost.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
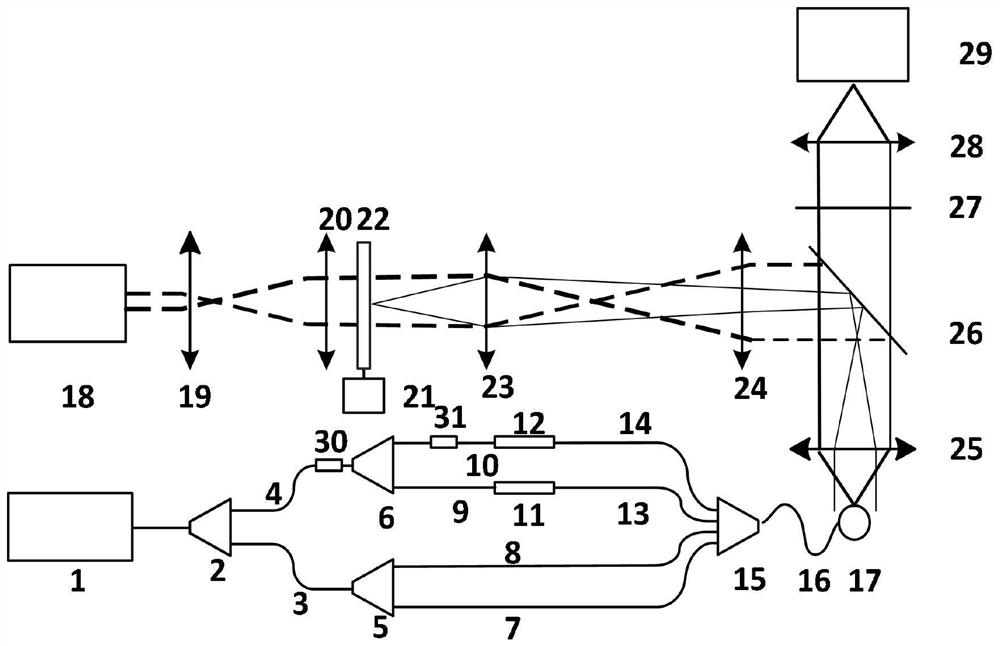
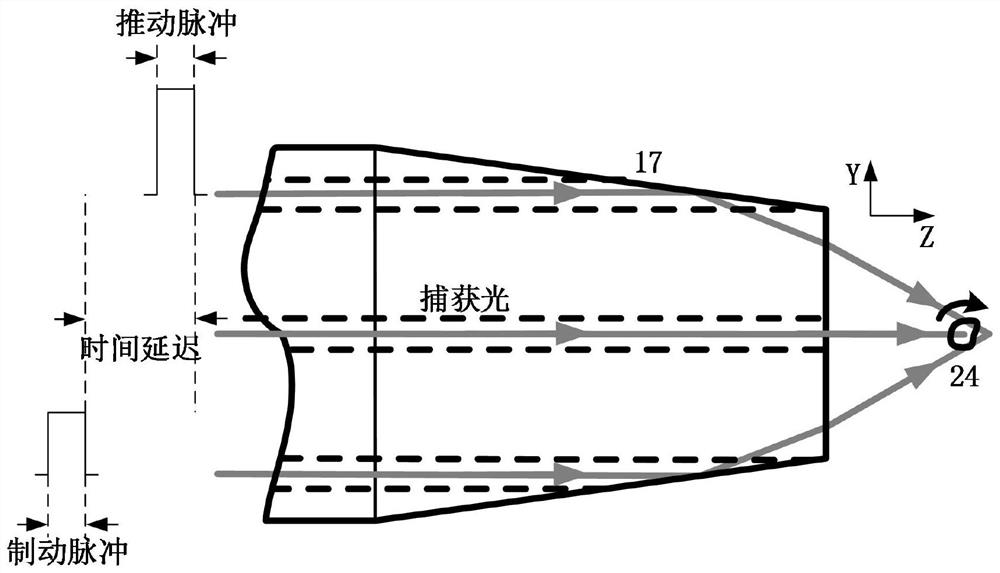
Microscopic imaging method and system based on double-core optical fiber light control and dynamic speckle illumination
ActiveCN112835190ACompact structureImprove time resolutionMicroscopesIndividual particle analysisFluorescenceTomographic image
The invention provides a microscopic imaging method and system based on double-core optical fiber light control and dynamic speckle illumination. The method is characterized in that a light control part of the device is formed by oppositely installing two two-core optical fibers of which the output end surfaces are processed into specific angles. Laser beams are respectively coupled into a two-core optical fiber through a single-mode optical fiber, a focusing light field is formed near an output end face, and cells to be detected are stably captured. And the cells rotate around a specific axis by adjusting the output power of each fiber core of the other two-core optical fiber. And after the cells rotate to a certain angle and reach a stable state every time, a tomographic image of the cells is acquired by using a dynamic speckle illumination wide-field fluorescence microscopy technology, and finally a three-dimensional structure image of the cells is reconstructed. The system constructed by the invention can be used for obtaining a three-dimensional structure image with high temporal and spatial resolution of a living single cell, has the characteristics of simple structure, low cost, simplicity and convenience in operation and the like, and has wide application prospects in numerous research fields such as biology, medicine, life science and the like.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Dynamic speckle eliminating device for laser projection display
InactiveCN109375382AReduced phase coherenceGood speckle effectProjectorsOptical elementsLight beamPrism
The invention disclose a dynamic speckle eliminating device for laser projection display, relates to the technical field of laser projection display, and aims at improving the speckle eliminating effect. The dynamic speckle eliminating device comprises a prism and a driving part, the prism includes first and second diffusing surfaces and a reflection surface, and a laser beam is input in the firstdiffusing surface, reflected in the reflection surface and finally output from the second diffusing surface; and the driving part drives the prism to vibrate according to a preset track and period. In the vibration process of the dynamic speckle eliminating device, the two diffusing surfaces generate different vibration tracks, so that the phase coherence of the laser beam is reduced greatly, anda better speckle eliminating effect is achieved. The dynamic speckle eliminating device is suitable for a laser projector.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Speckle elimination light path and three-color laser projection system
ActiveCN109270703AReduce volumeReduce in quantityProjectorsOptical elementsMiniaturizationProjection system
The invention discloses a speckle elimination light path and a three-color laser projection system, which relate to the technical field of laser display. The three-color laser projection system comprises a reflective optical path assembly, a dynamic speckle elimination device and an optical rod, wherein the dynamic speckle elimination device comprises a diffusing component and a driving componentconnected with the diffusing component; and the reflective optical path assembly focuses a laser beam passing through the diffusing component to an inlet of the optical rod after at least one reflection. The light path turns for multiple times by means of the reflective optical path assembly, the functions of a plurality of dynamic speckle elimination devices are realized by means of only one dynamic speckle elimination device disclosed by the invention, and a good speckle elimination effect is achieved. The laser speckle elimination light path provided by the invention is simple in structure,the reflection or refraction and reflection combined light path design makes the structure of an optical machine more compact, and the miniaturization of the three-color laser projection system is easy to realize.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Particle image velocimetry suitable for x-ray projection imaging
ActiveUS20140334710A1Improve overall utilizationMinimize exposureImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayDynamic speckle
A 2D or 3D velocity field is reconstructed from cross-correlation analysis of image pairs of a sample, without first reconstructing images of the sample spatial structure. The method can be implemented via computer tomographic X-ray particle image velocimetry, using multiple projection angles, with phase contrast images forming dynamic speckle patterns. Estimated cross-correlations may be generated via convolution of a measured autocorrelation function with a velocity probability density function, and the velocity coefficients iteratively optimised to minimise the error between the estimated cross-correlations and the measured cross-correlations. The method may be applied to measure blood flow, and the motion of tissue and organs such as heart and lungs.
Owner:4DX LTD
High-brightness controllable pseudo-thermal light source based on liquid crystal light valve modulation
ActiveCN101839763AReduce lossesAvoid difficultiesPhotometryNon-linear opticsLiquid crystal light valveRgb image
The invention discloses a high-brightness controllable pseudo-thermal light source based on liquid crystal light valve modulation, which comprises a pulsed laser, an adjustable beam expanding and collimating system, a polarizer, a first analyzer, an adjustable aperture diaphragm, a liquid crystal light valve, a second analyzer and a liquid crystal light valve control system. The pulsed laser, the adjustable beam expanding and collimating system, the polarizer, the first analyzer and the adjustable aperture diaphragm are arranged on the same optical axis. The optical axis is arranged on the incident light optical axis of the liquid crystal light valve. The second analyzer is arranged on the reflected light optical axis of the liquid crystal light valve corresponding to the incident light optical axis. Laser light output by the laser finally irradiates the liquid crystal light valve controlled by a liquid crystal light valve control system. Through controlling the liquid crystal light valve, a dynamic speckle field, i.e. a pseudo-thermal light field is obtained. The thermal fluctuation of the high-brightness controllable pseudo-thermal light source produced by the invention can be truly recorded by the photoelectric detection system of a limited transmission band, the cross spectrum purity conditions satisfying a true-thermal light field can be obtained through controlling RGB images loaded on the liquid crystal light valve and the pseudo-thermal light field produced at any time is controllable.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical vortices-based dynamic speckle test method
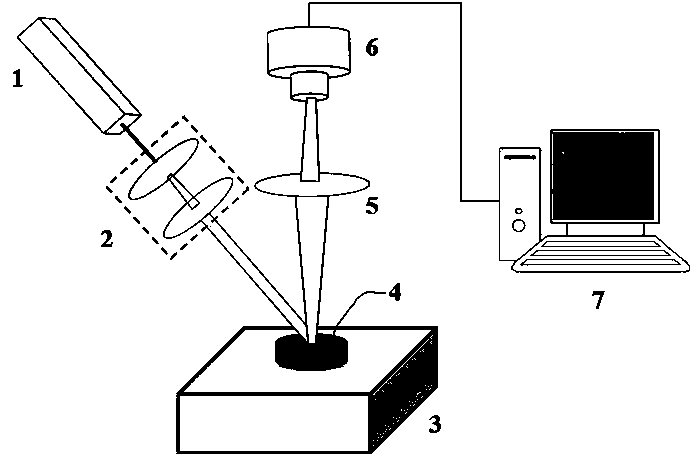
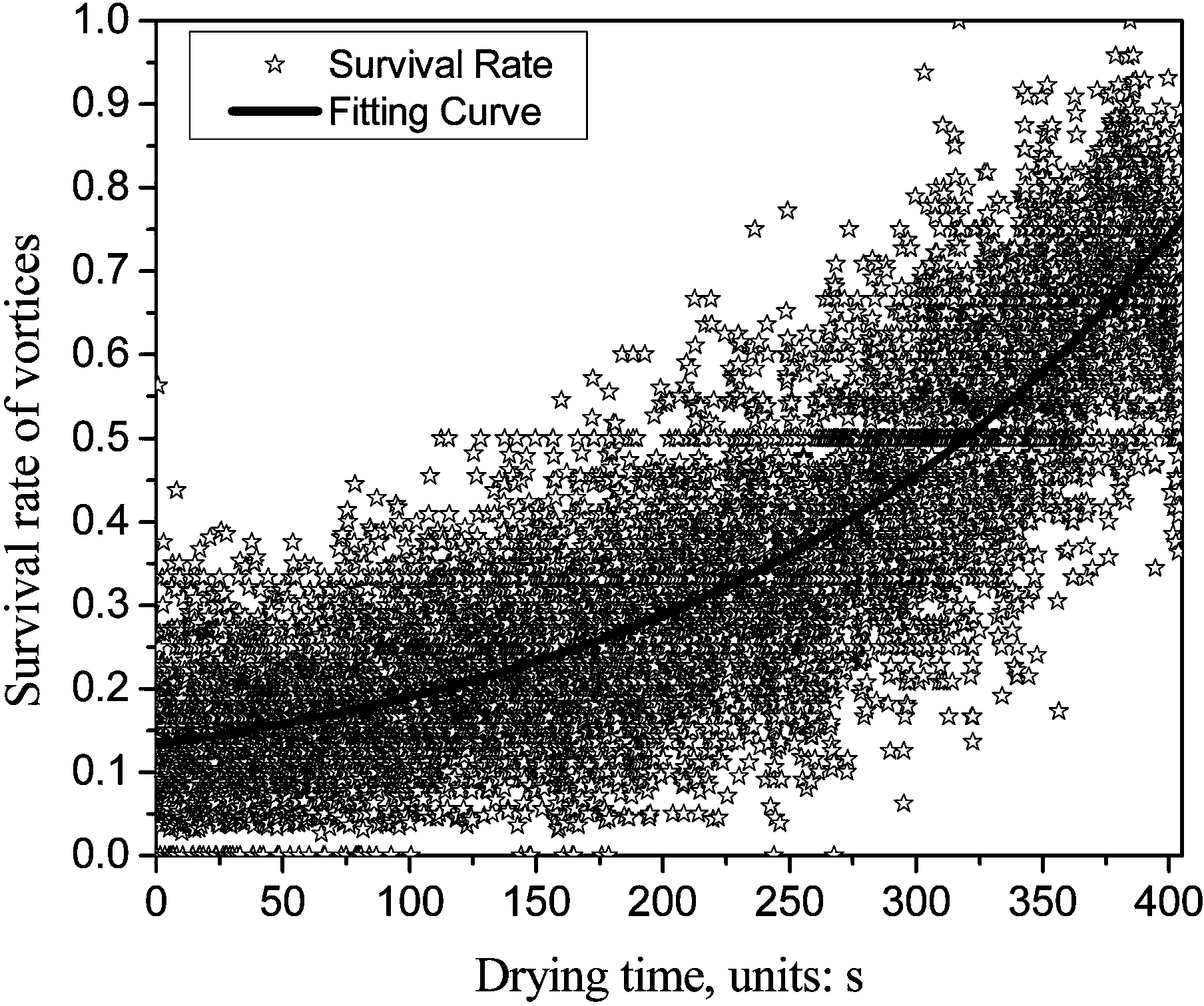
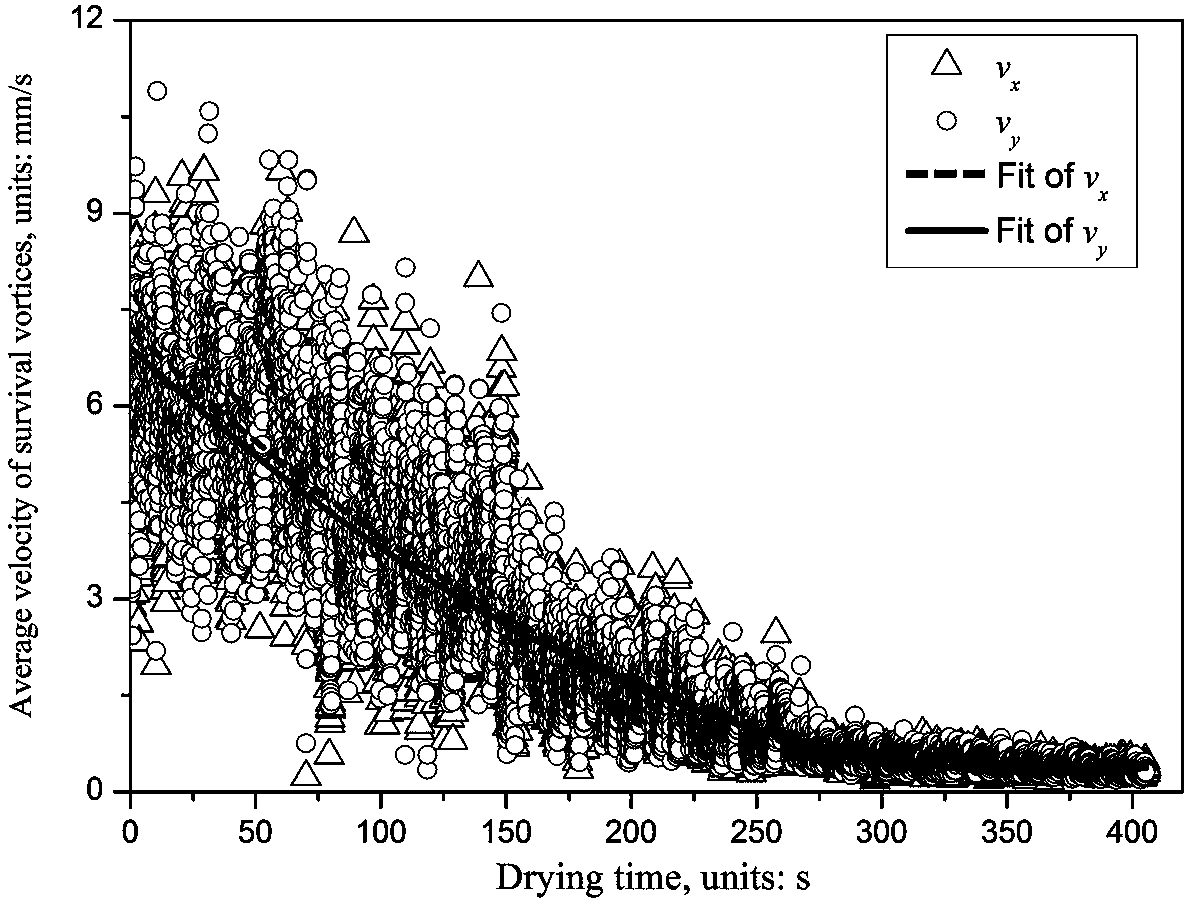
InactiveCN103383353AWith characteristicsHave made significant progressPhase-affecting property measurementsComputational physicsParticle physics
The invention discloses an optical vortices-based dynamic speckle test method. The optical vortices-based dynamic speckle test method comprises following steps: firstly, dynamic speckle sequential images of a dynamic changing process of an object is obtained; then the dynamic speckle sequential images are converted by a Laguerre-Gauss complex filter so as to obtain an optical vortices core structure parameter distribution matrix; and at last, quantitative analysis and measurement of the dynamic changing process are realized by using two novel characteristic factors, wherein the two novel characteristic factors are dynamic vortex survival rate and in-plane average speed of survival vortex. The optical vortices-based dynamic speckle test method is capable of realizing monitoring on dynamic random processes effectively, and is suitable for rapid changing and gradual changing processes, and quasi-static processes.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-brightness controllable pseudo-thermal light source based on liquid crystal light valve modulation
ActiveCN101839763BAvoid difficultiesReduce lossesPhotometryNon-linear opticsLiquid crystal light valveRgb image
The invention discloses a high-brightness controllable pseudo-thermal light source based on liquid crystal light valve modulation, which comprises a pulsed laser, an adjustable beam expanding and collimating system, a polarizer, a first analyzer, an adjustable aperture diaphragm, a liquid crystal light valve, a second analyzer and a liquid crystal light valve control system. The pulsed laser, theadjustable beam expanding and collimating system, the polarizer, the first analyzer and the adjustable aperture diaphragm are arranged on the same optical axis. The optical axis is arranged on the incident light optical axis of the liquid crystal light valve. The second analyzer is arranged on the reflected light optical axis of the liquid crystal light valve corresponding to the incident light optical axis. Laser light output by the laser finally irradiates the liquid crystal light valve controlled by a liquid crystal light valve control system. Through controlling the liquid crystal light valve, a dynamic speckle field, i.e. a pseudo-thermal light field is obtained. The thermal fluctuation of the high-brightness controllable pseudo-thermal light source produced by the invention can be truly recorded by the photoelectric detection system of a limited transmission band, the cross spectrum purity conditions satisfying a true-thermal light field can be obtained through controlling RGB images loaded on the liquid crystal light valve and the pseudo-thermal light field produced at any time is controllable.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser speckle contrast ratio measuring method
InactiveCN104457977AReduce evaluation errorsComplete Characterization of SpecklePhotometry using reference valueSpeckle contrastLaser intensity
The invention provides a laser speckle contrast ratio measuring method. The method includes the following steps of setting a template length NT, wherein the template length NT represents the number of pixels participating in calculation of the method each time, the value of NT ranges from 1 to N, and N represents the total number of pixels of a measured laser field; calculating the average laser intensity and variance of pixel positions N(n) within the range of the template length NT, wherein n is equal to 1, 2, ..., N-NT+1, and the value of N(n) ranges from 1 to NT; calculating the dynamic speckle contrast ratio of a speckle image, wherein the speckle contrast ratio of the template length NT is the ratio of the standard deviation of the pixel positions N(n) to the average laser intensity of the pixel positions N(n); moving the position of a template without changing the template length NT, and repeating the steps to obtain a series of speckle contrast ratios. By means of the method, the contrast ratio of the whole frame of image can be dynamically reflected, the characteristics of speckles can be completely presented, and the estimation errors of laser display system indexes can be reduced as well.
Owner:PHOEBUS VISION OPTO ELECTRONICS TECH
Dynamic speckle fluorescence microscopic imaging method and system based on four-core optical fiber light control
PendingCN113514442AFast imagingHigh resolutionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterFluorescence
The invention provides a dynamic speckle fluorescence microscopic imaging method and system based on four-core optical fiber light control. The device is characterized in that a light control part of the device is formed by mounting a four-core optical fiber of which the output end face is processed into a specific angle. A laser beam is divided into four beams through a beam splitter, the four beams are coupled into a four-core optical fiber through single-mode optical fibers respectively, a Bessel light field can be formed near the output end face, cells to be detected are stably captured, the output power of fiber cores of the optical fibers can be changed by adjusting a modulator, and the cells are made to rotate around a specific axis. And after the cells rotate to a certain angle and reach a stable state every time, a tomographic image of the cells is acquired by using a dynamic speckle illumination wide-field fluorescence microscopy technology, and a three-dimensional structure image of the cells is finally reconstructed. The constructed system has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in cost, easy to operate and the like, and has wide application prospects in many research fields such as biology, medicine and life science.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
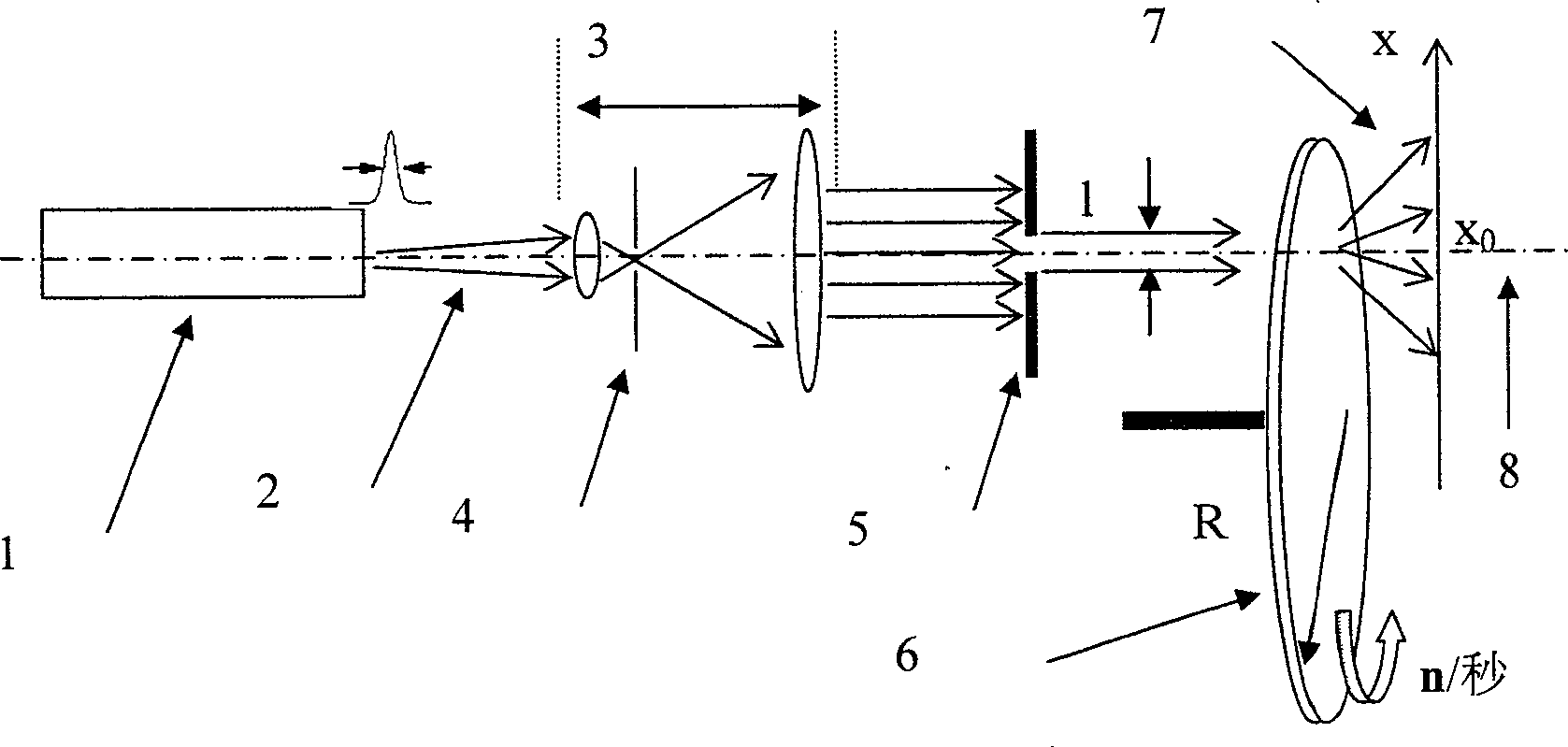
High-light pulse type pseudo-thermal light source
ActiveCN100514011CAvoid difficultiesOvercoming shortcomings of cross-spectrum purity conditionsLaser detailsPhotometryOptoelectronicsDynamic speckle
A high-brightness pulsed pseudothermal light source, which consists of a pulsed laser, a beam expander collimation system, a pinhole filter, an adjustable aperture stop, a frosted glass disc and a speed-regulating motor, the pulsed laser, beam expander The collimation system, the pinhole filter and the adjustable aperture stop are on the same optical axis, the pinhole filter is placed on the focal plane of the telescope of the beam expander collimation system, and the laser output from the pulsed laser Finally, it is irradiated on the frosted glass disk driven by the speed-adjusting motor to form a dynamic speckle field, which is the pseudo-thermal optical field. The thermal fluctuation of the pseudothermal optical field of the high-brightness pulsed pseudothermal light source of the present invention can be truly recorded by the photoelectric detection system with a limited passband, and is not affected by the passband of the photoelectric detection system used, meeting the requirements of the real thermal optical field Cross Spectrum Purity Conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A speckle-dissipating light path and three-color laser projection system
ActiveCN109270703BReduce volumeReduce in quantityProjectorsOptical elementsMiniaturizationEngineering
The invention discloses a speckle elimination light path and a three-color laser projection system, which relate to the technical field of laser display. The three-color laser projection system comprises a reflective optical path assembly, a dynamic speckle elimination device and an optical rod, wherein the dynamic speckle elimination device comprises a diffusing component and a driving componentconnected with the diffusing component; and the reflective optical path assembly focuses a laser beam passing through the diffusing component to an inlet of the optical rod after at least one reflection. The light path turns for multiple times by means of the reflective optical path assembly, the functions of a plurality of dynamic speckle elimination devices are realized by means of only one dynamic speckle elimination device disclosed by the invention, and a good speckle elimination effect is achieved. The laser speckle elimination light path provided by the invention is simple in structure,the reflection or refraction and reflection combined light path design makes the structure of an optical machine more compact, and the miniaturization of the three-color laser projection system is easy to realize.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Character recognition system and method
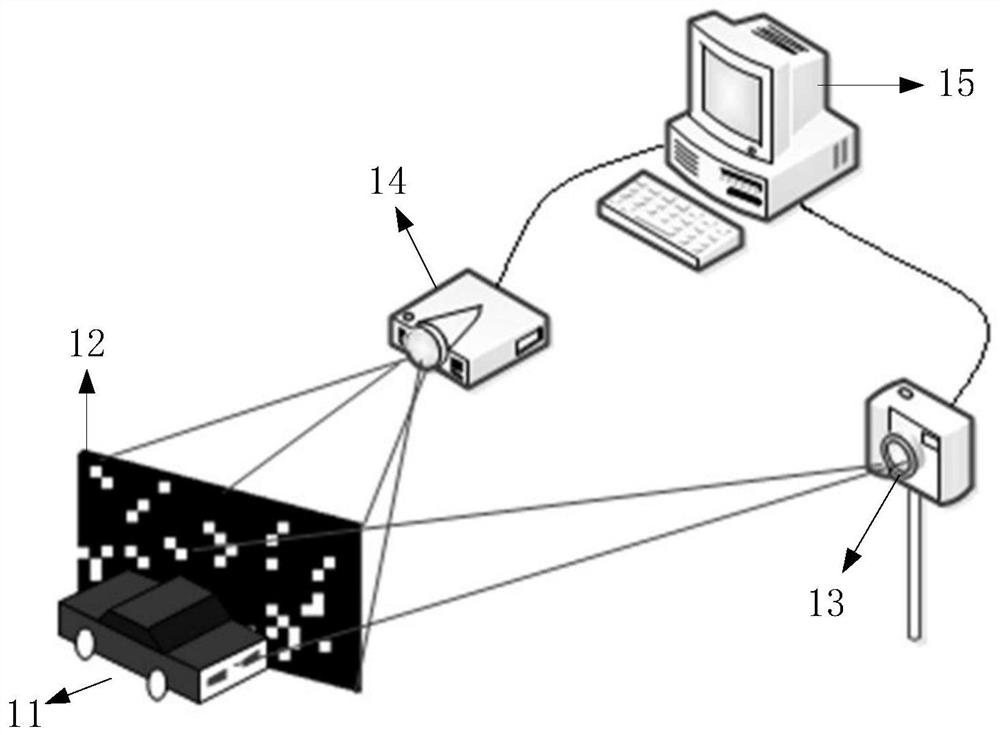
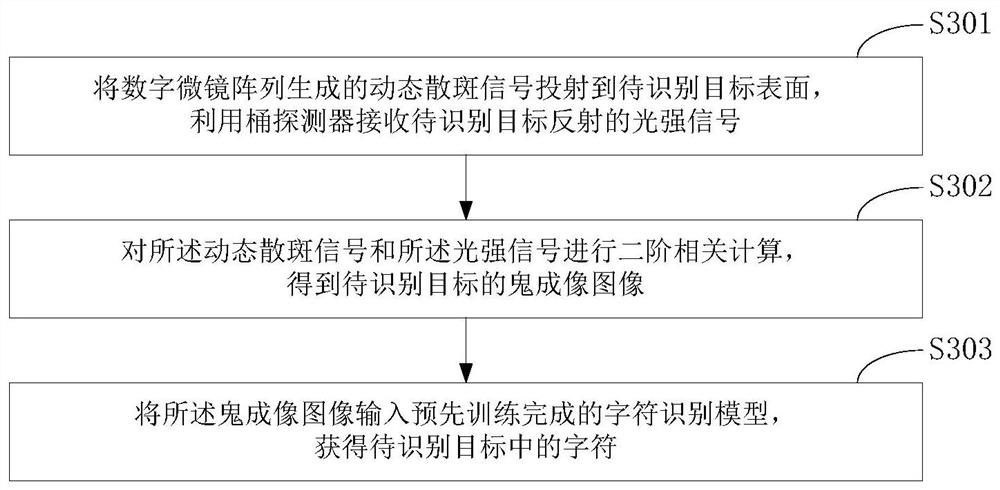
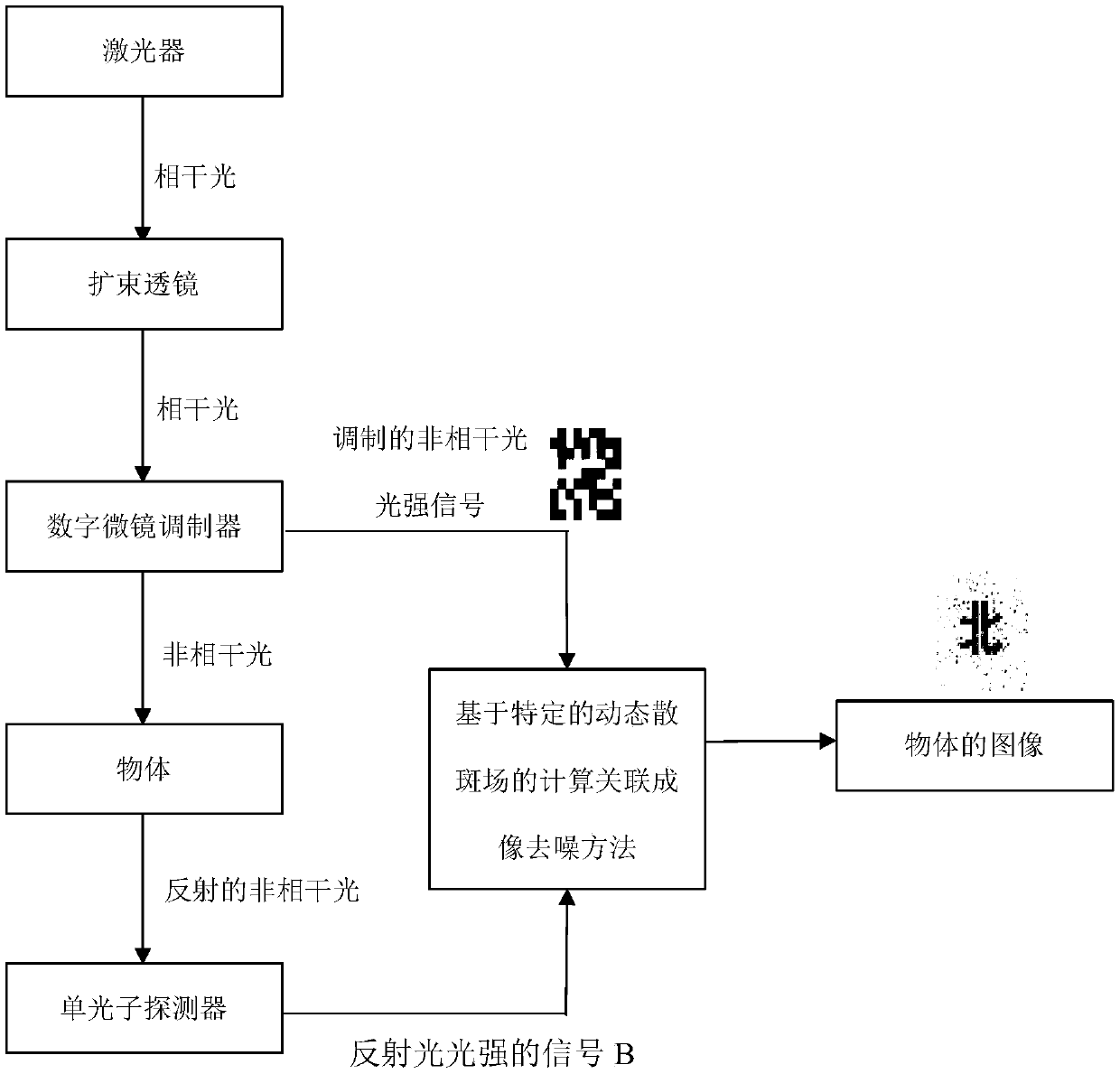
PendingCN111626285ALow costEnhanced feature informationImage enhancementImage analysisTarget surfaceRadiology
The invention relates to a character recognition system and method. One embodiment of the system comprises a light source, a digital micromirror array, a bucket detector and a computing device. The digital micromirror array converts light emitted by the light source into a dynamic speckle signal, and projects the dynamic speckle signal to the surface of a to-be-recognized target; the bucket detector receives a light intensity signal reflected by the to-be-recognized target; the calculation device performs second-order correlation calculation on the dynamic speckle signal and the light intensity signal to obtain a ghost imaging image of the to-be-recognized target; and inputting the ghost imaging image into a pre-trained character recognition model to obtain characters in a to-be-recognizedtarget. According to the embodiment, accurate recognition of the characters can be achieved with low cost.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
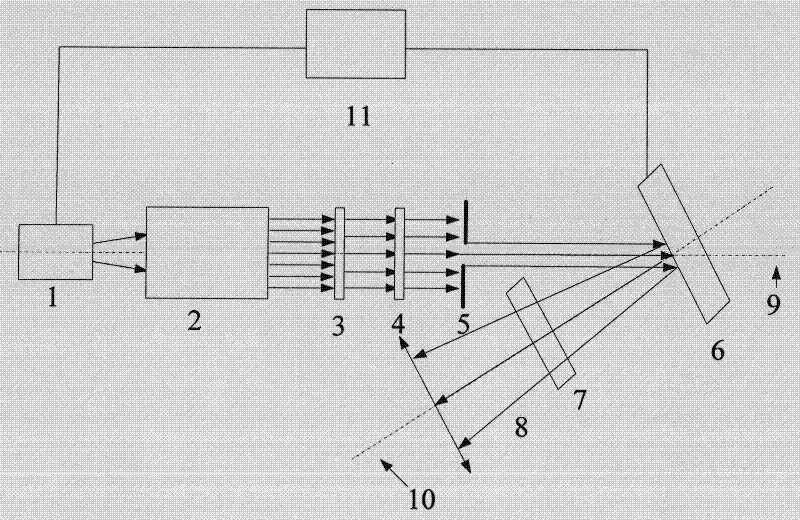
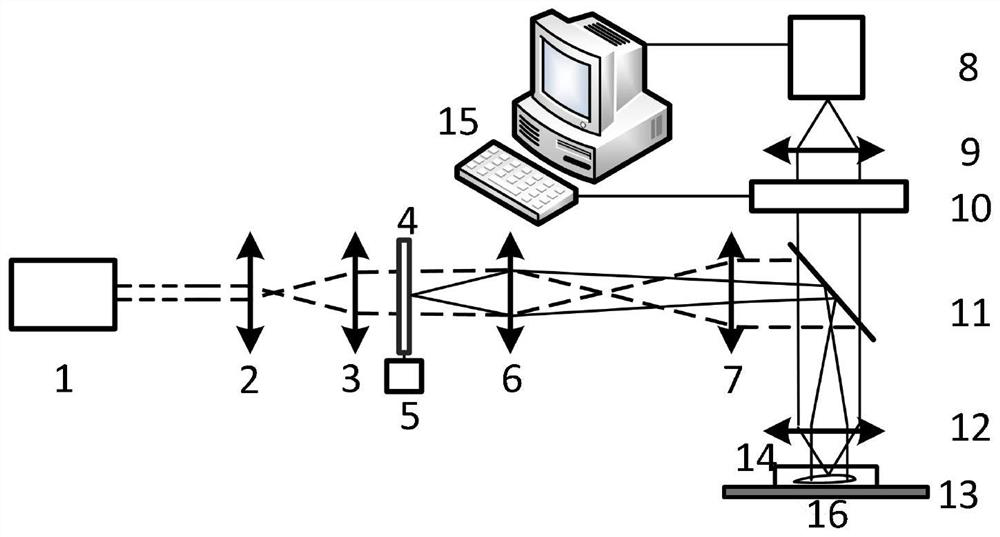
Method and device for testing dynamic speckles in laser display
A method for measuring dynamic speckles in laser display is characterized in that a test method and steps are as follows: a tested image is projected to a screen with a zone bit, the shooting direction of test equipment is perpendicular to the screen, focusing is performed until the image is clear, a first image is collected, the vertical distance between the test equipment and the screen is kept unchanged, and a second image is collected; after an image formed by the screen image on the test device is moved by using a moving device, the test device acquires a second image, so that the image acquisition unit acquires two images with the same test area and different observation positions, and the two images at least have a common test area with a flag bit as a boundary; and carrying out image correlation processing calculation on the two pictures to finally obtain the dynamic speckle contrast. Compared with a speckle contrast static testing method used in the industry at present, the dynamic speckle contrast obtained by the method is higher in accuracy, and the method can be widely applied to speckle measurement of laser display products such as laser televisions, laser projectors and laser cinemas.
Owner:上海唯视锐光电技术有限公司
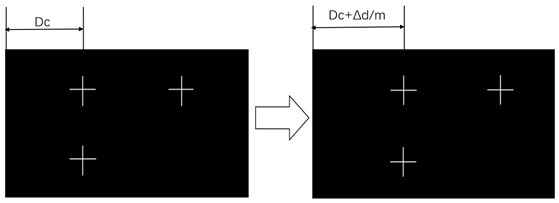
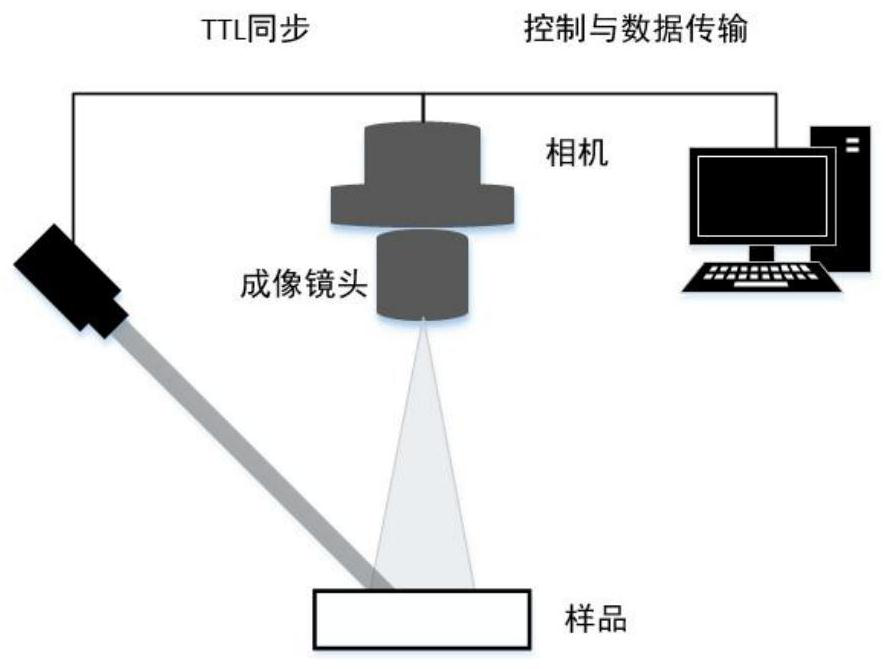
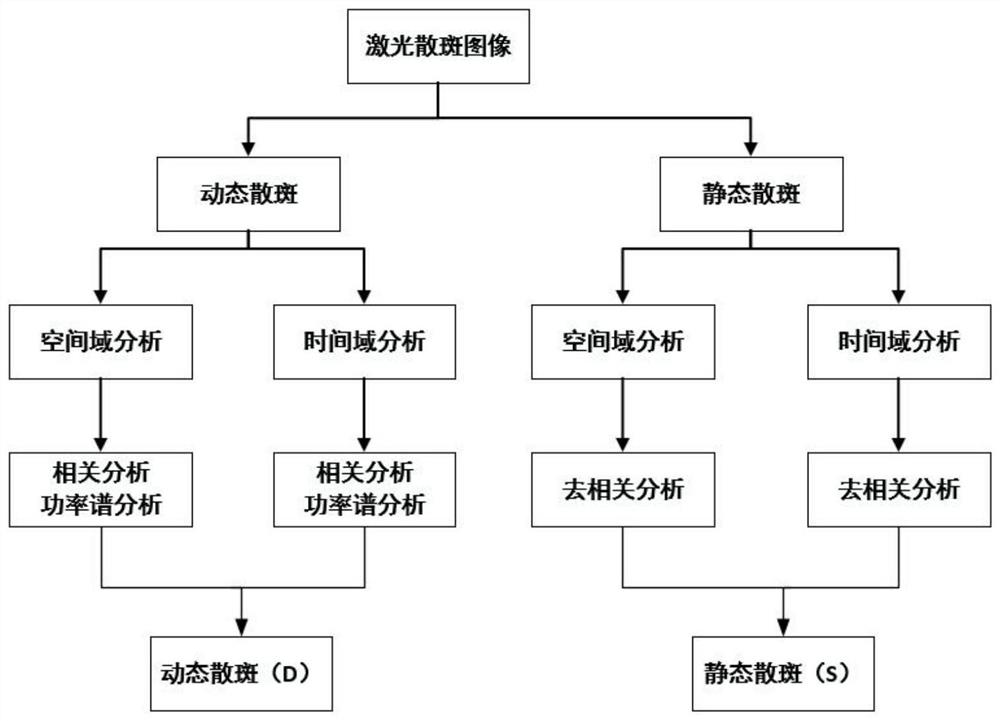
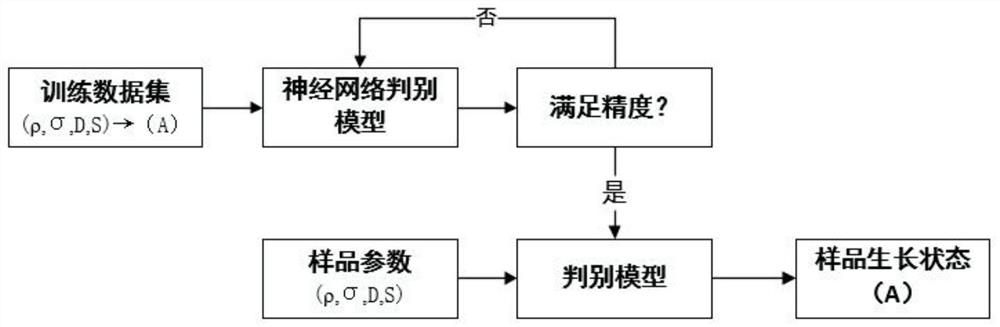
A method for monitoring plant growth process based on laser speckle technology
The invention relates to a method for monitoring plant growth process based on laser speckle technology, comprising the following steps: (1) plant speckle image acquisition and recording; (2) dynamicspeckle signal processing; (3) static speckle signal processing; (4) Image feature extraction; (5) establishment of an analytical model for the relationship between plant growth state and measured images and parameters: choose different kinds and different growth status of blade, which covers different color leaf blade growth status, as well as the budding leaves, mature leaves and withered leaves, wither, and according to the different location and plant diseases and insect pests position, classify blades, collect original speckle digital interference image respectively. After the image is extracted urgently, the leaf vascular density [rho] and the vascular connectivity [sigma] are obtained. Combined with the dynamic speckle intensity D and the static speckle intensity R, the measurementparameter set is constructed, and the neural network fitting classification model is established; (6) Plant growth state determination and evaluation.
Owner:苏州同阳科技发展有限公司
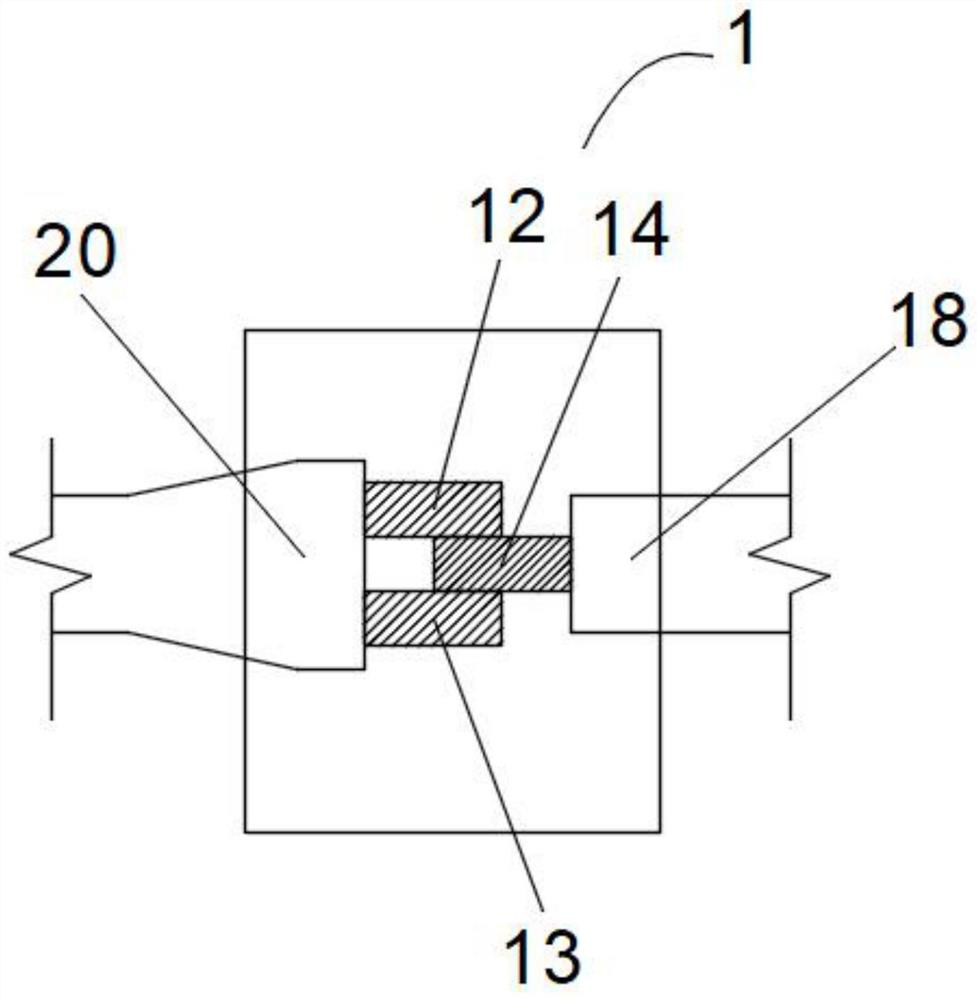
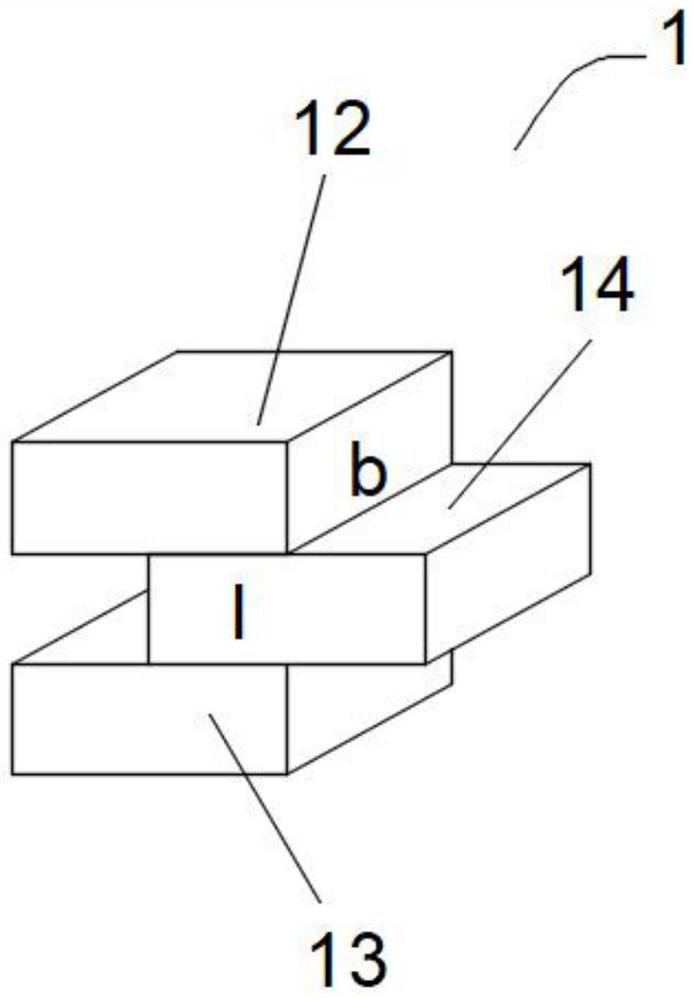
Double-sided dynamic shear testing device and method based on Hopkinson pressure bar system
PendingCN114674681ASolve the problem of dynamic clippingUsing optical meansMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesMeasurement deviceIncident energy
The invention relates to the technical field of measuring devices, in particular to a double-sided dynamic shear testing device and method based on a Hopkinson pressure bar system, and the double-sided dynamic shear testing device comprises a rock sample, a testing device, a force application mechanism, a signal shear mechanism and a displacement shear mechanism, the force applying mechanism impacts a rock sample subjected to normal stress, and the displacement shearing mechanism collects dynamic change of the rock sample to obtain a dynamic speckle image and analyzes the dynamic speckle image to obtain a rock sample surface displacement field evolution law and a dynamic slip rate; an incident pulse signal, a reflection pulse signal and a transmission pulse signal which are generated when the force applying mechanism impacts the rock sample are acquired and analyzed through the signal shearing mechanism, so that incident energy, reflection energy and transmission energy are obtained; the problem that direct shearing of an existing dynamic shearing and friction measuring device based on the Hopkinson pressure bar cannot dynamically shear a rock structural surface under the action of medium-high strain rate dynamic load is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Wide-field multispectral fluorescence microscopic imaging method and system based on dynamic speckle illumination
PendingCN113984631AWide spectral rangeFast imagingIndividual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceFemto second laserFemtosecond pulsed laser
The invention provides a wide-field multispectral fluorescence microscopic imaging method and system based on dynamic speckle illumination. The system is characterized in that a mode-locked titanium sapphire femtosecond pulse laser is used as a light source. A femtosecond laser pulse with a wide spectral range forms a speckle pattern after passing through a scatterer, full-field illumination is formed in the field of view of the microscope objective, and different types of fluorophores in a biological sample to be detected are excited at the same time. Illumination speckle patterns are sequentially changed, a CCD camera detects and receives fluorescence images obtained through illumination of the dynamically-changed speckle patterns, and the wide-field multispectral fluorescence microscopic imaging method based on dynamic speckle illumination is achieved through a tomography extraction algorithm. The system constructed by the invention can simultaneously and quickly acquire three-dimensional space distribution images of different types of fluorophores in a biological sample, has the characteristics of high temporal and spatial resolution, simple structure, easiness in operation and the like, and has wide application prospects in the research fields of biology, medicine, life science and the like.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Computational correlation imaging denoising method and system based on dynamic speckle field
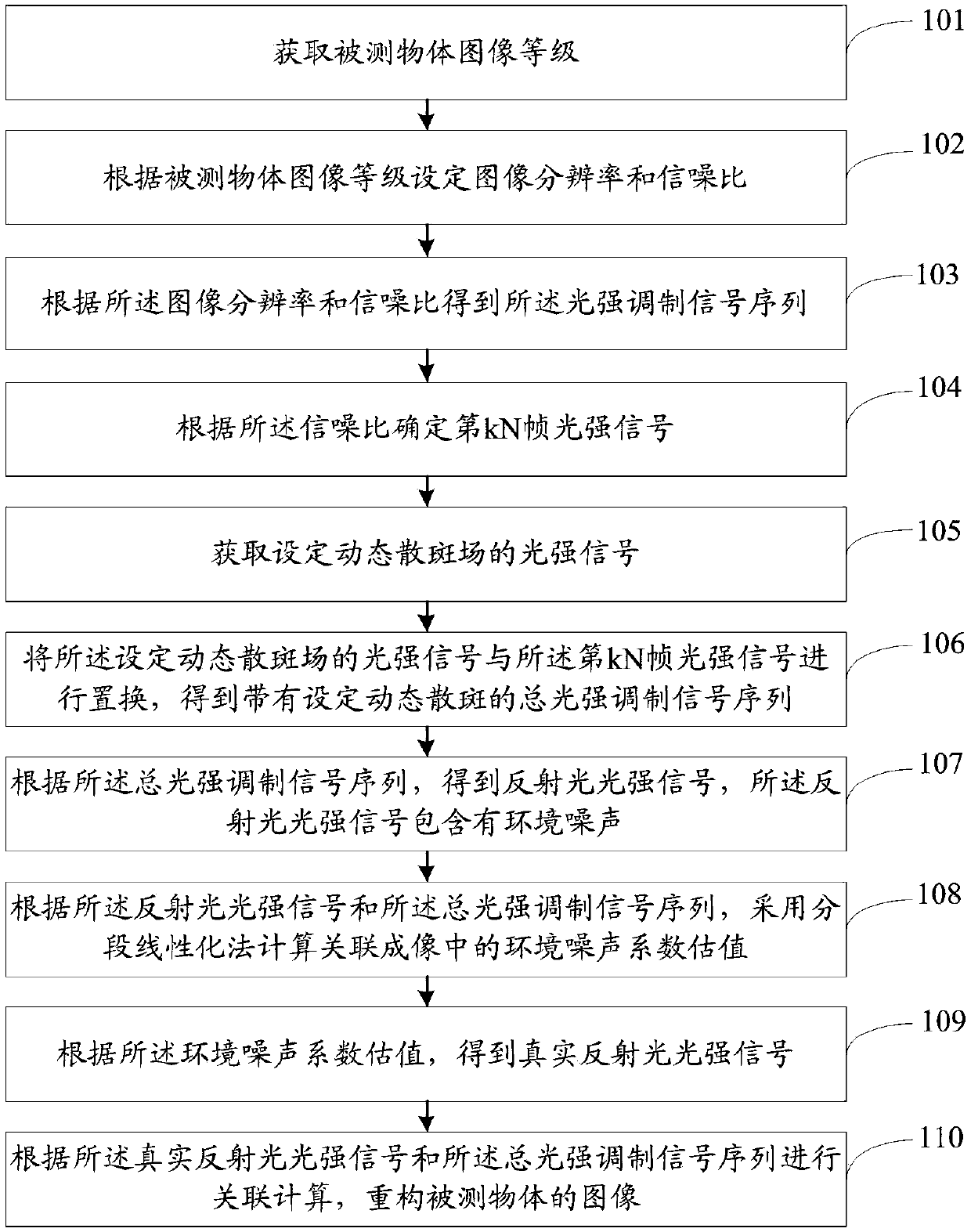
ActiveCN109100027AResistant to the effects of dynamic disturbancesInstrumentsDynamic speckleLight intensity
The invention discloses a computational correlation imaging denoising method and a system based on dynamic speckle field. The method comprises the following steps of substituting a fixed light intensity modulated signal with a frame in a digital micromirror modulator original light intensity modulated signal sequence; according to the substituted light intensity modulated signal, modulating the coherent light emitted by a laser into incoherent light, and using the modulated incoherent light to illuminate the object to linearly estimate the change of the noise and further recover the signal ofthe reflected light intensity of the real object; finally, reconstructing a image of the object to be measured by calculating and correlating the signal of the reflected light intensity with the lightintensity modulated signal of the incoherent light. The computational correlation imaging denoising method or system based on dynamic speckle field of the present invention is capable of resisting the effects of dynamic interference in associated imaging.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com