Rotary laser visual linear array space identification and positioning system
A laser line and rotary technology, applied in the field of rotary laser vision linear array space identification and positioning system, can solve the problems of complex processing technology, unable to expand the scanning range, effective distance limitation, etc. Simple, wide-ranging effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
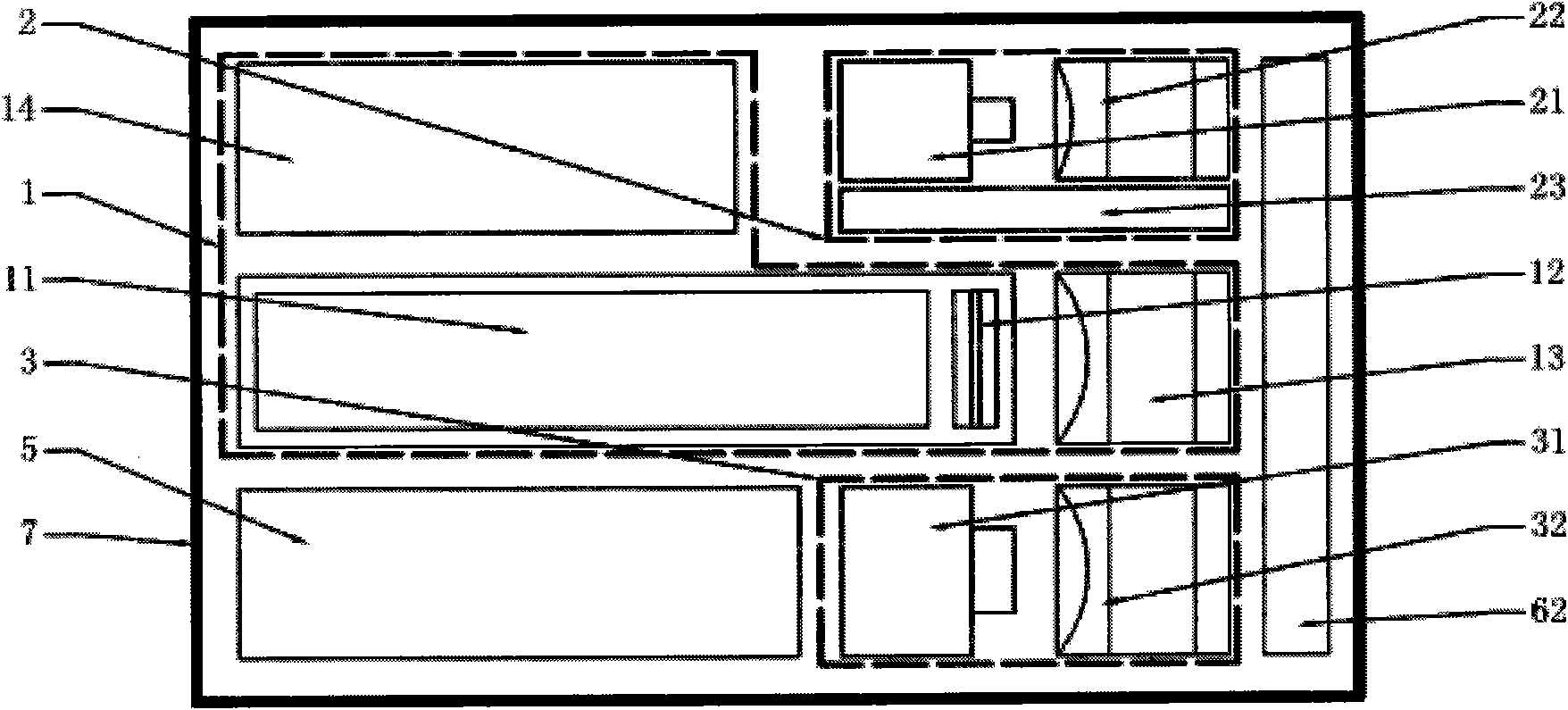
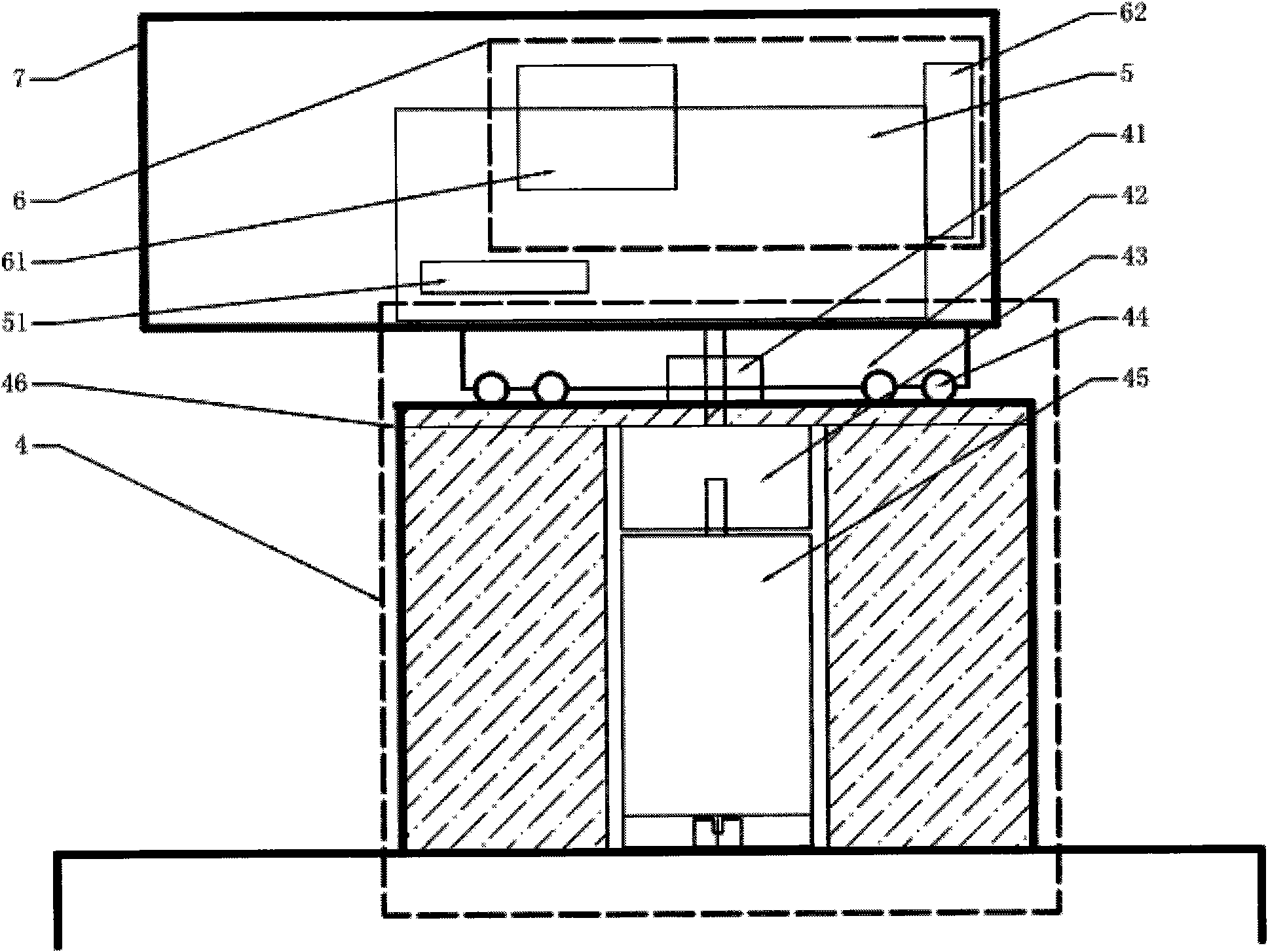
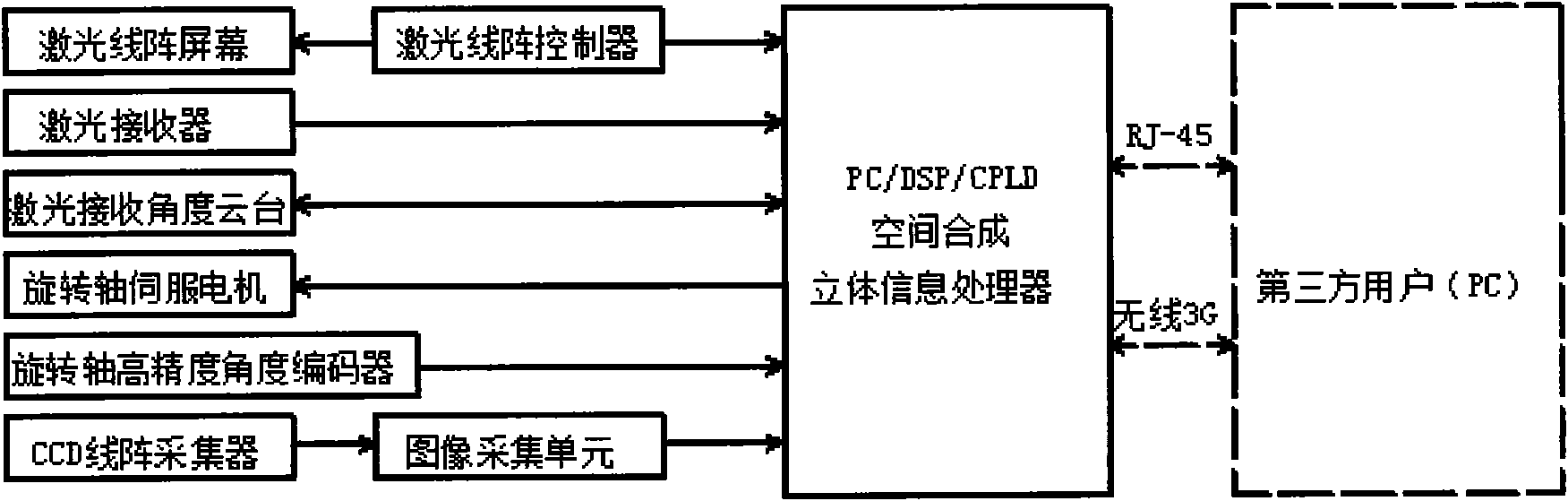
[0039] Attached below Figure 4 The rotary laser vision linear array space recognition and positioning system is further described, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0040] The first step: preparation work, adjust each lens group (12, 22, 32) to determine the best viewing range of the scanning target 8 longitudinal line array, determine the initial scanning origin position, input the rotation scanning angle a and the scanning precision subdivision n ;
[0041] The second step: the laser line array 1 scans the distance point by point, calculates the three-dimensional coordinate position in space according to the initial scanning origin position, the CCD line array 3 scans to obtain color information, and stores the obtained information data into the three-dimensional information processor 5 database;
[0042] Step 3: Wait for the linear array scanning to be completed, the servo motor 45 rotates the subdivision angle a b / n (n is the subdivision of the pres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com